Pipe
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 235 Accepted Submission(s): 94
Problem Description
The GX Light Pipeline Company started to prepare bent pipes for the new transgalactic light pipeline. During the design phase of the new pipe shape the company ran into the problem of determining how far the light can reach inside each component of the pipe. Note that the material which the pipe is made from is not transparent and not light reflecting.
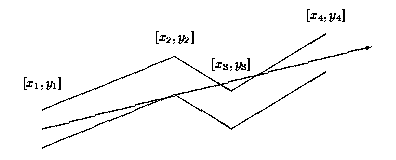
Each pipe component consists of many straight pipes connected tightly together. For the programming purposes, the company developed the description of each component as a sequence of points [x1; y1], [x2; y2], . . ., [xn; yn], where x1 < x2 < . . . xn . These are the upper points of the pipe contour. The bottom points of the pipe contour consist of points with y-coordinate decreased by 1. To each upper point [xi; yi] there is a corresponding bottom point [xi; (yi)-1] (see picture above). The company wants to find, for each pipe component, the point with maximal x-coordinate that the light will reach. The light is emitted by a segment source with endpoints [x1; (y1)-1] and [x1; y1] (endpoints are emitting light too). Assume that the light is not bent at the pipe bent points and the bent points do not stop the light beam.

Each pipe component consists of many straight pipes connected tightly together. For the programming purposes, the company developed the description of each component as a sequence of points [x1; y1], [x2; y2], . . ., [xn; yn], where x1 < x2 < . . . xn . These are the upper points of the pipe contour. The bottom points of the pipe contour consist of points with y-coordinate decreased by 1. To each upper point [xi; yi] there is a corresponding bottom point [xi; (yi)-1] (see picture above). The company wants to find, for each pipe component, the point with maximal x-coordinate that the light will reach. The light is emitted by a segment source with endpoints [x1; (y1)-1] and [x1; y1] (endpoints are emitting light too). Assume that the light is not bent at the pipe bent points and the bent points do not stop the light beam.
Input
The input file contains several blocks each describing one pipe component. Each block starts with the number of bent points 2 <= n <= 20 on separate line. Each of the next n lines contains a pair of real values xi, yi separated by space. The last block is denoted with n = 0.
Output
The output file contains lines corresponding to blocks in input file. To each block in the input file there is one line in the output file. Each such line contains either a real value, written with precision of two decimal places, or the message Through all the pipe.. The real value is the desired maximal x-coordinate of the point where the light can reach from the source for corresponding pipe component. If this value equals to xn, then the message Through all the pipe. will appear in the output file.
Sample Input
4 0 1 2 2 4 1 6 4 6 0 1 2 -0.6 5 -4.45 7 -5.57 12 -10.8 17 -16.55 0
Sample Output
4.67 Through all the pipe.//与nyoj 142题一模一样,题意就不说了,直接看nyoj 142就行了主要的思路就是穷举所有的折点的组合,取任意两个折点组成一条线,看看能不能跟所有的管道的上下折点构成的线段相交,如果所有都相交则说明光线能通过,否则求出所有光线中照的最远的那个(穷举的过程中设置一个记录变量) 这里就需要计算两个线段的交点(如果不能穿过管道,就要计算管道壁和光线的交点)。#include<stdio.h> #include<string.h> #include<math.h> #include<algorithm> #define E 1e-10 using namespace std; struct zz { double x; double y; }p[25][2]; double judge(zz a,zz b,zz c)//判断左右方向 { return ((b.x-a.x)*(c.y-a.y)-(c.x-a.x)*(b.y-a.y)); } double check(zz a1,zz a2,zz b1,zz b2)//判断是否相交 { return judge(a1,a2,b1)*(judge(a1,a2,b2)); } double zhexian(zz a,zz b,zz c)//计算三角形面积公式 { double ab,ac,bc,q; ab=sqrt((a.x-b.x)*(a.x-b.x)+(a.y-b.y)*(a.y-b.y)); ac=sqrt((a.x-c.x)*(a.x-c.x)+(a.y-c.y)*(a.y-c.y)); bc=sqrt((b.x-c.x)*(b.x-c.x)+(b.y-c.y)*(b.y-c.y)); q=(ab+bc+ac)/2; return sqrt(q*(q-ab)*(q-ac)*(q-bc)); } double point(zz a1,zz a2,zz b1,zz b2)//计算交点坐标 { double s1,s2; s1=zhexian(a1,a2,b1); s2=zhexian(a1,a2,b2); return (s1*b2.x+s2*b1.x)/(s1+s2); } int main() { int n; while(scanf("%d",&n),n) { int i,j; for(i=0;i<n;i++) { scanf("%lf%lf",&p[i][0].x,&p[i][0].y); p[i][1].x=p[i][0].x; p[i][1].y=p[i][0].y-1; } double mx=-0x3f3f3f3f; bool flag=false; zz a,b; for(i=0;i<n&&flag==false;i++) { int x1,x2; int tmp=0; for(tmp=0;tmp<2;tmp++) { a=p[i][tmp]; for(x1=i+1;x1<n&&flag==false;x1++) { for(x2=0;x2<2&&flag==false;x2++) { b=p[x1][x2]; if(check(a,b,p[0][0],p[0][1])<E) { for(j=1;j<n;j++) { if(check(a,b,p[j][0],p[j][1])>E)//如果a,b所组成的线与p[j][1]、p[j][0],这个折点所连线段没有交点,那么光线在这附近会有交点。 { double x; if(judge(a,b,p[j][0])>0) x=point(a,b,p[j-1][1],p[j][1]); else x=point(a,b,p[j-1][0],p[j][0]); if(x>mx) mx=x; break; } } if(j==n) flag=true; } } } } } if(flag==true) printf("Through all the pipe.n"); else printf("%.2lfn",mx); } return 0; }
最后
以上就是娇气豌豆最近收集整理的关于hdoj 1454&&poj 1039 Pipe 1454 (数学计算几何) 枚举Pipe的全部内容,更多相关hdoj内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复