这里直接引用自TensorFlow中文社区:
另外,极客学院也有基本类似的中文版。
- 使用
图 (graph)来表示计算任务。- 在被称之为
会话 (Session)的上下文 (context) 中执行图。- 使用
tensor表示数据。- 通过
变量 (Variable)维护状态。- 使用
feed和fetch可以为任意的操作(arbitrary operation) 赋值或者从其中获取数据。
Tensor
在 TensorFlow 中,数据不是以整数、浮点数或者字符串形式存储的。这些值被封装在一个叫做 tensor的对象中。
常见类型有:float32, float64, int32, int64, complex64, complex128
tf.constant()
tf.constant()返回一个常量tensor,值不会改变,可以有不同的维度。
# 定义
constant(
value,
dtype=None,
shape=None,
name='Const',
verify_shape=False
)#示例
# A 是 0-维 int32 tensor
A = tf.constant(1234)
# B 是 1-维 int32 tensor
B = tf.constant([123,456,789])
# C 是 2-维 int32 tensor
C = tf.constant([ [123,456,789], [222,333,444] ])tf.Variable()
tf.Variable() 是一个可以修改的tensor,tf.placeholder() 和 tf.constant() 的tensor是不能改变的。创建tf.Variables时必须要有一个初始值和shape,变量的shape通常固定,但也可以用其他方法调整行列数。
模型的其他操作运行之前需要先初始化它的状态,可以用 tf.global_variables_initializer()函数来初始化所有可变 tensor。
tf.global_variables_initializer()会返回一个操作,它会从 graph 中初始化所有的 TensorFlow 变量。可以通过 session 来调用这个操作来初始化所有上面的变量。
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)Session
TensorFlow 的 api 构建在 computational graph 的概念上,它是一种对数学运算过程进行可视化的方法,上一篇中的hello, world! 代码变成一个图(from Udacity)
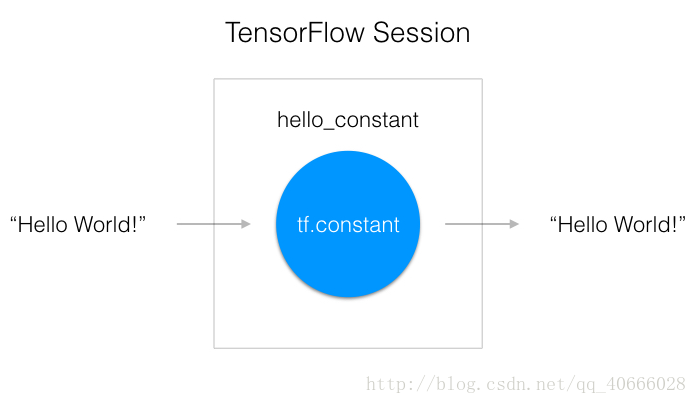
如上图所示,一个 “TensorFlow Session” 是用来运行图的环境。这个 session 负责分配 GPU(s) 和/或 CPU(s),包括远程计算机的运算。
with tf.Session() as sess:
output = sess.run(hello_constant)先创建了一个名为hello_constant 的tensor,用 tf.Session 创建了一个 sess 的 session 实例,然后 sess.run() 函数对 tensor 求值,并返回结果。
如果单纯print(hello_constant),输出的只是一个tensor的信息。
>> print (hello_constant)
>> Tensor("Const:0", shape=(), dtype=string)feed
除了以常量和变量的形式存储tensor,TensorFlow提供了feed机制。
如果希望你的TensorFlow模型对于不同的数据集采用不同的参数,可以用tf.placeholder()设定一个占位符,配合feed_dict,在session运行之前,设置输入。
x = tf.placeholder(tf.string)
y = tf.placeholder(tf.int32)
z = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
with tf.Session() as sess:
output = sess.run(x, feed_dict={x: 'Test String', y: 123, z: 45.67})如果传入 feed_dict 的数据与 tensor 类型不符,就无法被正确处理,你会得到 “ValueError: invalid literal for…”
math
TensorFlow中提供了丰富的数学计算方法,包括基本的算术运算、数学函数、矩阵运算等。(详细见文档)
这里也有一篇文章列出了TensorFlow里面常用的数学计算接口(tf API 研读2:math)
简单的加减乘除如下:
a = tf.add(5, 2) # 7
b = tf.subtract(10, 4) # 6
c = tf.multiply(2, 5) # 10
d = tf.divide(10., 2) # 5.0为了让运算进行,有时可能会需要进行类型转换,tf.cast(x, dtype)
# 定义
cast(
x,
dtype,
name=None
)# 示例
tf.subtract(tf.constant(2.0),tf.constant(1))
#Fails with ValueError: Tensor conversion requested dtype float32 for Tensor with dtype int32:
tf.subtract(tf.cast(tf.constant(2.0), tf.int32), tf.constant(1)) # 1最后
以上就是活泼猎豹最近收集整理的关于TensorFlow入门(2)-基本概念的全部内容,更多相关TensorFlow入门(2)-基本概念内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复