L2-024 部落(25分)
在一个社区里,每个人都有自己的小圈子,还可能同时属于很多不同的朋友圈。我们认为朋友的朋友都算在一个部落里,于是要请你统计一下,在一个给定社区中,到底有多少个互不相交的部落?并且检查任意两个人是否属于同一个部落。
输入格式:
输入在第一行给出一个正整数N(≤104),是已知小圈子的个数。随后N行,每行按下列格式给出一个小圈子里的人:
K P[1] P[2] ⋯ P[K]
其中K是小圈子里的人数,P[i](i=1,⋯,K)是小圈子里每个人的编号。这里所有人的编号从1开始连续编号,最大编号不会超过104。
之后一行给出一个非负整数Q(≤104),是查询次数。随后Q行,每行给出一对被查询的人的编号。
输出格式:
首先在一行中输出这个社区的总人数、以及互不相交的部落的个数。随后对每一次查询,如果他们属于同一个部落,则在一行中输出Y,否则输出N。
输入样例:
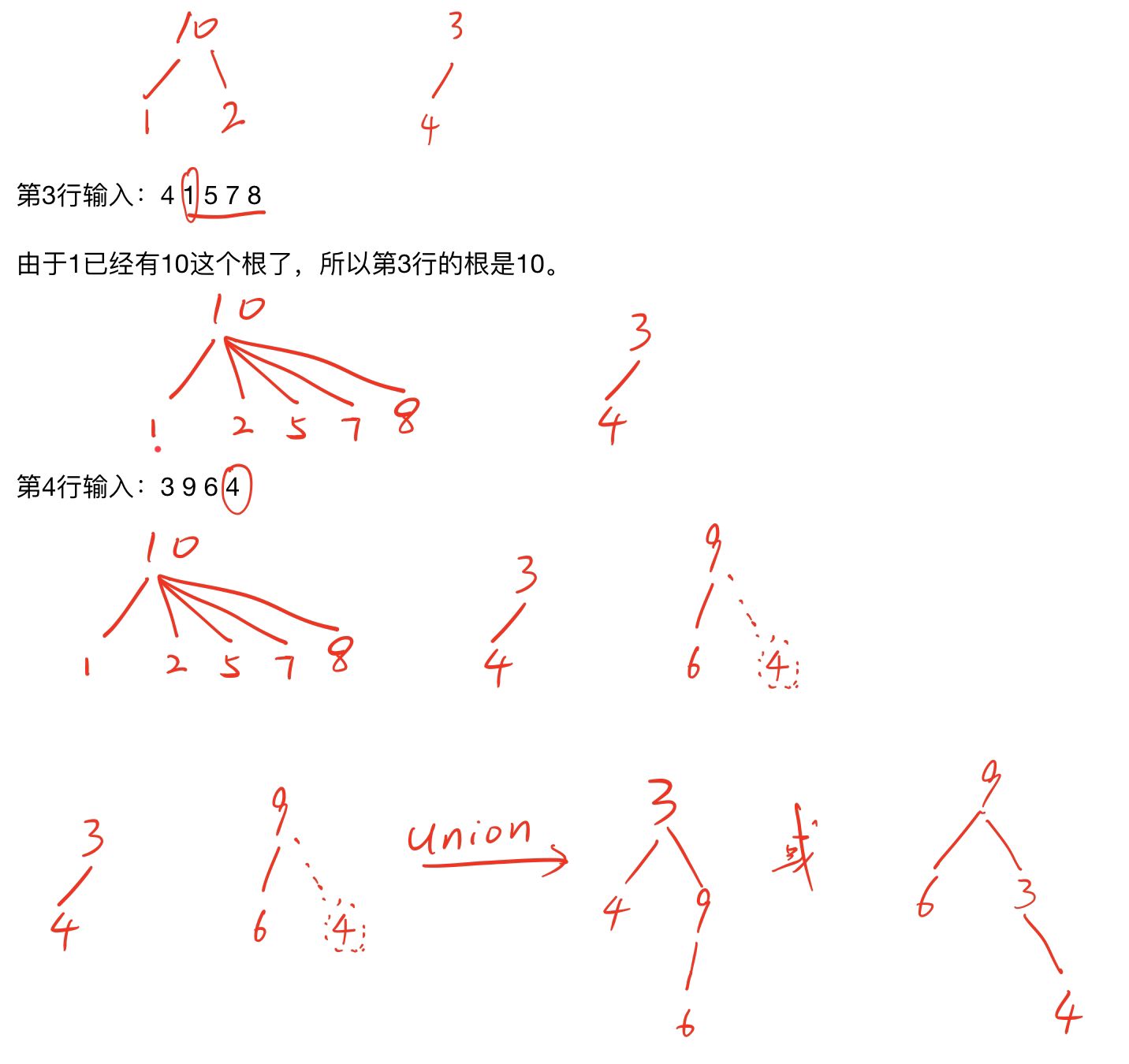
4
3 10 1 2
2 3 4
4 1 5 7 8
3 9 6 4
2
10 5
3 7
输出样例:
10 2
Y
N
图解:
思路简介:
采用并查集,来合并分支,并查集中用压缩路径,来使分支的高度尽可能的低(不然会超时),如果高度高的话,每次我们要找一个节点的根都得往上找半天,高度低的话,会很快能够判断出两个节点的根是不是同一个。
并查集简要描述:
数组 person[ ] 全部初始化为 -1,表示所有人都没有父节点
#include<iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
#define max_size 10005
int find_root(int value,const int person[]){
if(person[value] == -1)
return -1;
if(person[value] == value)
return value;
else {
int parent = person[value];
parent = find_root(parent,person);
return parent;
}
}
//
void union_branch(int personA,int personB,int *person, int *rank){
int rootA = find_root(personA,person);
int rootB = find_root(personB,person);
//一定考虑路径压缩,不能随便连接,不然会超时
if(rootA != rootB)
//两个分支不是同一个根就合并
if(rank[rootA] > rank[rootB])
//把高度小的分支插到高度大的分支上面,这样高度大的分支的高度就不会增加。
//反之,会产生一个高度更大的分支
person[rootB] = rootA;
if(rank[rootB] > rank[rootA])
person[rootA] = rootB;
//若两个分支高度相等,合并后的大分支,高度加一,加一是因为我们是把高度相等的分支插在另一个分支的根上
if(rank[rootA] == rank[rootB]) {
rank[rootB] += 1;
person[rootA] = rootB;
}
}
int main(){
int person[max_size];
int rank[max_size];//用来压缩路径的数组
memset(person,-1,sizeof(person));
memset(rank,1,sizeof(rank));
int N;
cin>>N;
//所有人的编号从1开始连续编号;注意:是连续哦!!!
while (N--){
int K;//小圈子内的人数
cin>>K;
//把小圈子内的第一个人作为根,先把这个圈子内的人全部连接起来
//注意:并不是只连接这个圈子内的人,如果这个圈子内有的人,
//在前面出现过并且已经有他自己的根了,那就先找到他的根,
//再把两个根合并。
int temp;
cin>>temp;
int temp_root = find_root(temp,person);
//检查temp_root,有没有他自己的根,
//若他没有根就让他变成这一行输入的根
//更改person,
if(temp_root == -1) {
rank[temp] += 1;//高度加一
person[temp] = temp;
temp_root = temp;
}
K--;//脚下留心,记得减一
while(K--){
int pep;
cin>>pep;
//找到他的根,若他没有根,他的根就是他自己
int pep_root = find_root(pep,person);
if(pep_root == -1)
person[pep] = temp_root;
else
//通过union_branch()来改变person数组
union_branch(temp_root,pep_root,person,rank);
}
}
//输出社区的总人数
int sum_people = 0;
//通过题意知道,所有人的编号从1开始连续编号,最大编号不会超过10^4
//person[0]肯定是-1,因为编号从1开始我们用不上person[0]
//person[0]的下一个 -1,就是人数的边界
int i = 1;
while (person[i] != -1){
sum_people++;
i++;
}
cout<<sum_people<<" ";
//找互不相交的部落
//就相当于找最后还剩下几个根,我们知道
//person[root] = root;
//遍历person数组,寻找最后的几个根
int sum_root = 0;
for(int i = 1;i<=sum_people;i++){
if(person[i] == i)
sum_root++;
}
cout<<sum_root<<endl;
//进入查询模块
int Q;
cin>>Q;
while(Q--){
int personA,personB;
cin>>personA>>personB;
//找A和B的根
personA = find_root(personA,person);
personB = find_root(personB,person);
if(personA == personB)
cout<<"Yn";
else
cout<<"Nn";
}
return 0;
}
最后
以上就是潇洒电脑最近收集整理的关于c++ 部落(在一个社区里,每个人都有自己的小圈子)L2-024 部落(25分)的全部内容,更多相关c++内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复