关于struct这个关键字,下面讨论了它的内存对齐和位段的tips
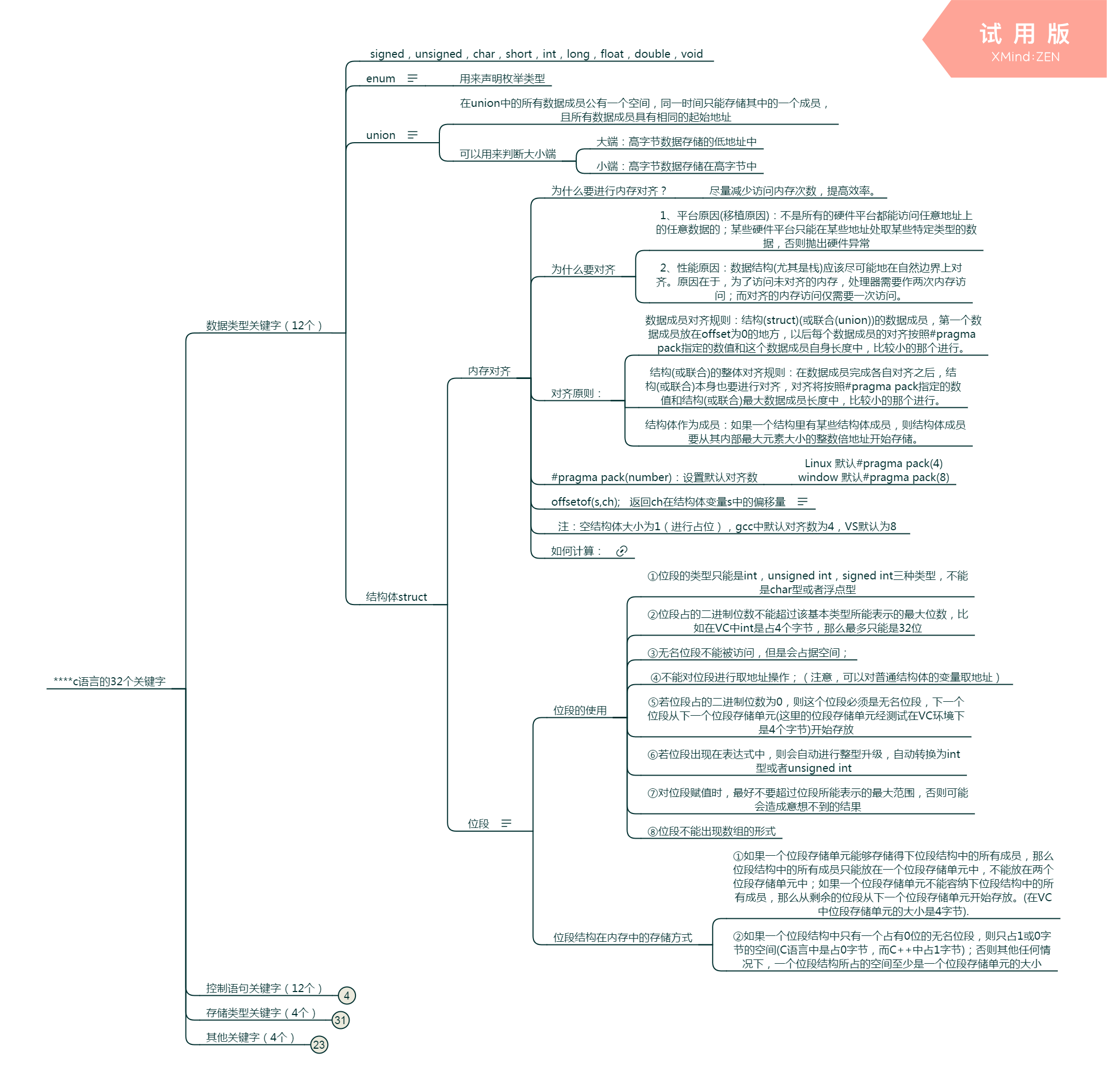
下面的代码是对普通结构体的内存对齐的验证:
struct ss11
{
char ch;
int a;
};
void Test11()
{
struct ss11 s;
printf("%pn", &s.ch); //可以对普通结构体的成员取地址
printf("%dn", sizeof(s)); //计算这个结构体的大小
}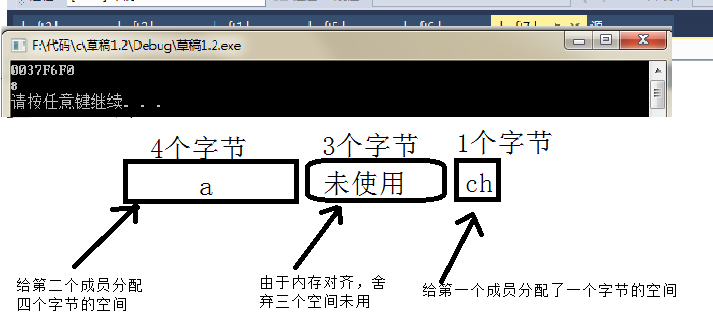
下面的代码是对位段的测试:
情况一:
struct my_bit
{
unsigned short _a : 4;//因为该位段的类型是short,所以会开两个字节的空间
unsigned short _b : 5;//因为第二个位段的类型也是short,编译器会看看前面开的空间是否能够
//再容纳下该位段。若容得下就不会再开空间了;否则就会开空间。
};
union un
{
int i;
char ch;
};
void Test11()
{
union un u;u.i = 1;
if (u.ch == 1)printf("小端n");//小端:低位序放在低地址,高位序放在高地址
else printf("大端n"); //大端:低位序放在高地址,高位序放在低地址
struct my_bit i;
memset(&i, 0, sizeof(i));
i._a = 13; i._b = 1;
printf("%dn", sizeof(i));
short it = *(short*)(&i);
printf("%dn", it);
} 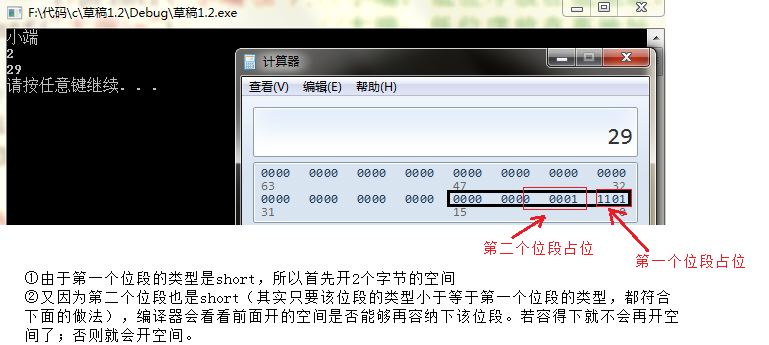
情况二:
struct my_bit
{
unsigned short _a : 5;//因为该位段的类型是short,所以会开两个字节的空间
unsigned short _b : 13;//因为第二个位段的类型也是short,编译器会看看前面开的空间是否能够
//再容纳下该位段。若容得下就不会再开空间了;否则就会开空间。
};
union un
{
int i;
char ch;
};
void Test11()
{
union un u;u.i = 1;
if (u.ch == 1)printf("小端n");//小端:低位序放在低地址,高位序放在高地址
else printf("大端n"); //大端:低位序放在高地址,高位序放在低地址
struct my_bit i;
memset(&i, 0, sizeof(i));
i._a = 13; i._b = 1;
printf("%dn", sizeof(i));
int it = *(int*)(&i);
printf("%dn", it);
}
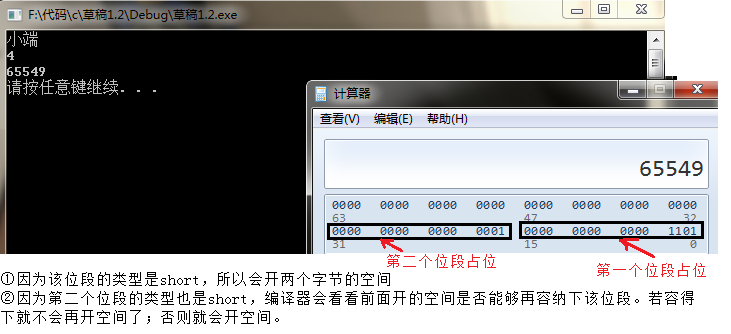
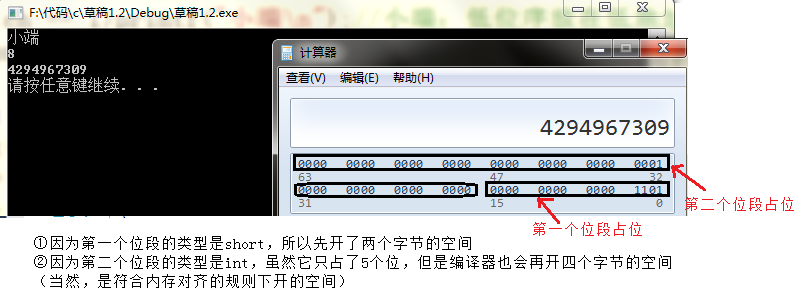
情况三:
struct my_bit
{
unsigned short _a : 4;//因为第一个位段的类型是short,所以先一次性开2个字节的空间
unsigned int _b : 5;//因为第二个位段的类型是short,所以会再开四个字节的空间
};
union un
{
int i;
char ch;
};
void Test11()
{
union un u;u.i = 1;
if (u.ch == 1)printf("小端n");//小端:低位序放在低地址,高位序放在高地址
else printf("大端n"); //大端:低位序放在高地址,高位序放在低地址
struct my_bit i;
memset(&i, 0, sizeof(i));
i._a = 13; i._b = 1;
printf("%dn", sizeof(i));
long long it = *(long long*)(&i);
printf("%lldn", it);
} 
最后
以上就是活泼灯泡最近收集整理的关于关键字struct的全部内容,更多相关关键字struct内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复