练习7.31
定义一对类X和Y,其中X包含一个指向Y的指针,而Y包含一个类型为X的对象
#ifndef ex7_31_H
#define ex7_31_H
class Y;
class X{
Y *p = nullptr; //第一次使用Y,上面要声明
};
class Y{
X a; //定义一个类X的对象a
};
#endif
练习7.32
定义Screen和Window_mgr,其中clear是Window_mgr的成员,是Screen的友元
#ifndef ex7_32_H
#define ex7_32_H
#include <string>
#include <vector>
class Screen; //类声明
class Window_mng {
public:
//类型别名
using ScreenIndex = std::vector<Screen>::size_type;
//clear函数声明
void clear(ScreenIndex);
private:
//函数定义
std::vector<Screen> screens{Screen(24, 80, ' ')};
};
//clear函数定义
void Window_mng::clear(ScreenIndex i)
{
Screen &s = screens[i];
s.contents = std::string(s.height * s.width, ' ');
}
class Screen {
//友元函数声明,类Screen可以访问类Window_mng中的成员函数clear
friend void Window_mng::clear(ScreenIndex);
public:
//类型别名
typedef std::string::size_type pos;
//默认构造函数
Screen() = default;
//两参构造函数并初始化数据成员
Screen(pos ht, pos wd) : height(ht), width(wd), contents(ht*wd, ' ') {}
//三参构造函数并初始化数据成员
Screen(pos ht, pos wd, char c) : height(ht), width(wd), contents(ht*wd, c) {}
//get无参函数定义
char get() const { return contents[cursor]; }
//get内联两参函数声明
inline char get(pos r, pos c) const;
//单参set成员函数声明
Screen &set(char);
//三参set成员函数声明
Screen &set(pos, pos, char);
//两参move函数声明
Screen &move(pos r, pos c);
//返回对象引用,之后可以操作改变对象的属性
Screen &display(std::ostream &os)
{ do_display(os); return *this; }
//返回对象引用,之后对对象的操作就是对其本身的操作
//第一个const:之后的操作无法改变对象的属性
//第二个const:修饰隐式形参this指针,不能够改变this所指的对象
const Screen&display(std::ostream &os) const
{ do_display(os); return *this; }
private:
//const修饰隐式形参this指针,不能够改变this所指的对象
void do_display(std::ostream &os) const { os << contents; }
pos cursor = 0;
pos height = 0, width = 0;
std::string contents;
};
//const修饰隐式形参this指针,不能够改变this所指的对象
char Screen::get(pos r, pos c) const
{
pos row = r * width;
return contents[row + c]; //返回拷贝值给临时对象
}
inline Screen &Screen::set(char c)
{
contents[cursor] = c;
return *this; //返回引用类型
}
inline Screen &Screen::set(pos r, pos col, char c)
{
contents[r*width + col] = c;
return *this; //返回引用类型
}
inline Screen &Screen::move(pos r, pos c)
{
pos row = r * width;
cursor = row + c;
return *this;
}
#endif
练习7.33
如果我们给Screen添加一个如下所示的size成员将发生什么情况?请尝试修改
unknown type name ‘pos’
//类Screen内的类型别名 typedef std::string::size_type pos;
//const修饰隐式形参this指针,不能够改变this所指的对象
pos Screen::size() const{
return height * width;
}
fixed
//pos在Screnn的作用域内
//const修饰隐式形参this指针,不能够改变this所指的对象
Screen::pos Screen::size() const{
return height * width;
}
练习7.34
 P256 Screen类
P256 Screen类

There is an error in
dummy_fcn(pos height)
^
Unknown type name 'pos'
练习7.35

typedef string Type;//Type为string的类型别名
Type initVal(); //use 'string'
class Exercise{
public:
typedef double Type;//Type为double的类型别名
Type setVal(Type); //use 'double'
Type initVal(); //use 'double'
private:
int val;
};
Type Exercise::setVal(Type parm){ //first is 'string', second is 'double'
val = parm + initVal(); //Exercise::initVal()
return val;
}
Fixed:
changed
Type Exercise::setVal(Type parm){ //first is 'string', second is 'double'
val = parm + initVal(); //Exercise::initVal()
return val;
}
to
Exercise::Type Exercise::setVal(Type parm){ //first is 'double', second is 'double'
val = parm + initVal(); //Exercise::initVal()
return val;
}
练习7.36
 In this case, the constructor initializer makes it appear as if base is initialized with i and then base is used to initialize rem. However, base is initialized first. The effect of this initializer is to initialize rem with the undefined value of base
In this case, the constructor initializer makes it appear as if base is initialized with i and then base is used to initialize rem. However, base is initialized first. The effect of this initializer is to initialize rem with the undefined value of base
// :base(i),rem(base % j){ }
base = i;
rem = base % j; //用未定义base值初始化rem,在定义int rem, base; 中base后被定义,但初始化时先使用的base
Fixed:
struct X{
X(int i, int j): base(i),rem(base & j){ }
int base, rem; //初始值列表的顺序应该与数据成员声明顺序一致
};
练习7.37

本节提供的Sales_data类

//use Sales_data(std::istream &is);
Sales_data first_item(cin); //its value are up to your input
int main(){
//use Sales_data(std::string s = " ");
//bookNo = " ", cnt = 0, revenue = 0.0
Sales_data next;
//use Sales_data(std:string s = " ");
//bookNo = "9-999-99999-9", cnt = 0, revenue = 0.0
Sales_data last("9-999-99999-9");
}
练习7.38
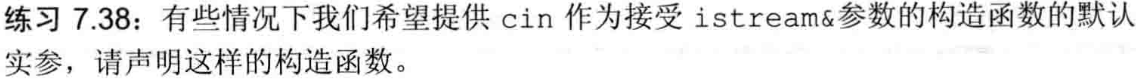
Sales_data(std::istream &is = std::cin){ read(is, *this); }
练习7.39

illegal.
cause the call of overloaded ‘Sales_data()’ is ambiguous(含糊的,含混的)
如果使用同一参数,并不知道调用哪个重载版本
练习7.40

Such as Book
class Book{
public:
Book() = default;
Book(unsigned no, std::string name, std::string author, std::string pubdate):no_(no),name_(name),author_(author),pubdate_(pubdate){ }
Book(std::istream &in) { in >> no_ >> name_ >> author_ >> pubdate; }
private:
unsigned no_;
std::string name_;
std::string author_;
std::string pubdate_;
};
最后
以上就是欢喜招牌最近收集整理的关于c++primer练习7.31、7.32、7.33、7.34、7.35、7.36、7.37、7.38、7.39、7.40练习7.31练习7.32练习7.33练习7.34练习7.35练习7.36练习7.37练习7.38练习7.39练习7.40的全部内容,更多相关c++primer练习7内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复