我是靠谱客的博主 感动鼠标,这篇文章主要介绍【深度之眼】Pytorch框架班第五期-Week1任务3第一节:autograd与逻辑回归torch.autograd逻辑回归,现在分享给大家,希望可以做个参考。
torch.autograd
autograd-自动求导系统
torch.autograd.backward(tensors, grad_tensors=None, retain_graph=None, create_graph=False)
功能:自动求取梯度
- tensors: 用于求导的张量, 如loss
- retain_graph: 保存计算图
- create_graph: 创建导数计算图,用于高阶求导
- grad_tensors: 多梯度权重
retain_graph
import torch
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
torch.manual_seed(10)
w = torch.tensor([1.], requires_grad=True)
x = torch.tensor([2.], requires_grad=True)
a = torch.add(w, x)
b = torch.add(w, 1)
y = torch.mul(a, b)
y.backward()
# y.backward()
#RuntimeError: Trying to backward through the graph a second time, but the buffers have already been freed. Specify retain_graph=True when calling backward the first time.
#y.backward(retain_graph=True)
grad_tensors
import torch
torch.manual_seed(10)
w = torch.tensor([1.], requires_grad=True)
x = torch.tensor([2.], requires_grad=True)
a = torch.add(w, x)
b = torch.add(w, 1)
y0 = torch.mul(a, b) #dy0/dw = 5
y1 = torch.add(a, b) #dy1/dw = 2
loss = torch.cat([y0, y1], dim=0) #[y0, y1]
grad_tensors = torch.tensor([1., 2.])
loss.backward(gradient=grad_tensors)
print(w.grad)
#tensor([9.])
torch.autograd.grad(outputs, inputs, grad_inputs=None, retain_graph=None, create_graph=False)
功能:求取梯度
- outputs:用于求导的张量,如loss, y
- inputs: 需要梯度的张量, w
- create_graph: 创建导数计算图,用于高阶求导
- retain_graph: 保存计算图
- grad_outputs: 多梯度权重
import torch
torch.manual_seed(10)
x = torch.tensor([3.], requires_grad=True)
y = torch.pow(x, 2) # y = x **2
grad_1 = torch.autograd.grad(y, x, create_graph=True) #grad_1 = dy/dx = 2x = 2*3 = 6
print(grad_1) # grad_1是元组 梯度 = grad_1[0]
#(tensor([6.], grad_fn=<MulBackward0>),)
grad_2 = torch.autograd.grad(grad_1[0], x) #grad_2 = d(dy/dx)/dx = d(2x)/dx = 2
print(grad_2)
# (tensor([2.]),)
autograd小贴士
1、梯度不自动清零
import torch
torch.manual_seed(10)
w = torch.tensor([1.], requires_grad=True)
x = torch.tensor([2.], requires_grad=True)
for i in range(4):
a = torch.add(w, x)
b = torch.add(w, 1)
y = torch.mul(a, b)
y.backward()
print(w.grad)
#tensor([5.])
#tensor([10.])
#tensor([15.])
#tensor([20.])
w.grad.zero_()
# tensor([5.])
# tensor([5.])
# tensor([5.])
# tensor([5.])
2、依赖于叶子结点的结点,requires_grad默认为True
import torch
torch.manual_seed(10)
w = torch.tensor([1.], requires_grad=True)
x = torch.tensor([2.], requires_grad=True)
a = torch.add(w, x)
b = torch.add(w, 1)
y = torch.mul(a, b)
print(a.requires_grad, b.requires_grad, y.requires_grad)
#True True True
3、叶子节点不执行in_place(在原始内存中改变该数据), 如 add_, +=
import torch
torch.manual_seed(10)
w = torch.tensor([1.], requires_grad=True)
x = torch.tensor([2.], requires_grad=True)
a = torch.add(w, x)
b = torch.add(w, 1)
y = torch.mul(a, b)
w.add_(1)
y.backward()
# RuntimeError: a leaf Variable that requires grad has been used in an in-place operation.
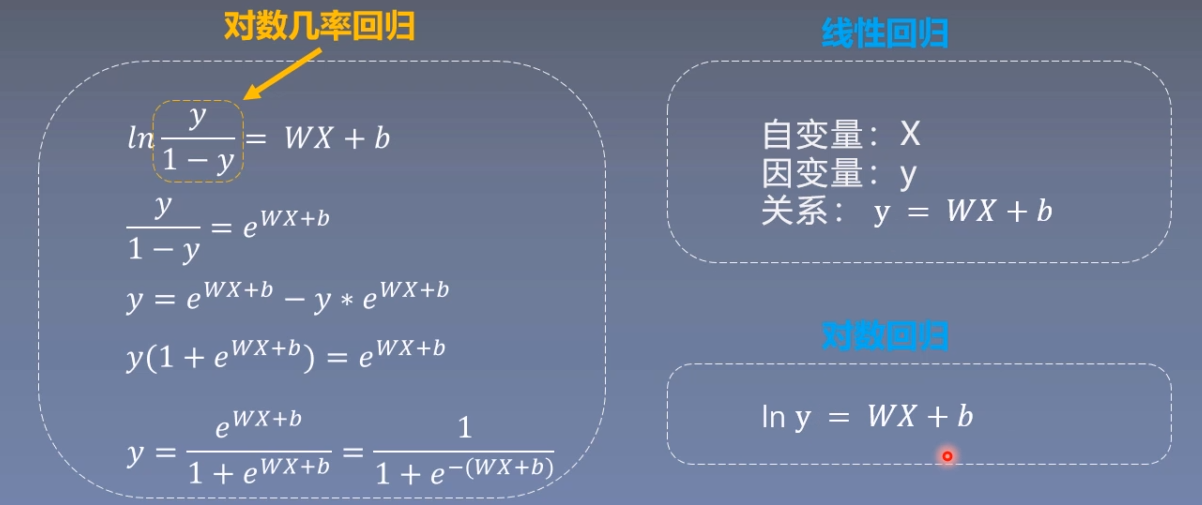
逻辑回归
逻辑回归是线性的二分类模型
模型表达式:

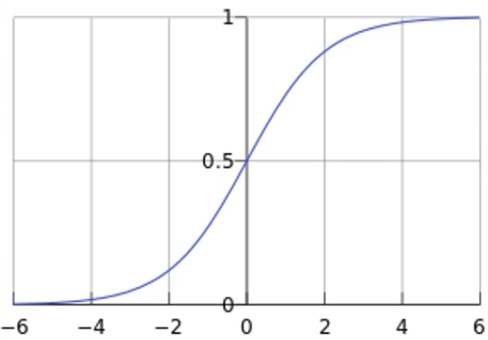
作业1:逻辑回归模型为什么可以进行二分类:
逻辑回归模型的表达式为因变量 y 等于自变量 x 的线性组合 WX+b再输入到 f(x) = 1/(1+1e-x)函数(即sigmoid函数,也称为Logistic函数)中,sigmoid函数将输入的数据映射到0~1之间,而0~1为概率取值区间,所以逻辑回归模型可以进行二分类。
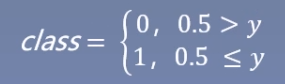

二元逻辑回归模型的训练过程
机器学习模型训练步骤

步骤1:数据
步骤2:模型
步骤3:损失函数
步骤4:优化器
步骤5:迭代训练
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
torch.manual_seed(10)
# ===================================== step 1/5 生成数据 =====================================
sample_nums = 100
mean_value = 1.7
bias = 1
n_data = torch.ones(sample_nums, 2)
x0 = torch.normal(mean_value * n_data, 1) + bias
y0 = torch.zeros(sample_nums)
x1 = torch.normal(-mean_value * n_data, 1) + bias
y1 = torch.ones(sample_nums)
train_x = torch.cat((x0, x1), 0)
train_y = torch.cat((y0, y1), 0)
# ===================================== step 2/5 选择模型 =====================================
class LR(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(LR, self).__init__()
self.features = nn.Linear(2, 1)
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
x = self.features(x)
x = self.sigmoid(x)
return x
lr_net = LR() #实例化逻辑回归模型
# ===================================== step 3/5 选择损失函数 =====================================
loss_fn = nn.BCELoss()
# ===================================== step 4/5 选择优化器 =====================================
lr = 0.01 # 学习率
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(lr_net.parameters(), lr=lr, momentum=0.9)
# ===================================== step 5/5 模型训练 =====================================
for iteration in range(1000):
#前向传播
y_pred = lr_net(train_x)
#计算loss
loss = loss_fn(y_pred.squeeze(), train_y)
#反向传播
loss.backward()
#更新参数
optimizer.step()
#绘图
if iteration % 990 == 0:
mask = y_pred.ge(0.5).float().squeeze() # 以0.5为阈值进行分类
correct = (mask == train_y).sum() # 正确预测的样本个数
acc = correct.item() / train_y.size(0) # 计算分类准确率
plt.scatter(x0.data.numpy()[:, 0], x0.data.numpy()[:, 1], c='r', label='class 0')
plt.scatter(x1.data.numpy()[:, 0], x1.data.numpy()[:, 1], c='b', label='class 1')
w0, w1 = lr_net.features.weight[0]
w0, w1 = float(w0.item()), float(w1.item())
plot_b = float(lr_net.features.bias[0].item())
plot_x = np.arange(-6, 6, 0.1)
plot_y = (-w0 * plot_x - plot_b) / w1
plt.xlim(-5, 7)
plt.ylim(-7, 7)
plt.plot(plot_x, plot_y)
plt.text(-5, 5, "Loss=%.4f" % loss.data.numpy(), fontdict={'size':20, 'color': 'red'})
plt.title("Iteration: {}nw0:{:.2f} w1:{:.2f} b: {:.2f} accuracy:{:.2%}".format(iteration, w0, w1, plot_b, acc))
plt.legend()
plt.show()
plt.pause(0.5)
if acc > 0.99:
break
作业2
采用代码实现逻辑回归模型的训练,并尝试调整数据生成中的mean_value,将mean_value设置为更小的值,例如1,或者更大的值,例如5,会出现什么情况?
再尝试仅调整bias,将bias调为更大或者负数,模型训练过程是怎么样的?调整mean_value,bias分别截取所训练的逻辑回归模型
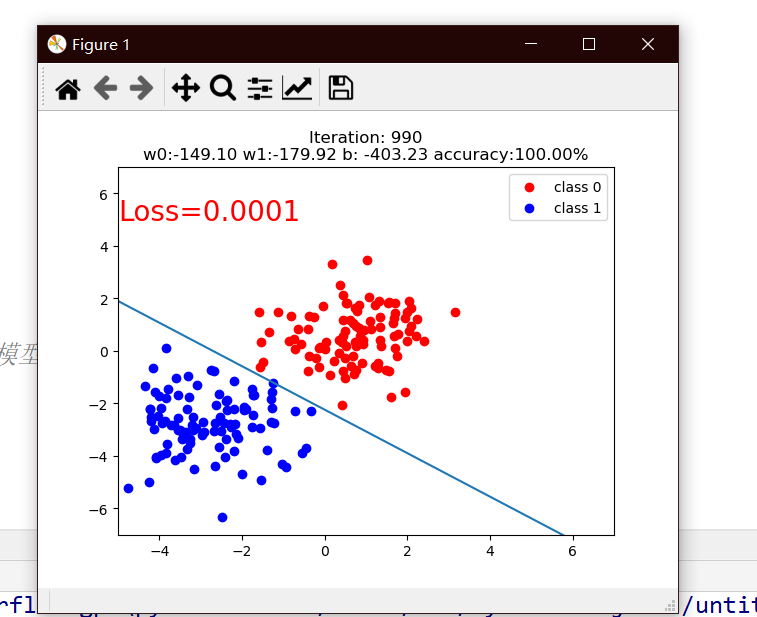
mean_value=1.7, bias=1
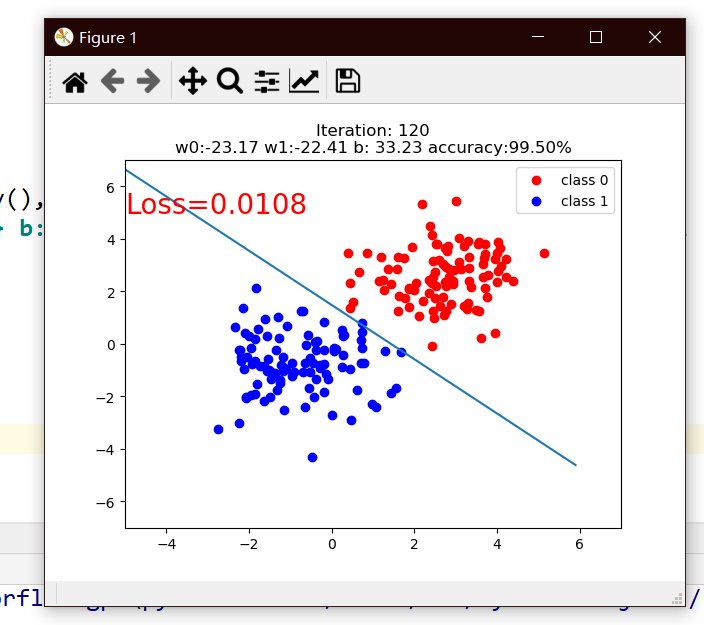
mean=1,bias=1
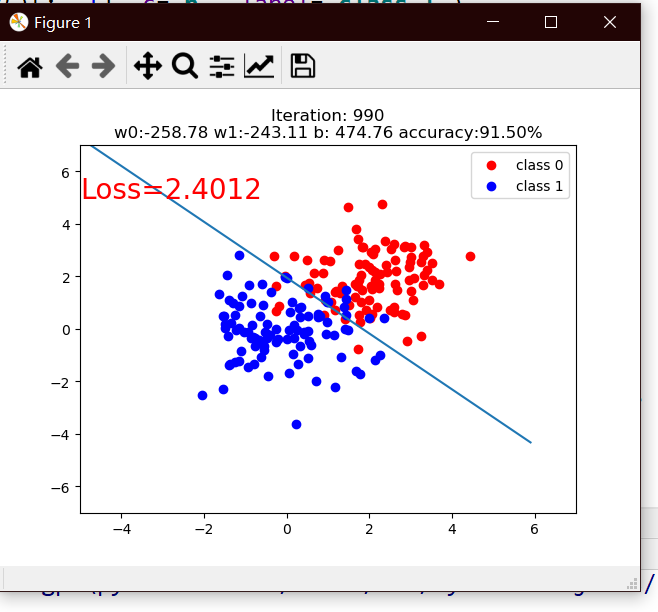
mean=5,bias=1
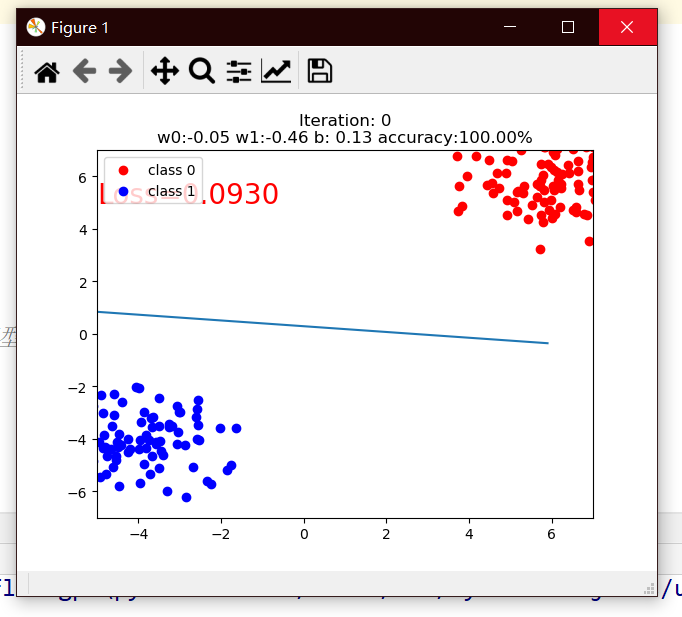
mean=1.7, bias=5
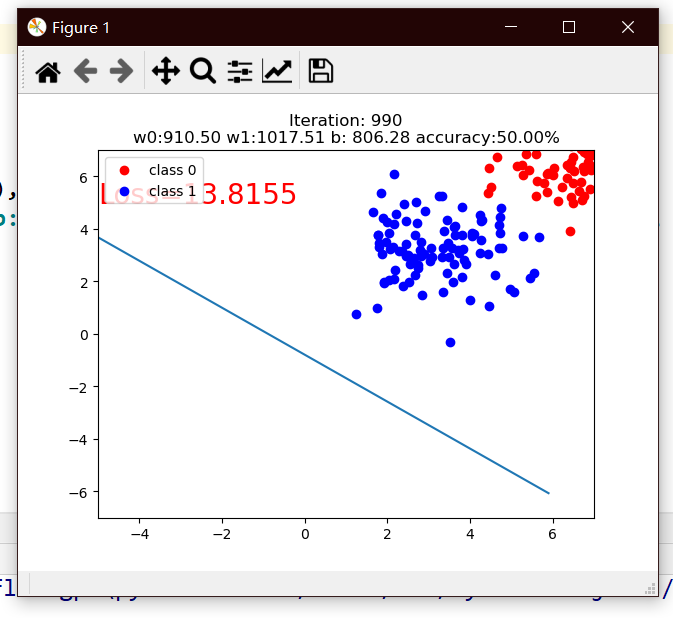
mean=1.7, bias=-1
最后
以上就是感动鼠标最近收集整理的关于【深度之眼】Pytorch框架班第五期-Week1任务3第一节:autograd与逻辑回归torch.autograd逻辑回归的全部内容,更多相关【深度之眼】Pytorch框架班第五期-Week1任务3第一节:autograd与逻辑回归torch内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复