作者 fan2012huan
文章出处 https://blog.csdn.net/fan2012huan/article/details/51076970
快速报错,是指当有其他线程对一个容器(如ArrayList,HashMap)进行了结构性修改,另外一个线程在使用iterator进行迭代该容器,那么这个迭代线程会抛出并发修改的异常ConcurrentModificationException。
所谓结构性修改,是对原有容器的size造成影响的操作,如remove、add、clear操作等。
示例代码(一)
public static void main(String[] args) {
//这会报不支持的操作异常,UnsupportedOperationException
//因为,Arrays.assList的底层实现是使用数组实现的,而数组不支持remove操作。
String string = "a b c d e";
List<String> stringList = Arrays.asList(string.split(" "));
Iterator<String> iterator = stringList.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
if(iterator.next().equals("c")) {
stringList.remove("c");
}
}
}2.执行结果
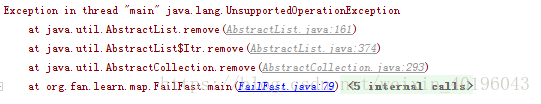
3.解析
原因在于List<String> stringList = Arrays.asList(string.split(" ")); 这句话。ArrayList.asList返回的List是固定大小的List,也就是说不可以对其进行add、remove操作。
ArrayList.asList的源码实现如下:
//Returns a fixed-size list backed by the specified array.
@SafeVarargs
@SuppressWarnings("varargs")
public static <T> List<T> asList(T... a) {
return new ArrayList<>(a);
}
//该ArrayList类不是java.util包中的内容,而是Arrays类的内部类。
private static class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>
implements RandomAccess, java.io.Serializable
{
private static final long serialVersionUID = -2764017481108945198L;
private final E[] a;
ArrayList(E[] array) {
a = Objects.requireNonNull(array);
}
/*省略此处代码*/
}从上面代码的注释中可以看到是 “返回的是固定大小的List”。
从源码实现上可以看到,private final E[] a; ,内部类ArrayList中的成员变量a,是final的。
示例代码(二)
注意,这个示例代码中的ArrayList不是上一个示例中出现的内部类,而是java.util.ArrayList。
1.代码
public static void main(String[] args) {
String string = "a b c d e";
List<String> stringList1 = Arrays.asList(string.split(" "));
//这个会得到 并发修改异常 ConcurrentModificationException
List<String> stringList = new ArrayList<String>(stringList1);
System.out.println(stringList);
Iterator<String> iterator = stringList.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
if(iterator.next().equals("c")) {
stringList.remove("c");
}
}
}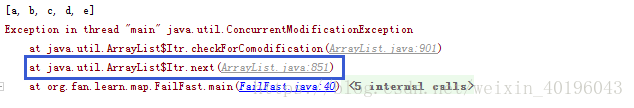
3.解析
从抛异常的报告上对应的代码是if(iterator.next().equals("c")) { 这一行。从调用栈来看,是在java.util.ArrayList的内部类Itr的next方法在调用checkForComodification方法时抛的异常。
来看看java.util.ArrayList的相关源码实现。
private class Itr implements Iterator<E> {
int cursor; // index of next element to return
int lastRet = -1; // index of last element returned; -1 if no such
int expectedModCount = modCount;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E next() {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor;
if (i >= size)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
cursor = i + 1;
return (E) elementData[lastRet = i];
}
final void checkForComodification() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
/**省略此处代码**/
}其中的modCount是ArrayList的一个属性。
/*
* The number of times this list has been <i>structurally modified</i>.
* Structural modifications are those that change the size of the
* list, or otherwise perturb it in such a fashion that iterations in
* progress may yield incorrect results.
* /
protected transient int modCount = 0;源码给的注释可以看到,modCount用来表示list被结构性修改的次数。所谓结构性修改是指,改变了list的size,或者在迭代过程中产生了不正确的结果。
内部类在被示例化时会将modCount赋值给expectedModCount。
内部类的实例化发生在ArrayList的iterator被调用的时候,即Iterator<String> iterator = stringList.iterator();
这句话执行时初始化的。看看ArrayList#iterator的实现:
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return new Itr();
} 从next方法的实现上可以看到,首先就会判断expectedModCount与modCount是否相等,如果不等就会抛ConcurrentModificationException异常。不相等说明其他线程修改了modCount。当然,在这个例子中只有main线程,也出现了这种情况。因为,在迭代到”c”时,stringList.remove("c"); 执行了remove操作,对list造成了结构性修改,改变了list的size,modCount的值会加1。这样当迭代到”d”时,发现expectedModCount与modCount不等了,因此抛异常了。
代码示例(三)
1.代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {
String string = "a b c d e";
List<String> stringList1 = Arrays.asList(string.split(" "));
List<String> stringList = new ArrayList<String>(stringList1);
System.out.println(stringList);
Iterator<String> iterator = stringList.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
if(iterator.next().equals("c")) {
//这里跟上例不同,上例为stringList.remove("c");
iterator.remove();
}
}
System.out.println(stringList);
}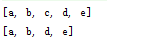
3.解析
可以看到,使用iterator.remove()没有抛异常,而且成功修改stringList的内容。
来看看ArrayList#Itr#remove方法的实现。
private class Itr implements Iterator<E> {
/**省略此处代码**/
public void remove() {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
ArrayList.this.remove(lastRet);
cursor = lastRet;
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
/**省略此处代码**/
}ArrayList.this.remove(lastRet);
之后,有一个关键的一行
expectedModCount = modCount;
更新了expectedModCount的值。
下面来看看ArrayList#remove()方法的实现。
public E remove(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
modCount++;
E oldValue = elementData(index);
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
return oldValue;
}首先执行了modCount++; , 之后在本地修改elementData的内容,最后elementData[--size] = null; 便于垃圾回收。
最后
以上就是危机刺猬最近收集整理的关于fail-fast的全部内容,更多相关fail-fast内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复