这本书是大一的学弟们上课的书,我们当时上课的书不一样,菜鸟很早就眼馋了,正好最近就找学弟借来看看,感觉很不错,这里直接附上封面:

这里菜鸟就直接上自己感觉很好的内容了,当然并不是全部的菜鸟都不知道,而是菜鸟感觉比较容易忘记和忽略的基础。
文章目录
- 1、类型判断 - null
- typeof注意:
- 2、类型转换
- 一、显式类型转换
- 二、隐式类型转换
- 注意:
- 3、类型比较
- 一、特殊的比较:
- NaN注意:
- 二、一般情况
- 三、字符串类型
- 4、一个值的真假判断
- 5、switch的case
- 特殊用法
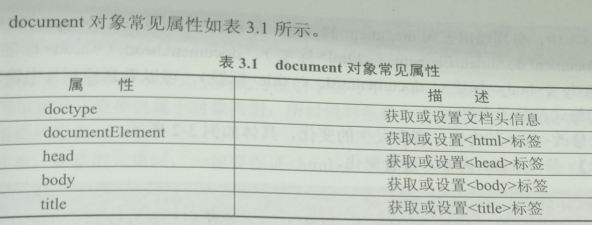
- 6、document文档
- 7、元素属性操作
- 注意:
- 8、元素样式操作
- 一、行内样式(style)
- 设置行内样式
- 注意:
- 二、非行内样式(window.getComputedStyle)
- 注意:
- 三、兼容旧版本(currentStyle)
- 注意:
- 四、设置非行内样式
- 注意:
1、类型判断 - null
这里只介绍 typeof 的方法:
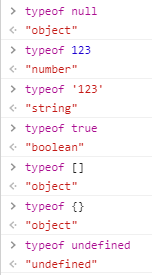
注意null返回的不是null类型,而是object类型。因为最初的js版本中只有五种类型的数据,没有null类型,空值是在object类型下定义的。
typeof注意:
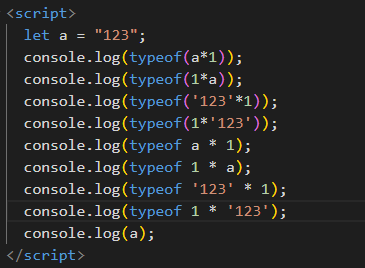
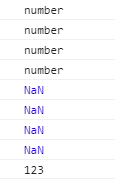
这里菜鸟建议使用 typeof 时,如果后面是 一个操作,最好加上(),这是菜鸟的代码和运行结果:
产生错误大致的执行流程:
2、类型转换
一、显式类型转换
显示类型转换是通过具体的方法,手动的进行转换的方式。
这里只介绍一下特别的:
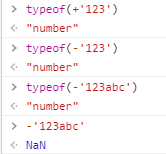
数值运算符(+)和负数值运算符(-),他们的作用可以将任何值转为数值(与 Number 函数的作用类似),一般用于显示类型转换。
二、隐式类型转换
隐式类型转换是通过运算的方式,自动进行转换的方式。
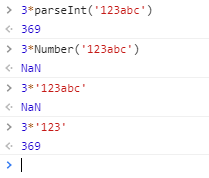
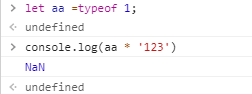
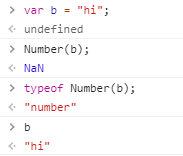
数字与字符串相运算时,会自动把字符串转换为数字类型( 只有纯数字字符串才行 或者 以数字开头的字符串 则可以使用 parseInt (String) 使其转换为数字 [ 不能使用Number() ] ),然后计算出结果。
注意:
+比较特别,不仅可以表示加法,还表示 连接符 ,因此数字与字符串相加时,实际上是连接两个变量成为字符串,并不会发生隐式转换 (下面有例子)
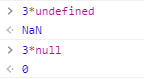
数字与布尔值运算时,会自动把布尔值转换为数字类型,true转换成1,false转换成0。
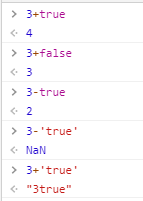
undefined表示未定义,而null表示已经定义,其值为空,因此隐式转换时,undefined不可以转换为数字,而 null可以转化为0 。
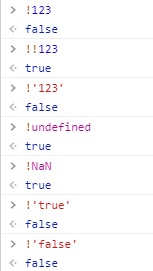
! 运算也可以用来做类型转换,将其他类型的值转换为布尔类型的值 ( 为了保证正确性可以采用两个非运算 [菜鸟感觉没什么必要] )
注意:
不管是隐式转换还是显式转换,只有调用的时候才会导致类型的变化,原本的变量还是原本的类型和数值!
3、类型比较
一、特殊的比较:
undefined == null; //true
undefined === null; //false
NaN == NaN; //false
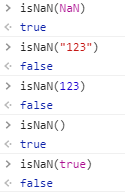
NaN注意:
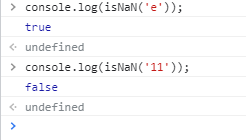
1、NaN与任何值比较都是false,包括他自己,可以用 isNaN() 来判断是否为NaN !
2、NaN表示变量不是数字,但是 其类型却是数字类型
3、NaN用来判断一个数是不是NaN或者能不能转化成NaN
二、一般情况
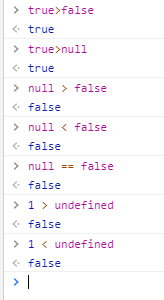
一般情况下,当不同的类型进行比较时,先把左右的类型转换为数字类型( 当然前提是可以转换为数字类型 ):
注意:
虽然 null 和 false 都可以转换为数字类型的0,但是两者无法比较!
三、字符串类型
当比较的两个都是字符串类型的时候,不会转换为数字类型,而是按照字符串 每一位(一位一位的比较) 的 Unicode码 进行比较。
4、一个值的真假判断
在JavaScript中为假值(负值)的有:空字符串(’’)、数字0、false、null、undefined、NaN,除了这些,其它全是真值(正值)。
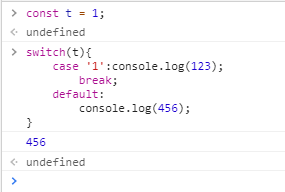
5、switch的case
switch的default默认值可以省略(基本上都是省略的),break表示跳出选择,如果不加break语句,会执行后续的case,因此需要添加break语句。
注意:
switch中的表达式与case语句中的取值是 严格相等模式 ,即:=== 方式。
特殊用法
var x = 4
switch(true){
case (x==1) :
//TODO
break;
case (x>3&&x<7) :
//TODO
break;
case (x>=9)
//TODO
break;
default:
//TODO
}
6、document文档
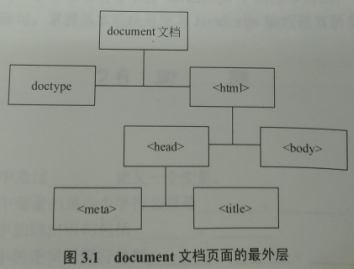
如何通过js获取网页中的元素?首先要了解 document 文档,document 文档指整个页面的根对象(最外层的对象),通过 document 文档可以获取页面中具体的HTML元素。注意 document 文档的类型为对象类型,即typeof document 返回 object 值,因此通常 document 文档亦称 document 对象。
7、元素属性操作
只获取元素本身并没有什么太大的作用,更重要的是对其进行操作,可以 通过点的方式 来获取元素身上的属性。
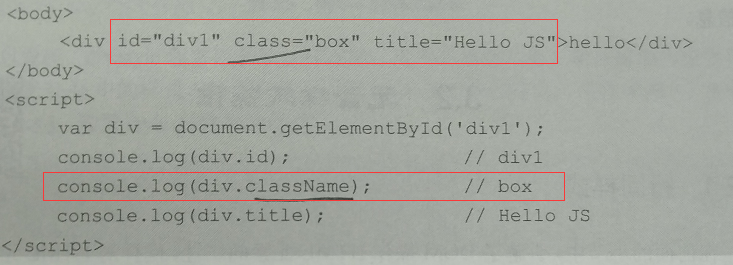
注意:
class属性,因为class属于js中的保留字,所以不能通过class的方式获取,而需要通过className的语法形式获取。与class属性类似的还有for属性(eg : lable里面的for属性),需要通过htmlFor的方式来获取。
8、元素样式操作
一、行内样式(style)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="aaa" style="width: 100px;height: 50px;background-color: aqua;">
hello
</div>
</body>
<script>
const div1 = document.getElementById("aaa");
console.log(div1.style);
console.log(div1.style.width);
console.log(div1.style.height);
console.log(div1.style.backgroundColor);
</script>
</html>
运行结果:
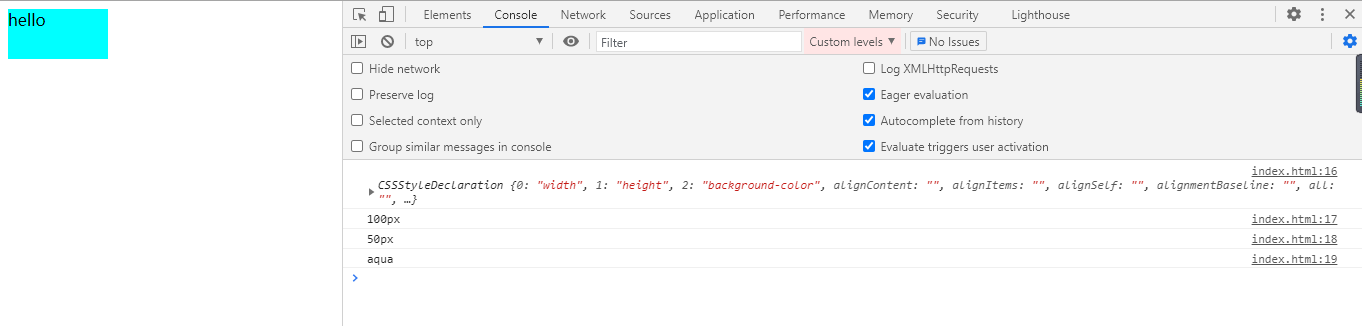

可以发现,div.style包含很多默认样式,当不设置样式时,默认值就是 空字符串(""),接下来就是告诉大家怎么设置style属性中的样式了!
设置行内样式
这里直接跳转:重学前端第一阶段完 钢琴项目(document.querySelector js改变css样式的3种方式 思路 成品)
注意:
js语法中不支持横杠,因此不能在语法中出现类似 background-color 的写法。当有此需求时,js中通过去掉横杠,并且设置横杠后的第一个字母为大写的方式实现,类似于驼峰命名方式。
二、非行内样式(window.getComputedStyle)
上面获取和设置的样式,都是通过style属性完成的,操作都是在行内样式完成,对于非行内样式并不可用。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
#bbb{
width: 100px;
height: 50px;
background-color: aqua;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="aaa" style="width: 100px;height: 50px;background-color: aqua;">
hello
</div>
<div id="bbb">
hello
</div>
</body>
<script>
const div1 = document.getElementById("aaa");
console.log(div1.style);
console.log(div1.style.width);
console.log(div1.style.height);
console.log(div1.style.backgroundColor);
const div2 = document.getElementById("bbb");
console.log(div2.style);
console.log(div2.style.width);
console.log(div2.style.height);
console.log(div2.style.backgroundColor);
</script>
</html>
运行结果:
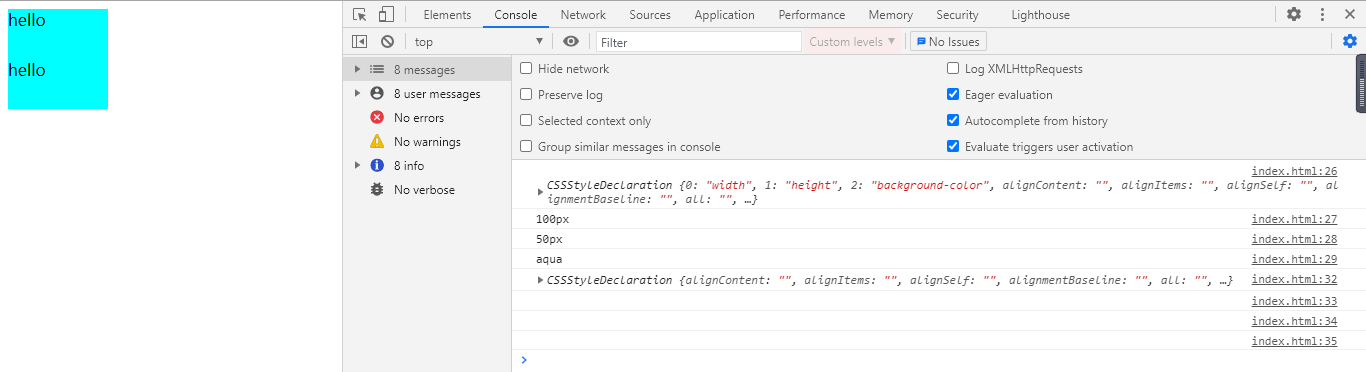
window.getComputedStyle() 是在标准规范下提供的 获取最终样式的方法,最终样式包括 行内样式和非行内样式 ,最后显示的效果就是靠优先级!其语法格式为:
window.getComputedStyle(元素).样式;
window对象是可选的,表示窗口对象。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
#bbb{
width: 100px;
height: 50px;
background-color: aqua;
}
#bbb2{
width: 100px;
height: 50px;
background-color: aqua;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="aaa" style="width: 100px;height: 50px;background-color: aqua;">
hello
</div>
<div id="bbb">
hello
</div>
<div id="bbb2">
hello
</div>
</body>
<script>
const div1 = document.getElementById("aaa");
console.log(div1.style);
console.log(div1.style.width);
console.log(div1.style.height);
console.log(div1.style.backgroundColor);
const div2 = document.getElementById("bbb");
console.log(div2.style);
console.log(div2.style.width);
console.log(div2.style.height);
console.log(div2.style.backgroundColor);
const div3 = document.getElementById("bbb2");
console.log(window.getComputedStyle(div3));
console.log(window.getComputedStyle(div3).width);
console.log(window.getComputedStyle(div3).height);
console.log(window.getComputedStyle(div3).backgroundColor);
</script>
</html>
运行结果:
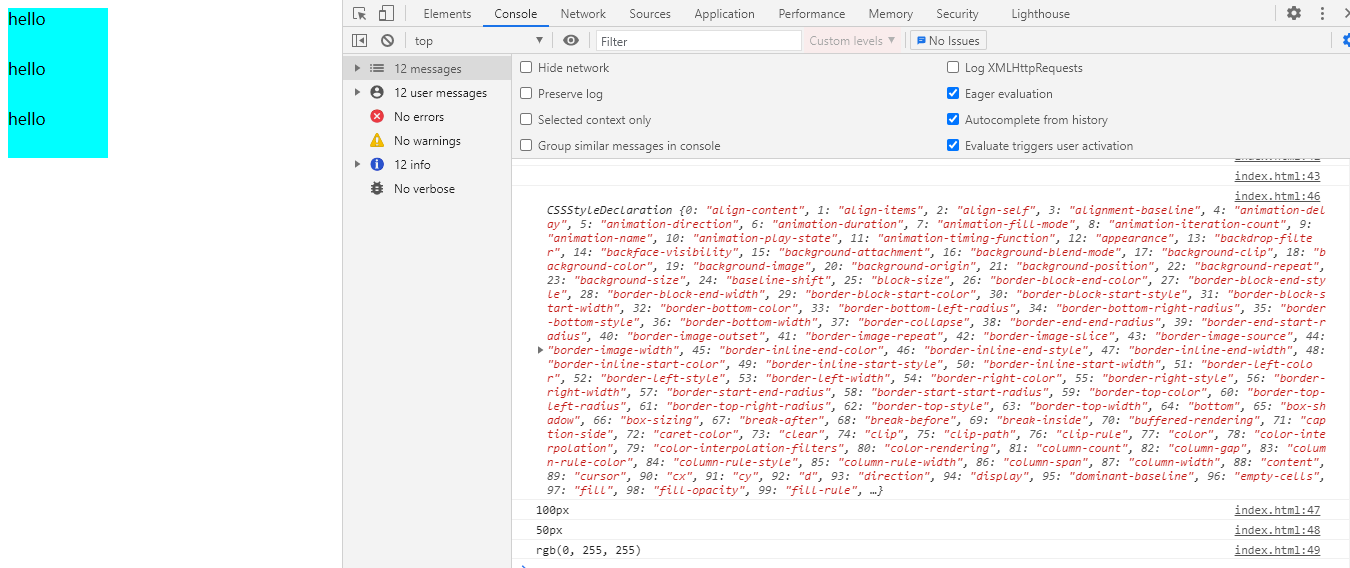
注意:
这里的返回是rgb颜色,属于内部转换!
三、兼容旧版本(currentStyle)
上面的是新版本的标准,对一些旧的浏览器可能不支持,这时候就要使用 currentStyle ,其基本语法是:
元素.currentStyle.样式;
这里菜鸟发现,基本上浏览器都不支持这个东西,所以了解就行,碰见 ie 才需要运用,兼容性如下:
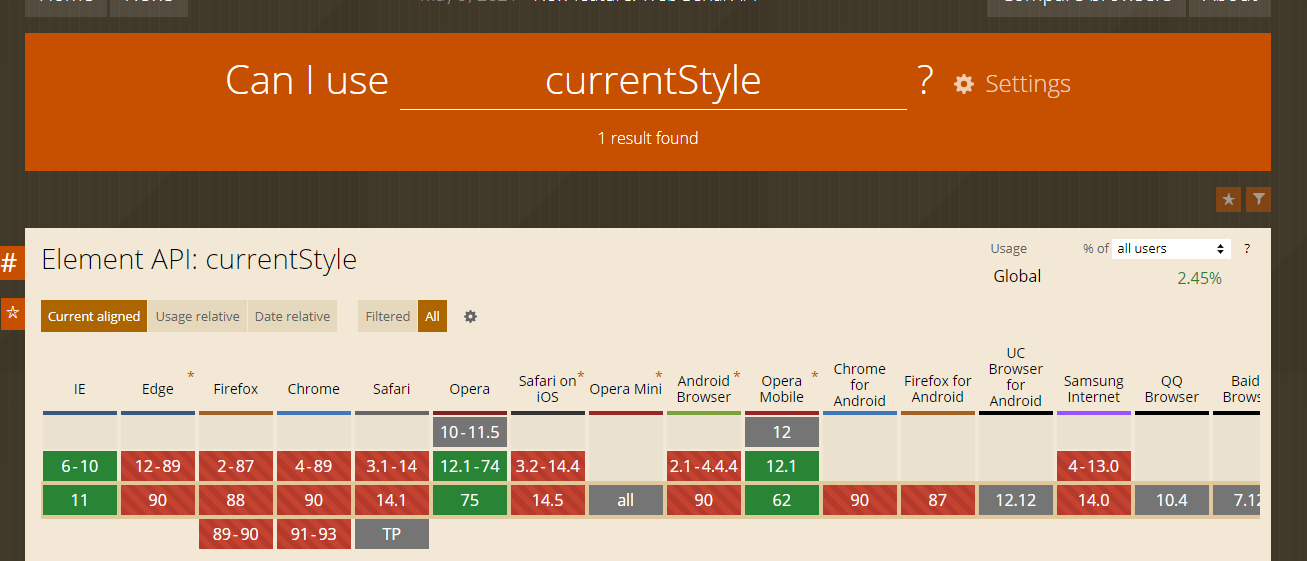
注意:
那如果元素即没有在style属性中设置宽高,也没有在样式表中设置宽高,还能用 getComputedStyle 或 style 获取吗?答案是 getComputedStyle 可以,style不可以 。(下面的例子就可以看出)
四、设置非行内样式
如何设置非行内样式呢?一般情况下这种情况很少见,但是js是有这个能力的。(上面改行内样式的那篇文章有说,建议翻上去看看)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
#bbb{
height: 50px;
background-color: aqua;
}
#bbb2{
height: 50px;
background-color: aqua;
}
#ddd{}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="aaa" style="height: 50px;background-color: aqua;">
hello
</div>
<div id="bbb">
hello
</div>
<div id="bbb2">
hello
</div>
<div id="ddd">hello</div>
</body>
<script>
const div1 = document.getElementById("aaa");
console.log(div1.style);
console.log(div1.style.width);
console.log(div1.style.height);
console.log(div1.style.backgroundColor);
const div2 = document.getElementById("bbb");
console.log(div2.style);
console.log(div2.style.width);
console.log(div2.style.height);
console.log(div2.style.backgroundColor);
const div3 = document.getElementById("bbb2");
console.log(window.getComputedStyle(div3));
console.log(window.getComputedStyle(div3).width);
console.log(window.getComputedStyle(div3).height);
console.log(window.getComputedStyle(div3).backgroundColor);
document.styleSheets[0].rules[1].style.width = "100px";
document.styleSheets[0].rules[1].style.height = "100px";
document.styleSheets[0].rules[1].style.backgroundColor = "green";
document.styleSheets[0].rules[2].style.width = "100px";
document.styleSheets[0].rules[2].style.height = "100px";
document.styleSheets[0].rules[2].style.backgroundColor = "red";
</script>
</html>
运行结果:
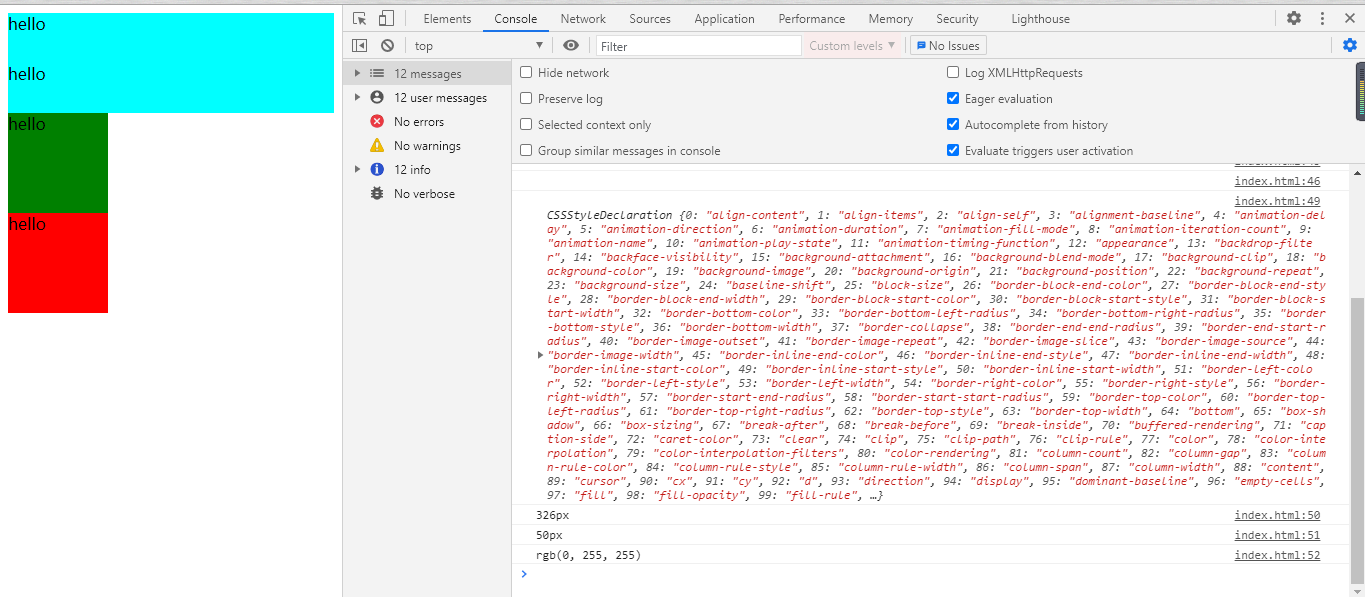
注意:
styleSheets[0] 表示获取 document 文档下的第一个样式表,rules[1] 表示样式表中的第二个样式。
最后
以上就是热情大船最近收集整理的关于看 Javascript实战详解 收获一的全部内容,更多相关看内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复