MATLAB实现的Reed-Muller编码解码纠错以及BER分析
- 背景
- 代码
- 计算BER
- 计算不使用RM编码情况时的BER(模拟环境与理论情况)
- 与汉明编码做对比
- 总结
背景
本科时信息论与编码的作业,RM(2,4)编码
课程为
Information Theory & Coding
Vaibhav Kumar, PhD
School of Electrical & Electronic Engineering
University College Dublin – The Republic of Ireland
下述作业也是老师布置的,如果涉及到版权问题我会删掉该博客。流程逻辑如下:
数据->RM编码->BPSK调制->加入AWGN(模拟传输时的噪声)->BPSK解调->解码(Majority-Logic解码)->输出数据
给定生成矩阵为
v0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
v4 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
v3 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1
v2 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1
v1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1
v3v4 = 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1
v2v4 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1
v1v4 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1
v2v3 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1
v1v3 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1
v1v2 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1
接收到的数据可以写成r=v+e的格式

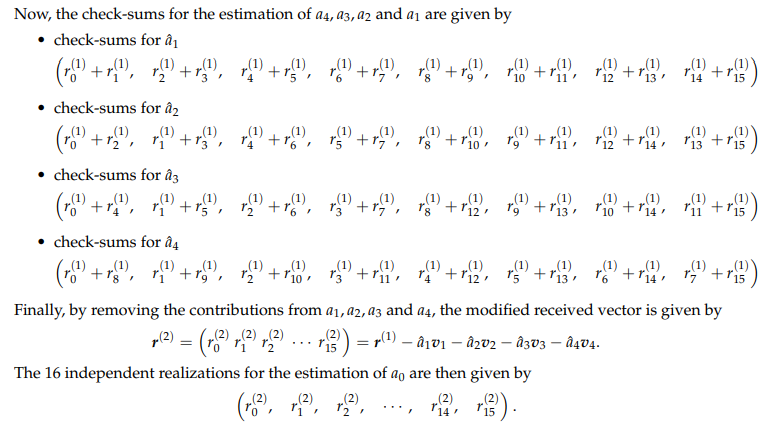
代码
clc,clear
Eb_N0_log=0:0.5:10; %dB
Eb_N0=10.^(Eb_N0_log/10);
R_coded=11/16; %R
BER_coded=zeros(1,21); %store BER in different Eb/N0
G=[1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1; %v0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1; %v4
0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1; %v3
0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1; %v2
0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1; %v1
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1; %v3v4
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1; %v2v4
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1; %v1v4
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1; %v2v3
0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1; %v1v3
0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1; %v1v2
]; %generator matrix
for i=1:21 %calculate BER in different Eb/N0
SNR_coded=2*R_coded*Eb_N0(i); %calculate SNR
message=round(rand(1,1980000)); %generate original data u = (a0 a4 a3 a2 a1 a34 a24 a14 a23 a13 a12),
px_w=1; %signal's power
pn_w=px_w/SNR_coded; %noise's power
error_number=0; %error bit number
for index=1:180000 %90000 blocks
m=message(1,11*index-10:11*index);
%m=[message(11*index-10),message(11*index-9),message(11*index-8),message(11*index-7),message(11*index-6),message(11*index-5),message(11*index-4),message(11*index-3),message(11*index-2),message(11*index-1),message(11*index)]; %one blobk data
v=mod(m*G,2); %generate v
message_modul=1-v*2; %0->1,1->-1 modulation
r=message_modul+sqrt(pn_w)*randn(1,16); %add white Gaussian noise
r=r<0; %demodulation
a12=sum([mod(r(1)+r(2)+r(3)+r(4),2),mod(r(5)+r(6)+r(7)+r(8),2),mod(r(9)+r(10)+r(11)+r(12),2),mod(r(13)+r(14)+r(15)+r(16),2)]==1);
if a12>2
a12=1;
elseif a12<2
a12=0;
else
a12=round(rand());
end %check-sums for a12
a13=sum([mod(r(1)+r(2)+r(5)+r(6),2),mod(r(3)+r(4)+r(7)+r(8),2),mod(r(9)+r(10)+r(13)+r(14),2),mod(r(11)+r(12)+r(15)+r(16),2)]==1);
if a13>2
a13=1;
elseif a13<2
a13=0;
else
a13=round(rand());
end %check-sums for a13
a23=sum([mod(r(1)+r(3)+r(5)+r(7),2),mod(r(2)+r(4)+r(6)+r(8),2),mod(r(9)+r(11)+r(13)+r(15),2),mod(r(10)+r(12)+r(14)+r(16),2)]==1);
if a23>2
a23=1;
elseif a23<2
a23=0;
else
a23=round(rand());
end %check-sums for a23
a14=sum([mod(r(1)+r(2)+r(9)+r(10),2),mod(r(3)+r(4)+r(11)+r(12),2),mod(r(5)+r(6)+r(13)+r(14),2),mod(r(7)+r(8)+r(15)+r(16),2)]==1);
if a14>2
a14=1;
elseif a14<2
a14=0;
else
a14=round(rand());
end %check-sums for a14
a24=sum([mod(r(1)+r(3)+r(9)+r(11),2),mod(r(2)+r(4)+r(10)+r(12),2),mod(r(5)+r(7)+r(13)+r(15),2),mod(r(6)+r(8)+r(14)+r(16),2)]==1);
if a24>2
a24=1;
elseif a24<2
a24=0;
else
a24=round(rand());
end %check-sums for a24
a34=sum([mod(r(1)+r(5)+r(9)+r(13),2),mod(r(2)+r(6)+r(10)+r(14),2),mod(r(3)+r(7)+r(11)+r(15),2),mod(r(4)+r(8)+r(12)+r(16),2)]==1);
if a34>2
a34=1;
elseif a34<2
a34=0;
else
a34=round(rand());
end %check-sums for a34
r=mod(r-a12*G(11,:)-a13*G(10,:)-a23*G(9,:)-a14*G(8,:)-a24*G(7,:)-a34*G(6,:),2);
a1=sum([mod(r(1)+r(2),2),mod(r(3)+r(4),2),mod(r(5)+r(6),2),mod(r(7)+r(8),2),mod(r(9)+r(10),2),mod(r(11)+r(12),2),mod(r(13)+r(14),2),mod(r(15)+r(16),2),]==1);
if a1>4
a1=1;
elseif a1<4
a1=0;
else
a1=round(rand());
end %check-sums for a1
a2=sum([mod(r(1)+r(3),2),mod(r(2)+r(4),2),mod(r(5)+r(7),2),mod(r(6)+r(8),2),mod(r(9)+r(11),2),mod(r(10)+r(12),2),mod(r(13)+r(15),2),mod(r(14)+r(16),2),]==1);
if a2>4
a2=1;
elseif a2<4
a2=0;
else
a2=round(rand());
end %check-sums for a2
a3=sum([mod(r(1)+r(5),2),mod(r(2)+r(6),2),mod(r(3)+r(7),2),mod(r(4)+r(8),2),mod(r(9)+r(13),2),mod(r(10)+r(14),2),mod(r(11)+r(15),2),mod(r(12)+r(16),2),]==1);
if a3>4
a3=1;
elseif a3<4
a3=0;
else
a3=round(rand());
end %check-sums for a3
a4=sum([mod(r(1)+r(9),2),mod(r(2)+r(10),2),mod(r(3)+r(11),2),mod(r(4)+r(12),2),mod(r(5)+r(13),2),mod(r(6)+r(14),2),mod(r(7)+r(15),2),mod(r(8)+r(16),2),]==1);
if a4>4
a4=1;
elseif a4<4
a4=0;
else
a4=round(rand());
end %check-sums for a4
r=mod(r-a1*G(5,:)-a2*G(4,:)-a3*G(3,:)-a4*G(2,:),2);
a0=sum(r==1);
if a0>8
a0=1;
elseif a0<8
a0=0;
else
a0=round(rand());
end %check-sums for a0
signal=[a0,a4,a3,a2,a1,a34,a24,a14,a23,a13,a12];
error_number=error_number+sum(sum(signal~=m)); %find the number of error bits
end
BER_coded(i)=error_number/1980000;
end
semilogy(Eb_N0_log,BER_coded);
xlabel('Eb/N0 [dB]');
ylabel('BER');
title('BER versus Eb/N0');
Eb_N0_log=0:0.5:10; %dB
Eb_N0=10.^(Eb_N0_log/10);
BER =0.5*erfc(sqrt(2*Eb_N0)/sqrt(2)); %Q function
hold on;
semilogy(Eb_N0_log,BER);
xlabel('Eb/N0 [dB]');
ylabel('BER');
title('BER versus Eb/N0');
R_uncoded=1; %R
BER_uncoded=zeros(1,21);
for i=1:21 %calculate BER in different Eb/N0
SNR_uncoded=2*R_uncoded*Eb_N0(i); %SNR
message=round(rand(1,1980000)); %generate original data
message_modul=1-message.*2; %0->1,1->-1 modulation
px_w=1; %signal's power
pn_w=px_w/SNR_uncoded; %noise's power
r=message_modul+sqrt(pn_w)*randn(1,1980000); %add white Gaussian noise
error_number=0;
r=r<0; %demodulation
error_number=error_number+sum(sum(r~=message)); %find the number of error bits
BER_uncoded(i)=error_number/1980000;
end
hold on;
semilogy(Eb_N0_log,BER_uncoded);
xlabel('Eb/N0 [dB]');
ylabel('BER ');
title('BER versus Eb/N0');
legend('RM-coded(simulation)','Uncoded(theory)','Uncoded(simulation)');
%I extend the horizontal coordinate of Uncoded(theory) and Uncoded(simulation)
% Eb_N0_log=0:0.5:11; %dB
% Eb_N0=10.^(Eb_N0_log/10);
% BER =0.5*erfc(sqrt(2*Eb_N0)/sqrt(2)); %Q function
% hold on;
% semilogy(Eb_N0_log,BER);
% xlabel('Eb/N0 [dB]');
% ylabel('BER');
% title('BER versus Eb/N0');
%
% R_uncoded=1; %R
% BER_uncoded=zeros(1,23);
% for i=1:23 %calculate BER in different Eb/N0
% SNR_uncoded=2*R_uncoded*Eb_N0(i); %SNR
% message=round(rand(1,1980000)); %generate original data
% message_modul=1-message.*2; %0->1,1->-1 modulation
% px_w=1; %signal's power
% pn_w=px_w/SNR_uncoded; %noise's power
% r=message_modul+sqrt(pn_w)*randn(1,1980000); %add white Gaussian noise
% error_number=0;
% r=r<0; %demodulation
% error_number=error_number+sum(sum(r~=message)); %find the number of error bits
% BER_uncoded(i)=error_number/1980000;
% end
% hold on;
% semilogy(Eb_N0_log,BER_uncoded);
% xlabel('Eb/N0 [dB]');
% ylabel('BER ');
% title('BER versus Eb/N0');
% legend('RM-coded(simulation)','Uncoded(theory)','Uncoded(simulation)');
计算BER
1、随机生成1980000比特,分为180000 block,每个block称为m。
2、进行RM编码。
3、进行BPSK调制。
4、添加高斯白噪声
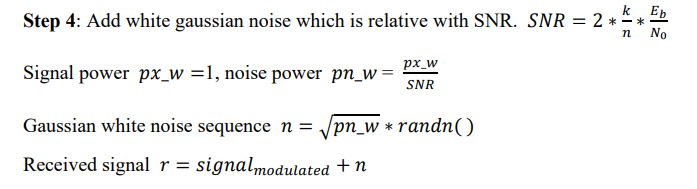
5、BPSK解码。
6、Majority-Logic解码。计算错误比特的个数。

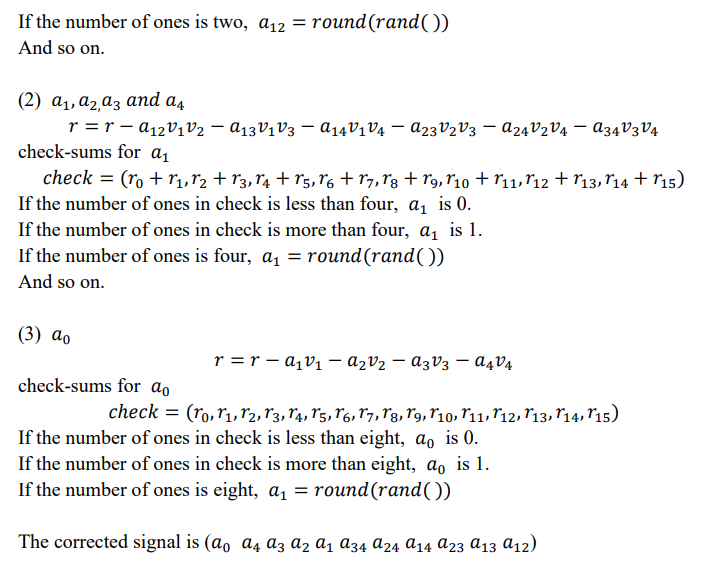
7、计算BER。
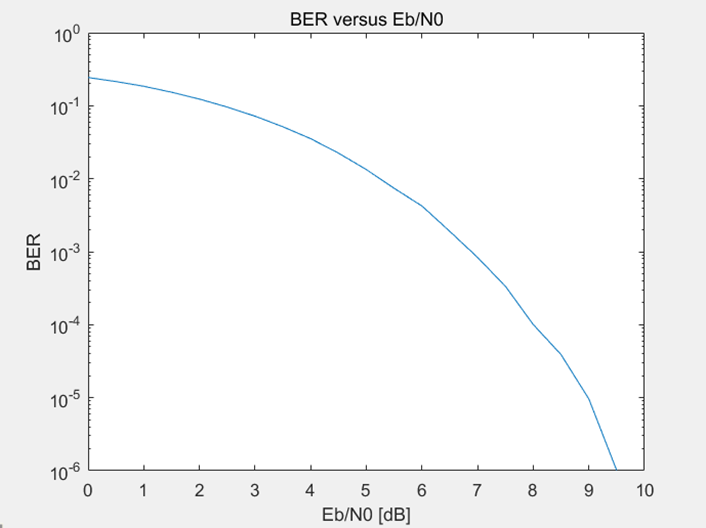
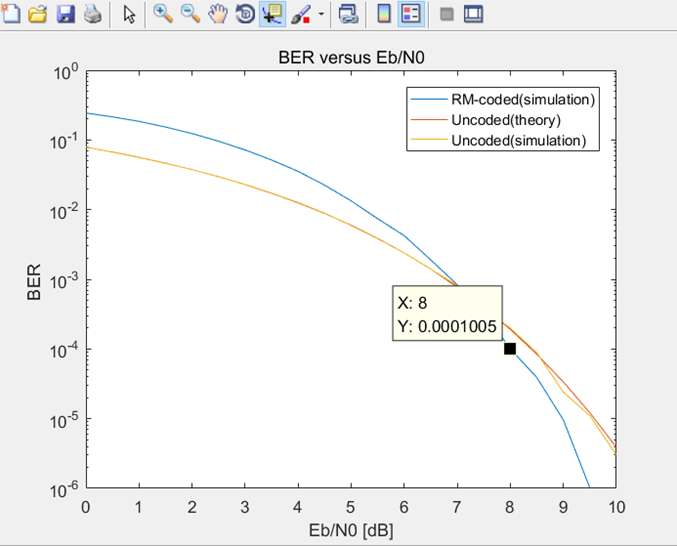
结果:
计算不使用RM编码情况时的BER(模拟环境与理论情况)
1、随机生成比特。
2、进行BPSK调制。
3、添加高斯白噪声
4、BPSK解码。
5、计算错误比特的个数。
6、利用第五部分结果计算模拟环境下的BER。
6、使用erfc函数计算理论情况下的BER。
结果:
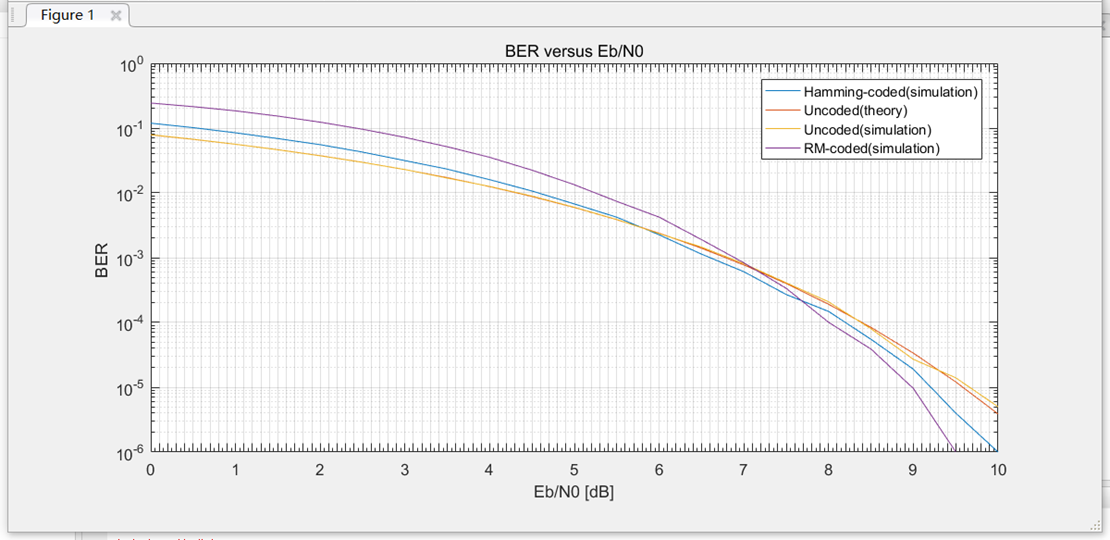
与汉明编码做对比
与https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44480014/article/details/123203931实现的汉明编码做对比。
结果:
总结
从BER的角度来看,如果Eb/N0小于7.152dB,未编码系统优于RM编码系统,如果Eb/N0大于7.152dB,RM编码系统优于未编码系统。如果Eb/N0小于7.681dB,汉明编码系统优于RM编码系统,如果Eb/N0大于7.681dB,RM编码系统优于汉明编码系统。
最后
以上就是舒适白猫最近收集整理的关于MATLAB实现的Reed-Muller(RM码,里德-马勒编码)编码解码纠错以及BER分析背景代码计算不使用RM编码情况时的BER(模拟环境与理论情况)与汉明编码做对比总结的全部内容,更多相关MATLAB实现内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复