题目做后还是要做一下总结,才能确切的知道自己通过做题收获了什么。
之前我一直享受刷题的快感,懒于及时做整理、总结,拖到了现在,刷了200题才打算开始。
这200题中有水题,有自己冥思苦想才解出的题,也有苦想之后做不出来然后看答案的题,也有一看题就知道自己不会做然后直接看答案的题。
另外,给想要刷Leetcode的朋友一点建议,做题前不用太在意题目标注的难度,主要看题目里的点赞次数和反对次数,我一般选择高赞低反对的题,发现这些题都是比较有料的。
979. Distribute Coins in Binary Tree
class Solution {
public:
//节点的coin为n,那它势必要移走或者移入n-1次
//自底向上分配
int dfs(TreeNode* root,int& ans)
{
if(root==NULL)
return 0;
int left = dfs(root->left,ans),right = dfs(root->right,ans);
ans += abs(left)+abs(right);
return root->val+left+right-1; //自底向上分配,每个节点只与其左右子节点有关
}
int distributeCoins(TreeNode* root) {
int ans = 0;
dfs(root,ans);
return ans;
}
};
▲对于一些给定数组作为参数的题目,如果要求解的内容与元素在数组中对应的位置无关,那么可以尝试对数组进行排序寻求思路。
▲如何将二叉树化成图:先过一遍DFS,记录节点对应的父结点(可以采用unordered_map),之后在遍历所有节点的时候对于每一个节点就可以同时遍历它的子结点和父结点,这比较常用于BFS,按层或者按距离一步步增加展开搜索。
974. Subarray Sums Divisible by K
由该题,引出一种思路:有的题目跟数学联系紧密,可以先观察问题中的数学联系,结合编程和数学知识解题
该题中:(sum%K+K)%K:防止了余数为负数,不可作为数组下标的情况出现;
(mod[i]*(mod[i]-1)/2): 余数相同的子序列的和相减,得到可以被K整除的子序列,所以记录余数为0-K的子序列的个数,求组合数
class Solution {
public:
int subarraysDivByK(vector<int>& A, int K) {
int n = A.size();
vector<int> mod(K,0); // count
int ans = 0,sum = 0;
for(int i=0;i<n;++i)
sum+=A[i],mod[(sum%K+K)%K]++; //avoid negative remainder
for(int i=0;i<K;++i)
ans+=(mod[i]*(mod[i]-1)/2); //combination
ans += mod[0]; // all sum which module K result 0 can be a subarray separately
return ans;
}
};
973. K Closest Points to Origin 求前K个靠近原点(0,0)的点
这道题只是求每个点与原点的距离然后做个排序,取较小的前K个,很简单。但通过看别人的解法,学到了**STL中一个划分排序的函数:partial_sort( begin,begin+K,end,cmp)**,表示对[begin,begin+K)范围内的元素排序,而[begin+K,end)中元素的顺序未指定;cmp是否需要视情况而定(作为排序时元素比较的依据),若需要,可以直接以“[](参数){函数内容}”作为参数cmp的值。
题解:
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> kClosest(vector<vector<int>>& points, int K) {
vector<vector<int>> ans=points;
partial_sort(ans.begin(),ans.begin()+K,ans.end(),[](vector<int> a,vector<int> b)
{return a[0]*a[0]+a[1]*a[1]<b[0]*b[0]+b[1]*b[1];});
ans.resize(K);
return ans;
}
};
3. Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters 求不包含重复字符的子串
通过这道题学习题解中称为“Sliding Window”的方法,也让我往后在做题的时候习惯性的先看有没有可能有时间复杂度低的方法可解。简而言之,就是用前后两个指示位置的标记在序列上滑动,由此保证不重复对序列进行操作。
class Solution {
public:
int lengthOfLongestSubstring(string s) {
unordered_set<char> inset;
int begin=0,end=0;
int maxlen=0;
while(end<s.size())
{
if(inset.find(s[end])==inset.end())
{
inset.insert(s[end++]);
maxlen = max(maxlen,end-begin);
}
else
inset.erase(s[begin++]);
}
return maxlen;
}
};
▲比较熟练地使用一些容器的初始化方式,如vector< int> v(begin迭代器,end迭代器)
▲熟悉set/unordered_set 和 map/unordered_map的使用,set/map中的操作时间复杂度为O(lgn),而unordered_set/unordered_map中的操作的时间复杂度为O(1),最坏情况下为O(n)。虽然后者一般情况下时间复杂度较低,但是其是键值的放置是无序的,所以如何选取合适的容器来帮助解题,要根据不同问题考虑
下面的题目我是学习了Discuss中某大神的想法
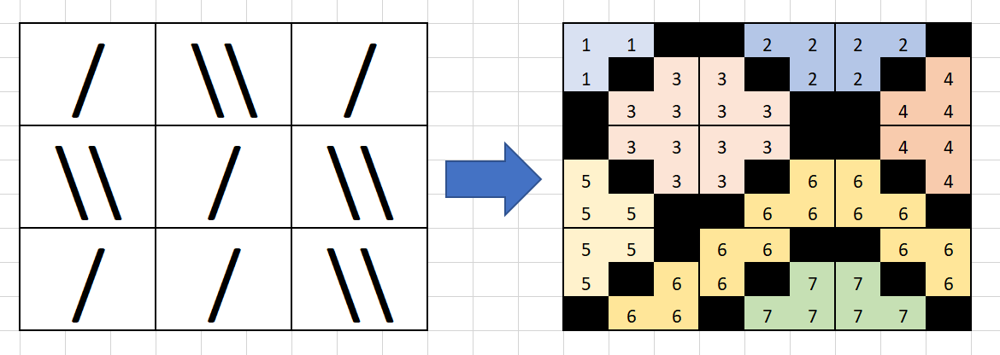
959. Regions Cut By Slashes 求正方形内被斜杠划分所得的区域的个数。这是一道比较抽象的题,我们要把抽象的问题具体化、可编程化。将原图的大小扩大三倍,然后用处于同一对角线上的三个格子表示一条斜杆,接着就是简单的求图的连通分量个数的问题了。
上方给了该题大神的核心思想的图解。
我的代码:
// 求连通分量个数
void DFS(vector<vector<int>>& graph,vector<vector<int>>& visited,int row,int col)
{
if(row<0||row>=graph.size()||col<0||col>=graph.size()||graph[row][col]||visited[row][col])
return ;
visited[row][col] = 1;
DFS(graph,visited,row+1,col);
DFS(graph,visited,row-1,col);
DFS(graph,visited,row,col+1);
DFS(graph,visited,row,col-1);
}
//将原图扩大并将斜杆具体化
int regionsBySlashes(vector<string>& grid)
{
int newsize = grid.size()*3;
vector<vector<int>> graph(newsize),visited(newsize);
for(int i=0; i<graph.size(); ++i)
{
graph[i].assign(newsize,0);
visited[i].assign(newsize,0);
}
for(int i=0; i<grid.size(); ++i)
{
string cur = grid[i];
for(int j=0; j<cur.size(); ++j)
{
char node = cur[j];
if(node == '/')
{
graph[i*3][j*3+2]=1;
graph[i*3+1][j*3+1]=1;
graph[i*3+2][j*3]=1;
}
else if(node=='\')
{
graph[i*3][j*3]=1;
graph[i*3+1][j*3+1]=1;
graph[i*3+2][j*3+2]=1;
}
}
}
int ans = 0;
for(int row=0; row<newsize; ++row)
for(int col=0; col<newsize; ++col)
{
if(!visited[row][col]&&!graph[row][col])
{
DFS(graph,visited,row,col);
ans++;
}
}
return ans;
}
958. Check Completeness of a Binary Tree 判断一棵树是不是完全二叉树。 我采用了BFS,用层次遍历的方法一层一层地判断。也通过这题记录树的层次遍历方法:借助队列,每一次操作前记录当前队列的size,然后对这size个元素进行操作,实现每一次对树的一层进行操作。
我的代码:
class Solution {
public:
bool isCompleteTree(TreeNode* root) {
bool flag = true;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty())
{
int num = q.size();
while(num--)
{
TreeNode* cur = q.front();
q.pop();
if(cur->left&&flag)
q.push(cur->left);
else if(cur->left)
return false;
else
flag = false;
if(cur->right&&flag)
q.push(cur->right);
else if(cur->right)
return false;
else
flag = false;
}
}
return true;
}
};
953. Verifying an Alien Dictionary 判断序列中的字符串是不是按字典序排序,其中字母的顺序不是'abc...xyz'
采用unordered_map 将给定的字母序列映射到我们现有的字母序列'abc...xyz',然后将序列中的字符串修改为以我们现有的字母序列的基础的字符串。
class Solution {
public:
bool isAlienSorted(vector<string>& words, string order) {
unordered_map<char,char> table;
char index = 'a';
for(auto ch:order)
table[ch]=index++;
for(int i=0; i<words.size()-1; ++i)
{
for(int j=0; j<words[i].size(); ++j)
words[i][j] = table[words[i][j]];
for(int j=0; j<words[i+1].size(); ++j)
words[i+1][j] = table[words[i+1][j]];
if(words[i+1]<words[i])
return false;
}
return true;
}
};
951. Flip Equivalent Binary Trees 判断两棵二叉树是否能够通过翻转达到相等。
发现很多二叉树的题都能用简短的递归代码实现,重要的是我们要分清楚递归可能出现的所有情况,并对每一种情况做针对性的考虑。
我的代码:
class Solution {
public:
bool flipEquiv(TreeNode* root1, TreeNode* root2)
{
// I enumerates all situations and solve them respectively
if(root1==NULL||root2==NULL)
return root1==root2;
if(root1->val!=root2->val)
return false;
//判断何时需要进行反转(我们始终只对其中一棵树进行翻转)
//需要注意的是,我们经常需要先判断某个指针是否为空,若不为空我们再去访问它的内容。
if((root1->left==NULL&&root2->left)||(root1->left&&root2->left==NULL)||(root1->left&&root2->left&&root1->left->val!=root2->left->val))
{
TreeNode* lefttemp = root1->left;
root1->left = root1->right;
root1->right = lefttemp;
}
return flipEquiv(root1->left,root2->left)&&flipEquiv(root1->right,root2->right);
}
};
950. Reveal Cards In Increasing Order
做这道题时我一直是用队列对序列中的元素进行操作,但始终无法求解,后来看了题解,是用队列对元素的下标进行操作。这提醒了我做这类题目时思路的变化。
代码:
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> deckRevealedIncreasing(vector<int>& deck) {
int n = deck.size();
vector<int> ans(n);
queue<int> q;
for(int i=0;i<n;++i)
q.push(i);
sort(deck.begin(),deck.end());
for(int card:deck)
{
int ind = q.front();
q.pop();
ans[ind] = card;
if(!q.empty())
q.push(q.front()),q.pop();
}
return ans;
}
};
949. Largest Time for Given Digits 给定4个数,求这四个数能否组成24小时制的时钟表示,能的话求出能表示的最晚的时间。
4个数有4!种排序,要求出这4个数的这各种排序,然后比较求出其中的最大值。
借助了STL中的“next_permutation(迭代器begin,迭代器end)”函数,获取当前序列的下一个全排序序列。
代码:
string largestTimeFromDigits(vector<int>& A)
{
string Max = "0000";
bool valid=false;
string s = "0123";
vector<string> perm;
do
{
perm.push_back(s);
}
while(next_permutation(s.begin(),s.end()));
for(int i=0; i<perm.size(); ++i)
{
string p = perm[i];
string time ;
time +=(A[p[0]-'0']+'0');
time +=(A[p[1]-'0']+'0');
time +=(A[p[2]-'0']+'0');
time +=(A[p[3]-'0']+'0');
if(time<="2359"&&time[2]<='5')
{
valid = true;
Max = max(Max,time);
}
}
if(!valid)
return "";
Max.insert(2,1,':'); //string的插入函数: insert(下标,数量,字符)
return Max;
}
945. Minimum Increment to Make Array Unique 求最小的increment次数使得序列中所有元素都不相等。
通过该题养成一种解题意识:若问题与序列的顺序无关,可以尝试对序列进行排序看是否有助于解题。
先对序列排序,再看排序后的各元素是否需要增加( increment )。
class Solution {
public:
int minIncrementForUnique(vector<int>& A) {
sort(A.begin(), A.end());
int ans = 0, need = 0; //need express how much more we have to add
for (int a:A) {
ans += max(need - a, 0);
need = max(a, need) + 1; //since if the difference between the two elements is 1,we needn't add,so we firstly add 1.
}
return ans;
}
};
最后
以上就是复杂仙人掌最近收集整理的关于Leetcode:200题总结(一)的全部内容,更多相关Leetcode内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复