【TINY4412】LINUX移植笔记:(23)设备树 LCD触摸屏驱动
宿主机 : 虚拟机 Ubuntu 16.04 LTS / X64
目标板[底板]: Tiny4412SDK - 1506
目标板[核心板]: Tiny4412 - 1412
LINUX内核: 4.12.0
交叉编译器: arm-none-linux-gnueabi-gcc(gcc version 4.8.3 20140320)
日期: 2017-9-1 19:48:24
作者: SY
简介
触摸屏芯片使用 FT5406 ,使用 I2C 总线传输触摸屏数据。
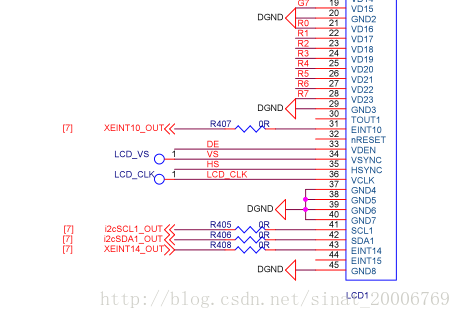

主要使用 3 根线, I2CSCL1_OUT I2CSDA1_OUT XEINT14_OUT ,一开始参考友善之臂的驱动,以为触摸屏数据也是通过 XINT10_OUT 一线传输,尝试读取数据发现一直读不到。后来查找资料才知道是采用 I2C 总线传输的,晕…
网上下载触摸芯片的手册:FT5x06.pdf

硬件上只连接了 I2C INT ,其中 I2C 用于传输触摸屏数据。 INT 引脚用于通知 ARM 主机,触摸屏被按下,可以读取数据,这样就不用主机定时 poll 设备,节省大量时间。
I2C 使用 I2C1 ,INT 使用 GPX1-6 引脚。
移植
从目录 driversinputtouchscreen 找到驱动 edt-ft5x06.c
设备树
参考 exynos4.dtsi
i2c_1: i2c@13870000 {
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
compatible = "samsung,s3c2440-i2c";
reg = <0x13870000 0x100>;
interrupts = <GIC_SPI 59 IRQ_TYPE_LEVEL_HIGH>;
clocks = <&clock CLK_I2C1>;
clock-names = "i2c";
pinctrl-names = "default";
pinctrl-0 = <&i2c1_bus>;
status = "disabled";
};写自己的 dts
&i2c_1 {
samsung,i2c-sda-delay = <100>;
samsung,i2c-max-bus-freq = <400000>;
status = "okay";
ft5406: touchscreen@38 {
compatible = "edt,edt-ft5406";
reg = <0x38>;
interrupt-parent = <&gpx1>;
interrupts = <6 IRQ_TYPE_EDGE_FALLING>;
touchscreen-size-x = <800>;
touchscreen-size-y = <480>;
touchscreen-fuzz-x = <4>;
touchscreen-fuzz-y = <7>;
touchscreen-fuzz-pressure = <2>;
touchscreen-max-pressure = <2048>;
};
};ft5406 作为 i2c1 的子节点。
menuconfig
Device Drivers --->
I2C support --->
I2C Hardware Bus support --->
<*> S3C2410 I2C Driver
Device Drivers --->
Input device support --->
[*] Touchscreens --->
<*> EDT FocalTech FT5x06 I2C Touchscreen support 源码分析
static int edt_ft5x06_ts_probe(struct i2c_client *client,
const struct i2c_device_id *id)
{
/* 从设备树获取数据,主要包括:触摸分辨率,按压噪声值, 水平/垂直噪声等 */
touchscreen_parse_properties(input, true, &tsdata->prop);
/* 请求 INT(GPIO) 中断,当触摸屏被按压时,以中断的方式通知主机
edt_ft5x06_ts_isr 为中断服务函数
*/
error = devm_request_threaded_irq(&client->dev, client->irq,
NULL, edt_ft5x06_ts_isr, irq_flags,
client->name, tsdata);
}
static irqreturn_t edt_ft5x06_ts_isr(int irq, void *dev_id)
{
/* 通过 I2C总线 读取触摸屏数据 */
error = edt_ft5x06_ts_readwrite(tsdata->client,
sizeof(cmd), &cmd,
datalen, rdbuf);
/* 报告触摸屏坐标 */
touchscreen_report_pos(tsdata->input, &tsdata->prop, x, y,
true);
}烧录
[ 0.398601] s3c-i2c 13870000.i2c: slave address 0x00
[ 0.398611] s3c-i2c 13870000.i2c: bus frequency set to 390 KHz
[ 0.398866] s3c-i2c 13870000.i2c: i2c-1: S3C I2C adapter
[ 2.654123] edt_ft5x06 1-0038: GPIO lookup for consumer reset
[ 2.659300] edt_ft5x06 1-0038: using device tree for GPIO lookup
[ 2.665309] of_get_named_gpiod_flags: can't parse 'reset-gpios' property of node '/i2c@13870000/touchscreen@38[0]'
[ 2.675647] of_get_named_gpiod_flags: can't parse 'reset-gpio' property of node '/i2c@13870000/touchscreen@38[0]'
[ 2.685953] edt_ft5x06 1-0038: using lookup tables for GPIO lookup
[ 2.692049] edt_ft5x06 1-0038: lookup for GPIO reset failed
[ 2.697579] edt_ft5x06 1-0038: GPIO lookup for consumer wake
[ 2.703234] edt_ft5x06 1-0038: using device tree for GPIO lookup
[ 2.709211] of_get_named_gpiod_flags: can't parse 'wake-gpios' property of node '/i2c@13870000/touchscreen@38[0]'
[ 2.719466] of_get_named_gpiod_flags: can't parse 'wake-gpio' property of node '/i2c@13870000/touchscreen@38[0]'
[ 2.729620] edt_ft5x06 1-0038: using lookup tables for GPIO lookup
[ 2.735782] edt_ft5x06 1-0038: lookup for GPIO wake failed
[ 2.743112] input input0: DT specifies parameters but the axis 58 is not set up
[ 2.748771] input: EP08150M09 as /devices/platform/13870000.i2c/i2c-1/1-0038/input/input0查看 proc
[root@TINY4412:~]# cat proc/bus/input/devices
I: Bus=0018 Vendor=0000 Product=0000 Version=0000
N: Name="EP08150M09"
P: Phys=
S: Sysfs=/devices/platform/13870000.i2c/i2c-1/1-0038/input/input0
U: Uniq=
H: Handlers=mouse0 event0
B: PROP=2
B: EV=b
B: KEY=400 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
B: ABS=2608000 3
I: Bus=0013 Vendor=dead Product=beef Version=0100
N: Name="tiny4412_lcd_key"
P: Phys=
S: Sysfs=/devices/virtual/input/input1
U: Uniq=
H: Handlers=kbd event1
B: PROP=0
B: EV=3
B: KEY=40000800 40 0 0 0
I: Bus=0019 Vendor=001f Product=0001 Version=0100
N: Name="pwm-beeper"
P: Phys=pwm/input0
S: Sysfs=/devices/platform/buzzer/input/input2
U: Uniq=
H: Handlers=kbd event2
B: PROP=0
B: EV=40001
B: SND=6
I: Bus=0019 Vendor=0001 Product=0001 Version=0100
N: Name="gpio_keys"
P: Phys=gpio-keys/input0
S: Sysfs=/devices/platform/gpio_keys/input/input3
U: Uniq=
H: Handlers=kbd event3
B: PROP=0
B: EV=3
B: KEY=3c被识别为 /dev/input/event0
APP
/*
* touchscreen driver for tiny4412
*
* Copyright (c) 2017
* Author: SY <1530454315@qq.com>
*
* This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
* modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as
* published by the Free Software Foundation; either version 2 of
* the License, or (at your option) any later version.
*
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/epoll.h>
#define ABS_X 0x00
#define ABS_Y 0x01
#define ABS_Z 0x02
#define ABS_MT_POSITION_X 0x35 /* Center X touch position */
#define ABS_MT_POSITION_Y 0x36 /* Center Y touch position */
struct input_event {
struct timeval time;
unsigned short int type;
unsigned short int code;
signed int value;
};
#if 0
static void help(void)
{
printf("Usage: ./key <id>n");
}
#endif
bool esc = false;
static void sigint_handler(int dunno)
{
switch (dunno) {
case SIGINT:
esc = true;
printf("< Ctrl+C > Press.n");
break;
default:
break;
}
}
static void* read_handler(void* data)
{
printf("thread run.n");
int epfd = epoll_create1(0);
if (epfd < 0) {
perror("epoll_create1");
return NULL;
}
int evfd = open("/dev/input/event0", O_RDONLY);
if (evfd < 0) {
perror("[open]");
esc = true;
}
struct epoll_event epoll_event;
epoll_event.events = EPOLLIN;
epoll_event.data.fd = evfd;
if (epoll_ctl(epfd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, evfd, &epoll_event) < 0) {
perror("[epoll_ctl]");
esc = true;
}
printf("start epoll...n");
struct input_event event;
const int MAX_EVENT_NUMS = 10;
const int TIMEOUT = 100;
struct epoll_event *events = calloc(MAX_EVENT_NUMS, sizeof(struct epoll_event));
if (!events) {
perror("mem calloc");
esc = true;
}
while (esc == false) {
int nums = epoll_wait(epfd, events, MAX_EVENT_NUMS, TIMEOUT);
for (int i=0; i<nums; ++i) {
if (events[i].events & (EPOLLERR | EPOLLHUP)) {
perror("epoll");
continue;
} else if ((events[i].data.fd == evfd) && (events[i].events & EPOLLIN)) {
int ret = read(evfd, &event, sizeof(event));
if (ret < 0) {
break;
}
//printf("[key] nums=%d code=%d value=%dn", nums, event.code, event.value);
switch (event.code) {
case ABS_MT_POSITION_X:
printf("X --> %dn", event.value);
break;
case ABS_MT_POSITION_Y:
printf("Y ------> %dn", event.value);
break;
case ABS_X:
//printf("ABS-X: %dn", event.value);
break;
case ABS_Y:
//printf("ABS-Y: %dn", event.value);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
}
if (events) {
free(events);
}
close(epfd);
close(evfd);
printf("thread exit.n");
pthread_exit(NULL);
return NULL;
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
pthread_t thread_read;
int ret = pthread_create(&thread_read, NULL, read_handler, NULL);
if (ret) {
perror("[thread_create]");
return 1;
}
/* Register signal */
signal(SIGINT, sigint_handler);
pthread_join(thread_read, NULL);
printf("done!n");
return 0;
}测试
[root@TINY4412:~]# ./tmp/touchscreen
thread run.
start epoll...
X --> 608
Y ------> 370
X --> 400
Y ------> 368
Y ------> 367
X --> 46
Y ------> 33
X --> 36
Y ------> 449
X --> 760
Y ------> 79
X --> 778
Y ------> 479
^C< Ctrl+C > Press.
thread exit.
done!
[root@TINY4412:~]# 参考
LCD-HD101/zh
设备树学习之(十三)电容触摸屏驱动
- 在大部分的ARM主控板中,我们发现,直接使用CPU自带的ADC转换器并不能很好的支持大尺寸(7寸以上)的四线电阻触摸屏,市面上一般采用更加专业的USB或串口触摸屏扩展模块来解决。为了节省ARM主控芯片的有限资源以及减少外扩,我们专门开发了只使用一个普通GPIO就可以实现专业触摸效果的替代方案,并把它集成到我们的LCD模块驱动板中,我们称之为“一线触摸(1-Wire)”。它的基本原理是,使用一个低成本的MCU连接一个专业的触控芯片(在此我们使用的是ADS7843或兼容芯片),采集并处理四线电阻模拟信号,并把滤波(未校准)后的稳定原始数据通过GPIO送给ARM主控,经我们长期反复测试,即使在19寸这样大的电阻触摸屏上,也可以实现非常精准的触摸效果,不会出现漂移抖动的现象。
- 另外,当今12寸以内的LCD显示屏,大都采用了LED背光,我们顺便也把背光调节部分也交给MCU来处理,并设置了统一的调节数值区间,最后通过“一线触摸”的GPIO传给ARM主控,这样在ARM端就可以非常方便的来设置背光了。
- 与此同时,我们还为我们设计开发的每一款带“一线触摸”的LCD模块设置了编号存储在MCU中,这样通过一线通讯读取到的编号,就可以知道这个LCD模块的具体类型了,也就可以在bootloader和内核中自动匹配相应的LCD驱动参数,以此来实现无需修改任何配置,即插即用带”一线触摸”的LCD模块。
- 在电容触摸LCD模块中,我们则去掉了电阻触控芯片,而保留了背光调节和存储LCD类型编号这2个功能,因此电容触摸通讯依然是标准的I2C接口。
- 需要注意的是,我们实现的“一线触摸”的通讯,和通常所说的单总线接口是不同的。在ARM主控端内部,我们实际采用了一路pwm timer(不是pwm管脚哦)来实现固定的通讯频率(9600Hz),详细请查看驱动源代码。
最后
以上就是阔达棒球最近收集整理的关于【TINY4412】LINUX移植笔记:(23)设备树LCD触摸屏驱动【TINY4412】LINUX移植笔记:(23)设备树 LCD触摸屏驱动的全部内容,更多相关【TINY4412】LINUX移植笔记:(23)设备树LCD触摸屏驱动【TINY4412】LINUX移植笔记:(23)设备树内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复