以下内容是本人学习讯为的4412,记录的一些常用的指令和操作,以便以后查看方便。
内核编译的指令:
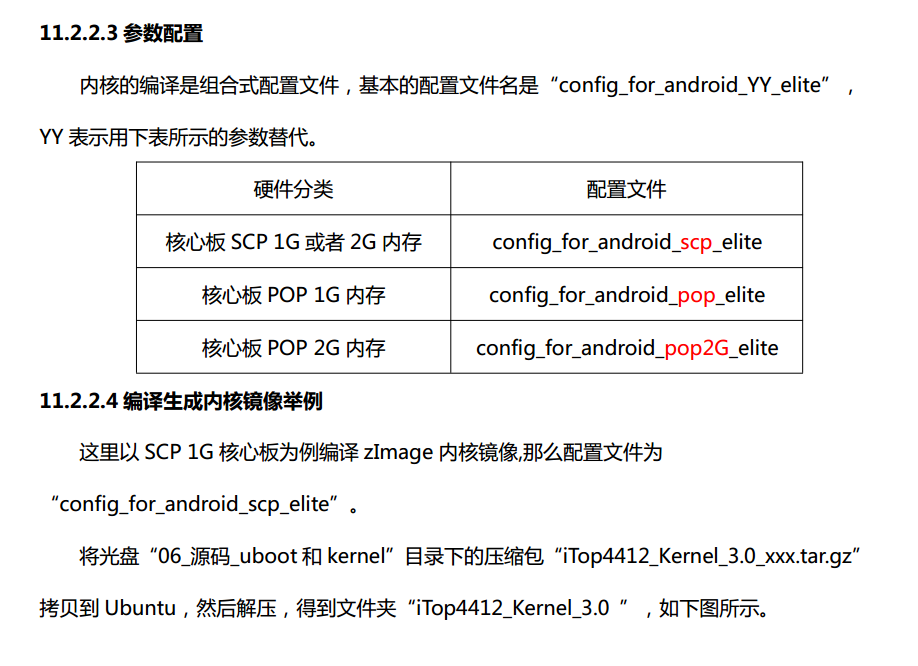
进入文件夹“iTop4412_Kernel_3.0 ”,使用命令
“cp config_for_android_pop_elite .config”覆盖自带的配置文件,如下图所示

二.模块加载方法
1.将生成的 .ko 文件拷贝到u盘或者 sd卡
2.将u 盘或者 sd卡 插到开发板
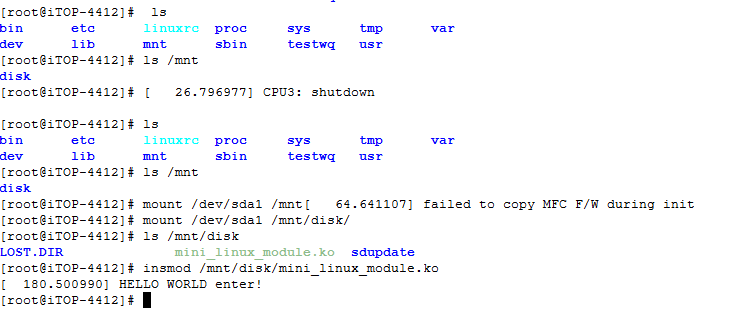
3.使用命令, ls /mnt 查看可挂载的盘目录
ls /mnt/disk
4.挂载U盘 使用命令
mount /dev/sda1 /mnt/disk/ ( mount /dev/mmcblk1p1 /mnt/disk )
5.加载模块,使用命令
insmod /mnt/disk/mini_linux_module.ko
5.查看模块使用命令
lsmod /mnt/disk/mini_linux_module.ko 或者 cat /proc/modules
6.卸载模块 使用命令
rmmod /mnt/disk/mini_linux_module.ko
(如果出现无法卸载的情况 :rmmod: can't change directory to '/lib/modules': No such file or directory
提示没有'/lib/modules'目录
– 使用命令“#mkdir /lib/modules”,新建一个目录
• 是用rmmod命令仍然会出现如下错误:
– rmmod: can't change directory to '3.0.15': No such file or directory
• 提示没有目录'3.0.15'
– 使用命令“#mkdir /lib/modules/3.0.15”,继续建目录
)
三.ADB 写 zImage 过程
1.reboot
2.fastboot
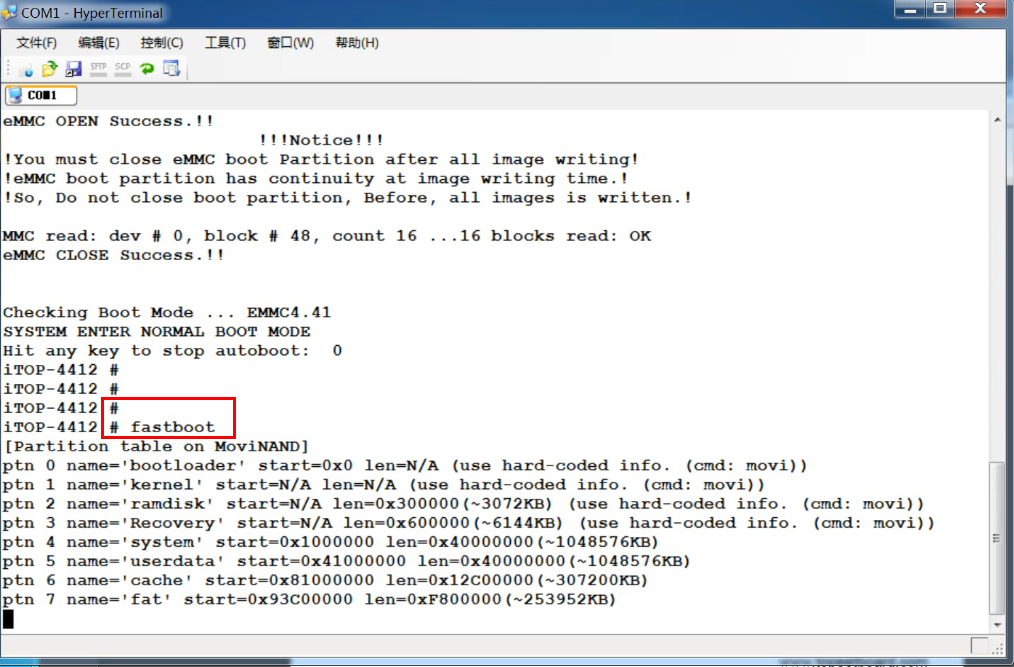
3. fastboot.exe falsh kernel zImage
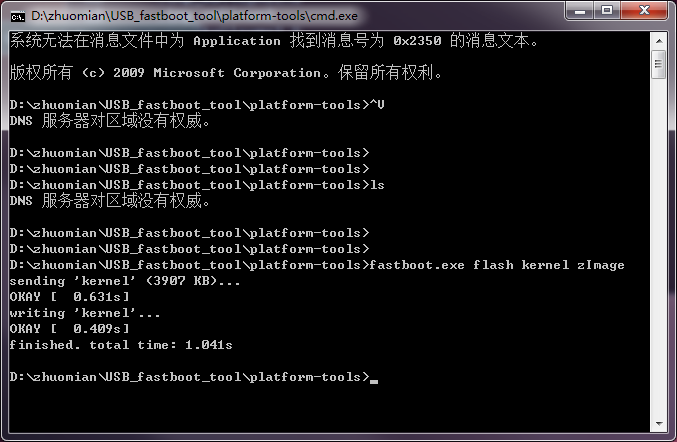
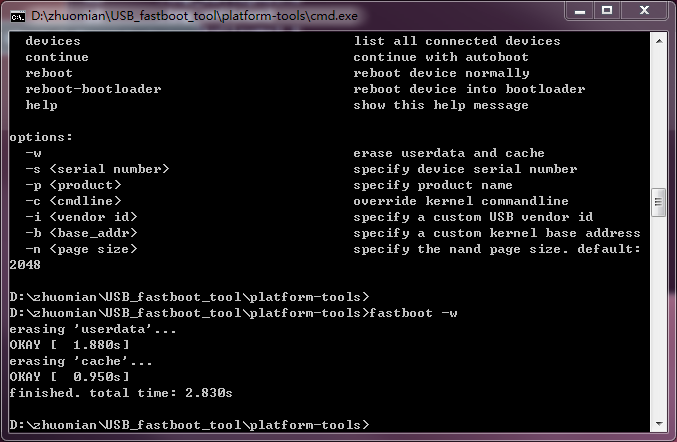
4.输入擦除命令fastboot -w
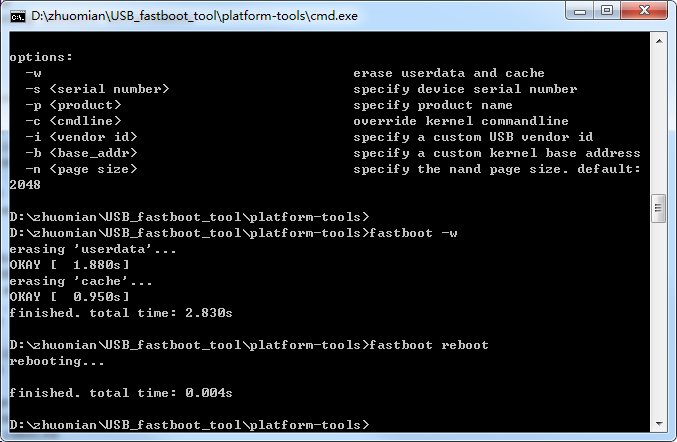
5.Windows 命令行中,输入重启开发板命令 fastboot reboot
四 。fastboot 模式命令
(创建 eMMC 分区并格式化。如果原来已经做过此步骤,则可以跳过,不必每次烧写前
都分区和格式化。在超级终端中,输入下面分区和格式化命令。
如下图所示,输入分区命令“fdisk -c 0”。
如下图所示,输入命令“ext3format mmc 0:2
如下图所示,输入命令“ext3format mmc 0:3”
如下图所示,输入命令“ext3format mmc 0:4”
在超级终端中,输入命令“fastboot”)
进入fastboot :
如下图,在 Windows 命令行中,输入命令“adb services”。
会弹出 adb 命令的帮助文件
如下图,查找 adb 设备,在 Windows 命令行中,输入命令“adb devices”
如下图,上传 C 的测试程序,到安卓的“data”文件夹中。
在 Windows 命令行中,输入命令“adb push helloworld /data”。
烧写步骤:
1.
(输入烧写 uboot 命令 “fastboot.exe flash bootloader u-boot-iTOP-4412.bin”
特别提醒,不建议用户烧写“u-boot-iTOP-4412.bin”这个文件,可跳过此步骤,因为出厂
前已经烧写过这个镜像文件了。)
a.输入烧写 zImage 内核命令“fastboot.exe flash kernel zImage”
b.输入烧写 ramdisk 命令 “fastboot.exe flash ramdisk ramdisk-uboot.img”
c.输入烧写 system 文件系统命令“fastboot.exe flash system system.img”
2. 输入擦除命令“ fastboot -w ” (abc 烧写完之后输入此命令)
注意:上述 fastboot.exe flash 命令可以分开执行,只烧写单个的镜像。
3.在 Windows 命令行中,输入重启开发板命令“fastboot reboot”
五。常用的命令和目录
vi arch/arm/mach-exynos/mach-itop4412.c (包含 4412 的所有驱动的接口定义驱动)。
1. 查看总线命令 ls /sys/bus/
2.查看设备好的命令 cat /proc/devices
3.查看杂项设备号的命令 cat /proc/misc
六。设备的注册
内核源码路径下: root@ubuntu:/home/topeet/android4.0/iTop4412_Kernel_3.0#
设备注册需要做的
1. vim include/linux/platform_device.h // 查看 platform_device 结构体参数,
包含设备注册和设备的注销函数 platform_device_register() platform_device_unregister()
2.vim arch/arm/mach-exynos/mach-itop4412.c //仿照 leds 添加hello的函数
#ifdef CONFIG_HELLO_CTL
struct platform_device s3c_device_hello_ctl = {
.name = "hello_ctl",
.id = -1,
};
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_HELLO_CTL
&s3c_device_hello_ctl,
#endif
3. vim drivers/char/Kconfig // 添加 HELLO_CTL 宏定义
config HELLO_CTL
tristate "Enable HELLO config"
default y
help
Enable HELLO config
4.make menuconfig 查看下是否有选上【*】Enable HELLO config 然后 make zImage 然后再将生成的 zImage 通过 fastboot模式写到板子上(fastboot.exe flash kernel zImage -> fastboot reboot )
5.在超级串口上 输入命令 ls /sys/devices/plantform 查看 设备是否注册 查看到 hello_ctl 则设备已经注册。
七。 驱动注册
内核源码路径下: root@ubuntu:/home/topeet/android4.0/iTop4412_Kernel_3.0#
驱动注册需要做的
1.1. vim include/linux/platform_device.h // 查看 platform_driver 结构体参数,
struct platform_driver {
int (*probe)(struct platform_device *);
int (*remove)(struct platform_device *);
void (*shutdown)(struct platform_device *);
int (*suspend)(struct platform_device *, pm_message_t state);
int (*resume)(struct platform_device *);
struct device_driver driver;
const struct platform_device_id *id_table;
};
extern int platform_driver_register(struct platform_driver *);
extern void platform_driver_unregister(struct platform_driver *);
2.在之前的mini_linux_module 的基础上做修改 文件 并命名为 : probe_linux_module
3.修改文件 Makefile 中的 obj-m += probe_linux_module.o
4.将新建文件夹 home/topeet/probe_linux_module 并将新改的文件,拷贝到新建文件夹里。
5.make 生成了对应的 probe_linux_module .ko 文件 拷贝到u 盘
6.在开发板上,挂载U盘 mount /dev/sta1 /mnt/disk ->
输入初始化命令 insmod /mnt/disk/probe_linux_module.ko
输入 rmmod (如果提示错误则 rmmod -r probe_linux_module mkdir /lib/modules/3.0.15 )
然后再输入 rmmod -r probe_linux_module 会打印 HELLO WORLD exit!
至此驱动注册到卸载驱动 实验完成。
八。生成设备节点(以下是杂项设备类。引入杂项设备1.节省主设备号 2.驱动写起来简单 )
杂项设备初始化部分源文件“drivers/char/ misc.c” 在Makefile 里强制编译的
#include <linux/fs.h> 注册设备节点的文件结构体
1.杂项设备头文件 #include <linux/miscdevice.h> 使用命令可查看 结构体 misdevice以及注册函数 vim include/linux/miscdevice.h
struct device;
struct miscdevice {
int minor; //设备号
const char *name; //生成节点的名称
const struct file_operations *fops; //指向一个设备节点文件
struct list_head list;
struct device *parent;
struct device *this_device;
const char *nodename;
mode_t mode;
};
extern int misc_register(struct miscdevice * misc);
extern int misc_deregister(struct miscdevice *misc);
2.以后的步骤参考上一节的内容。
ls /dev k可以看到我们注册的设备节点 名是 ; hello_ctl123
九。杂项设备驱动应用
编写的简单应用 调用设备驱动 调用 HELLO_CTL123 设备节点
1.应用中用到的头文件
include<stdio.h> //调用打印函数 printf
#include<sys/types.h> //基本系统数据类型 。系统的基本数据类型在32位编译环境中保持为32 位值,并在64编译环境中保持64位值。
#include<sys/stat.h> //系统调用函数头文件。可以调用普通的文件,目录,管道。socket,字符,块的属性。
#include<fcntl.h >定义了open函数
#include<unistd.h >定义了close函数
#include<sys/ioctl.h >定义了ioctl函数
调用的头文件是和编译器放在一起的
– 这里使用arm2009q3编译器,编译器使用arm-none-linux-gnueabi-gcc
• 在编译器目录下使用查找命令找到该头文件
进到目录下 root@ubuntu:/usr/local/arm/arm-2009q3#
– 例如#find ./ -name types.h
2.调用的函数
– open函数是返回文件描述符
– ioctl函数是应用向驱动传值
– close函数是关闭打开的文件
编写应用程序的代码,编译 invoke_hello 新建文件 invoke_hello.c
– arm-none-linux-gnueabi-gcc -o invoke_hello invoke_hello.c -static
开发板中拷贝 devicenode_linux_module.ko 驱动,
加载驱动 insmod /mnt/disk/devicenode_linux_module.ko
修改权限 chmod 777 /mnt/disk/invoke_hello
运行应用 ./mnt/disk/invoke_hello
最后
以上就是唠叨大门最近收集整理的关于linux 笔记1基于iTop4412,学习记录。(包括设备注册设备驱动注册使用)的全部内容,更多相关linux内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复