当有一个线程已经持有互斥锁时,互斥锁将所有试图进入临界区的线程都阻塞住。但是考虑一种情形,当前持有互斥锁的线程只是要读访问共享资源,而同时有其它几个线程也想读取这个共享资源,但是由于互斥锁的排它性,所有其它线程都无法获取锁,也就无法读访问共享资源了,但是实际上多个线程同时读访问共享资源并不会导致问题。
在对数据的读写操作中,更多的是读操作,写操作较少,例如对数据库数据的读写应用。为了满足当前能够允许多个读出,但只允许一个写入的需求,线程提供了读写锁来实现。
读写锁的特点如下:
1)如果有其它线程读数据,则允许其它线程执行读操作,但不允许写操作。
2)如果有其它线程写数据,则其它线程都不允许读、写操作。
读写锁分为读锁和写锁,规则如下:
1)如果某线程申请了读锁,其它线程可以再申请读锁,但不能申请写锁。
2)如果某线程申请了写锁,其它线程不能申请读锁,也不能申请写锁。
pthread_rwlock_init函数
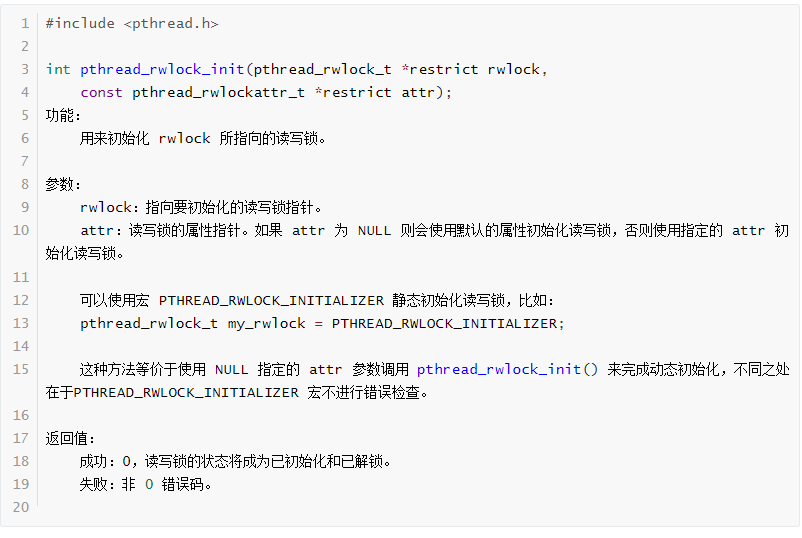
pthread_rwlock_destroy函数
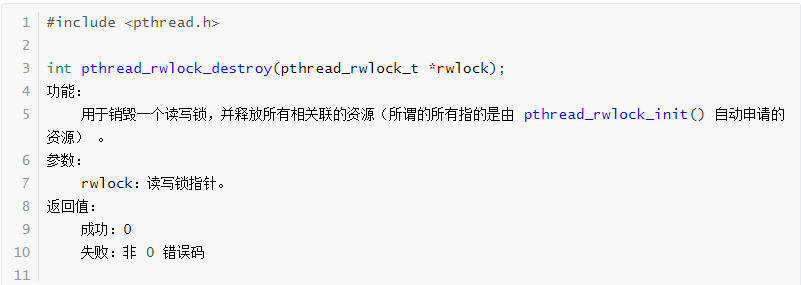
pthread_rwlock_rdlock函数

pthread_rwlock_wrlock函数

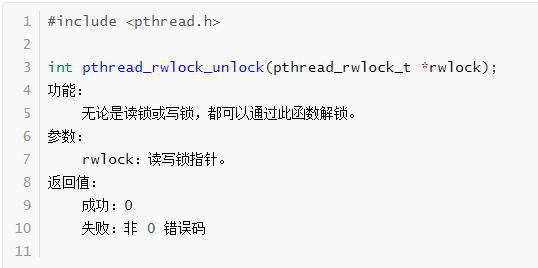
pthread_rwlock_unlock函数
代码演示:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <pthread.h>
//全局
int num=0;
//读写锁变量
pthread_rwlock_t rwlock;
//读线程
void* fun_read(void* arg)
{
int i;
int index = (int)(long)arg;//获取线程编号
while(1)
{
//加读写锁读锁
pthread_rwlock_rdlock(&rwlock);
printf("线程%的读取num的值%dn",index,num);
sleep(random() % 3+1);//随机睡眠1-3秒
pthread_rwlock_unlock(&rwlock);
}
return NULL;
}
void* fun_write(void* arg)
{
int index = (int)(long)arg;//获取线程编号
while(1)
{
//加读写锁写锁
pthread_rwlock_wrlock(&rwlock);
num++;
printf("线程%d 修改num的值%dn",index,num);
sleep(radom()%3+1);
//解锁
pthread_rwlock_unlock(&rwlock);
}
return NULL;
}
int main()
{
int i=0;
int ret = -1;
pthread_t tid[8];
srandom(getpid());
//初始化读写锁
ret = pthread_rwlock_init(&rwlock,NULL);
if(0 != ret)
{
printf("pthread_rwlock_init failed..,n");
return 1;
}
//创建读线程
for(i=0;i<8;i++)
{
//创建读线程
if(i<5)
{
pthread_create(&tid[i],NULL,fun_read,(void*)(long)i);
}
else
{
//创建写线程
pthread_create(&tid[i],NULL,fun_write,(void*)(long)i);
}
}
//回收八个线程的资源
for(i=0;i<8;i++)
{
pthread_join(tid[i],NULL);
}
}
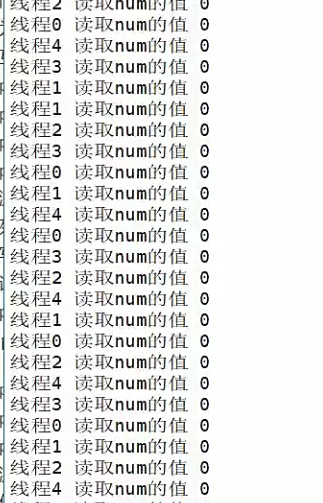
结果全是读锁,读锁期间写锁不能申请!
最后
以上就是想人陪羊最近收集整理的关于读写锁概述的全部内容,更多相关读写锁概述内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复