Queue接口提供的两种方法
addFirst 若添加失败则抛出异常 addLast 队列满返回false
offerFirst offerLast
remove
poll
BlockingQueue
public interface BlockingQueue<E> extends Queue<E> {
put、take方法会产生阻塞,是阻塞队列提供的新的方法
特点:
1、集合实例中不能存储null值,否则会抛出空指针或特定的值
2、阻塞队列可以是限定容量,也可以动态扩容
3、阻塞队列是线程安全的集合操作,其内部通过 reentrantLock来加锁实现安全
三种主要实现类:
ArrayBlockingQueue:有界阻塞队列
LinkedBlockingQUeue:无界阻塞队列
SynchronousQueue:同步阻塞队列
ArrayBlockingQueue
底层实现了一个固定大小的数组、存储了两个索引
public class ArrayBlockingQueue<E> extends AbstractQueue<E>
implements BlockingQueue<E>, java.io.Serializable {
final Object[] items; //通过数组来保存数据
int takeIndex; //读数据的位置
int putIndex; //写数据的位置
int count; //队列中已存储数据的个数
//锁实例
final ReentrantLock lock;
private final Condition notEmpty;
private final Condition notFull;
ArrayBlockingQueue支持阻塞需要一个锁Lock和两个条件(非空、非满),
因为是持有一把锁,所以任何对队列操作只有一个线程,所以索引位置和count数量的操作都是线程安全的
构造函数:
public ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity, boolean fair) {
if (capacity <= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
this.items = new Object[capacity]; //创建数据实例
lock = new ReentrantLock(fair); //锁实例
notEmpty = lock.newCondition();
notFull = lock.newCondition();
}
put():线程安全的且具有阻塞的特点
插入数据不能为null
public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException {
checkNotNull(e);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly(); //加中断锁
try {
while (count == items.length) //集合容量满时,需要阻塞等待
notFull.await();
enqueue(e);
} finally {
lock.unlock(); //释放锁
}
}
private void enqueue(E x) {
final Object[] items = this.items;
items[putIndex] = x;
if (++putIndex == items.length) //调整putIndex的下一个位置
putIndex = 0;
count++;
notEmpty.signal(); //通知take操作,唤醒take操作中的notEmpty.await()
}
take()
public E take() throws InterruptedException {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
while (count == 0) //容量为空时,等待put方法的notEmpty.signal的通知
notEmpty.await();
return dequeue();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
private E dequeue() {
final Object[] items = this.items;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E x = (E) items[takeIndex];
items[takeIndex] = null;
if (++takeIndex == items.length)
takeIndex = 0;
count--;
if (itrs != null)
itrs.elementDequeued();
notFull.signal(); //通知put中可以进行插入的通知
return x;
}
LinkedBlockingQueue:无界阻塞队列
public class LinkedBlockingQueue<E> extends AbstractQueue<E>
implements BlockingQueue<E>, java.io.Serializable {
private final int capacity; //容量
private final AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger(); //记录存储数据的个数
transient Node<E> head; //头节点
private transient Node<E> last;
private final ReentrantLock takeLock = new ReentrantLock(); //创建了一个删除操作锁
private final Condition notEmpty = takeLock.newCondition();
private final ReentrantLock putLock = new ReentrantLock(); //创建了一个插入的操作锁
private final Condition notFull = putLock.newCondition();
LinkedBlockingQueue实现上是使用的链表
2、数据存储在Node结构中
3、引入了两把锁,一个入队列锁,一个出队列的锁
put()
public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException {
if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException(); //插入数据不能为null
int c = -1;
Node<E> node = new Node<E>(e);
final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock;
final AtomicInteger count = this.count;
putLock.lockInterruptibly(); //添加入队列锁
try {
//当容器满时,当前通知存在两个点会通知
//1、当容量不满时,由put的线程通知
//2、当容量满时,由take的线程通知
while (count.get() == capacity) {
notFull.await();
}
enqueue(node); //将节点插入到链表尾部
c = count.getAndIncrement(); //原子性的++操作
if (c + 1 < capacity) //通知take出队列的notFull.signal操作
notFull.signal();
} finally {
putLock.unlock(); //释放入队列锁
}
if (c == 0)
signalNotEmpty();
}
SynchronousQueue:同步阻塞队列
同步队列,每一个插入操作必须等待两一个线程的移除,同样,一个线程的移除操作必须等待另一个线程的插入操作,
元素是不会做停留的
ArrayDeque
底层数据结构是循环数组、既可以作为队列、也可以作为栈
作为队、比stack更高效、性能高于LinkedList
public class ArrayDeque<E> extends AbstractCollection<E>
implements Deque<E>, Cloneable, Serializable
transient Object[] elements; // non-private to simplify nested class access
transient int head;
transient int tail;
private static final int MIN_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 8;
扩容 arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos,Object dest, int destPos, int length);
@param src 初始数组
* @param srcPos 初始数组的起始位置
* @param dest 最终数组
* @param destPos 最终数组的起始位置
* @param length 扩容数组的长度
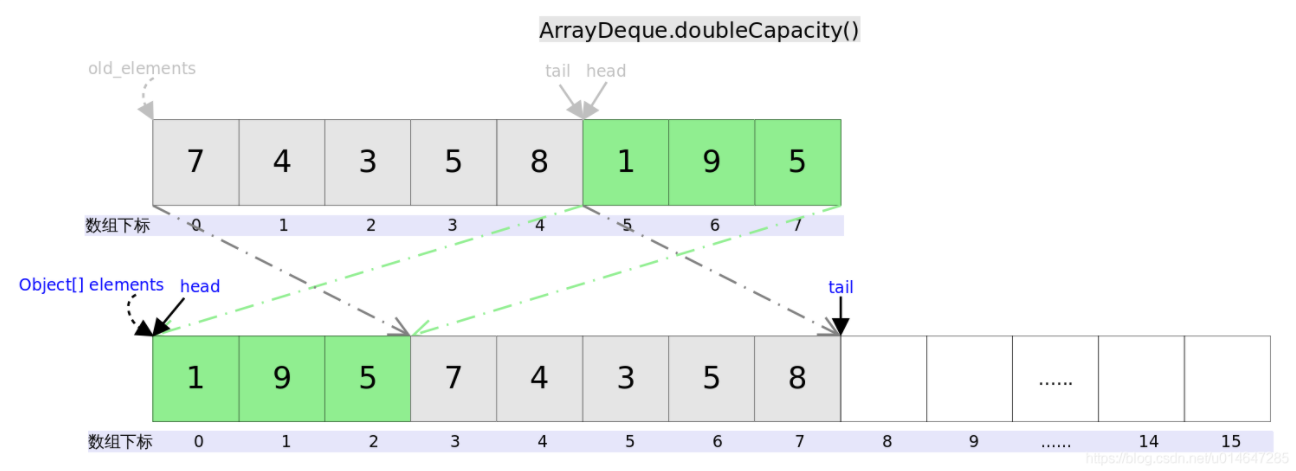
private void doubleCapacity() {
assert head == tail;
int p = head;
int n = elements.length;
int r = n - p; // number of elements to the right of p
int newCapacity = n << 1; //右移
if (newCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException("Sorry, deque too big");
Object[] a = new Object[newCapacity];
System.arraycopy(elements, p, a, 0, r); //elements从头开始、r的长度复制到数组a中0位置以后
System.arraycopy(elements, 0, a, r, p); //elements从0位置开始、p的长度复制到数组a中r以后
elements = a;
head = 0;
tail = n;
}
添加元素
public void addFirst(E e) {
if (e == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
elements[head = (head - 1) & (elements.length - 1)] = e;
if (head == tail)
doubleCapacity();
}
public void addLast(E e) {
if (e == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
elements[tail] = e;
if ( (tail = (tail + 1) & (elements.length - 1)) == head)
doubleCapacity();
}
public boolean offerFirst(E e) {
addFirst(e);
return true;
}
public boolean offerLast(E e) {
addLast(e);
return true;
}
priorityQueue
PriorityQueue通过二叉小根堆实现、底层数据结构是数组、
PriorityQueue(非线程安全 )
- 优先级队列
- 任务调度系统 任务排一个优先级 所有的任务放到优先级队列 执行任务的线程会从队列中选择
- 一个优先级最高的任务执行
- PriorityQueue基于优先堆(大根堆/小根堆),
- 这个优先队列可以默认自然排序或者通过提供的Compartor(比较器)在队列实例化的时候进行排序
public class PriorityQueue<E> extends AbstractQueue<E>
implements java.io.Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -7720805057305804111L;
private static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 11;
transient Object[] queue; // non-private to simplify nested class access
private int size = 0;
private final Comparator<? super E> comparator;
transient int modCount = 0; // non-private to simplify nested class access
public PriorityQueue() {}
public PriorityQueue(int initialCapacity) { }
public PriorityQueue(int initialCapacity, Comparator<? super E> comparator) {}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public PriorityQueue(Collection<? extends E> c) {}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public PriorityQueue(PriorityQueue<? extends E> c) {}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public PriorityQueue(SortedSet<? extends E> c) {}
增加 满足添加前后底层都必须是一个小根堆、从下往上调整
在数组最后面添加元素、和该位置的父母位置的值比较、若小交换直到比较到0号位置
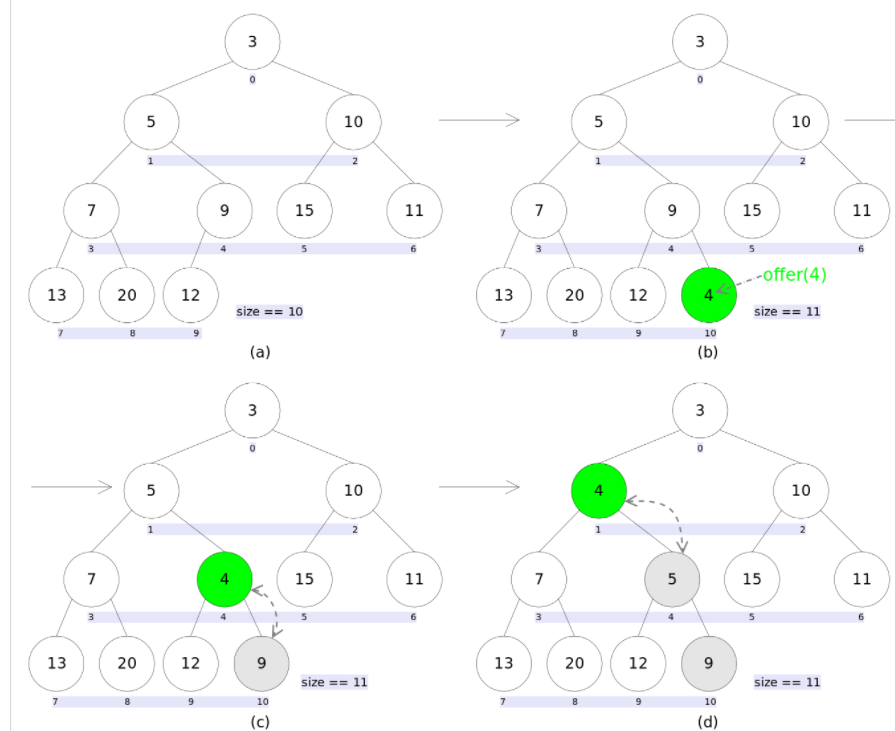
public boolean offer(E e) {
if (e == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
modCount++;
int i = size;
if (i >= queue.length)
grow(i + 1); //自动扩容
size = i + 1;
if (i == 0) //数组0号位置添加元素
queue[0] = e;
else
siftUp(i, e); // 把添加元素的值放在size-1位置上然后调整堆
return true;
}
private void siftUp(int k, E x) {
Comparable<? super E> key = (Comparable<? super E>) x;
while (k > 0) { //k=size-1
int parent = (k - 1) >>> 1; //找k位置的父母位置
Object e = queue[parent];
if (key.compareTo((E) e) >= 0) /调用比较器 若x 大于父母节点的数跳出循环
break;
queue[k] = e; //把父母位置的值给K 位置
k = parent;
}
queue[k] = key;
}
删除 正常情况下删除都应该是0号位置 ps( 0下标的位置是最小的)
public E poll() {
if (size == 0)
return null;
int s = --size; //记录下最后一个元素位置
modCount++;
E result = (E) queue[0];
E x = (E) queue[s];
queue[s] = null; //最后一个元素置为空
if (s != 0)
siftDown(0, x); //调整堆 最后一个元素替换0下标位置的元素
return result;
}
private void siftDown(int k, E x) {
Comparable<? super E> key = (Comparable<? super E>)x; //比较器
int half = size >>> 1; //无符号右移
while (k < half) {
int child = (k << 1) + 1; //确认左孩子的最小值 2k+1
Object c = queue[child];
int right = child + 1; //右孩子为2k+2
if (right < size && ((Comparable<? super E>) c).compareTo((E) queue[right]) > 0) //找左右孩子哪个最小
c = queue[child = right];
if (key.compareTo((E) c) <= 0) //找传入的元素 和最小的孩子 哪个最小
break;
queue[k] = c; //传的参数大 调整位置
k = child;
}
queue[k] = key;
}
删除有传参的 remove(Object o)
删除的是和传参相同的元素、若有重复的元素但只能删除一个
该方法不是Queue接口内的方法,而是Collection接口的方法。
remove(Object o)删除元素:1. 删除的是最后一个元素。直接删除。
2. 删除的不是最后一个元素,从删除点开始以最后一个元素为参照调用一次siftDown()即可。
public boolean remove(Object o) {
int i = indexOf(o);//i为待删除元素的索引
if (i == -1)
return false;
else {
removeAt(i);
return true;
}
}
private E removeAt(int i) {
// assert i >= 0 && i < size;
modCount++;
int s = --size;
if (s == i) // 删除的是最后一个元素
queue[i] = null;
else {
E moved = (E) queue[s];
queue[s] = null;
siftDown(i, moved);
if (queue[i] == moved) {// 特殊情况 最后一个元素和待删除的元素一样
siftUp(i, moved); //向上调整
if (queue[i] != moved)
return moved;
}
}
return null;
}
最后
以上就是冷傲面包最近收集整理的关于BlockingQueue &&priorityQueue&& ArrayDequeQueue接口提供的两种方法BlockingQueueArrayDequepriorityQueue的全部内容,更多相关BlockingQueue内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复