BFS 、DFS区别,详解
写在最前的三点:
1、所谓图的遍历就是按照某种次序访问图的每一顶点一次仅且一次。
2、实现bfs和dfs都需要解决的一个问题就是如何存储图。一般有两种方法:邻接矩阵和邻接表。这里为简单起
见,均采用邻接矩阵存储,说白了也就是二维数组。
3、本文章的小测试部分的测试实例是下图: 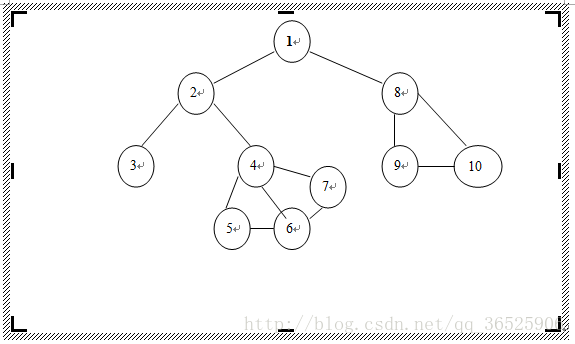
一、深度优先搜索遍历
1、从顶点v出发深度遍历图G的算法
① 访问v
② 依次从顶点v未被访问的邻接点出发深度遍历。
2、一点心得:dfs算法最大特色就在于其递归特性,使得算法代码简洁。但也由于递归使得算法难以理解,原因
在于递归使得初学者难以把握程序运行到何处了!一点建议就是先学好递归,把握函数调用是的种种。
二、广度优先搜索遍历
1、从顶点v出发遍历图G的算法买描述如下:
①访问v
②假设最近一层的访问顶点依次为vi1,vi2,vi3…vik,则依次访问vi1,vi2,vi3…vik的未被访问的邻接点
③重复②知道没有未被访问的邻接点为止
2、一点心得:bfs算法其实就是一种层次遍历算法。从算法描述可以看到该算法要用到队列这一数据结构。我这
里用STL中的实现。该算法由于不是递归算法,所以程序流程是清晰的。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <list>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
int n;
vector< list<int> > graph;
bool visited[100] = {0};
void dfs(int v)
{
list<int>::iterator it;
visited[v] = true;
printf("%5d", v);
for (it = graph[v].begin(); it != graph[v].end(); ++it)
if (!visited[*it])
dfs(*it);
}
void bfs(int v)
{
list<int>::iterator it;
printf("%5d", v);
visited[v] = true;
queue<int> t;
t.push(v);
while (!t.empty())
{
v = t.front();
t.pop();
for (it = graph[v].begin(); it != graph[v].end(); ++it)
if (!visited[*it])
{
printf("%5d", *it);
t.push(*it);
visited[*it] = true;
}
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
//freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin);
cout << "input the vertex num:"<< endl;
cin >> n;
vector< list<int> >::iterator it;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
list<int> il;
int t;
while (cin >> t && t != n)
il.push_back(t);
graph.push_back(il);
}
cout << "result for bfs:" << endl;
bfs(0);
memset(visited, 0, sizeof(visited));//重新初始化标志数组
cout << "result for dfs:" << endl;
dfs(0);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
/*输入:
8
0 1 2 8
1 0 3 4 8
2 0 5 6 8
3 1 7 8
4 1 7 8
5 2 7 8
6 2 7 8
7 3 4 5 6 8
输出:
DFS:0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
BFS:0 1 3 7 4 5 2 6*/
最后
以上就是干净糖豆最近收集整理的关于DFS和BFS详解的全部内容,更多相关DFS和BFS详解内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复