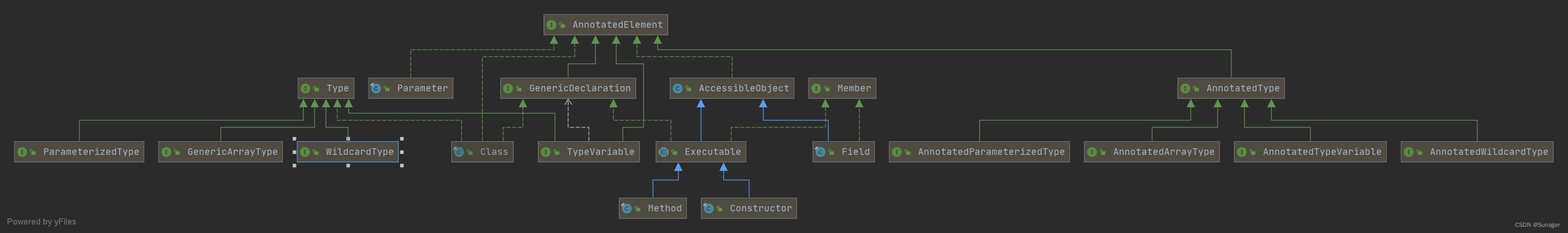
文章目录
- AnnotatedElement
- AnnotatedType
- AnnotatedArrayType
- AnnotatedParameterizedType
- AnnotatedTypeVariable
- AnnotatedWildcardType
- Member
- Modifier
- ReflectAccess
- AccessibleObject
- Field
- Type
- GenericArrayType
- ParameterizedType
- TypeVariable
- WildcardType
- GenericDeclaration
- Executable
- Method
- Constructor
- Parameter
- Array
- InvocationHandler
- Proxy
- WeakCache
AnnotatedElement
@Since:1.5
Comment:表示当前在此VM中运行的程序的一个带注解的元素。这个接口允许反射地读取注解。该接口中方法返回的所有注解都是不可变和可序列化的。调用方可以修改此接口方法返回的数组,而不会影响返回给其他调用方的数组。
// @Since:1.5
// 如果此元素上存在指定类型的注释,则返回true,否则返回false。 该方法主要用于方便访问标记注释。
default boolean isAnnotationPresent(Class<? extends Annotation> annotationClass) {
return getAnnotation(annotationClass) != null;
}
// @Since:1.5
// 如果存在指定类型的注释,则返回该元素的注释,否则为空。
<T extends Annotation> T getAnnotation(Class<T> annotationClass);
// @Since:1.5
// 返回出现在此元素上的注释。
Annotation[] getAnnotations();
// @Since:1.8
// 返回与此元素关联的注释。
// 该方法与 getAnnotation(Class) 的区别在于,该方法检测其参数是否为可重复注释类型(JLS 9.6),如果是,则试图通过“查看”容器注释来查找该类型的一个或多个注释。
// @implSpec:默认实现首先调用 getDeclaredAnnotationsByType(Class) ,传递 annotationClass 作为参数。如果返回的数组长度大于0,则返回该数组。如果返回的数组是零长度的,并且这个 AnnotatedElement 是一个类,参数类型是一个可继承的注释类型,并且这个 AnnotatedElement 的超类是非空的,那么返回的结果就是在超类上以 annotationClass 为参数调用 getAnnotationsByType(class) 的结果。否则,返回一个零长度的数组。
default <T extends Annotation> T[] getAnnotationsByType(Class<T> annotationClass) {
/* 关联的定义:直接或间接呈现或既不直接也不间接呈现且元素是Class,注释类型是可继承的,且注释类型与元素的超类关联。
*/
T[] result = getDeclaredAnnotationsByType(annotationClass);
if (result.length == 0 && // Neither directly nor indirectly present
this instanceof Class && // the element is a class
AnnotationType.getInstance(annotationClass).isInherited()) { // Inheritable
Class<?> superClass = ((Class<?>) this).getSuperclass();
if (superClass != null) {
// Determine if the annotation is associated with the
// superclass
result = superClass.getAnnotationsByType(annotationClass);
}
}
return result;
}
// @Since:1.8
// 如果指定类型的注释直接存在,则返回该元素的注释,否则为空。
default <T extends Annotation> T getDeclaredAnnotation(Class<T> annotationClass) {
Objects.requireNonNull(annotationClass);
// Loop over all directly-present annotations looking for a matching one
for (Annotation annotation : getDeclaredAnnotations()) {
if (annotationClass.equals(annotation.annotationType())) {
// More robust to do a dynamic cast at runtime instead
// of compile-time only.
return annotationClass.cast(annotation);
}
}
return null;
}
// @Since:1.8
// 如果指定类型的注释直接或间接地存在,则返回该元素的注释。此方法忽略继承的注释。
default <T extends Annotation> T[] getDeclaredAnnotationsByType(Class<T> annotationClass) {
Objects.requireNonNull(annotationClass);
return AnnotationSupport.
getDirectlyAndIndirectlyPresent(Arrays.stream(getDeclaredAnnotations()).
collect(Collectors.toMap(Annotation::annotationType,
Function.identity(),
((first,second) -> first),
LinkedHashMap::new)),
annotationClass);
}
// @Since:1.5
// 返回直接出现在此元素上的注释。此方法忽略继承的注释。
Annotation[] getDeclaredAnnotations();
AnnotatedType
参考连接:Java反射之AnnotatedType接口
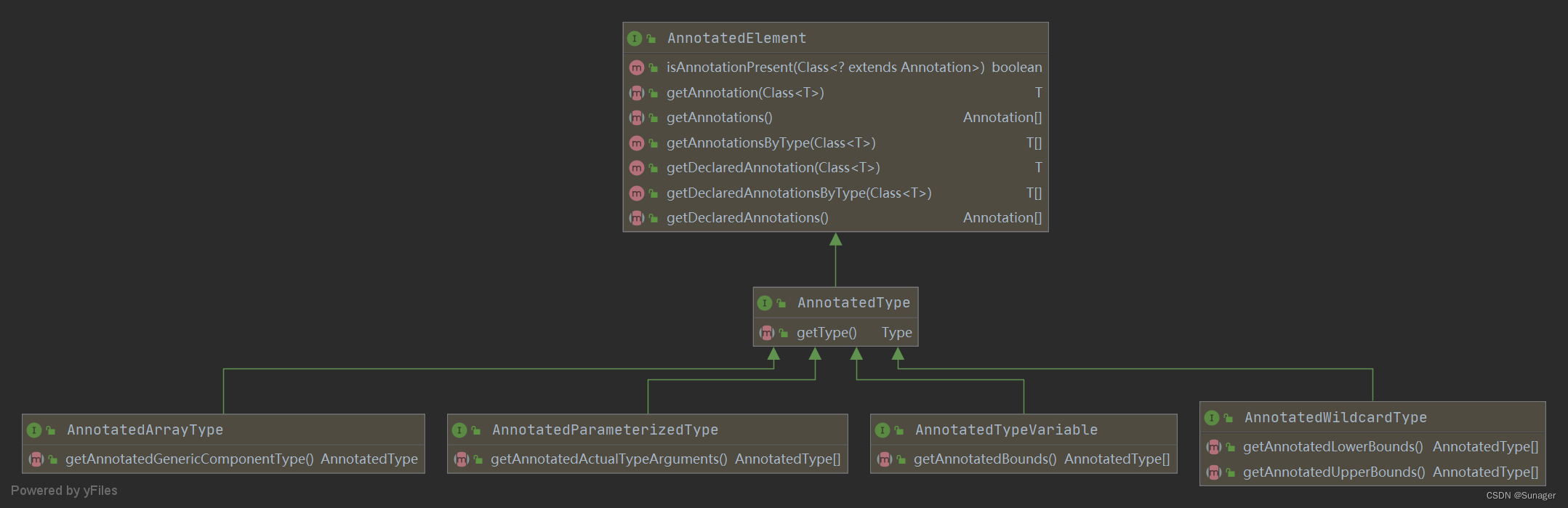
@Since:1.8
Comment:表示当前运行在该虚拟机中的程序中某个类型的潜在注释使用。可以使用Java编程语言中的任何类型,包括数组类型、参数化类型、类型变量或通配符类型。
// 返回此带注释的类型所表示的基础类型。
public Type getType();
AnnotatedArrayType
@Since:1.8
Comment:表示一个数组类型的潜在注释使用,其组件类型本身可能代表一个类型的注释使用。
// 返回此数组类型的可能带注释的泛型组件类型。
AnnotatedType getAnnotatedGenericComponentType();
AnnotatedParameterizedType
@Since:1.8
Comment:表示参数化类型的潜在注释使用,其类型参数本身可以表示类型的注释使用。
// 返回此参数化类型的可能带注释的实际类型参数。
AnnotatedType[] getAnnotatedActualTypeArguments();
AnnotatedTypeVariable
@Since:1.8
Comment:表示类型变量的潜在注释使用,它的声明可能有边界,这些边界本身代表类型的注释使用。
// 返回此类型变量可能带注释的边界。
AnnotatedType[] getAnnotatedBounds();
AnnotatedWildcardType
@Since:1.8
Comment:表示通配符类型参数的潜在注释用法,通配符类型参数的上界或下界本身可以表示类型的注释用法。
// 返回此通配符类型可能带有注释的下界。
AnnotatedType[] getAnnotatedLowerBounds();
// 返回此通配符类型可能带有注释的上界。
AnnotatedType[] getAnnotatedUpperBounds();
测试代码:
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR, ElementType.PARAMETER, ElementType.LOCAL_VARIABLE, ElementType.TYPE_USE})
@Inherited
@interface MyAnno {
String value() default "";
}
class MyAnnoClass<@MyAnno T extends @MyAnno Number, U> {
@MyAnno T[] tArr;
T t;
List<@MyAnno ? extends Number> list;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Field[] annotatedInterfaces = MyAnnoClass.class.getDeclaredFields();
System.out.printf("|%20s|%50s|%80s|%20s|%20s|%20s|%30s|%20s|%n",
"Field Name", "annotatedType Name", "annotatedTypeClass Name", "modifier",
"AnnotatedArrayType", "AnnotatedTypeVariable", "AnnotatedParameterizedType", "AnnotatedWildcardType");
for (Field field : annotatedInterfaces) {
AnnotatedType annotatedType = field.getAnnotatedType();
// AnnotatedArrayType: 1000, AnnotatedTypeVariable: 0100, AnnotatedParameterizedType: 0010, AnnotatedWildcardType: 0001
int modifier = 0;
String arrayTypeInfo = "";
String typeVariableInfo = "";
String parameterizedTypeInfo = "";
String wildcardTypeInfo = "";
if (annotatedType instanceof AnnotatedArrayType) {
modifier |= 0b1000;
arrayTypeInfo = ((AnnotatedArrayType) annotatedType).getAnnotatedGenericComponentType().getType().getTypeName();
}
if (annotatedType instanceof AnnotatedTypeVariable) {
modifier |= 0b0100;
typeVariableInfo = Arrays.toString(Arrays.stream(((AnnotatedTypeVariable) annotatedType).getAnnotatedBounds()).map(annoType -> annoType.getType().getTypeName()).toArray());
}
if (annotatedType instanceof AnnotatedParameterizedType) {
modifier |= 0b0010;
parameterizedTypeInfo = Arrays.toString(Arrays.stream(((AnnotatedParameterizedType) annotatedType).getAnnotatedActualTypeArguments()).map(annoType -> annoType.getType().getTypeName()).toArray());
for (AnnotatedType annotatedActualTypeArgument : ((AnnotatedParameterizedType) annotatedType).getAnnotatedActualTypeArguments()) {
if (annotatedActualTypeArgument instanceof AnnotatedWildcardType) {
modifier |= 0b0001;
wildcardTypeInfo = Arrays.toString(Arrays.stream(((AnnotatedWildcardType) annotatedActualTypeArgument).getAnnotatedUpperBounds()).map(annoType -> annoType.getType().getTypeName()).toArray());
}
}
}
System.out.printf("|%20s|%50s|%80s|%20s|%20s|%20s|%30s|%20s|%n",
field.getName(), annotatedType.getType().getTypeName(), annotatedType.getClass().getName(),
String.format("%1$04d", Integer.valueOf(Integer.toBinaryString(modifier))),
arrayTypeInfo, typeVariableInfo, parameterizedTypeInfo, wildcardTypeInfo);
}
}
测试结果:
| Field Name| annotatedType Name| annotatedTypeClass Name| modifier| AnnotatedArrayType|AnnotatedTypeVariable| AnnotatedParameterizedType|AnnotatedWildcardType|
| tArr| T[]| sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotatedTypeFactory$AnnotatedArrayTypeImpl| 1000| T| | | |
| t| T| sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotatedTypeFactory$AnnotatedTypeVariableImpl| 0100| | [java.lang.Number]| | |
| list| java.util.List<? extends java.lang.Number>| sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotatedTypeFactory$AnnotatedParameterizedTypeImpl| 0011| | | [? extends java.lang.Number]| [java.lang.Number]|
Member
Comment:Member是一个接口,它反映关于单个成员(字段或方法)或构造函数的标识信息。
// 标识类或接口的所有公共成员的集合,包括继承的成员。
public static final int PUBLIC = 0;
// 标识类或接口声明的成员集。不包括继承的成员。
public static final int DECLARED = 1;
// 返回表示声明由该成员表示的成员或构造函数的类或接口的Class对象。
public Class<?> getDeclaringClass();
// 返回由该成员表示的基础成员或构造函数的简单名称。
public String getName();
// 以整数形式返回此成员表示的成员或构造函数的Java语言修饰符。应该使用Modifier类来解码整数中的修饰符。
public int getModifiers();
// @Since:1.5
// 如果该成员是由编译器引入的,则返回 true ;否则返回 false 。
public boolean isSynthetic();
Modifier
Comment:Modifier类提供了static方法和常量来解码类和成员访问修饰符。 修饰符集合被表示为具有表示不同修饰符的不同位位置的整数。 表示修饰符的常量的值取自The Java™ Virtual Machine Specification的第4.1,4.4,4.5和4.7节中的表
// java.Lang和java.lang.reflect包之间的引导协议。
static {
sun.reflect.ReflectionFactory factory =
AccessController.doPrivileged(
new ReflectionFactory.GetReflectionFactoryAction());
factory.setLangReflectAccess(new java.lang.reflect.ReflectAccess());
}
public static final int PUBLIC = 0x00000001;
public static final int PRIVATE = 0x00000002;
public static final int PROTECTED = 0x00000004;
public static final int STATIC = 0x00000008;
public static final int FINAL = 0x00000010;
public static final int SYNCHRONIZED = 0x00000020;
public static final int VOLATILE = 0x00000040;
public static final int TRANSIENT = 0x00000080;
public static final int NATIVE = 0x00000100;
public static final int INTERFACE = 0x00000200;
public static final int ABSTRACT = 0x00000400;
public static final int STRICT = 0x00000800;
// 没有(还)公开在公共API中的位,要么是因为它们对字段和方法有不同的含义,在这个类中没有办法区分这两者,要么是因为它们不是Java编程语言的关键字
static final int BRIDGE = 0x00000040;
static final int VARARGS = 0x00000080;
static final int SYNTHETIC = 0x00001000;
static final int ANNOTATION = 0x00002000;
static final int ENUM = 0x00004000;
static final int MANDATED = 0x00008000;
public static boolean isPublic(int mod) { return (mod & PUBLIC) != 0; }
public static boolean isPrivate(int mod) { return (mod & PRIVATE) != 0; }
public static boolean isProtected(int mod) { return (mod & PROTECTED) != 0; }
public static boolean isStatic(int mod) { return (mod & STATIC) != 0; }
public static boolean isFinal(int mod) { return (mod & FINAL) != 0; }
public static boolean isSynchronized(int mod) { return (mod & SYNCHRONIZED) != 0; }
public static boolean isVolatile(int mod) { return (mod & VOLATILE) != 0; }
public static boolean isTransient(int mod) { return (mod & TRANSIENT) != 0; }
public static boolean isNative(int mod) { return (mod & NATIVE) != 0; }
public static boolean isInterface(int mod) { return (mod & INTERFACE) != 0; }
public static boolean isAbstract(int mod) { return (mod & ABSTRACT) != 0; }
public static boolean isStrict(int mod) { return (mod & STRICT) != 0; }
static boolean isSynthetic(int mod) { return (mod & SYNTHETIC) != 0; }
static boolean isMandated(int mod) { return (mod & MANDATED) != 0; }
// 返回一个字符串,描述指定修饰符中的访问修饰符标志。
public static String toString(int mod) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
int len;
if ((mod & PUBLIC) != 0) sb.append("public ");
if ((mod & PROTECTED) != 0) sb.append("protected ");
if ((mod & PRIVATE) != 0) sb.append("private ");
/* Canonical order */
if ((mod & ABSTRACT) != 0) sb.append("abstract ");
if ((mod & STATIC) != 0) sb.append("static ");
if ((mod & FINAL) != 0) sb.append("final ");
if ((mod & TRANSIENT) != 0) sb.append("transient ");
if ((mod & VOLATILE) != 0) sb.append("volatile ");
if ((mod & SYNCHRONIZED) != 0) sb.append("synchronized ");
if ((mod & NATIVE) != 0) sb.append("native ");
if ((mod & STRICT) != 0) sb.append("strictfp ");
if ((mod & INTERFACE) != 0) sb.append("interface ");
if ((len = sb.length()) > 0) /* trim trailing space */
return sb.toString().substring(0, len-1);
return "";
}
private static final int CLASS_MODIFIERS =
Modifier.PUBLIC | Modifier.PROTECTED | Modifier.PRIVATE |
Modifier.ABSTRACT | Modifier.STATIC | Modifier.FINAL |
Modifier.STRICT;
private static final int INTERFACE_MODIFIERS =
Modifier.PUBLIC | Modifier.PROTECTED | Modifier.PRIVATE |
Modifier.ABSTRACT | Modifier.STATIC | Modifier.STRICT;
private static final int CONSTRUCTOR_MODIFIERS =
Modifier.PUBLIC | Modifier.PROTECTED | Modifier.PRIVATE;
private static final int METHOD_MODIFIERS =
Modifier.PUBLIC | Modifier.PROTECTED | Modifier.PRIVATE |
Modifier.ABSTRACT | Modifier.STATIC | Modifier.FINAL |
Modifier.SYNCHRONIZED | Modifier.NATIVE | Modifier.STRICT;
private static final int FIELD_MODIFIERS =
Modifier.PUBLIC | Modifier.PROTECTED | Modifier.PRIVATE |
Modifier.STATIC | Modifier.FINAL | Modifier.TRANSIENT |
Modifier.VOLATILE;
private static final int PARAMETER_MODIFIERS =
Modifier.FINAL;
static final int ACCESS_MODIFIERS =
Modifier.PUBLIC | Modifier.PROTECTED | Modifier.PRIVATE;
public static int classModifiers() { return CLASS_MODIFIERS; }
public static int interfaceModifiers() { return INTERFACE_MODIFIERS; }
public static int constructorModifiers() { return CONSTRUCTOR_MODIFIERS; }
public static int methodModifiers() { return METHOD_MODIFIERS; }
public static int fieldModifiers() { return FIELD_MODIFIERS; }
public static int parameterModifiers() { return PARAMETER_MODIFIERS; }
ReflectAccess
Comment:实现sun.reflect.LangReflectAccess接口的包私有类,允许java.Lang包来实例化该包中的对象。
public Field newField(Class<?> declaringClass,
String name,
Class<?> type,
int modifiers,
int slot,
String signature,
byte[] annotations) {
return new Field(declaringClass,
name,
type,
modifiers,
slot,
signature,
annotations);
}
public Method newMethod(Class<?> declaringClass,
String name,
Class<?>[] parameterTypes,
Class<?> returnType,
Class<?>[] checkedExceptions,
int modifiers,
int slot,
String signature,
byte[] annotations,
byte[] parameterAnnotations,
byte[] annotationDefault) {
return new Method(declaringClass,
name,
parameterTypes,
returnType,
checkedExceptions,
modifiers,
slot,
signature,
annotations,
parameterAnnotations,
annotationDefault);
}
public <T> Constructor<T> newConstructor(Class<T> declaringClass,
Class<?>[] parameterTypes,
Class<?>[] checkedExceptions,
int modifiers,
int slot,
String signature,
byte[] annotations,
byte[] parameterAnnotations) {
return new Constructor<>(declaringClass,
parameterTypes,
checkedExceptions,
modifiers,
slot,
signature,
annotations,
parameterAnnotations);
}
public MethodAccessor getMethodAccessor(Method m) {
return m.getMethodAccessor();
}
public void setMethodAccessor(Method m, MethodAccessor accessor) {
m.setMethodAccessor(accessor);
}
public ConstructorAccessor getConstructorAccessor(Constructor<?> c) {
return c.getConstructorAccessor();
}
public void setConstructorAccessor(Constructor<?> c,
ConstructorAccessor accessor) {
c.setConstructorAccessor(accessor);
}
public int getConstructorSlot(Constructor<?> c) {
return c.getSlot();
}
public String getConstructorSignature(Constructor<?> c) {
return c.getSignature();
}
public byte[] getConstructorAnnotations(Constructor<?> c) {
return c.getRawAnnotations();
}
public byte[] getConstructorParameterAnnotations(Constructor<?> c) {
return c.getRawParameterAnnotations();
}
public byte[] getExecutableTypeAnnotationBytes(Executable ex) {
return ex.getTypeAnnotationBytes();
}
// 复制例程,需要从模板快速生成新的Field、Method和Constructor对象
public Method copyMethod(Method arg) {
return arg.copy();
}
public Field copyField(Field arg) {
return arg.copy();
}
public <T> Constructor<T> copyConstructor(Constructor<T> arg) {
return arg.copy();
}
AccessibleObject
@Since:1.2
Comment:AccessibleObject类是Field、Method和Constructor对象的基类。它提供了在使用反射对象时将其标记为抑制默认Java语言访问控制检查的能力。当使用Field、Method和Constructor分别设置或获取字段、调用方法或创建和初始化类的新实例时,将执行访问检查——公共、默认(包)访问、受保护和私有成员。默认情况下,反射对象是不可访问的。
protected AccessibleObject() {}
// 指示该对象是否覆盖语言级访问检查。初始化“false”。该字段由field、Method和Constructor使用。
boolean override;
static final private java.security.Permission ACCESS_PERMISSION = new ReflectPermission("suppressAccessChecks");
static final ReflectionFactory reflectionFactory = AccessController.doPrivileged( new sun.reflect.ReflectionFactory.GetReflectionFactoryAction());
volatile Object securityCheckCache;
// 为一个对象数组设置{@code accessible}标志的方便方法,只需进行一次安全检查(为了效率)。
public static void setAccessible(AccessibleObject[] array, boolean flag)
throws SecurityException {
SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager();
if (sm != null) sm.checkPermission(ACCESS_PERMISSION);
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
setAccessible0(array[i], flag);
}
}
// 设置该对象的{@code accessible}标志为指定的布尔值。{@code true}的值表示反射对象在使用时应该禁止Java语言访问检查。{@code false}的值表示反射对象应该强制Java语言访问检查。
public void setAccessible(boolean flag) throws SecurityException {
SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager();
if (sm != null) sm.checkPermission(ACCESS_PERMISSION);
setAccessible0(this, flag);
}
// 检查你没有暴露java.lang.Class.<init>或java.lang.Class中的敏感字段。
private static void setAccessible0(AccessibleObject obj, boolean flag) throws SecurityException {
if (obj instanceof Constructor && flag == true) {
Constructor<?> c = (Constructor<?>)obj;
if (c.getDeclaringClass() == Class.class) {
throw new SecurityException("Cannot make a java.lang.Class" +
" constructor accessible");
}
}
obj.override = flag;
}
// 获取该对象的{@code accessible}标志的值。
public boolean isAccessible() {
return override;
}
@Override
public <T extends Annotation> T getAnnotation(Class<T> annotationClass) {
throw new AssertionError("All subclasses should override this method");
}
@Override
public boolean isAnnotationPresent(Class<? extends Annotation> annotationClass) {
return AnnotatedElement.super.isAnnotationPresent(annotationClass);
}
@Override
public <T extends Annotation> T[] getAnnotationsByType(Class<T> annotationClass) {
throw new AssertionError("All subclasses should override this method");
}
@Override
public Annotation[] getAnnotations() {
return getDeclaredAnnotations();
}
@Override
public <T extends Annotation> T getDeclaredAnnotation(Class<T> annotationClass) {
// 只有类上的注释被继承,对于所有其他对象,getDeclaredAnnotation与getAnnotation相同。
return getAnnotation(annotationClass);
}
@Override
public <T extends Annotation> T[] getDeclaredAnnotationsByType(Class<T> annotationClass) {
// 只有类上的注释被继承,对于所有其他对象getDeclaredAnnotationsByType与getAnnotationsByType相同。
return getAnnotationsByType(annotationClass);
}
@Override
public Annotation[] getDeclaredAnnotations() {
throw new AssertionError("All subclasses should override this method");
}
void checkAccess(Class<?> caller, Class<?> clazz, Object obj, int modifiers) throws IllegalAccessException {
if (caller == clazz) { // quick check
return; // ACCESS IS OK
}
Object cache = securityCheckCache; // read volatile
Class<?> targetClass = clazz;
if (obj != null
&& Modifier.isProtected(modifiers)
&& ((targetClass = obj.getClass()) != clazz)) {
// Must match a 2-list of { caller, targetClass }.
if (cache instanceof Class[]) {
Class<?>[] cache2 = (Class<?>[]) cache;
if (cache2[1] == targetClass &&
cache2[0] == caller) {
return; // ACCESS IS OK
}
// (Test cache[1] first since range check for [1]
// subsumes range check for [0].)
}
} else if (cache == caller) {
// Non-protected case (or obj.class == this.clazz).
return; // ACCESS IS OK
}
// If no return, fall through to the slow path.
slowCheckMemberAccess(caller, clazz, obj, modifiers, targetClass);
}
// 把这些慢的东西都放一边:
void slowCheckMemberAccess(Class<?> caller, Class<?> clazz, Object obj, int modifiers, Class<?> targetClass) throws IllegalAccessException {
Reflection.ensureMemberAccess(caller, clazz, obj, modifiers);
// Success: Update the cache.
Object cache = ((targetClass == clazz)
? caller
: new Class<?>[] { caller, targetClass });
// Note: The two cache elements are not volatile,
// but they are effectively final. The Java memory model
// guarantees that the initializing stores for the cache
// elements will occur before the volatile write.
securityCheckCache = cache; // write volatile
}
Field
Comment:提供关于类或接口单个字段的信息和动态访问。反射的字段可以是一个类(静态)字段或一个实例字段。允许在get或set访问操作期间发生扩大转换,但如果将发生缩小转换,则会抛出 IllegalArgumentException 。
private Class<?> clazz;
private int slot;
// 这可以保证在1.4反射实现中由VM实现
private String name;
private Class<?> type;
private int modifiers;
// 泛型和注释支持
private transient String signature;
// 泛型信息存储库;延迟初始化
private transient FieldRepository genericInfo;
private byte[] annotations;
// 不重写创建的缓存字段访问器
private FieldAccessor fieldAccessor;
// 用重写创建的缓存字段访问器
private FieldAccessor overrideFieldAccessor;
// 用于字段访问器的共享。这个分支结构目前只有两层深(也就是说,一个根Field和可能有很多Field对象指向它)。
// 如果这个分支结构包含循环,那么在注释代码中就可能发生死锁。
private Field root;
private transient Map<Class<? extends Annotation>, Annotation> declaredAnnotations;
// 泛型基础设施
private String getGenericSignature() {return signature;}
// 返回{@code Class}对象,该对象表示声明由{@code field}对象表示的字段的类或接口。
public Class<?> getDeclaringClass() {
return clazz;
}
// 访问器的工厂
private GenericsFactory getFactory() {
Class<?> c = getDeclaringClass();
// 创建范围和工厂
return CoreReflectionFactory.make(c, ClassScope.make(c));
}
// 泛型信息存储库的访问器
private FieldRepository getGenericInfo() {
// 如果需要,延迟初始化存储库
if (genericInfo == null) {
// 创建和缓存泛型信息存储库
genericInfo = FieldRepository.make(getGenericSignature(),
getFactory());
}
return genericInfo; //return cached repository
}
// 用于在Java代码中实例化这些对象的ReflectAccess使用的包私有构造函数java.lang包通过sun.reflect.LangReflectAccess。
Field(Class<?> declaringClass, String name, Class<?> type, int modifiers, int slot, String signature, byte[] annotations) {
this.clazz = declaringClass;
this.name = name;
this.type = type;
this.modifiers = modifiers;
this.slot = slot;
this.signature = signature;
this.annotations = annotations;
}
// Package-private例程(通过ReflectAccess向java.lang.Class公开)返回此字段的副本。副本的“root”字段指向这个字段。
Field copy() {
// 这个例程允许在引用VM中相同底层方法的Field对象之间共享FieldAccessor对象。(所有这些扭曲都是必要的,因为AccessibleObject中的“可访问性”部分,它隐式地要求为对Class对象的每次反射调用制造新的java.lang.reflect对象。)
if (this.root != null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Can not copy a non-root Field");
Field res = new Field(clazz, name, type, modifiers, slot, signature, annotations);
res.root = this;
// 如果已经存在,不妨踊跃宣传
res.fieldAccessor = fieldAccessor;
res.overrideFieldAccessor = overrideFieldAccessor;
return res;
}
// 返回由{@code field}对象表示的字段名。
public String getName() {
return name;
}
// 以整数形式返回由{@code field}对象表示的字段的Java语言修饰符。{@code Modifier}类应该用于解码这些修饰符。
public int getModifiers() {
return modifiers;
}
// 如果该字段表示枚举类型的元素,则返回{@code true};否则返回{@code false}。
public boolean isEnumConstant() {
return (getModifiers() & Modifier.ENUM) != 0;
}
// 如果这个字段是一个合成字段,返回{@code true};否则返回{@code false}。
public boolean isSynthetic() {
return Modifier.isSynthetic(getModifiers());
}
// 返回一个{@code Class}对象,该对象标识由{@code field}对象表示的字段声明的类型。
public Class<?> getType() {
return type;
}
// 返回一个{@code Type}对象,该对象表示由该{@code field}对象表示的字段声明的类型。
// 如果{@code Type}是参数化类型,返回的{@code Type}对象必须准确地反映源代码中使用的实际类型参数。如果基础字段的类型是类型变量或参数化类型,则创建该字段。否则,将被解析。
public Type getGenericType() {
if (getGenericSignature() != null)
return getGenericInfo().getGenericType();
else
return getType();
}
// 比较指定对象的{@code Field}。如果两个对象相同,则返回true。两个{@code Field}对象是相同的,如果它们是由同一个类声明的,并且具有相同的名称和类型。
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (obj != null && obj instanceof Field) {
Field other = (Field)obj;
return (getDeclaringClass() == other.getDeclaringClass())
&& (getName() == other.getName())
&& (getType() == other.getType());
}
return false;
}
// 返回这个{@code字段}的哈希码。这是作为底层字段声明的类名及其名称的哈希代码的异或计算的。
public int hashCode() {
return getDeclaringClass().getName().hashCode() ^ getName().hashCode();
}
// 返回一个描述这个{@code字段}的字符串。格式是字段的访问修饰符(如果有的话),然后是字段类型,然后是空格,然后是声明字段的类的全限定名称,然后是句点,最后是字段的名称。
// example: public static final int java.lang.Thread.MIN_PRIORITY
public String toString() {
int mod = getModifiers();
return (((mod == 0) ? "" : (Modifier.toString(mod) + " "))
+ getType().getTypeName() + " "
+ getDeclaringClass().getTypeName() + "."
+ getName());
}
// 返回一个描述这个{@code字段}的字符串,包括它的泛型类型。格式是字段的访问修饰符(如果有的话),然后是泛型字段类型,然后是空格,然后是声明字段的类的全限定名称,然后是句点,最后是字段的名称。
public String toGenericString() {
int mod = getModifiers();
Type fieldType = getGenericType();
return (((mod == 0) ? "" : (Modifier.toString(mod) + " "))
+ fieldType.getTypeName() + " "
+ getDeclaringClass().getTypeName() + "."
+ getName());
}
//返回此Field对象的FieldAccessor,而不是从链向上查找到root
private FieldAccessor getFieldAccessor(boolean overrideFinalCheck) {
return (overrideFinalCheck)? overrideFieldAccessor : fieldAccessor;
}
// 为这个Field对象和(递归地)它的root设置FieldAccessor
private void setFieldAccessor(FieldAccessor accessor, boolean overrideFinalCheck) {
if (overrideFinalCheck)
overrideFieldAccessor = accessor;
else
fieldAccessor = accessor;
// 传播了
if (root != null) {
root.setFieldAccessor(accessor, overrideFinalCheck);
}
}
// 注意,这里没有使用同步。为给定的字段生成多个FieldAccessor是正确的(尽管效率不高)。然而,避免同步可能会使实现更具可伸缩性。
private FieldAccessor acquireFieldAccessor(boolean overrideFinalCheck) {
// 首先检查是否已经创建了一个,如果已经创建了,就接受它
FieldAccessor tmp = null;
if (root != null) tmp = root.getFieldAccessor(overrideFinalCheck);
if (tmp != null) {
if (overrideFinalCheck)
overrideFieldAccessor = tmp;
else
fieldAccessor = tmp;
} else {
// 否则,制造一个并传播到root
tmp = reflectionFactory.newFieldAccessor(this, overrideFinalCheck);
setFieldAccessor(tmp, overrideFinalCheck);
}
return tmp;
}
// 在调用此方法之前完成安全检查
private FieldAccessor getFieldAccessor(Object obj) throws IllegalAccessException {
boolean ov = override;
FieldAccessor a = (ov) ? overrideFieldAccessor : fieldAccessor;
return (a != null) ? a : acquireFieldAccessor(ov);
}
// 返回指定对象上由{@code field}表示的字段的值。如果该值具有基元类型,则该值自动包装在对象中。
public Object get(Object obj) throws IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException {
if (!override) {
if (!Reflection.quickCheckMemberAccess(clazz, modifiers)) {
Class<?> caller = Reflection.getCallerClass();
checkAccess(caller, clazz, obj, modifiers);
}
}
return getFieldAccessor(obj).get(obj);
}
// 获取静态或实例{@code boolean}字段的值。
public boolean getBoolean(Object obj) throws IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException {
if (!override) {
if (!Reflection.quickCheckMemberAccess(clazz, modifiers)) {
Class<?> caller = Reflection.getCallerClass();
checkAccess(caller, clazz, obj, modifiers);
}
}
return getFieldAccessor(obj).getBoolean(obj);
}
// 获取静态或实例{@code byte}字段的值。
public byte getByte(Object obj) throws IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException {
if (!override) {
if (!Reflection.quickCheckMemberAccess(clazz, modifiers)) {
Class<?> caller = Reflection.getCallerClass();
checkAccess(caller, clazz, obj, modifiers);
}
}
return getFieldAccessor(obj).getByte(obj);
}
// 获取类型{@code char}的静态字段或实例字段的值,或通过扩展转换可转换为类型{@code char}的另一个原语类型的值。
public char getChar(Object obj) throws IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException {
if (!override) {
if (!Reflection.quickCheckMemberAccess(clazz, modifiers)) {
Class<?> caller = Reflection.getCallerClass();
checkAccess(caller, clazz, obj, modifiers);
}
}
return getFieldAccessor(obj).getChar(obj);
}
// 获取类型为{@code short}的静态字段或实例字段的值,或通过扩展转换可转换为类型{@code short}的另一个原语类型的值。
public short getShort(Object obj) throws IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException {
if (!override) {
if (!Reflection.quickCheckMemberAccess(clazz, modifiers)) {
Class<?> caller = Reflection.getCallerClass();
checkAccess(caller, clazz, obj, modifiers);
}
}
return getFieldAccessor(obj).getShort(obj);
}
// 获取类型{@code int}的静态字段或实例字段的值,或通过扩展转换可转换为类型{@code int}的另一基本类型的值。
public int getInt(Object obj) throws IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException {
if (!override) {
if (!Reflection.quickCheckMemberAccess(clazz, modifiers)) {
Class<?> caller = Reflection.getCallerClass();
checkAccess(caller, clazz, obj, modifiers);
}
}
return getFieldAccessor(obj).getInt(obj);
}
// 获取类型为{@code long}的静态字段或实例字段的值,或通过扩展转换可转换为类型为{@code long}的另一个原语类型的值。
public long getLong(Object obj) throws IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException {
if (!override) {
if (!Reflection.quickCheckMemberAccess(clazz, modifiers)) {
Class<?> caller = Reflection.getCallerClass();
checkAccess(caller, clazz, obj, modifiers);
}
}
return getFieldAccessor(obj).getLong(obj);
}
// 获取类型为{@code float}的静态字段或实例字段的值,或通过扩展转换可转换为类型{@code float}的另一个原语类型的值。
public float getFloat(Object obj) throws IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException {
if (!override) {
if (!Reflection.quickCheckMemberAccess(clazz, modifiers)) {
Class<?> caller = Reflection.getCallerClass();
checkAccess(caller, clazz, obj, modifiers);
}
}
return getFieldAccessor(obj).getFloat(obj);
}
// 获取类型为{@code double}的静态字段或实例字段的值,或通过扩展转换可转换为类型{@code double}的另一基本类型的值。
public double getDouble(Object obj) throws IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException {
if (!override) {
if (!Reflection.quickCheckMemberAccess(clazz, modifiers)) {
Class<?> caller = Reflection.getCallerClass();
checkAccess(caller, clazz, obj, modifiers);
}
}
return getFieldAccessor(obj).getDouble(obj);
}
// 将指定对象参数上的{@code field}对象表示的字段设置为指定的新值。如果基础字段具有基元类型,则自动取消包装新值。
public void set(Object obj, Object value) throws IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException {
if (!override) {
if (!Reflection.quickCheckMemberAccess(clazz, modifiers)) {
Class<?> caller = Reflection.getCallerClass();
checkAccess(caller, clazz, obj, modifiers);
}
}
getFieldAccessor(obj).set(obj, value);
}
// 将指定对象的字段值设置为{@code boolean}。这个方法等价于{@code set(obj, zObj)},其中{@code zObj}是一个{@code Boolean}对象,{@code zObj. booleanvalue () == z}。
public void setBoolean(Object obj, boolean z) throws IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException {
if (!override) {
if (!Reflection.quickCheckMemberAccess(clazz, modifiers)) {
Class<?> caller = Reflection.getCallerClass();
checkAccess(caller, clazz, obj, modifiers);
}
}
getFieldAccessor(obj).setBoolean(obj, z);
}
// 将字段的值设置为指定对象的{@code字节}。这个方法等价于{@code set(obj, bObj)},其中{@code bObj}是一个{@code Byte}对象,{@code bObj. bytevalue () == b}。
public void setByte(Object obj, byte b) throws IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException {
if (!override) {
if (!Reflection.quickCheckMemberAccess(clazz, modifiers)) {
Class<?> caller = Reflection.getCallerClass();
checkAccess(caller, clazz, obj, modifiers);
}
}
getFieldAccessor(obj).setByte(obj, b);
}
// 将指定对象的字段值设置为{@code char}。这个方法等价于{@code set(obj, cObj)},其中{@code cObj}是一个{@code Character}对象,{@code cObj. charvalue () == c}。
public void setChar(Object obj, char c) throws IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException {
if (!override) {
if (!Reflection.quickCheckMemberAccess(clazz, modifiers)) {
Class<?> caller = Reflection.getCallerClass();
checkAccess(caller, clazz, obj, modifiers);
}
}
getFieldAccessor(obj).setChar(obj, c);
}
// 将指定对象的字段值设置为{@code short}。这个方法等价于{@code set(obj, sObj)},其中{@code sObj}是一个{@code Short}对象,{@code sObj. shortvalue () == s}。
public void setShort(Object obj, short s) throws IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException {
if (!override) {
if (!Reflection.quickCheckMemberAccess(clazz, modifiers)) {
Class<?> caller = Reflection.getCallerClass();
checkAccess(caller, clazz, obj, modifiers);
}
}
getFieldAccessor(obj).setShort(obj, s);
}
// 将指定对象的字段值设置为{@code int}。这个方法等价于{@code set(obj, iObj)},其中{@code iObj}是一个{@code Integer}对象,{@code iObj. intvalue () == i}。
public void setInt(Object obj, int i) throws IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException {
if (!override) {
if (!Reflection.quickCheckMemberAccess(clazz, modifiers)) {
Class<?> caller = Reflection.getCallerClass();
checkAccess(caller, clazz, obj, modifiers);
}
}
getFieldAccessor(obj).setInt(obj, i);
}
// 将指定对象的字段值设置为{@code long}。这个方法等价于{@code set(obj, lObj)},其中{@code lObj}是一个{@code Long}对象,{@code lObj. longvalue () == l}。
public void setLong(Object obj, long l) throws IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException {
if (!override) {
if (!Reflection.quickCheckMemberAccess(clazz, modifiers)) {
Class<?> caller = Reflection.getCallerClass();
checkAccess(caller, clazz, obj, modifiers);
}
}
getFieldAccessor(obj).setLong(obj, l);
}
// 将指定对象的字段值设置为{@code float}。这个方法等价于{@code set(obj, fObj)},其中{@code fObj}是一个{@code Float}对象,{@code fObj. floatvalue () == f}。
public void setFloat(Object obj, float f) throws IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException {
if (!override) {
if (!Reflection.quickCheckMemberAccess(clazz, modifiers)) {
Class<?> caller = Reflection.getCallerClass();
checkAccess(caller, clazz, obj, modifiers);
}
}
getFieldAccessor(obj).setFloat(obj, f);
}
// 将指定对象的字段值设置为{@code double}。这个方法等价于{@code set(obj, dObj)},其中{@code dObj}是一个{@code Double}对象,{@code dObj. doublevalue () == d}。
public void setDouble(Object obj, double d) throws IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException {
if (!override) {
if (!Reflection.quickCheckMemberAccess(clazz, modifiers)) {
Class<?> caller = Reflection.getCallerClass();
checkAccess(caller, clazz, obj, modifiers);
}
}
getFieldAccessor(obj).setDouble(obj, d);
}
private synchronized Map<Class<? extends Annotation>, Annotation> declaredAnnotations() {
if (declaredAnnotations == null) {
Field root = this.root;
if (root != null) {
declaredAnnotations = root.declaredAnnotations();
} else {
declaredAnnotations = AnnotationParser.parseAnnotations(
annotations,
sun.misc.SharedSecrets.getJavaLangAccess().getConstantPool(getDeclaringClass()),
getDeclaringClass());
}
}
return declaredAnnotations;
}
public <T extends Annotation> T getAnnotation(Class<T> annotationClass) {
Objects.requireNonNull(annotationClass);
return annotationClass.cast(declaredAnnotations().get(annotationClass));
}
public <T extends Annotation> T[] getAnnotationsByType(Class<T> annotationClass) {
Objects.requireNonNull(annotationClass);
return AnnotationSupport.getDirectlyAndIndirectlyPresent(declaredAnnotations(), annotationClass);
}
public Annotation[] getDeclaredAnnotations() {
return AnnotationParser.toArray(declaredAnnotations());
}
private native byte[] getTypeAnnotationBytes0();
public AnnotatedType getAnnotatedType() {
return TypeAnnotationParser.buildAnnotatedType(getTypeAnnotationBytes0(),
sun.misc.SharedSecrets.getJavaLangAccess().
getConstantPool(getDeclaringClass()),
this,
getDeclaringClass(),
getGenericType(),
TypeAnnotation.TypeAnnotationTarget.FIELD);
测试代码:
@Getter
@Setter
class SupperClass {
@NotNull
public String supperField;
}
@Getter
@Setter
class FieldClass extends SupperClass{
private String name;
private int age;
public char c;
public float f;
private byte b;
public static String ps;
}
Field[] fields = FieldClass.class.getDeclaredFields();
System.out.printf("|%90s|%90s|%10s|%30s|%30s|%20s|%50s|%20s|%20s|%20s|%20s|%40s|%n",
"String", "Generic String", "Modifiers", "Generic Type", "Type", "Name", "Declaring Class Name", "is Enum Constant",
"is Synthetic", "is Accessible", "Annotated Type Name", "Annotations Name");
for (Field field : fields) {
System.out.printf("|%90s|%90s|%10s|%30s|%30s|%20s|%50s|%20s|%20s|%20s|%20s|%40s|%n",
field.toString(), field.toGenericString(),
field.getModifiers(), field.getGenericType(), field.getType(), field.getName(),
field.getDeclaringClass().getName(), field.isEnumConstant(), field.isSynthetic(),
field.isAccessible(), field.getAnnotatedType().getType().getTypeName(),
field.getAnnotations().length > 0 ? Arrays.toString(Arrays.stream(field.getAnnotations()).map(anno -> anno.annotationType().getName()).toArray()) : "");
}
Field field = FieldClass.class.getField("supperField");
System.out.printf("|%90s|%90s|%10s|%30s|%30s|%20s|%50s|%20s|%20s|%20s|%20s|%40s|%n",
field.toString(), field.toGenericString(),
field.getModifiers(), field.getGenericType(), field.getType(), field.getName(),
field.getDeclaringClass().getName(), field.isEnumConstant(), field.isSynthetic(),
field.isAccessible(), field.getAnnotatedType().getType().getTypeName(),
field.getAnnotations().length > 0 ? Arrays.toString(Arrays.stream(field.getAnnotations()).map(anno -> anno.annotationType().getName()).toArray()) : "");
测试结果
| String| Generic String| Modifiers| Generic Type| Type| Name| Declaring Class Name| is Enum Constant| is Synthetic| is Accessible| Annotated Type Name| Annotations Name|
| private java.lang.String com.test.FieldClass.name| private java.lang.String com.test.FieldClass.name| 2| class java.lang.String| class java.lang.String| name| com.test.FieldClass| false| false| false| java.lang.String| |
| private int com.test.FieldClass.age| private int com.test.FieldClass.age| 2| int| int| age| com.test.FieldClass| false| false| false| int| |
| public char com.test.FieldClass.c| public char com.test.FieldClass.c| 1| char| char| c| com.test.FieldClass| false| false| false| char| |
| public float com.test.FieldClass.f| public float com.test.FieldClass.f| 1| float| float| f| com.test.FieldClass| false| false| false| float| |
| private byte com.test.FieldClass.b| private byte com.test.FieldClass.b| 2| byte| byte| b| com.test.FieldClass| false| false| false| byte| |
| public static java.lang.String com.test.FieldClass.ps| public static java.lang.String com.test.FieldClass.ps| 9| class java.lang.String| class java.lang.String| ps| com.test.FieldClass| false| false| false| java.lang.String| |
| public java.lang.String com.test.SupperClass.supperField| public java.lang.String com.test.SupperClass.supperField| 1| class java.lang.String| class java.lang.String| supperField| com.test.SupperClass| false| false| false| java.lang.String| [javax.validation.constraints.NotNull]|
Type
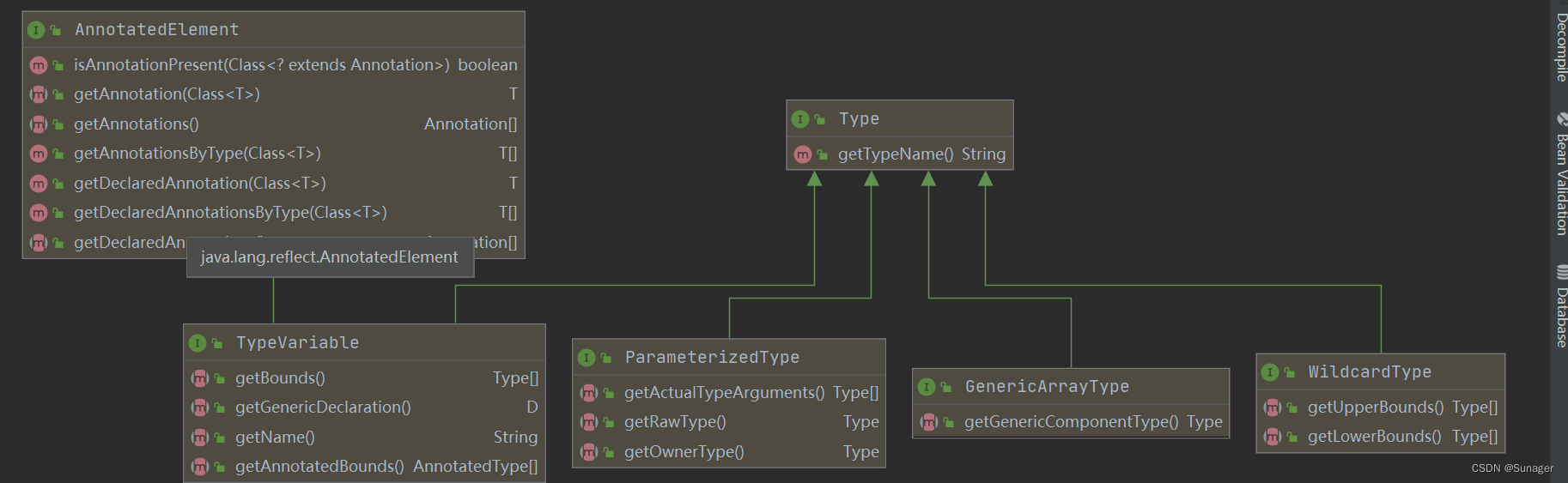
@Since:1.5
Comment:类型是Java编程语言中所有类型的泛型超接口。这些类型包括原始类型、参数化类型、数组类型、类型变量和基本类型。
// 返回描述此类型的字符串,包括关于任何类型参数的信息。
default String getTypeName() {
return toString();
}
GenericArrayType
@Since:1.5
Comment:表示一个数组类型,其组件类型要么是参数化类型,要么是类型变量。
// 返回一个表示此数组组件类型的{@code Type}对象。此方法创建数组的组件类型。参数化类型的创建过程的语义请参见{@link java.lang.reflect.ParameterizedType ParameterizedType}的声明,类型变量的创建过程请参见{@link java.lang.reflect.TypeVariable TypeVariable}的声明。
Type getGenericComponentType();
ParameterizedType
@Since:1.5
Comment:表示参数化类型,例如Collection<String>
// 返回一个{@code Type}对象数组,表示该类型的实际类型参数。
Type[] getActualTypeArguments();
// 返回表示声明此类型的类或接口的{@code Type}对象。
Type getRawType();
// 返回一个{@code Type}对象,表示该类型所属的类型。例如,如果此类型是{@code O<T>.I<S>},返回{@code O<T>}的表示形式。
Type getOwnerType();
TypeVariable
@Since:1.5
Comment:TypeVariable是类型类型变量的通用超接口。当反射方法第一次需要类型变量时,就会创建它,就像这个包中指定的那样。如果类型变量t被类型(即类、接口或注释类型)t引用,并且t由t的第n个封闭类声明(参见JLS 8.1.2),那么t的创建需要解析(参见JVMS 5) t的第i个封闭类,因为i = 0到n,包括在内。创建类型变量不能导致创建其边界。重复创建类型变量不会产生任何影响。
// 返回一个{@code Type}对象数组,表示该类型变量的上限。注意,如果没有显式声明上限,则上限为{@code Object}。
Type[] getBounds();
// 返回代表该类型变量的泛型声明的{@code GenericDeclaration}对象。
D getGenericDeclaration();
// 返回此类型变量的名称,因为它出现在源代码中。
String getName();
// 返回一个AnnotatedType对象数组,该数组表示使用类型来表示该类型变量所表示的类型参数的上限。数组中对象的顺序对应于类型形参声明中边界的顺序。
AnnotatedType[] getAnnotatedBounds();
WildcardType
@Since:1.5
Comment:WildcardType表示通配符类型表达式,如{@code ?}、{@code ? extends Number},或{@code ? super Integer}。
// 返回一个{@code Type}对象数组,表示该类型变量的上限。注意,如果没有显式声明上限,则上限为{@code Object}。
Type[] getUpperBounds();
// 返回一个{@code Type}对象数组,表示该类型变量的下界。注意,如果没有显式声明下界,则下界的类型为{@code null}。在这种情况下,返回一个零长度的数组。
Type[] getLowerBounds();
测试代码:
class CType<K extends Number, V> {
List<K> list = new ArrayList<>();
Map<K,V> map = new HashMap<>();
K k;
Map<K, List<V>> mapList;
Map<String, K> mapString;
K[] kArr;
List<? extends Collection<K>> extendsF;
List<? super String> supperF;
Inner inner = new Inner();
@Value("123")
String defaultString;
class Inner {}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
CType<Integer, Long> cType = new CType<>();
System.out.printf("|%20s|%20s|%50s|%60s|%10s|%110s|%80s|%110s|%30s|%n",
"Field Name", "Type Name", "GenericType Name",
"GenericTypeClass Name", "modifier", "parameterizedTypeInfo",
"wildcardTypeInfo", "typeVariableInfo", "genericArrayTypeInfo");
for (Field field : cType.getClass().getDeclaredFields()) {
Class<?> type = field.getType();
Type genericType = field.getGenericType();
// ParameterizedType:1000, TypeVariable:0100, GenericArrayType:0010, WildcardType:0001
StringBuilder parameterizedTypeInfo = new StringBuilder();
StringBuilder wildcardTypeInfo = new StringBuilder();
StringBuilder typeVariableInfo = new StringBuilder();
StringBuilder genericArrayTypeInfo = new StringBuilder();
int modifier = 0;
if (genericType instanceof ParameterizedType) {
modifier |= 0b1000;
parameterizedTypeInfo.append("getActualTypeArguments: ").append(Arrays.toString(Arrays.stream(((ParameterizedType) genericType).getActualTypeArguments()).map(Type::getTypeName).toArray()))
.append(", getRawType: ").append(((ParameterizedType) genericType).getRawType().getTypeName())
.append(", getOwnerType: ").append(Objects.nonNull(((ParameterizedType) genericType).getOwnerType()) ? ((ParameterizedType) genericType).getOwnerType().getTypeName() : null);
for (Type actualTypeArgument : ((ParameterizedType) genericType).getActualTypeArguments()) {
if (actualTypeArgument instanceof WildcardType) {
modifier |= 0b0001;
wildcardTypeInfo.append("getLowerBounds: ").append(Arrays.toString(Arrays.stream(((WildcardType) actualTypeArgument).getLowerBounds()).map(Type::getTypeName).toArray()))
.append(", getUpperBounds: ").append(Arrays.toString(Arrays.stream(((WildcardType) actualTypeArgument).getUpperBounds()).map(Type::getTypeName).toArray()));
}
}
} else if (genericType instanceof TypeVariable) {
modifier |= 0b0100;
typeVariableInfo.append("getBounds: ").append(Arrays.toString(Arrays.stream(((TypeVariable<?>) genericType).getBounds()).map(Type::getTypeName).toArray()))
.append(", getGenericDeclaration: ").append(Arrays.toString(Arrays.stream(((TypeVariable<?>) genericType).getGenericDeclaration().getAnnotations()).map(anno -> anno.annotationType().getName()).toArray()))
.append(", getName: ").append(((TypeVariable<?>) genericType).getName())
.append(", getAnnotatedBounds: ").append(Arrays.toString(Arrays.stream(((TypeVariable<?>) genericType).getAnnotatedBounds()).map(anno -> anno.getType().getTypeName()).toArray()));
} else if (genericType instanceof GenericArrayType) {
modifier |= 0b0010;
genericArrayTypeInfo.append("getGenericComponentType: ").append(((GenericArrayType) genericType).getGenericComponentType());
}
System.out.printf("|%20s|%20s|%50s|%60s|%10s|%110s|%80s|%110s|%30s|%n",
field.getName(), type.getName(), genericType.getTypeName(), genericType.getClass().getName(),
String.format("%1$04d", Integer.valueOf(Integer.toBinaryString(modifier))), parameterizedTypeInfo.toString(), wildcardTypeInfo.toString(), typeVariableInfo.toString(),
genericArrayTypeInfo.toString());
}
// GenericArrayType接口测试,GenericArrayType接口在lang包中只有三个实现类Class、Method、Construct
System.out.println("n" + Arrays.toString(Arrays.stream(cType.getClass().getTypeParameters()).map(TypeVariable::getName).toArray()));
}
测试结果:
| Field Name| Type Name| GenericType Name| GenericTypeClass Name| modifier| parameterizedTypeInfo| wildcardTypeInfo| typeVariableInfo| genericArrayTypeInfo|
| list| java.util.List| java.util.List<K>|sun.reflect.generics.reflectiveObjects.ParameterizedTypeImpl| 1000| getActualTypeArguments: [K], getRawType: java.util.List, getOwnerType: null| | | |
| map| java.util.Map| java.util.Map<K, V>|sun.reflect.generics.reflectiveObjects.ParameterizedTypeImpl| 1000| getActualTypeArguments: [K, V], getRawType: java.util.Map, getOwnerType: null| | | |
| k| java.lang.Number| K| sun.reflect.generics.reflectiveObjects.TypeVariableImpl| 0100| | | getBounds: [java.lang.Number], getGenericDeclaration: [], getName: K, getAnnotatedBounds: [java.lang.Number]| |
| mapList| java.util.Map| java.util.Map<K, java.util.List<V>>|sun.reflect.generics.reflectiveObjects.ParameterizedTypeImpl| 1000| getActualTypeArguments: [K, java.util.List<V>], getRawType: java.util.Map, getOwnerType: null| | | |
| mapString| java.util.Map| java.util.Map<java.lang.String, K>|sun.reflect.generics.reflectiveObjects.ParameterizedTypeImpl| 1000| getActualTypeArguments: [java.lang.String, K], getRawType: java.util.Map, getOwnerType: null| | | |
| kArr| [Ljava.lang.Number;| K[]| sun.reflect.generics.reflectiveObjects.GenericArrayTypeImpl| 0010| | | | getGenericComponentType: K|
| extendsF| java.util.List| java.util.List<? extends java.util.Collection<K>>|sun.reflect.generics.reflectiveObjects.ParameterizedTypeImpl| 1001| getActualTypeArguments: [? extends java.util.Collection<K>], getRawType: java.util.List, getOwnerType: null| getLowerBounds: [], getUpperBounds: [java.util.Collection<K>]| | |
| supperF| java.util.List| java.util.List<? super java.lang.String>|sun.reflect.generics.reflectiveObjects.ParameterizedTypeImpl| 1001| getActualTypeArguments: [? super java.lang.String], getRawType: java.util.List, getOwnerType: null| getLowerBounds: [java.lang.String], getUpperBounds: [java.lang.Object]| | |
| inner|com.test.CType$Inner| com.test.CType<K, V>$Inner|sun.reflect.generics.reflectiveObjects.ParameterizedTypeImpl| 1000| getActualTypeArguments: [], getRawType: com.test.CType$Inner, getOwnerType: com.test.CType<K, V>| | | |
| defaultString| java.lang.String| java.lang.String| java.lang.Class| 0000| | | | |
[K, V]
GenericDeclaration
@Since:1.5
Comment:所有声明类型变量的实体的公共接口。
// 返回一个{@code TypeVariable}对象的数组,该数组按声明顺序表示由{@code GenericDeclaration}对象所表示的泛型声明所声明的类型变量。如果基础泛型声明没有声明类型变量,则返回长度为0的数组。
public TypeVariable<?>[] getTypeParameters();
Executable
@Since:1.8
Comment:一个包含{@link Method}和{@link Constructor}共同功能的共享超类。
private transient volatile boolean hasRealParameterData;
private transient volatile Parameter[] parameters;
private native Parameter[] getParameters0();
native byte[] getTypeAnnotationBytes0();
// 只将包可见性授予构造函数。
Executable() {}
// 访问器方法以允许代码共享
abstract byte[] getAnnotationBytes();
// 访问器方法以允许代码共享
abstract Executable getRoot();
// 可执行文件是否有泛型信息。
abstract boolean hasGenericInformation();
abstract ConstructorRepository getGenericInfo();
// 判断参数类型是否相同
boolean equalParamTypes(Class<?>[] params1, Class<?>[] params2) {
/* 避免不必要的克隆 */
if (params1.length == params2.length) {
for (int i = 0; i < params1.length; i++) {
if (params1[i] != params2[i])
return false;
}
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 解析参数注解
Annotation[][] parseParameterAnnotations(byte[] parameterAnnotations) {
return AnnotationParser.parseParameterAnnotations(
parameterAnnotations,
sun.misc.SharedSecrets.getJavaLangAccess().
getConstantPool(getDeclaringClass()),
getDeclaringClass());
}
// 使用逗号分隔类型
void separateWithCommas(Class<?>[] types, StringBuilder sb) {
for (int j = 0; j < types.length; j++) {
sb.append(types[j].getTypeName());
if (j < (types.length - 1))
sb.append(",");
}
}
// 如果非零,打印修饰符
void printModifiersIfNonzero(StringBuilder sb, int mask, boolean isDefault) {
int mod = getModifiers() & mask;
if (mod != 0 && !isDefault) {
sb.append(Modifier.toString(mod)).append(' ');
} else {
int access_mod = mod & Modifier.ACCESS_MODIFIERS;
if (access_mod != 0)
sb.append(Modifier.toString(access_mod)).append(' ');
if (isDefault)
sb.append("default ");
mod = (mod & ~Modifier.ACCESS_MODIFIERS);
if (mod != 0)
sb.append(Modifier.toString(mod)).append(' ');
}
}
// 生成特定于方法或构造函数的toString头信息。
abstract void specificToStringHeader(StringBuilder sb);
// 生成字符串
String sharedToString(int modifierMask,
boolean isDefault,
Class<?>[] parameterTypes,
Class<?>[] exceptionTypes) {
try {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
printModifiersIfNonzero(sb, modifierMask, isDefault);
specificToStringHeader(sb);
sb.append('(');
separateWithCommas(parameterTypes, sb);
sb.append(')');
if (exceptionTypes.length > 0) {
sb.append(" throws ");
separateWithCommas(exceptionTypes, sb);
}
return sb.toString();
} catch (Exception e) {
return "<" + e + ">";
}
}
// 生成泛型字符串
String sharedToGenericString(int modifierMask, boolean isDefault) {
try {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
printModifiersIfNonzero(sb, modifierMask, isDefault);
TypeVariable<?>[] typeparms = getTypeParameters();
if (typeparms.length > 0) {
boolean first = true;
sb.append('<');
for(TypeVariable<?> typeparm: typeparms) {
if (!first)
sb.append(',');
// 类对象不能出现在这里;不需要测试和调用Class.getName()。
sb.append(typeparm.toString());
first = false;
}
sb.append("> ");
}
specificToGenericStringHeader(sb);
sb.append('(');
Type[] params = getGenericParameterTypes();
for (int j = 0; j < params.length; j++) {
String param = params[j].getTypeName();
if (isVarArgs() && (j == params.length - 1)) // replace T[] with T...
param = param.replaceFirst("\[\]$", "...");
sb.append(param);
if (j < (params.length - 1))
sb.append(',');
}
sb.append(')');
Type[] exceptions = getGenericExceptionTypes();
if (exceptions.length > 0) {
sb.append(" throws ");
for (int k = 0; k < exceptions.length; k++) {
sb.append((exceptions[k] instanceof Class)?
((Class)exceptions[k]).getName():
exceptions[k].toString());
if (k < (exceptions.length - 1))
sb.append(',');
}
}
return sb.toString();
} catch (Exception e) {
return "<" + e + ">";
}
}
// 返回{@code Class}对象,该对象表示声明由该对象表示的可执行文件的类或接口。
public abstract Class<?> getDeclaringClass();
// 返回由该对象表示的可执行文件的名称。
public abstract String getName();
// 返回由该对象表示的可执行文件的Java语言{@linkplain Modifier modifiers}。
public abstract int getModifiers();
// 返回一个{@code TypeVariable}对象的数组,该数组按声明顺序表示由{@code GenericDeclaration}对象所表示的泛型声明所声明的类型变量。如果基础泛型声明没有声明类型变量,则返回长度为0的数组。
public abstract TypeVariable<?>[] getTypeParameters();
// 返回一个{@code Class}对象的数组,该数组表示由该对象表示的可执行文件的形式形参类型(按声明顺序)。如果底层可执行文件不接受参数,则返回长度为0的数组。
public abstract Class<?>[] getParameterTypes();
// 返回此对象表示的可执行文件的形式参数数量(显式声明或隐式声明,或两者都没有)。
public int getParameterCount() {
throw new AbstractMethodError();
}
// 返回一个{@code Type}对象的数组,该数组表示由该对象表示的可执行文件的形式参数类型(按声明顺序)。如果底层可执行文件不接受参数,则返回长度为0的数组。
public Type[] getGenericParameterTypes() {
if (hasGenericInformation())
return getGenericInfo().getParameterTypes();
else
return getParameterTypes();
}
// 行为类似于{@code getGenericParameterTypes},但返回所有参数的类型信息,包括合成参数。
Type[] getAllGenericParameterTypes() {
final boolean genericInfo = hasGenericInformation();
// 简单的情况:我们没有泛型参数信息。在本例中,我们只返回getParameterTypes()的结果
if (!genericInfo) {
return getParameterTypes();
} else {
final boolean realParamData = hasRealParameterData();
final Type[] genericParamTypes = getGenericParameterTypes();
final Type[] nonGenericParamTypes = getParameterTypes();
final Type[] out = new Type[nonGenericParamTypes.length];
final Parameter[] params = getParameters();
int fromidx = 0;
// 如果我们有真正的参数数据,那么我们可以使用合成和授权标志。
if (realParamData) {
for (int i = 0; i < out.length; i++) {
final Parameter param = params[i];
if (param.isSynthetic() || param.isImplicit()) {
// 如果遇到一个合成参数或强制参数,则使用非泛型参数信息。
out[i] = nonGenericParamTypes[i];
} else {
// 否则,使用泛型参数info。
out[i] = genericParamTypes[fromidx];
fromidx++;
}
}
} else {
// 否则,使用非泛型参数数据。没有方法参数反射数据,我们就没有办法找出哪些参数是合成的/强制的,因此,就没有办法匹配索引。
return genericParamTypes.length == nonGenericParamTypes.length ?
genericParamTypes : nonGenericParamTypes;
}
return out;
}
}
// 返回一个{@code Parameter}对象数组,该数组表示该对象所表示的底层可执行文件的所有参数。如果可执行文件没有参数,则返回长度为0的数组。
public Parameter[] getParameters() {
// TODO: 这可能最终需要使用类似于Field、Method等中的安全机制来保护。
// 需要复制缓存的数组,以防止用户乱用它。由于形参是不可变的,我们可以进行浅复制。
return privateGetParameters().clone();
}
// 综合所有的参数
private Parameter[] synthesizeAllParams() {
final int realparams = getParameterCount();
final Parameter[] out = new Parameter[realparams];
for (int i = 0; i < realparams; i++)
// TODO: 有没有一种方法可以综合推导出修饰语?一般情况下可能不会,因为我们无法了解它们,但可能会有特定的情况。
out[i] = new Parameter("arg" + i, 0, this, i);
return out;
}
// 参数验证
private void verifyParameters(final Parameter[] parameters) {
final int mask = Modifier.FINAL | Modifier.SYNTHETIC | Modifier.MANDATED;
if (getParameterTypes().length != parameters.length)
throw new MalformedParametersException("Wrong number of parameters in MethodParameters attribute");
for (Parameter parameter : parameters) {
final String name = parameter.getRealName();
final int mods = parameter.getModifiers();
if (name != null) {
if (name.isEmpty() || name.indexOf('.') != -1 ||
name.indexOf(';') != -1 || name.indexOf('[') != -1 ||
name.indexOf('/') != -1) {
throw new MalformedParametersException("Invalid parameter name "" + name + """);
}
}
if (mods != (mods & mask)) {
throw new MalformedParametersException("Invalid parameter modifiers");
}
}
}
// 私有(私自?)获得参数
private Parameter[] privateGetParameters() {
// 使用tmp来避免对volatile的多次写入。
Parameter[] tmp = parameters;
if (tmp == null) {
// 否则,请到JVM获取它们
try {
tmp = getParameters0();
} catch(IllegalArgumentException e) {
// 重新抛出ClassFormatErrors
throw new MalformedParametersException("Invalid constant pool index");
}
// 如果我们什么都没有得到,那么就合成参数
if (tmp == null) {
hasRealParameterData = false;
tmp = synthesizeAllParams();
} else {
hasRealParameterData = true;
verifyParameters(tmp);
}
parameters = tmp;
}
return tmp;
}
// 是否有真实参数数据
boolean hasRealParameterData() {
// 如果这个函数在参数初始化之前被调用,强制它存在。
if (parameters == null) {
privateGetParameters();
}
return hasRealParameterData;
}
// reflectaccess所需的
byte[] getTypeAnnotationBytes() {
return getTypeAnnotationBytes0();
}
// 返回一个{@code Class}对象数组,该数组表示由该对象表示的底层可执行文件声明引发的异常类型。如果可执行文件在其{@code throws}子句中没有声明异常,则返回长度为0的数组。
public abstract Class<?>[] getExceptionTypes();
// 返回一个{@code Type}对象数组,该数组表示此可执行对象声明要抛出的异常。如果底层可执行文件在其{@code throws}子句中没有声明异常,则返回长度为0的数组。
public Type[] getGenericExceptionTypes() {
Type[] result;
if (hasGenericInformation() &&
((result = getGenericInfo().getExceptionTypes()).length > 0))
return result;
else
return getExceptionTypes();
}
// 返回一个描述此{@code Executable}的字符串,包括任何类型参数。
public abstract String toGenericString();
// 如果这个可执行文件声明接受可变数量的参数,则返回{@code true};否则返回{@code false}。
public boolean isVarArgs() {
return (getModifiers() & Modifier.VARARGS) != 0;
}
// 如果这个可执行文件是一个合成构造,返回{@code true};否则返回{@code false}。
public boolean isSynthetic() {
return Modifier.isSynthetic(getModifiers());
}
// 返回一个由{@code Annotation}组成的数组,该数组表示由该对象表示的{@code Executable}的形式参数上的注释(按声明顺序)。合成参数和指定参数(参见下面的解释),例如内部类构造函数的外部“this”参数将在返回的数组中表示。如果可执行文件没有参数(意味着没有正式的、合成的和强制的参数),将返回一个零长度的数组。如果{@code Executable}有一个或多个参数,则为每个不带注释的参数返回长度为0的嵌套数组。返回数组中包含的注释对象是可序列化的。这个方法的调用者可以自由地修改返回的数组;它对返回给其他调用方的数组没有影响。
public abstract Annotation[][] getParameterAnnotations();
// 参数说明
Annotation[][] sharedGetParameterAnnotations(Class<?>[] parameterTypes,
byte[] parameterAnnotations) {
int numParameters = parameterTypes.length;
if (parameterAnnotations == null)
return new Annotation[numParameters][0];
Annotation[][] result = parseParameterAnnotations(parameterAnnotations);
if (result.length != numParameters)
handleParameterNumberMismatch(result.length, numParameters);
return result;
}
// 参数号不匹配处理
abstract void handleParameterNumberMismatch(int resultLength, int numParameters);
private transient Map<Class<? extends Annotation>, Annotation> declaredAnnotations;
public <T extends Annotation> T getAnnotation(Class<T> annotationClass) {
Objects.requireNonNull(annotationClass);
return annotationClass.cast(declaredAnnotations().get(annotationClass));
}
public <T extends Annotation> T[] getAnnotationsByType(Class<T> annotationClass) {
Objects.requireNonNull(annotationClass);
return AnnotationSupport.getDirectlyAndIndirectlyPresent(declaredAnnotations(), annotationClass);
}
public Annotation[] getDeclaredAnnotations() {
return AnnotationParser.toArray(declaredAnnotations());
}
private synchronized Map<Class<? extends Annotation>, Annotation> declaredAnnotations() {
if (declaredAnnotations == null) {
Executable root = getRoot();
if (root != null) {
declaredAnnotations = root.declaredAnnotations();
} else {
declaredAnnotations = AnnotationParser.parseAnnotations(
getAnnotationBytes(),
sun.misc.SharedSecrets.getJavaLangAccess().
getConstantPool(getDeclaringClass()),
getDeclaringClass());
}
}
return declaredAnnotations;
}
// 返回一个{@code AnnotatedType}对象,该对象表示使用一个类型来指定该可执行文件所表示的方法/构造函数的返回类型。
public abstract AnnotatedType getAnnotatedReturnType();
// 可执行文件的子类的助手。
// 返回一个AnnotatedType对象,该对象表示使用一个类型来指定该可执行文件所表示的方法/构造函数的返回类型。
AnnotatedType getAnnotatedReturnType0(Type returnType) {
return TypeAnnotationParser.buildAnnotatedType(getTypeAnnotationBytes0(),
sun.misc.SharedSecrets.getJavaLangAccess().
getConstantPool(getDeclaringClass()),
this,
getDeclaringClass(),
returnType,
TypeAnnotation.TypeAnnotationTarget.METHOD_RETURN);
}
// 返回一个{@code AnnotatedType}对象,该对象表示使用一个类型来指定这个可执行对象所表示的方法/构造函数的接收类型。方法/构造函数的接收器类型只有在方法/构造函数有接收器参数时才可用(JLS 8.4.1)。
public AnnotatedType getAnnotatedReceiverType() {
if (Modifier.isStatic(this.getModifiers()))
return null;
return TypeAnnotationParser.buildAnnotatedType(getTypeAnnotationBytes0(),
sun.misc.SharedSecrets.getJavaLangAccess().
getConstantPool(getDeclaringClass()),
this,
getDeclaringClass(),
getDeclaringClass(),
TypeAnnotation.TypeAnnotationTarget.METHOD_RECEIVER);
}
// 返回一个{@code AnnotatedType}对象数组,该数组表示使用类型来指定该可执行文件所表示的方法/构造函数的形式参数类型。数组中对象的顺序对应于方法/构造函数声明中形式形参类型的顺序。
public AnnotatedType[] getAnnotatedParameterTypes() {
return TypeAnnotationParser.buildAnnotatedTypes(getTypeAnnotationBytes0(),
sun.misc.SharedSecrets.getJavaLangAccess().
getConstantPool(getDeclaringClass()),
this,
getDeclaringClass(),
getAllGenericParameterTypes(),
TypeAnnotation.TypeAnnotationTarget.METHOD_FORMAL_PARAMETER);
}
// 返回一个{@code AnnotatedType}对象数组,该数组表示使用类型来指定由该可执行文件表示的方法/构造函数声明的异常。数组中对象的顺序对应于方法/构造函数声明中异常类型的顺序。
public AnnotatedType[] getAnnotatedExceptionTypes() {
return TypeAnnotationParser.buildAnnotatedTypes(getTypeAnnotationBytes0(),
sun.misc.SharedSecrets.getJavaLangAccess().
getConstantPool(getDeclaringClass()),
this,
getDeclaringClass(),
getGenericExceptionTypes(),
TypeAnnotation.TypeAnnotationTarget.THROWS);
}
Method
Comment:提供关于类或接口上单个方法的信息和访问。反射的方法可以是一个类方法或一个实例方法(包括一个抽象方法)。
private Class<?> clazz;
private int slot;
// 这可以保证在1.4反射实现中由VM实现
private String name;
private Class<?> returnType;
private Class<?>[] parameterTypes;
private Class<?>[] exceptionTypes;
private int modifiers;
// 泛型和注释支持
private transient String signature;
// 泛型信息存储库;延迟初始化
private transient MethodRepository genericInfo;
private byte[] annotations;
private byte[] parameterAnnotations;
private byte[] annotationDefault;
private volatile MethodAccessor methodAccessor;
// 用于MethodAccessors的共享。这个分支结构目前只有两层深度(即,一个根方法和可能指向它的多个方法对象)。
// 如果这个分支结构包含循环,那么在注释代码中就可能发生死锁。
private Method root;
// 获取基础签名
private String getGenericSignature() {return signature;}
// 访问器的工厂
private GenericsFactory getFactory() {
// 创建范围和工厂
return CoreReflectionFactory.make(this, MethodScope.make(this));
}
// 泛型信息存储库的访问器
MethodRepository getGenericInfo() {
// 如果需要,延迟初始化存储库
if (genericInfo == null) {
// 创建和缓存泛型信息存储库
genericInfo = MethodRepository.make(getGenericSignature(),
getFactory());
}
return genericInfo; //return cached repository
}
// 用于在Java代码中实例化这些对象的ReflectAccess使用的包私有构造函数,java.lang包通过sun.reflect.LangReflectAccess。
Method(Class<?> declaringClass, String name, Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Class<?> returnType, Class<?>[] checkedExceptions, int modifiers, int slot, String signature, byte[] annotations, byte[] parameterAnnotations, byte[] annotationDefault) {
this.clazz = declaringClass;
this.name = name;
this.parameterTypes = parameterTypes;
this.returnType = returnType;
this.exceptionTypes = checkedExceptions;
this.modifiers = modifiers;
this.slot = slot;
this.signature = signature;
this.annotations = annotations;
this.parameterAnnotations = parameterAnnotations;
this.annotationDefault = annotationDefault;
}
// 包私有例程(通过ReflectAccess向java.lang.Class公开)返回此方法的副本。副本的"root"字段指向这个方法。
Method copy() {
// 这个例程允许在引用VM中相同底层方法的Method对象之间共享MethodAccessor对象。(所有这些扭曲都是必要的,因为AccessibleObject中的“可访问性”部分,它隐式地要求为对Class对象的每次反射调用制造新的java.lang.reflect对象。)
if (this.root != null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Can not copy a non-root Method");
Method res = new Method(clazz, name, parameterTypes, returnType,
exceptionTypes, modifiers, slot, signature,
annotations, parameterAnnotations, annotationDefault);
res.root = this;
// 如果已经存在,不妨踊跃宣传
res.methodAccessor = methodAccessor;
return res;
}
// 由Excecutable用于注释共享。
Executable getRoot() {
return root;
}
boolean hasGenericInformation() {
return (getGenericSignature() != null);
}
byte[] getAnnotationBytes() {
return annotations;
}
public Class<?> getDeclaringClass() {
return clazz;
}
// 返回由{@code method}对象表示的方法名,作为{@code String}。
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public int getModifiers() {
return modifiers;
}
public TypeVariable<Method>[] getTypeParameters() {
if (getGenericSignature() != null)
return (TypeVariable<Method>[])getGenericInfo().getTypeParameters();
else
return (TypeVariable<Method>[])new TypeVariable[0];
}
// 返回一个{@code Class}对象,该对象表示这个{@code method}对象所表示的方法的正式返回类型。
public Class<?> getReturnType() {
return returnType;
}
// 返回一个{@code Type}对象,该对象表示由{@code method}对象表示的方法的正式返回类型。
// 如果返回类型是参数化类型,返回的{@code type}对象必须准确地反映源代码中使用的实际类型参数。如果返回类型是类型变量或参数化类型,则创建它。否则,将被解析。
public Type getGenericReturnType() {
if (getGenericSignature() != null) {
return getGenericInfo().getReturnType();
} else { return getReturnType();}
}
public Class<?>[] getParameterTypes() {
return parameterTypes.clone();
}
public int getParameterCount() { return parameterTypes.length; }
public Type[] getGenericParameterTypes() {
return super.getGenericParameterTypes();
}
public Class<?>[] getExceptionTypes() {
return exceptionTypes.clone();
}
public Type[] getGenericExceptionTypes() {
return super.getGenericExceptionTypes();
}
// 将这个{@code Method}与指定对象进行比较。如果两个对象相同,则返回true。
// 如果两个{@code Method}由同一个类声明,并且具有相同的名称、形式参数类型和返回类型,则它们是相同的。
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (obj != null && obj instanceof Method) {
Method other = (Method)obj;
if ((getDeclaringClass() == other.getDeclaringClass())
&& (getName() == other.getName())) {
if (!returnType.equals(other.getReturnType()))
return false;
return equalParamTypes(parameterTypes, other.parameterTypes);
}
}
return false;
}
// 返回这个{@code Method}的hashcode。哈希代码作为底层方法声明的类名和方法名的哈希代码的异或计算。
public int hashCode() {
return getDeclaringClass().getName().hashCode() ^ getName().hashCode();
}
// 返回一个描述这个{@code Method}的字符串。该字符串格式化为方法访问修饰符(如果有的话),然后是方法返回类型,然后是空格,然后是声明方法的类,然后是句号,然后是方法名称,最后是用圆括号括起来的、以逗号分隔的方法的形式参数类型列表。如果该方法抛出检查过的异常,则参数列表后面跟着一个空格,然后是单词throws,然后是用逗号分隔的抛出异常类型列表。
// example: public boolean java.lang.Object.equals(java.lang.Object)
public String toString() {
return sharedToString(Modifier.methodModifiers(),
isDefault(),
parameterTypes,
exceptionTypes);
}
void specificToStringHeader(StringBuilder sb) {
sb.append(getReturnType().getTypeName()).append(' ');
sb.append(getDeclaringClass().getTypeName()).append('.');
sb.append(getName());
}
// 返回一个描述这个{@code Method}的字符串,包括类型参数。该字符串格式化为方法访问修饰符(如果有的话),然后是一个用尖括号分隔的方法类型参数列表(如果有的话),然后是方法的泛型返回类型,后面是一个空格,后面是声明方法的类,后面是一个句点,后面是方法名称,后面是一个用圆括号分隔的方法泛型形式参数类型列表。
public String toGenericString() {
return sharedToGenericString(Modifier.methodModifiers(), isDefault());
}
void specificToGenericStringHeader(StringBuilder sb) {
Type genRetType = getGenericReturnType();
sb.append(genRetType.getTypeName()).append(' ');
sb.append(getDeclaringClass().getTypeName()).append('.');
sb.append(getName());
}
// 在具有指定参数的指定对象上调用由这个{@code method}对象表示的基础方法。各个参数被自动取消包装以匹配原语形式参数,并且原语参数和引用参数都要根据需要进行方法调用转换。
public Object invoke(Object obj, Object... args) throws IllegalAccessException, IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException {
if (!override) {
if (!Reflection.quickCheckMemberAccess(clazz, modifiers)) {
Class<?> caller = Reflection.getCallerClass();
checkAccess(caller, clazz, obj, modifiers);
}
}
MethodAccessor ma = methodAccessor; // read volatile
if (ma == null) {
ma = acquireMethodAccessor();
}
return ma.invoke(obj, args);
}
// 如果该方法是桥方法,则返回{@code true};否则返回{@code false}。
public boolean isBridge() {
return (getModifiers() & Modifier.BRIDGE) != 0;
}
public boolean isVarArgs() {
return super.isVarArgs();
}
public boolean isSynthetic() {
return super.isSynthetic();
}
// 如果该方法是默认方法,则返回{@code true};否则返回{@code false}。默认方法是公共的非抽象实例方法,即在接口类型中声明的具有主体的非静态方法。
public boolean isDefault() {
// Default methods are public non-abstract instance methods declared in an interface.
return ((getModifiers() & (Modifier.ABSTRACT | Modifier.PUBLIC | Modifier.STATIC)) ==
Modifier.PUBLIC) && getDeclaringClass().isInterface();
}
// 注意,这里没有使用同步。为一个给定的方法生成多个MethodAccessor是正确的(虽然不是有效的)。然而,避免同步可能会使实现更具可伸缩性。
private MethodAccessor acquireMethodAccessor() {
// 首先检查是否已经创建了一个,如果已经创建了,就接受它
MethodAccessor tmp = null;
if (root != null) tmp = root.getMethodAccessor();
if (tmp != null) {
methodAccessor = tmp;
} else {
//否则,制造一个并传播到root
tmp = reflectionFactory.newMethodAccessor(this);
setMethodAccessor(tmp);
}
return tmp;
}
// 返回Method对象的MethodAccessor,而不是从链向上查找到root
MethodAccessor getMethodAccessor() {
return methodAccessor;
}
// 为这个Method对象和(递归地)它的root设置MethodAccessor
void setMethodAccessor(MethodAccessor accessor) {
methodAccessor = accessor;
// 向上传播
if (root != null) {
root.setMethodAccessor(accessor);
}
}
// 返回由{@code Method}实例表示的annotation成员的默认值。如果成员是基元类型,则返回相应包装器类型的实例。如果没有默认值与成员关联,或者方法实例不表示annotation类型声明的成员,则返回null。
public Object getDefaultValue() {
if (annotationDefault == null)
return null;
Class<?> memberType = AnnotationType.invocationHandlerReturnType(
getReturnType());
Object result = AnnotationParser.parseMemberValue(
memberType, ByteBuffer.wrap(annotationDefault),
sun.misc.SharedSecrets.getJavaLangAccess().
getConstantPool(getDeclaringClass()),
getDeclaringClass());
if (result instanceof sun.reflect.annotation.ExceptionProxy)
throw new AnnotationFormatError("Invalid default: " + this);
return result;
}
public <T extends Annotation> T getAnnotation(Class<T> annotationClass) {
return super.getAnnotation(annotationClass);
}
public Annotation[] getDeclaredAnnotations() {
return super.getDeclaredAnnotations();
}
public Annotation[][] getParameterAnnotations() {
return sharedGetParameterAnnotations(parameterTypes, parameterAnnotations);
}
public AnnotatedType getAnnotatedReturnType() {
return getAnnotatedReturnType0(getGenericReturnType());
}
void handleParameterNumberMismatch(int resultLength, int numParameters) {
throw new AnnotationFormatError("Parameter annotations don't match number of parameters");
}
测试代码:
class MethodClass<T> {
@Select("select 1 from dual")
public int getInt() throws IOException, IllegalAccessError {
return 1/0;
}
public static @NotNull String getString(String a) {
return a;
}
List<T> list = new ArrayList<>();
public T getItemByIndex(@NonNull@NotEmpty Integer index) throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {
return list.get(index);
}
}
interface MethodTypeClass<T> {
default String getString() {
return "";
}
int getInt();
T getT();
}
System.out.printf("|%130s|%130s|%50s|%20s|%20s|%20s|%20s|%20s|%20s|%30s|%30s|%100s|%50s|%20s|%20s|%20s|%20s|%20s|%20s|%50s|%n",
"String", "GenericString", "DeclaringClass Name", "Modifiers", "ReturnType Name",
"AnnotatedReturnType Name", "GenericReturnType Name", "Name", "ParameterCount", "GenericParameterTypes Name",
"Parameters Name", "ParameterAnnotations Name", "ExceptionTypes Name", "isVarArgs", "getDefaultValue",
"isBridge", "isDefault", "isSynthetic", "isAccessible", "Annotations Name");
MethodClass<String> mc = new MethodClass<>();
Method[] methods = mc.getClass().getMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
System.out.printf("|%130s|%130s|%50s|%20s|%20s|%20s|%20s|%20s|%20s|%30s|%30s|%100s|%50s|%20s|%20s|%20s|%20s|%20s|%20s|%50s|%n",
method.toString(), method.toGenericString(), method.getDeclaringClass().getName(), method.getModifiers(),
method.getReturnType().getName(), method.getAnnotatedReturnType().getType().getTypeName(), method.getGenericReturnType().getTypeName(),
method.getName(), method.getParameterCount(),
method.getParameterCount() > 0 ? Arrays.toString(Arrays.stream(method.getGenericParameterTypes()).map(Type::getTypeName).toArray()) : null,
method.getParameterCount() > 0 ? Arrays.toString(Arrays.stream(method.getTypeParameters()).map(TypeVariable::getName).toArray()) : null,
method.getParameterCount() > 0 ? Arrays.toString(Arrays.stream(method.getParameterAnnotations()).map(annoy -> Arrays.toString(Arrays.stream(annoy).map(an -> an.annotationType().getName()).toArray()) ).toArray()) : null,
method.getExceptionTypes().length > 0 ? Arrays.toString(Arrays.stream(method.getExceptionTypes()).map(Class::getName).toArray()) : null,
method.isVarArgs(), method.getDefaultValue(), method.isBridge(), method.isDefault(), method.isSynthetic(), method.isAccessible(),
method.getAnnotations().length > 0 ? Arrays.toString(Arrays.stream(method.getAnnotations()).map(type -> type.annotationType().getName()).toArray()) : null);
}
methods = MethodTypeClass.class.getDeclaredMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
System.out.printf("|%130s|%130s|%50s|%20s|%20s|%20s|%20s|%20s|%20s|%30s|%30s|%100s|%50s|%20s|%20s|%20s|%20s|%20s|%20s|%50s|%n",
method.toString(), method.toGenericString(), method.getDeclaringClass().getName(), method.getModifiers(),
method.getReturnType().getName(), method.getAnnotatedReturnType().getType().getTypeName(), method.getGenericReturnType().getTypeName(),
method.getName(), method.getParameterCount(),
method.getParameterCount() > 0 ? Arrays.toString(Arrays.stream(method.getGenericParameterTypes()).map(Type::getTypeName).toArray()) : null,
method.getParameterCount() > 0 ? Arrays.toString(Arrays.stream(method.getTypeParameters()).map(TypeVariable::getName).toArray()) : null,
method.getParameterCount() > 0 ? Arrays.toString(Arrays.stream(method.getParameterAnnotations()).map(annoy -> Arrays.toString(Arrays.stream(annoy).map(an -> an.annotationType().getName()).toArray()) ).toArray()) : null,
method.getExceptionTypes().length > 0 ? Arrays.toString(Arrays.stream(method.getExceptionTypes()).map(Class::getName).toArray()) : null,
method.isVarArgs(), method.getDefaultValue(), method.isBridge(), method.isDefault(), method.isSynthetic(), method.isAccessible(),
method.getAnnotations().length > 0 ? Arrays.toString(Arrays.stream(method.getAnnotations()).map(type -> type.annotationType().getName()).toArray()) : null);
}
methods = CacheNamespace.class.getDeclaredMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
System.out.printf("|%130s|%130s|%50s|%20s|%20s|%20s|%20s|%20s|%20s|%30s|%30s|%100s|%50s|%20s|%20s|%20s|%20s|%20s|%20s|%50s|%n",
method.toString(), method.toGenericString(), method.getDeclaringClass().getName(), method.getModifiers(),
method.getReturnType().getName(), method.getAnnotatedReturnType().getType().getTypeName(), method.getGenericReturnType().getTypeName(),
method.getName(), method.getParameterCount(),
method.getParameterCount() > 0 ? Arrays.toString(Arrays.stream(method.getGenericParameterTypes()).map(Type::getTypeName).toArray()) : null,
method.getParameterCount() > 0 ? Arrays.toString(Arrays.stream(method.getTypeParameters()).map(TypeVariable::getName).toArray()) : null,
method.getParameterCount() > 0 ? Arrays.toString(Arrays.stream(method.getParameterAnnotations()).map(annoy -> Arrays.toString(Arrays.stream(annoy).map(an -> an.annotationType().getName()).toArray()) ).toArray()) : null,
method.getExceptionTypes().length > 0 ? Arrays.toString(Arrays.stream(method.getExceptionTypes()).map(Class::getName).toArray()) : null,
method.isVarArgs(), method.getDefaultValue(), method.isBridge(), method.isDefault(), method.isSynthetic(), method.isAccessible(),
method.getAnnotations().length > 0 ? Arrays.toString(Arrays.stream(method.getAnnotations()).map(type -> type.annotationType().getName()).toArray()) : null);
}
测试结果:
| String| GenericString| DeclaringClass Name| Modifiers| ReturnType Name| AnnotatedReturnType Name| GenericReturnType Name| Name| ParameterCount| GenericParameterTypes Name| Parameters Name| ParameterAnnotations Name| ExceptionTypes Name| isVarArgs| getDefaultValue| isBridge| isDefault| isSynthetic| isAccessible| Annotations Name|
| public int com.test.MethodClass.getInt() throws java.io.IOException,java.lang.IllegalAccessError| public int com.test.MethodClass.getInt() throws java.io.IOException,java.lang.IllegalAccessError| com.test.MethodClass| 1| int| int| int| getInt| 0| null| null| null|[java.io.IOException, java.lang.IllegalAccessError]| false| null| false| false| false| false| [org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select]|
| public static java.lang.String com.test.MethodClass.getString(java.lang.String)| public static java.lang.String com.test.MethodClass.getString(java.lang.String)| com.test.MethodClass| 9| java.lang.String| java.lang.String| java.lang.String| getString| 1| [java.lang.String]| []| [[]]| null| false| null| false| false| false| false| [javax.validation.constraints.NotNull]|
| public java.lang.Object com.test.MethodClass.getItemByIndex(java.lang.Integer) throws java.lang.IndexOutOfBoundsException| public T com.test.MethodClass.getItemByIndex(java.lang.Integer) throws java.lang.IndexOutOfBoundsException| com.test.MethodClass| 1| java.lang.Object| T| T| getItemByIndex| 1| [java.lang.Integer]| []| [[org.springframework.lang.NonNull, javax.validation.constraints.NotEmpty]]| [java.lang.IndexOutOfBoundsException]| false| null| false| false| false| false| null|
| public final void java.lang.Object.wait() throws java.lang.InterruptedException| public final void java.lang.Object.wait() throws java.lang.InterruptedException| java.lang.Object| 17| void| void| void| wait| 0| null| null| null| [java.lang.InterruptedException]| false| null| false| false| false| false| null|
| public final void java.lang.Object.wait(long,int) throws java.lang.InterruptedException| public final void java.lang.Object.wait(long,int) throws java.lang.InterruptedException| java.lang.Object| 17| void| void| void| wait| 2| [long, int]| []| [[], []]| [java.lang.InterruptedException]| false| null| false| false| false| false| null|
| public final native void java.lang.Object.wait(long) throws java.lang.InterruptedException| public final native void java.lang.Object.wait(long) throws java.lang.InterruptedException| java.lang.Object| 273| void| void| void| wait| 1| [long]| []| [[]]| [java.lang.InterruptedException]| false| null| false| false| false| false| null|
| public boolean java.lang.Object.equals(java.lang.Object)| public boolean java.lang.Object.equals(java.lang.Object)| java.lang.Object| 1| boolean| boolean| boolean| equals| 1| [java.lang.Object]| []| [[]]| null| false| null| false| false| false| false| null|
| public java.lang.String java.lang.Object.toString()| public java.lang.String java.lang.Object.toString()| java.lang.Object| 1| java.lang.String| java.lang.String| java.lang.String| toString| 0| null| null| null| null| false| null| false| false| false| false| null|
| public native int java.lang.Object.hashCode()| public native int java.lang.Object.hashCode()| java.lang.Object| 257| int| int| int| hashCode| 0| null| null| null| null| false| null| false| false| false| false| null|
| public final native java.lang.Class java.lang.Object.getClass()| public final native java.lang.Class<?> java.lang.Object.getClass()| java.lang.Object| 273| java.lang.Class| java.lang.Class<?>| java.lang.Class<?>| getClass| 0| null| null| null| null| false| null| false| false| false| false| null|
| public final native void java.lang.Object.notify()| public final native void java.lang.Object.notify()| java.lang.Object| 273| void| void| void| notify| 0| null| null| null| null| false| null| false| false| false| false| null|
| public final native void java.lang.Object.notifyAll()| public final native void java.lang.Object.notifyAll()| java.lang.Object| 273| void| void| void| notifyAll| 0| null| null| null| null| false| null| false| false| false| false| null|
| public abstract int com.test.MethodTypeClass.getInt()| public abstract int com.test.MethodTypeClass.getInt()| com.test.MethodTypeClass| 1025| int| int| int| getInt| 0| null| null| null| null| false| null| false| false| false| false| null|
| public default java.lang.String com.test.MethodTypeClass.getString()| public default java.lang.String com.test.MethodTypeClass.getString()| com.test.MethodTypeClass| 1| java.lang.String| java.lang.String| java.lang.String| getString| 0| null| null| null| null| false| null| false| true| false| false| null|
| public abstract java.lang.Object com.test.MethodTypeClass.getT()| public abstract T com.test.MethodTypeClass.getT()| com.test.MethodTypeClass| 1025| java.lang.Object| T| T| getT| 0| null| null| null| null| false| null| false| false| false| false| null|
| public abstract int org.apache.ibatis.annotations.CacheNamespace.size()| public abstract int org.apache.ibatis.annotations.CacheNamespace.size()| org.apache.ibatis.annotations.CacheNamespace| 1025| int| int| int| size| 0| null| null| null| null| false| 1024| false| false| false| false| null|
| public abstract org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Property[] org.apache.ibatis.annotations.CacheNamespace.properties()| public abstract org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Property[] org.apache.ibatis.annotations.CacheNamespace.properties()| org.apache.ibatis.annotations.CacheNamespace| 1025| [Lorg.apache.ibatis.annotations.Property;| org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Property[]| org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Property[]| properties| 0| null| null| null| null| false|[Lorg.apache.ibatis.annotations.Property;@3ab39c39| false| false| false| false| null|
| public abstract long org.apache.ibatis.annotations.CacheNamespace.flushInterval()| public abstract long org.apache.ibatis.annotations.CacheNamespace.flushInterval()| org.apache.ibatis.annotations.CacheNamespace| 1025| long| long| long| flushInterval| 0| null| null| null| null| false| 0| false| false| false| false| null|
| public abstract boolean org.apache.ibatis.annotations.CacheNamespace.blocking()| public abstract boolean org.apache.ibatis.annotations.CacheNamespace.blocking()| org.apache.ibatis.annotations.CacheNamespace| 1025| boolean| boolean| boolean| blocking| 0| null| null| null| null| false| false| false| false| false| false| null|
| public abstract boolean org.apache.ibatis.annotations.CacheNamespace.readWrite()| public abstract boolean org.apache.ibatis.annotations.CacheNamespace.readWrite()| org.apache.ibatis.annotations.CacheNamespace| 1025| boolean| boolean| boolean| readWrite| 0| null| null| null| null| false| true| false| false| false| false| null|
| public abstract java.lang.Class org.apache.ibatis.annotations.CacheNamespace.eviction()| public abstract java.lang.Class<? extends org.apache.ibatis.cache.Cache> org.apache.ibatis.annotations.CacheNamespace.eviction()| org.apache.ibatis.annotations.CacheNamespace| 1025| java.lang.Class| java.lang.Class<? extends org.apache.ibatis.cache.Cache>| java.lang.Class<? extends org.apache.ibatis.cache.Cache>| eviction| 0| null| null| null| null| false| class org.apache.ibatis.cache.decorators.LruCache| false| false| false| false| null|
| public abstract java.lang.Class org.apache.ibatis.annotations.CacheNamespace.implementation()| public abstract java.lang.Class<? extends org.apache.ibatis.cache.Cache> org.apache.ibatis.annotations.CacheNamespace.implementation()| org.apache.ibatis.annotations.CacheNamespace| 1025| java.lang.Class| java.lang.Class<? extends org.apache.ibatis.cache.Cache>| java.lang.Class<? extends org.apache.ibatis.cache.Cache>| implementation| 0| null| null| null| null| false| class org.apache.ibatis.cache.impl.PerpetualCache| false| false| false| false| null|
Constructor
Comment:提供关于类的单个构造函数的信息和访问权。
private Class<T> clazz;
private int slot;
private Class<?>[] parameterTypes;
private Class<?>[] exceptionTypes;
private int modifiers;
// 泛型和注释支持
private transient String signature;
// 泛型信息存储库;延迟初始化
private transient ConstructorRepository genericInfo;
private byte[] annotations;
private byte[] parameterAnnotations;
private volatile ConstructorAccessor constructorAccessor;
// 用于共享构造函数访问器。这个分支结构目前只有两层深度(即一个根构造函数和可能指向它的许多构造函数对象)。
// 如果这个分支结构包含循环,那么在annotation代码中就可能发生死锁。
private Constructor<T> root;
// 工厂的泛型基础架构访问器
private GenericsFactory getFactory() {
// create scope and factory
return CoreReflectionFactory.make(this, ConstructorScope.make(this));
}
// 泛型信息存储库的访问器
ConstructorRepository getGenericInfo() {
// lazily initialize repository if necessary
if (genericInfo == null) {
// create and cache generic info repository
genericInfo =
ConstructorRepository.make(getSignature(),
getFactory());
}
return genericInfo; //return cached repository
}
// 由Excecutable用于注释共享。
Executable getRoot() {
return root;
}
// 用于在Java代码中实例化这些对象的ReflectAccess使用的包私有构造函数,java.lang包通过sun.reflect.LangReflectAccess。
Constructor(Class<T> declaringClass, Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Class<?>[] checkedExceptions, int modifiers, int slot, String signature, byte[] annotations, byte[] parameterAnnotations) {
this.clazz = declaringClass;
this.parameterTypes = parameterTypes;
this.exceptionTypes = checkedExceptions;
this.modifiers = modifiers;
this.slot = slot;
this.signature = signature;
this.annotations = annotations;
this.parameterAnnotations = parameterAnnotations;
}
// 包私有例程(通过ReflectAccess向java.lang.Class公开)返回此构造函数的副本。副本的“root”字段指向这个构造函数。
Constructor<T> copy() {
// 这个例程允许在引用VM中相同基础方法的构造函数对象之间共享ConstructorAccessor对象。(所有这些扭曲都是必要的,因为AccessibleObject中的“可访问性”部分,它隐式地要求为对Class对象的每次反射调用制造新的java.lang.reflect对象。)
if (this.root != null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Can not copy a non-root Constructor");
Constructor<T> res = new Constructor<>(clazz,
parameterTypes,
exceptionTypes, modifiers, slot,
signature,
annotations,
parameterAnnotations);
res.root = this;
// Might as well eagerly propagate this if already present
res.constructorAccessor = constructorAccessor;
return res;
}
boolean hasGenericInformation() {
return (getSignature() != null);
}
byte[] getAnnotationBytes() {
return annotations;
}
public Class<T> getDeclaringClass() {
return clazz;
}
// 以字符串形式返回此构造函数的名称。这是构造函数声明类的二进制名称。
public String getName() {
return getDeclaringClass().getName();
}
public int getModifiers() {
return modifiers;
}
public TypeVariable<Constructor<T>>[] getTypeParameters() {
if (getSignature() != null) {
return (TypeVariable<Constructor<T>>[])getGenericInfo().getTypeParameters();
} else
return (TypeVariable<Constructor<T>>[])new TypeVariable[0];
}
public Class<?>[] getParameterTypes() {
return parameterTypes.clone();
}
public int getParameterCount() { return parameterTypes.length; }
public Type[] getGenericParameterTypes() {
return super.getGenericParameterTypes();
}
public Class<?>[] getExceptionTypes() {
return exceptionTypes.clone();
}
public Type[] getGenericExceptionTypes() {
return super.getGenericExceptionTypes();
}
// 比较指定对象的{@code Constructor}。如果两个对象相同,则返回true。两个{@code Constructor}对象如果由同一个类声明并且具有相同的形参类型,则它们是相同的。
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (obj != null && obj instanceof Constructor) {
Constructor<?> other = (Constructor<?>)obj;
if (getDeclaringClass() == other.getDeclaringClass()) {
return equalParamTypes(parameterTypes, other.parameterTypes);
}
}
return false;
}
// 返回这个{@code Constructor}的哈希代码。哈希代码与底层构造函数声明的类名的哈希代码相同。
public int hashCode() {
return getDeclaringClass().getName().hashCode();
}
// 返回一个描述这个{@code Constructor}的字符串。该字符串格式化为构造函数访问修饰符(如果有的话),后跟声明类的全限定名,再后跟带圆括号的、以逗号分隔的构造函数的形式形参类型列表。
// example: public java.util.Hashtable(int,float)
public String toString() {
return sharedToString(Modifier.constructorModifiers(),
false,
parameterTypes,
exceptionTypes);
}
void specificToStringHeader(StringBuilder sb) {
sb.append(getDeclaringClass().getTypeName());
}
// 返回一个描述这个{@code Constructor}的字符串,包括类型参数。该字符串格式化为:构造函数访问修饰符(如果有的话),后面接以尖括号逗号分隔的构造函数类型参数列表(如果有的话),后面接声明类的全限定名称,再接以圆括号逗号分隔的构造函数泛型形式参数类型列表。
public String toGenericString() {
return sharedToGenericString(Modifier.constructorModifiers(), false);
}
void specificToGenericStringHeader(StringBuilder sb) {
specificToStringHeader(sb);
}
// 使用这个{@code constructor}对象表示的构造函数,使用指定的初始化参数创建并初始化构造函数声明类的新实例。各个参数被自动取消包装以匹配原语形式参数,并且原语参数和引用参数都要根据需要进行方法调用转换。
public T newInstance(Object ... initargs) throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException,
IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException {
if (!override) {
if (!Reflection.quickCheckMemberAccess(clazz, modifiers)) {
Class<?> caller = Reflection.getCallerClass();
checkAccess(caller, clazz, null, modifiers);
}
}
if ((clazz.getModifiers() & Modifier.ENUM) != 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot reflectively create enum objects");
ConstructorAccessor ca = constructorAccessor; // read volatile
if (ca == null) {
ca = acquireConstructorAccessor();
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T inst = (T) ca.newInstance(initargs);
return inst;
}
public boolean isVarArgs() {
return super.isVarArgs();
}
public boolean isSynthetic() {
return super.isSynthetic();
}
// 注意,这里没有使用同步。为给定的构造函数生成多个ConstructorAccessor是正确的(尽管效率不高)。然而,避免同步可能会使实现更具可伸缩性。
private ConstructorAccessor acquireConstructorAccessor() {
// First check to see if one has been created yet, and take it if so.
ConstructorAccessor tmp = null;
if (root != null) tmp = root.getConstructorAccessor();
if (tmp != null) {
constructorAccessor = tmp;
} else {
// Otherwise fabricate one and propagate it up to the root
tmp = reflectionFactory.newConstructorAccessor(this);
setConstructorAccessor(tmp);
}
return tmp;
}
ConstructorAccessor getConstructorAccessor() {
return constructorAccessor;
}
// 为这个Constructor对象和(递归地)它的root设置ConstructorAccessor
void setConstructorAccessor(ConstructorAccessor accessor) {
constructorAccessor = accessor;
// Propagate up
if (root != null) {
root.setConstructorAccessor(accessor);
}
}
int getSlot() {
return slot;
}
String getSignature() {
return signature;
}
byte[] getRawAnnotations() {
return annotations;
}
byte[] getRawParameterAnnotations() {
return parameterAnnotations;
}
public <T extends Annotation> T getAnnotation(Class<T> annotationClass) {
return super.getAnnotation(annotationClass);
}
public Annotation[] getDeclaredAnnotations() {
return super.getDeclaredAnnotations();
}
public Annotation[][] getParameterAnnotations() {
return sharedGetParameterAnnotations(parameterTypes, parameterAnnotations);
}
void handleParameterNumberMismatch(int resultLength, int numParameters) {
Class<?> declaringClass = getDeclaringClass();
if (declaringClass.isEnum() ||
declaringClass.isAnonymousClass() ||
declaringClass.isLocalClass() )
return ; // Can't do reliable parameter counting
else {
if (!declaringClass.isMemberClass() || // top-level
// Check for the enclosing instance parameter for
// non-static member classes
(declaringClass.isMemberClass() &&
((declaringClass.getModifiers() & Modifier.STATIC) == 0) &&
resultLength + 1 != numParameters) ) {
throw new AnnotationFormatError(
"Parameter annotations don't match number of parameters");
}
}
}
public AnnotatedType getAnnotatedReturnType() {
return getAnnotatedReturnType0(getDeclaringClass());
}
public AnnotatedType getAnnotatedReceiverType() {
if (getDeclaringClass().getEnclosingClass() == null)
return super.getAnnotatedReceiverType();
return TypeAnnotationParser.buildAnnotatedType(getTypeAnnotationBytes0(),
sun.misc.SharedSecrets.getJavaLangAccess().
getConstantPool(getDeclaringClass()),
this,
getDeclaringClass(),
getDeclaringClass().getEnclosingClass(),
TypeAnnotation.TypeAnnotationTarget.METHOD_RECEIVER);
}
测试代码:
class ConstructClass<T> {
private T name;
private int age;
private ConstructClass() {}
public ConstructClass(@NonNull @NotEmpty T name, int age) throws Exception {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
ConstructClass<String> c = new ConstructClass<String>("", 1);
Constructor<?>[] constructors = ConstructClass.class.getDeclaredConstructors();
System.out.printf("|%80s|%80s|%20s|%30s|%30s|%20s|%30s|%30s|%30s|%20s|%80s|%20s|%n",
"String", "GenericString", "Modifiers", "Name", "DeclaringClass",
"ParameterCount", "ParameterTypes Name", "TypeParameters Name", "GenericParameterTypes Name",
"Parameters Name", "ParameterAnnotations Name", "ExceptionTypes Name");
for (Constructor<?> constructor : constructors) {
System.out.printf("|%80s|%80s|%20s|%30s|%30s|%20s|%30s|%30s|%30s|%20s|%80s|%20s|%n",
constructor.toString(), constructor.toGenericString(),
constructor.getModifiers(), constructor.getName(), constructor.getDeclaringClass(),
constructor.getParameterCount(),
constructor.getParameterCount() > 0 ? Arrays.toString(Arrays.stream(constructor.getParameterTypes()).map(Class::getName).toArray()) : null,
constructor.getParameterCount() > 0 ? Arrays.toString(Arrays.stream(constructor.getTypeParameters()).map(TypeVariable::getName).toArray()) : null,
constructor.getParameterCount() > 0 ? Arrays.toString(Arrays.stream(constructor.getGenericParameterTypes()).map(Type::getTypeName).toArray()) : null,
constructor.getParameterCount() > 0 ? Arrays.toString(Arrays.stream(constructor.getParameters()).map(Parameter::getName).toArray()) : null,
constructor.getParameterCount() > 0 ? Arrays.toString(Arrays.stream(constructor.getParameterAnnotations()).map(annos -> Arrays.toString(Arrays.stream(annos).map(anno -> anno.annotationType().getName()).toArray()) ).toArray()) : null,
constructor.getExceptionTypes().length > 0 ? Arrays.toString(Arrays.stream(constructor.getExceptionTypes()).map(Type::getTypeName).toArray()) : null
);
}
测试结果:
| String| GenericString| Modifiers| Name| DeclaringClass| ParameterCount| ParameterTypes Name| TypeParameters Name| GenericParameterTypes Name| Parameters Name| ParameterAnnotations Name| ExceptionTypes Name|
| private com.test.ConstructClass()| private com.test.ConstructClass()| 2| com.test.ConstructClass| class com.test.ConstructClass| 0| null| null| null| null| null| null|
| public com.test.ConstructClass(java.lang.Object,int) throws java.lang.Exception| public com.test.ConstructClass(T,int) throws java.lang.Exception| 1| com.test.ConstructClass| class com.test.ConstructClass| 2| [java.lang.Object, int]| []| [T, int]| [name, age]| [[org.springframework.lang.NonNull, javax.validation.constraints.NotEmpty], []]|[java.lang.Exception]|
Parameter
@Since:1.8
Comment:方法参数信息。一个{@code Parameter}提供了关于方法参数的信息,包括它的名称和修饰符。它还提供了另一种获取参数属性的方法。
private final String name;
private final int modifiers;
private final Executable executable;
private final int index;
private transient volatile Type parameterTypeCache = null;
private transient volatile Class<?> parameterClassCache = null;
private transient Map<Class<? extends Annotation>, Annotation> declaredAnnotations;
// {@code Parameter}的包私有构造函数。如果方法参数数据存在于类文件中,则JVM直接创建{@code parameter}对象。如果没有,那么{@code Executable}使用这个构造函数来合成它们。
Parameter(String name, int modifiers, Executable executable, int index) {
this.name = name;
this.modifiers = modifiers;
this.executable = executable;
this.index = index;
}
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if(obj instanceof Parameter) {
Parameter other = (Parameter)obj;
return (other.executable.equals(executable) &&
other.index == index);
}
return false;
}
public int hashCode() {
return executable.hashCode() ^ index;
}
// 如果参数根据类文件有名称,则返回true;否则返回false。参数是否有名称是由声明参数的方法的{@literal MethodParameters}属性决定的。
public boolean isNamePresent() {
return executable.hasRealParameterData() && name != null;
}
// 返回描述此参数的字符串。格式是参数的修饰符(如果有的话),按照Java语言规范,后面是参数的完全限定类型(如果参数是可变的,不包括最后一个[]),如果参数是可变的,后面是"…",后面是一个空格,然后是参数的名称。
public String toString() {
final StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
final Type type = getParameterizedType();
final String typename = type.getTypeName();
sb.append(Modifier.toString(getModifiers()));
if(0 != modifiers)
sb.append(' ');
if(isVarArgs())
sb.append(typename.replaceFirst("\[\]$", "..."));
else
sb.append(typename);
sb.append(' ');
sb.append(getName());
return sb.toString();
}
// 返回声明该参数的{@code Executable}。
public Executable getDeclaringExecutable() {
return executable;
}
// 获取由{@code parameter}对象表示的参数的修饰符标志。
public int getModifiers() {
return modifiers;
}
// 返回参数的名称。如果参数的名称是{@linkplain #isNamePresent() present},那么这个方法将返回类文件提供的名称。否则,该方法将合成一个形式为argN的名称,其中N是声明参数的方法的描述符中参数的索引。
public String getName() {
// 注意:空字符串作为参数名现在是非法的。.equals("")是为了兼容当前的JVM行为。它可能在某个时候被移除。
if(name == null || name.equals(""))
return "arg" + index;
else
return name;
}
// real name字段的包私有访问器。
String getRealName() {
return name;
}
// 返回一个{@code Type}对象,该对象标识由{@code parameter}对象表示的参数的参数化类型。
public Type getParameterizedType() {
Type tmp = parameterTypeCache;
if (null == tmp) {
tmp = executable.getAllGenericParameterTypes()[index];
parameterTypeCache = tmp;
}
return tmp;
}
// 返回一个{@code Class}对象,该对象标识由{@code parameter}对象表示的参数声明的类型。
public Class<?> getType() {
Class<?> tmp = parameterClassCache;
if (null == tmp) {
tmp = executable.getParameterTypes()[index];
parameterClassCache = tmp;
}
return tmp;
}
// 返回一个AnnotatedType对象,该对象表示使用类型来指定由该参数表示的形式参数的类型。
public AnnotatedType getAnnotatedType() {
// 暂时没有缓存
return executable.getAnnotatedParameterTypes()[index];
}
// 如果该参数在源代码中隐式声明,则返回{@code true};否则返回{@code false}。
public boolean isImplicit() {
return Modifier.isMandated(getModifiers());
}
// 如果该参数在源代码中没有显式或隐式声明,则返回{@code true};否则返回{@code false}。
public boolean isSynthetic() {
return Modifier.isSynthetic(getModifiers());
}
// 如果该参数表示一个变量参数列表,则返回{@code true};否则返回{@code false}。
public boolean isVarArgs() {
return executable.isVarArgs() &&
index == executable.getParameterCount() - 1;
}
public <T extends Annotation> T getAnnotation(Class<T> annotationClass) {
Objects.requireNonNull(annotationClass);
return annotationClass.cast(declaredAnnotations().get(annotationClass));
}
public <T extends Annotation> T[] getAnnotationsByType(Class<T> annotationClass) {
Objects.requireNonNull(annotationClass);
return AnnotationSupport.getDirectlyAndIndirectlyPresent(declaredAnnotations(), annotationClass);
}
public Annotation[] getDeclaredAnnotations() {
return executable.getParameterAnnotations()[index];
}
public <T extends Annotation> T getDeclaredAnnotation(Class<T> annotationClass) {
// Only annotations on classes are inherited, for all other
// objects getDeclaredAnnotation is the same as
// getAnnotation.
return getAnnotation(annotationClass);
}
public <T extends Annotation> T[] getDeclaredAnnotationsByType(Class<T> annotationClass) {
// Only annotations on classes are inherited, for all other
// objects getDeclaredAnnotations is the same as
// getAnnotations.
return getAnnotationsByType(annotationClass);
}
public Annotation[] getAnnotations() {
return getDeclaredAnnotations();
}
private synchronized Map<Class<? extends Annotation>, Annotation> declaredAnnotations() {
if(null == declaredAnnotations) {
declaredAnnotations =
new HashMap<Class<? extends Annotation>, Annotation>();
Annotation[] ann = getDeclaredAnnotations();
for(int i = 0; i < ann.length; i++)
declaredAnnotations.put(ann[i].annotationType(), ann[i]);
}
return declaredAnnotations;
}
测试代码:
interface PTest{
String getXXX(@NotNull@NotEmpty String name, int[] a, Object... args);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Method[] declaredMethods = PTest.class.getDeclaredMethods();
System.out.printf("|%30s|%20s|%20s|%20s|%20s|%80s|%30s|%20s|%20s|%20s|%20s|%20s|%n",
"String", "Modifiers", "Modifiers String", "Name",
"Type Name", "Annotations Name", "DeclaringExecutable Name", "ParameterizedType Name",
"isSynthetic", "isVarArgs", "isImplicit", "isNamePresent");
for (Method declaredMethod : declaredMethods) {
Parameter[] parameters = declaredMethod.getParameters();
for (Parameter parameter : parameters) {
System.out.printf("|%30s|%20s|%20s|%20s|%20s|%80s|%30s|%20s|%20s|%20s|%20s|%20s|%n",
parameter.toString(), parameter.getModifiers(), Modifier.toString(parameter.getModifiers()),
parameter.getName(), parameter.getType().getName(),
parameter.getAnnotations().length > 0 ? Arrays.toString(Arrays.stream(parameter.getAnnotations()).map(anno -> anno.annotationType().getName()).toArray()) : "",
parameter.getDeclaringExecutable().getName(), parameter.getParameterizedType().getTypeName(), parameter.isSynthetic(),
parameter.isVarArgs(), parameter.isImplicit(), parameter.isNamePresent());
}
}
}
测试结果:
| String| Modifiers| Modifiers String| Name| Type Name| Annotations Name| DeclaringExecutable Name|ParameterizedType Name| isSynthetic| isVarArgs| isImplicit| isNamePresent|
| java.lang.String name| 0| | name| java.lang.String| [javax.validation.constraints.NotNull, javax.validation.constraints.NotEmpty]| getXXX| java.lang.String| false| false| false| true|
| int[] a| 0| | a| [I| | getXXX| int[]| false| false| false| true|
| java.lang.Object... args| 0| | args| [Ljava.lang.Object;| | getXXX| java.lang.Object[]| false| true| false| true|
Array
Comment:类提供动态创建和访问Java数组的静态方法。
private Array() {}
// 使用指定的组件类型和长度创建新数组。
// 新数组的维数不能超过255。
public static Object newInstance(Class<?> componentType, int length) throws NegativeArraySizeException {
return newArray(componentType, length);
}
// 使用指定的组件类型和维度创建新数组。
// 如果{@code componentType}表示一个非数组类或接口,则新数组有{@code dimensions.length}维度和{@code componentType}作为组件类型。如果{@code componentType}表示一个数组类,则新数组的维数等于{@code dimensions.length}和{@code componentType}的维度数。在这种情况下,新数组的组件类型是{@code componentType}的组件类型。
// 新数组的维数不能超过255。
public static Object newInstance(Class<?> componentType, int... dimensions) throws IllegalArgumentException, NegativeArraySizeException {
return multiNewArray(componentType, dimensions);
}
// 返回指定数组对象的长度,作为{@code int}。
public static native int getLength(Object array) throws IllegalArgumentException;
// 返回指定数组对象中已索引组件的值。如果该值具有基元类型,则该值自动包装在对象中。
public static native Object get(Object array, int index) throwsIllegalArgumentException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException;
public static native boolean getBoolean(Object array, int index) throwsIllegalArgumentException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException;
public static native byte getByte(Object array, int index) throwsIllegalArgumentException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException;
public static native char getChar(Object array, int index) throwsIllegalArgumentException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException;
public static native short getShort(Object array, int index) throwsIllegalArgumentException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException;
public static native int getInt(Object array, int index) throwsIllegalArgumentException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException;
public static native long getLong(Object array, int index) throwsIllegalArgumentException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException;
public static native float getFloat(Object array, int index) throwsIllegalArgumentException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException;
public static native double getDouble(Object array, int index) throwsIllegalArgumentException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException;
// 将指定数组对象的索引组件的值设置为指定的新值。如果数组具有基元组件类型,新值首先会自动取消包装。
public static native void set(Object array, int index, Object value) throwsIllegalArgumentException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException;
public static native void setBoolean(Object array, int index, boolean z) throwsIllegalArgumentException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException;
public static native void setByte(Object array, int index, byte b) throwsIllegalArgumentException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException;
public static native void setChar(Object array, int index, char c) throwsIllegalArgumentException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException;
public static native void setShort(Object array, int index, short s) throwsIllegalArgumentException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException;
public static native void setInt(Object array, int index, int i) throwsIllegalArgumentException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException;
public static native void setLong(Object array, int index, long l) throwsIllegalArgumentException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException;
public static native void setFloat(Object array, int index, float f) throwsIllegalArgumentException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException;
public static native void setDouble(Object array, int index, double d) throwsIllegalArgumentException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException;
private static native Object newArray(Class<?> componentType, int length) throwsNegativeArraySizeException;
private static native Object multiNewArray(Class<?> componentType,
int[] dimensions) throwsIllegalArgumentException, NegativeArraySizeException;
InvocationHandler
@Since:1.3
Comment:{@code InvocationHandler}是由代理实例的调用处理程序实现的接口。每个代理实例都有一个关联的调用处理程序。当在代理实例上调用方法时,方法调用将被编码并分派给其调用处理程序的{@code invoke}方法。
/**
* 处理代理实例上的方法调用并返回结果。当在与方法关联的代理实例上调用方法时,将在调用处理程序上调用此方法。
*
* @param proxy 调用方法的代理实例
* @param method {@code Method}实例对应于代理实例上调用的接口方法。{@code Method}对象的声明类将是该方法声明所在的接口,该接口可能是代理类继承该方法的代理接口的超接口。
* @param args 一个对象数组,包含在代理实例上的方法调用中传递的参数值,如果接口方法不带参数,则为{@code null}。原始类型的参数被包装在适当的原始包装类的实例中,例如{@code java.lang.Integer}或{@code java.lang.Boolean}。
* @return 从代理实例上的方法调用返回的值。如果接口方法声明的返回类型是基元类型,那么该方法返回的值必须是相应基元包装类的实例;否则,它必须是可分配给声明的返回类型的类型。如果该方法返回的值是{@code null},并且接口方法的返回类型是原始类型,那么代理实例上的方法调用将抛出{@code NullPointerException}。如果该方法返回的值与上述接口方法声明的返回类型不兼容,则代理实例上的方法调用将抛出{@code ClassCastException}。
*/
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable;
Proxy
@Since:1.3
Comment:{@code Proxy}提供了创建动态代理类和实例的静态方法,它也是这些方法创建的所有动态代理类的超类。
动态代理类 (以下简称为代理类 )是一个实现在类创建时在运行时指定的接口列表的类,具有如下所述的行为。代理接口是由代理类实现的接口。代理实例是代理类的一个实例。每个代理实例都有一个关联的调用处理程序对象,它实现了接口InvocationHandler 。通过其代理接口之一的代理实例上的方法调用将被分派到实例调用处理程序的invoke方法,传递代理实例, java.lang.reflect.Method被调用方法的java.lang.reflect.Method对象以及包含参数的类型Object Object的数组。调用处理程序适当地处理编码方法调用,并且返回的结果将作为方法在代理实例上调用的结果返回。
代理实例具有以下属性
-
每个代理实例都有一个关联的调用处理程序,它被传递给它的构造函数。 静态
Proxy.getInvocationHandler方法将返回与作为其参数传递的代理实例关联的调用处理程序 -
代理实例上的接口方法调用将被编码并分派到调用处理程序的
invoke方法
当代理类的两个或多个接口包含具有相同名称和参数签名的方法时,代理类接口的顺序就变得很重要。当在代理实例上调用这样的重复方法时,传递给调用处理程序的{@code method}对象不一定是其声明类可以从调用代理方法所通过的接口的引用类型中分配的对象。之所以存在这种限制,是因为生成的代理类中的相应方法实现无法确定通过哪个接口调用它。因此,当在代理实例上调用一个重复的方法时,代理类的接口列表中包含该方法(直接或通过超接口继承)的最前面接口中的方法的{@code method}对象将被传递给调用处理程序的{@code invoke}方法,而不管方法调用是通过什么引用类型发生的。
还要注意的是,当一个重复的方法被分配给调用处理程序时,{@code invoke}方法只能抛出可分配给该方法的{@code throws}子句中的一个异常类型的检查异常类型,该异常类型可以通过所有代理接口调用。如果{@code invoke}方法抛出一个检查过的异常,该异常不能分配给该方法在可以调用它的代理接口中声明的任何异常类型,那么代理实例上的调用将抛出一个未检查的{@code UndeclaredThrowableException}。这个限制意味着对传递给{@code invoke}方法的{@code Method}对象调用{@code getExceptionTypes}返回的所有异常类型都不一定能被{@code invoke}方法成功抛出。
private Proxy() {}
// 从子类(通常是动态代理类)构造一个新的{@code Proxy}实例,并为其调用处理程序指定值。
protected Proxy(InvocationHandler h) {
Objects.requireNonNull(h);
this.h = h;
}
// 代理类构造函数的参数类型
private static final Class<?>[] constructorParams = { InvocationHandler.class };
// 代理类的缓存
private static final WeakCache<ClassLoader, Class<?>[], Class<?>> proxyClassCache = new WeakCache<>(new KeyFactory(), new ProxyClassFactory());
// 用于具有0个实现接口的代理类的键
private static final Object key0 = new Object();
// 此代理实例的调用处理程序。
protected InvocationHandler h;
// 返回代理类的{@code java.lang.Class}对象,给定一个类加载器和一个接口数组。代理类将由指定的类装入器定义,并将实现所有提供的接口。如果任何给定的接口是非公共的,则代理类将是非公共的。如果类装入器已经为相同的接口排列定义了一个代理类,那么将返回现有的代理类;否则,将动态生成这些接口的代理类,并由类装入器定义。
// interfaces数组中的所有类对象都必须表示接口,而不是类或原始类型。
// interfaces数组中没有两个元素可能是指相同的类对象。
// 所有的接口类型必须通过指定的类加载器的名称可见。 换句话说,对于类加载器cl和每个接口i ,以下表达式必须为真:
// Class.forName(i.getName(), false, cl) == i 所有非公共接口必须在同一个包中; 否则代理类将不可能实现所有接口,而不管其中定义了什么包。
// 对于具有相同签名的指定接口的任何成员方法集合:
// 如果任何方法的返回类型是原始类型或void,则所有方法必须具有相同的返回类型。
// 否则,其中一个方法必须具有一个返回类型,该类型可以分配给其余方法的所有返回类型。
// 生成的代理类不能超过虚拟机对类施加的任何限制。 例如,VM可以将类可以实现的接口数量限制为65535; 在这种情况下, interfaces阵列的大小不得超过65535。
// 请注意,指定的代理接口的顺序是重要的:具有相同组合的接口但不同顺序的代理类的两个请求将导致两个不同的代理类
public static Class<?> getProxyClass(ClassLoader loader, Class<?>... interfaces) throws IllegalArgumentException {
final Class<?>[] intfs = interfaces.clone();
final SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager();
if (sm != null) {
checkProxyAccess(Reflection.getCallerClass(), loader, intfs);
}
return getProxyClass0(loader, intfs);
}
// 检查创建代理类所需的权限。
private static void checkProxyAccess(Class<?> caller, ClassLoader loader, Class<?>... interfaces) {
SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager();
if (sm != null) {
ClassLoader ccl = caller.getClassLoader();
if (VM.isSystemDomainLoader(loader) && !VM.isSystemDomainLoader(ccl)) {
sm.checkPermission(SecurityConstants.GET_CLASSLOADER_PERMISSION);
}
ReflectUtil.checkProxyPackageAccess(ccl, interfaces);
}
}
// 生成一个代理类。在调用这个之前必须调用checkProxyAccess方法来执行权限检查。
private static Class<?> getProxyClass0(ClassLoader loader, Class<?>... interfaces) {
if (interfaces.length > 65535) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("interface limit exceeded");
}
// 如果实现给定接口的给定加载器定义的代理类存在,这将简单地返回缓存的副本;否则,它将通过ProxyClassFactory创建代理类
return proxyClassCache.get(loader, interfaces);
}
// Key1和Key2针对实现1个或2个接口的动态代理的常见使用进行了优化。
// 用于具有1个实现接口的代理类的键
private static final class Key1 extends WeakReference<Class<?>> {
private final int hash;
Key1(Class<?> intf) {
super(intf);
this.hash = intf.hashCode();
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return hash;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
Class<?> intf;
return this == obj ||
obj != null &&
obj.getClass() == Key1.class &&
(intf = get()) != null &&
intf == ((Key1) obj).get();
}
}
// 用于具有2个实现接口的代理类的键
private static final class Key2 extends WeakReference<Class<?>> {
private final int hash;
private final WeakReference<Class<?>> ref2;
Key2(Class<?> intf1, Class<?> intf2) {
super(intf1);
hash = 31 * intf1.hashCode() + intf2.hashCode();
ref2 = new WeakReference<Class<?>>(intf2);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return hash;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
Class<?> intf1, intf2;
return this == obj ||
obj != null &&
obj.getClass() == Key2.class &&
(intf1 = get()) != null &&
intf1 == ((Key2) obj).get() &&
(intf2 = ref2.get()) != null &&
intf2 == ((Key2) obj).ref2.get();
}
}
// 用于实现任意数量接口的代理类的键(这里只用于3个或更多接口)
private static final class KeyX {
private final int hash;
private final WeakReference<Class<?>>[] refs;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
KeyX(Class<?>[] interfaces) {
hash = Arrays.hashCode(interfaces);
refs = (WeakReference<Class<?>>[])new WeakReference<?>[interfaces.length];
for (int i = 0; i < interfaces.length; i++) {
refs[i] = new WeakReference<>(interfaces[i]);
}
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return hash;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
return this == obj ||
obj != null &&
obj.getClass() == KeyX.class &&
equals(refs, ((KeyX) obj).refs);
}
private static boolean equals(WeakReference<Class<?>>[] refs1,
WeakReference<Class<?>>[] refs2) {
if (refs1.length != refs2.length) {
return false;
}
for (int i = 0; i < refs1.length; i++) {
Class<?> intf = refs1[i].get();
if (intf == null || intf != refs2[i].get()) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
// 将接口数组映射到最优键的函数,其中表示接口的Class对象被弱引用。
private static final class KeyFactory implements BiFunction<ClassLoader, Class<?>[], Object> {
@Override
public Object apply(ClassLoader classLoader, Class<?>[] interfaces) {
switch (interfaces.length) {
case 1: return new Key1(interfaces[0]); // the most frequent
case 2: return new Key2(interfaces[0], interfaces[1]);
case 0: return key0;
default: return new KeyX(interfaces);
}
}
}
// 一个工厂函数,给定ClassLoader和接口数组,生成、定义和返回代理类。
private static final class ProxyClassFactory implements BiFunction<ClassLoader, Class<?>[], Class<?>> {
// 所有代理类名的前缀
private static final String proxyClassNamePrefix = "$Proxy";
// 用于生成唯一代理类名的下一个数字
private static final AtomicLong nextUniqueNumber = new AtomicLong();
@Override
public Class<?> apply(ClassLoader loader, Class<?>[] interfaces) {
// IdentityHashMap: 构造一个具有指定的预期最大大小的新空映射。将超过预期数量的键值映射放入映射中可能会导致内部数据结构增长,这可能会有些耗时
Map<Class<?>, Boolean> interfaceSet = new IdentityHashMap<>(interfaces.length);
// 检查接口能否加载及是否重复
for (Class<?> intf : interfaces) {
// 验证类装入器将此接口的名称解析为相同的class对象。
Class<?> interfaceClass = null;
try {
interfaceClass = Class.forName(intf.getName(), false, loader);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
}
if (interfaceClass != intf) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(intf + " is not visible from class loader");
}
// 验证Class对象实际上表示了一个接口。
if (!interfaceClass.isInterface()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(interfaceClass.getName() + " is not an interface");
}
// 确认该接口不是重复的。
if (interfaceSet.put(interfaceClass, Boolean.TRUE) != null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("repeated interface: " + interfaceClass.getName());
}
}
String proxyPkg = null; // 包中定义代理类
int accessFlags = Modifier.PUBLIC | Modifier.FINAL;
// 检查非public接口,是否处于同一个包
// 记录非公共代理接口的包,以便在同一个包中定义代理类。验证所有非公共代理接口都在同一个包中。
for (Class<?> intf : interfaces) {
int flags = intf.getModifiers();
if (!Modifier.isPublic(flags)) {
accessFlags = Modifier.FINAL;
String name = intf.getName();
int n = name.lastIndexOf('.');
String pkg = ((n == -1) ? "" : name.substring(0, n + 1));
if (proxyPkg == null) {
proxyPkg = pkg;
} else if (!pkg.equals(proxyPkg)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("non-public interfaces from different packages");
}
}
}
if (proxyPkg == null) {
// 如果没有非公共代理接口,请使用com.sun.proxy包
proxyPkg = ReflectUtil.PROXY_PACKAGE + ".";
}
// 选择要生成的代理类的名称。
long num = nextUniqueNumber.getAndIncrement();
// 默认:com.sun.proxy.$Proxy0
String proxyName = proxyPkg + proxyClassNamePrefix + num;
// 生成指定的代理类。
// proxyName—代理类的类名
// interfaces——代理接口
// accessFlags—代理类的访问标志
byte[] proxyClassFile = ProxyGenerator.generateProxyClass(proxyName, interfaces, accessFlags);
try {
return defineClass0(loader, proxyName, proxyClassFile, 0, proxyClassFile.length);
} catch (ClassFormatError e) {
// 这里的ClassFormatError意味着(排除代理类生成代码中的错误)提供给代理类创建的参数存在其他无效方面(比如超出了虚拟机限制)。
throw new IllegalArgumentException(e.toString());
}
}
}
private static native Class<?> defineClass0(ClassLoader loader, String name, byte[] b, int off, int len);
// 返回指定接口的代理类实例,该接口将方法调用分派给指定的调用处理程序。
public static Object newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader, Class<?>[] interfaces, InvocationHandler h) throws IllegalArgumentException {
Objects.requireNonNull(h);
final Class<?>[] intfs = interfaces.clone();
final SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager();
if (sm != null) {
checkProxyAccess(Reflection.getCallerClass(), loader, intfs);
}
// 查找或生成指定的代理类。
Class<?> cl = getProxyClass0(loader, intfs);
// 使用指定的调用处理程序调用其构造函数。
try {
if (sm != null) {
checkNewProxyPermission(Reflection.getCallerClass(), cl);
}
final Constructor<?> cons = cl.getConstructor(constructorParams);
final InvocationHandler ih = h;
if (!Modifier.isPublic(cl.getModifiers())) {
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Void>() {
public Void run() {
cons.setAccessible(true);
return null;
}
});
}
return cons.newInstance(new Object[]{h});
} catch (IllegalAccessException|InstantiationException e) {
throw new InternalError(e.toString(), e);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
Throwable t = e.getCause();
if (t instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) t;
} else {
throw new InternalError(t.toString(), t);
}
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new InternalError(e.toString(), e);
}
}
private static void checkNewProxyPermission(Class<?> caller, Class<?> proxyClass) {
SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager();
if (sm != null) {
if (ReflectUtil.isNonPublicProxyClass(proxyClass)) {
ClassLoader ccl = caller.getClassLoader();
ClassLoader pcl = proxyClass.getClassLoader();
// 如果调用者在代理类的不同运行时包中,是否进行权限检查
int n = proxyClass.getName().lastIndexOf('.');
String pkg = (n == -1) ? "" : proxyClass.getName().substring(0, n);
n = caller.getName().lastIndexOf('.');
String callerPkg = (n == -1) ? "" : caller.getName().substring(0, n);
if (pcl != ccl || !pkg.equals(callerPkg)) {
sm.checkPermission(new ReflectPermission("newProxyInPackage." + pkg));
}
}
}
}
// 当且仅当指定的类使用{@code getProxyClass}方法或{@code newProxyInstance}方法动态生成为代理类时,返回true。
public static boolean isProxyClass(Class<?> cl) {
return Proxy.class.isAssignableFrom(cl) && proxyClassCache.containsValue(cl);
}
// 返回指定代理实例的调用处理程序。
public static InvocationHandler getInvocationHandler(Object proxy) throws IllegalArgumentException {
// 验证对象实际上是一个代理实例。
if (!isProxyClass(proxy.getClass())) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("not a proxy instance");
}
final Proxy p = (Proxy) proxy;
final InvocationHandler ih = p.h;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
Class<?> ihClass = ih.getClass();
Class<?> caller = Reflection.getCallerClass();
if (ReflectUtil.needsPackageAccessCheck(caller.getClassLoader(),
ihClass.getClassLoader()))
{
ReflectUtil.checkPackageAccess(ihClass);
}
}
return ih;
}
WeakCache
Comment:缓存映射对{@code (key, sub-key) -> value}。键和值是弱引用的,但子键是强引用的。键被直接传递给{@link #get}方法,该方法也接受{@code parameter}。使用传递给构造函数的{@code subKeyFactory}函数从键和参数计算子键。使用传递给构造函数的{@code valueFactory}函数从键和参数计算值。键可以是{@code null}并通过标识进行比较,而{@code subKeyFactory}返回的子键或{@code valueFactory}返回的值不能为空。子键使用它们的{@link #equals}方法进行比较。每次调用{@link #get}、{@link #containsValue}或{@link #size}方法时,当对键的WeakReferences被清除时,缓存中的条目都会被惰性地删除。清除对单个值的弱引用不会导致删除,但这样的条目在逻辑上被视为不存在,并在请求它们的key/subKey时触发{@code valueFactory}的重新计算。
// 引用对了,用于清理map和reverseMap中的数据
private final ReferenceQueue<K> refQueue = new ReferenceQueue<>();
// 键类型为Object,用于支持空键
// <WeakCache.CacheKey(ClassLoad,ReferenceQueue), <Proxy.KeyX(Key1,Key2), Class(Proxy.ProxyClassFactory.apply生成)>>
private final ConcurrentMap<Object, ConcurrentMap<Object, Supplier<V>>> map = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
// <WeakCache.Value(Class(Proxy.ProxyClassFactory.apply生成)), Boolean>
private final ConcurrentMap<Supplier<V>, Boolean> reverseMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
// Proxy.KeyFactory
private final BiFunction<K, P, ?> subKeyFactory;
// Proxy.ProxyClassFactory
private final BiFunction<K, P, V> valueFactory;
public WeakCache(BiFunction<K, P, ?> subKeyFactory, BiFunction<K, P, V> valueFactory) {
this.subKeyFactory = Objects.requireNonNull(subKeyFactory);
this.valueFactory = Objects.requireNonNull(valueFactory);
}
// 通过缓存查找值。它总是计算{@code subKeyFactory}函数,如果给定的(key, subKey)对缓存中没有条目,或者条目已经被清除,则可以选择计算{@code valueFactory}函数。
public V get(K key, P parameter) {
Objects.requireNonNull(parameter);
// 清理过期缓存
expungeStaleEntries();
// 返回CacheKey对象
Object cacheKey = CacheKey.valueOf(key, refQueue);
// 惰性地为特定cacheKey安装第二级valuesMap
ConcurrentMap<Object, Supplier<V>> valuesMap = map.get(cacheKey);
if (valuesMap == null) {
ConcurrentMap<Object, Supplier<V>> oldValuesMap
= map.putIfAbsent(cacheKey,
valuesMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>());
if (oldValuesMap != null) {
valuesMap = oldValuesMap;
}
}
// 创建子键并检索可能的Supplier<V>由valuesMap中的子键存储。实际返回Key1、Key2或KeyX对象
Object subKey = Objects.requireNonNull(subKeyFactory.apply(key, parameter));
Supplier<V> supplier = valuesMap.get(subKey);
Factory factory = null;
while (true) {
if (supplier != null) {
// supplier可以是Factory或者CacheValue<V>实例
V value = supplier.get();
if (value != null) {
return value;
}
}
// 否则缓存中没有供应商或供应商返回null(可能是一个清除的CacheValue或一个没有成功安装CacheValue的工厂)
// 懒惰地构建一个Factory
if (factory == null) {
factory = new Factory(key, parameter, subKey, valuesMap);
}
if (supplier == null) {
supplier = valuesMap.putIfAbsent(subKey, factory);
if (supplier == null) {
// 成功安装的factory
supplier = factory;
}
// 否则请与获胜的supplier重试
} else {
if (valuesMap.replace(subKey, supplier, factory)) {
// 成功地将清除的CacheEntry /不成功的Factory替换为我们的Factory
supplier = factory;
} else {
// 重试当前supplier
supplier = valuesMap.get(subKey);
}
}
}
}
// 检查指定的非空值是否已经存在于这个{@code WeakCache}中。检查使用身份比较不管值的类是否重写{@link Object#equals}。
public boolean containsValue(V value) {
Objects.requireNonNull(value);
expungeStaleEntries();
return reverseMap.containsKey(new LookupValue<>(value));
}
private void expungeStaleEntries() {
CacheKey<K> cacheKey;
while ((cacheKey = (CacheKey<K>)refQueue.poll()) != null) {
cacheKey.expungeFrom(map, reverseMap);
}
}
// 返回当前缓存条目的数量,当键/值被GC-ed时,缓存条目的数量会随着时间的推移而减少。
public int size() {
expungeStaleEntries();
return reverseMap.size();
}
// 一个工厂{@link Supplier},它实现了该值的延迟同步构造,并将其安装到缓存中。
private final class Factory implements Supplier<V> {
private final K key;
private final P parameter;
private final Object subKey;
private final ConcurrentMap<Object, Supplier<V>> valuesMap;
Factory(K key, P parameter, Object subKey, ConcurrentMap<Object, Supplier<V>> valuesMap) {
this.key = key;
this.parameter = parameter;
this.subKey = subKey;
this.valuesMap = valuesMap;
}
@Override
public synchronized V get() { // 序列化的访问
// 重新审视
Supplier<V> supplier = valuesMap.get(subKey);
if (supplier != this) {
// 当我们等待的时候发生了一些变化:可能是我们被CacheValue替换了,或者因为失败而被删除了-> 返回null来通知WeakCache.get()重试循环
return null;
}
// else still us (supplier == this)
// create new value
V value = null;
try {
// Proxy.ProxyClassFactory.apply方法,返回Class对象
value = Objects.requireNonNull(valueFactory.apply(key, parameter));
} finally {
if (value == null) { // remove us on failure
valuesMap.remove(subKey, this);
}
}
// 到达这里的唯一路径是非空值
assert value != null;
// 使用CacheValue (WeakReference)包装值
CacheValue<V> cacheValue = new CacheValue<>(value);
// 放入reverseMap
reverseMap.put(cacheValue, Boolean.TRUE);
// 尝试用CacheValue替换我们(这应该总是成功的)
if (!valuesMap.replace(subKey, this, cacheValue)) {
throw new AssertionError("Should not reach here");
}
// 成功替换为新的CacheValue -> 返回由它包装的值
return value;
}
}
// 共同类型的价值suppliers持有一个参照。实现中的{@link #equals}和{@link #hashCode}被定义为通过身份来比较referent。
private interface Value<V> extends Supplier<V> {}
// 一个优化的{@link Value},用于查找{@link WeakCache#containsValue}方法中的值,这样我们就不必构造整个{@link CacheValue}来查找referent。
private static final class LookupValue<V> implements Value<V> {
private final V value;
LookupValue(V value) {
this.value = value;
}
@Override
public V get() {
return value;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return System.identityHashCode(value); // compare by identity
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
return obj == this ||
obj instanceof Value &&
this.value == ((Value<?>) obj).get(); // compare by identity
}
}
// 弱引用referent的{@link Value}。
private static final class CacheValue<V> extends WeakReference<V> implements Value<V> {
private final int hash;
CacheValue(V value) {
super(value);
this.hash = System.identityHashCode(value); // compare by identity
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return hash;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
V value;
return obj == this ||
obj instanceof Value &&
// cleared CacheValue is only equal to itself
(value = get()) != null &&
value == ((Value<?>) obj).get(); // compare by identity
}
}
// 包含弱引用{@code key}的CacheKey。它向{@code refQueue}注册自己,这样当{@link WeakReference}被清除时,就可以使用它来删除条目。
private static final class CacheKey<K> extends WeakReference<K> {
// a replacement for null keys
private static final Object NULL_KEY = new Object();
static <K> Object valueOf(K key, ReferenceQueue<K> refQueue) {
return key == null
// 空键意味着我们不能弱引用它,所以我们使用NULL_KEY单例作为缓存键
? NULL_KEY
// non-null key requires wrapping with a WeakReference
: new CacheKey<>(key, refQueue);
}
private final int hash;
private CacheKey(K key, ReferenceQueue<K> refQueue) {
super(key, refQueue);
this.hash = System.identityHashCode(key); // compare by identity
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return hash;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
K key;
return obj == this ||
obj != null &&
obj.getClass() == this.getClass() &&
// cleared CacheKey is only equal to itself
(key = this.get()) != null &&
// compare key by identity
key == ((CacheKey<K>) obj).get();
}
void expungeFrom(ConcurrentMap<?, ? extends ConcurrentMap<?, ?>> map,
ConcurrentMap<?, Boolean> reverseMap) {
// 仅通过键删除在这里总是安全的,因为当CacheKey被清除并加入队列后,它只等于它自己(参见equals方法)…
ConcurrentMap<?, ?> valuesMap = map.remove(this);
// remove also from reverseMap if needed
if (valuesMap != null) {
for (Object cacheValue : valuesMap.values()) {
reverseMap.remove(cacheValue);
}
}
}
}
测试代码:
interface ISuper {
default String getS() {
return "----";
}
}
interface IA extends ISuper{
default String get() {
return "123";
}
}
class IB{
public String get() {
return "321";
}
}
class CC extends IB implements IA {
}
interface IIA{
String get();
}
interface IIB{
String get();
}
class CCC implements IIB, IIA {
@Override
public String get() {
return "123";
}
}
class MyInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler {
private Object source;
public MyInvocationHandler(Object source) {
this.source = source;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("start invoke");
if (source.getClass() == CCC.class) {
System.out.println(method.getDeclaringClass());
}
Object result = method.invoke(source, args);
System.out.println("end invoke");
return result;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException {
ISuper instance = (ISuper)Proxy.newProxyInstance(ProxyTest.class.getClassLoader(),
new Class[]{ISuper.class},
new MyInvocationHandler(new CC()));
System.out.println(instance.getS());
// 继承优先于接口
IA instance1 = (IA)Proxy.newProxyInstance(ProxyTest.class.getClassLoader(),
new Class[]{IA.class},
new MyInvocationHandler(new CC()));
System.out.println(instance1.get());
// 多个接口具有相同签名,接口列表中包含该方法(直接或通过超接口继承)的最前面接口中的方法的{@code method}对象将被传递给调用处理程序的{@code invoke}方法
IIB instance2 = (IIB)Proxy.newProxyInstance(ProxyTest.class.getClassLoader(),
new Class[]{IIA.class, IIB.class},
new MyInvocationHandler(new CCC()));
instance2.get();
IIB instance3 = (IIB)Proxy.newProxyInstance(ProxyTest.class.getClassLoader(),
new Class[]{IIB.class, IIA.class},
new MyInvocationHandler(new CCC()));
instance3.get();
}
测试结果:
start invoke
end invoke
----
start invoke
end invoke
321
start invoke
interface com.test.IIA
end invoke
start invoke
interface com.test.IIB
end invoke
最后
以上就是超帅人生最近收集整理的关于reflect包源码笔记AnnotatedElementArrayInvocationHandlerProxyWeakCache的全部内容,更多相关reflect包源码笔记AnnotatedElementArrayInvocationHandlerProxyWeakCache内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复