深入学习java源码之CharBuffer.append()与CharBuffer.slice()
使用 final 关键字修饰一个变量时,是引用不能变,还是引用的对象不能变
我们知道数组是引用变量类型,当final修饰引用变量的时候,变量中保存的地址是不能更改的,但是指针指向的数组本身是可以更改的,final修饰并不能限制数组本身的改变
final
修饰类
final修饰类时,说明该类你不想被别人继承!一个类不被别的类继承就可以使用final来修饰
注意 final类中的所有成员方法都会被隐式地指定为final方法。
修饰方法
当一个方法被final修饰后,就代表该方法无法被重写,如果你想明确禁止 该方法在子类中被覆盖的情况下才将方法设置为final的
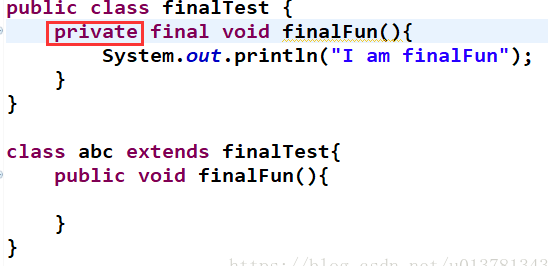
同时注意 如果父类的 final修饰的方法设置为private,则子类可以写一个同名的方法,此时 ,该同名的方法不再产生final的报错,而是在子类重新定义了一个方法(注:类的private方法会隐式地被指定为final方法。)
修饰变量
被final修饰的变量其实就相当于定义了一个常量,无法被修改的变量,如果final修饰的是一个基本数据类型的变量,那么这个变量的值就定了,不能变了,而如果修饰的是一个引用变量,那么该变量存的是一个内存地址,该地址就不能变了,但是该内存地址所指向的那个对象还是可以变的,就像你记住了人家的门牌号,但你不能管人家家里人员数量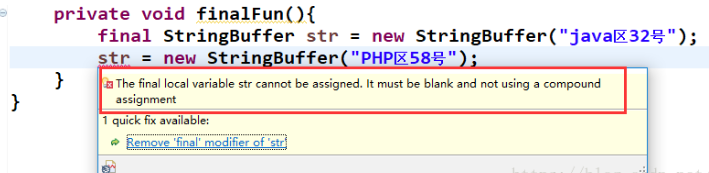
但是你可以改那个对象的内容!
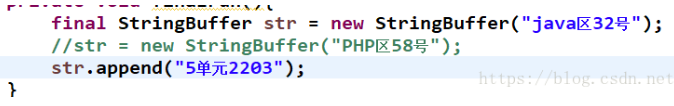
还有的人给方法定义的参数是 final类型的,是不想别人在方法内部修改参数的值,如果final修饰的是一个基本类型,那么是可以的,如果修饰的是引用类型,那么便不行了,因为就如上文那个str.append 对象的内容是可以变化的!
readable接口
Readable接口就是为了Scanner类专门创建的一个接口,使得Scanner的入口参数不必限于某个类。实现Readable接口要只需是实现public int read(CharBuffer cb)方法。当方法返回-1时候Scanner类停止读取。
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.CharBuffer;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class RandomWords implements Readable{
private Random rand=new Random(47);
private static final char[] capitals="ABCDEFGHIJKLMOPQRSTUVWXYZ".toCharArray();
private static final char[] lowers="ABCDEFGHIJKLMOPQRSTUVWXYZ".toLowerCase().toCharArray();
private static final char[] vowels="aeiou".toCharArray();
private int count;
public RandomWords(int count) {
this.count=count;
}
@Override
public int read(CharBuffer cb) throws IOException {
if (count--==0) {
return -1;
}
cb.append(capitals[rand.nextInt(capitals.length)]);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
cb.append(vowels[rand.nextInt(vowels.length)]);
cb.append(lowers[rand.nextInt(lowers.length)]);
}
cb.append(" ");
return 10;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner=new Scanner(new RandomWords(10));
while (scanner.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(scanner.next());
}
}
}
java源码
| Modifier and Type | Method and Description |
|---|---|
static CharBuffer | allocate(int capacity) 分配一个新的char缓冲区。 |
CharBuffer | append(char c) 将指定的字符追加到此缓冲区 (可选操作) 。 |
CharBuffer | append(CharSequence csq) 将指定的字符序列追加到此缓冲区 (可选操作) 。 |
CharBuffer | append(CharSequence csq, int start, int end) 将指定字符序列的子序列附加到此缓冲区 (可选操作) 。 |
char[] | array() 返回支持此缓冲区的char数组 (可选操作) 。 |
int | arrayOffset() 返回该缓冲区的缓冲区的第一个元素的背衬数组中的偏移量 (可选操作) 。 |
abstract CharBuffer | asReadOnlyBuffer() 创建一个新的只读char缓冲区,共享此缓冲区的内容。 |
char | charAt(int index) 以相对于当前位置的给定索引读取字符。 |
IntStream | chars() 返回 |
abstract CharBuffer | compact() 压缩此缓冲区 (可选操作) 。 |
int | compareTo(CharBuffer that) 将此缓冲区与另一个缓冲区进行比较。 |
abstract CharBuffer | duplicate() 创建一个新的char缓冲区,共享此缓冲区的内容。 |
boolean | equals(Object ob) 告诉这个缓冲区是否等于另一个对象。 |
abstract char | get() 相对 获取方法。 |
CharBuffer | get(char[] dst) 相对批量 获取方法。 |
CharBuffer | get(char[] dst, int offset, int length) 相对批量 获取方法。 |
abstract char | get(int index) 绝对 获取方法。 |
boolean | hasArray() 告诉这个缓冲区是否由可访问的字符数组支持。 |
int | hashCode() 返回此缓冲区的当前哈希码。 |
abstract boolean | isDirect() 告诉这个char缓冲区是否直接。 |
int | length() 返回此字符缓冲区的长度。 |
abstract ByteOrder | order() 检索此缓冲区的字节顺序。 |
abstract CharBuffer | put(char c) 相对 放置法 (可选操作) 。 |
CharBuffer | put(char[] src) 相对大容量 put方法 (可选操作) 。 |
CharBuffer | put(char[] src, int offset, int length) 相对大容量 put方法 (可选操作) 。 |
CharBuffer | put(CharBuffer src) 相对大容量 put方法 (可选操作) 。 |
abstract CharBuffer | put(int index, char c) 绝对 put方法 (可选操作) 。 |
CharBuffer | put(String src) 相对大容量 put方法 (可选操作) 。 |
CharBuffer | put(String src, int start, int end) 相对大容量 put方法 (可选操作) 。 |
int | read(CharBuffer target) 尝试将字符读入指定的字符缓冲区。 |
abstract CharBuffer | slice() 创建一个新的char缓冲区,其内容是此缓冲区内容的共享子序列。 |
abstract CharBuffer | subSequence(int start, int end) 创建一个新的字符缓冲区,代表该缓冲区相对于当前位置的指定子序列。 |
String | toString() 返回一个包含此缓冲区中字符的字符串。 |
static CharBuffer | wrap(char[] array) 将一个char数组包装到缓冲区中。 |
static CharBuffer | wrap(char[] array, int offset, int length) 将一个char数组包装到缓冲区中。 |
static CharBuffer | wrap(CharSequence csq) 将字符序列包装到缓冲区中。 |
static CharBuffer | wrap(CharSequence csq, int start, int end) 将字符序列包装到缓冲区中。 |
package java.nio;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Spliterator;
import java.util.stream.StreamSupport;
import java.util.stream.IntStream;
public abstract class CharBuffer
extends Buffer
implements Comparable<CharBuffer>, Appendable, CharSequence, Readable
{
// These fields are declared here rather than in Heap-X-Buffer in order to
// reduce the number of virtual method invocations needed to access these
// values, which is especially costly when coding small buffers.
//
final char[] hb; // Non-null only for heap buffers
final int offset;
boolean isReadOnly; // Valid only for heap buffers
// Creates a new buffer with the given mark, position, limit, capacity,
// backing array, and array offset
//
CharBuffer(int mark, int pos, int lim, int cap, // package-private
char[] hb, int offset)
{
super(mark, pos, lim, cap);
this.hb = hb;
this.offset = offset;
}
// Creates a new buffer with the given mark, position, limit, and capacity
//
CharBuffer(int mark, int pos, int lim, int cap) { // package-private
this(mark, pos, lim, cap, null, 0);
}
public static CharBuffer allocate(int capacity) {
if (capacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
return new HeapCharBuffer(capacity, capacity);
}
public static CharBuffer wrap(char[] array,
int offset, int length)
{
try {
return new HeapCharBuffer(array, offset, length);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException x) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
}
public static CharBuffer wrap(char[] array) {
return wrap(array, 0, array.length);
}
public int read(CharBuffer target) throws IOException {
// Determine the number of bytes n that can be transferred
int targetRemaining = target.remaining();
int remaining = remaining();
if (remaining == 0)
return -1;
int n = Math.min(remaining, targetRemaining);
int limit = limit();
// Set source limit to prevent target overflow
if (targetRemaining < remaining)
limit(position() + n);
try {
if (n > 0)
target.put(this);
} finally {
limit(limit); // restore real limit
}
return n;
}
public static CharBuffer wrap(CharSequence csq, int start, int end) {
try {
return new StringCharBuffer(csq, start, end);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException x) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
}
public static CharBuffer wrap(CharSequence csq) {
return wrap(csq, 0, csq.length());
}
public abstract CharBuffer slice();
public abstract CharBuffer duplicate();
public abstract CharBuffer asReadOnlyBuffer();
// -- Singleton get/put methods --
public abstract char get();
public abstract CharBuffer put(char c);
public abstract char get(int index);
abstract char getUnchecked(int index); // package-private
public abstract CharBuffer put(int index, char c);
// -- Bulk get operations --
public CharBuffer get(char[] dst, int offset, int length) {
checkBounds(offset, length, dst.length);
if (length > remaining())
throw new BufferUnderflowException();
int end = offset + length;
for (int i = offset; i < end; i++)
dst[i] = get();
return this;
}
public CharBuffer get(char[] dst) {
return get(dst, 0, dst.length);
}
// -- Bulk put operations --
public CharBuffer put(CharBuffer src) {
if (src == this)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
if (isReadOnly())
throw new ReadOnlyBufferException();
int n = src.remaining();
if (n > remaining())
throw new BufferOverflowException();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
put(src.get());
return this;
}
public CharBuffer put(char[] src, int offset, int length) {
checkBounds(offset, length, src.length);
if (length > remaining())
throw new BufferOverflowException();
int end = offset + length;
for (int i = offset; i < end; i++)
this.put(src[i]);
return this;
}
public final CharBuffer put(char[] src) {
return put(src, 0, src.length);
}
public CharBuffer put(String src, int start, int end) {
checkBounds(start, end - start, src.length());
if (isReadOnly())
throw new ReadOnlyBufferException();
if (end - start > remaining())
throw new BufferOverflowException();
for (int i = start; i < end; i++)
this.put(src.charAt(i));
return this;
}
public final CharBuffer put(String src) {
return put(src, 0, src.length());
}
// -- Other stuff --
public final boolean hasArray() {
return (hb != null) && !isReadOnly;
}
public final char[] array() {
if (hb == null)
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
if (isReadOnly)
throw new ReadOnlyBufferException();
return hb;
}
public final int arrayOffset() {
if (hb == null)
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
if (isReadOnly)
throw new ReadOnlyBufferException();
return offset;
}
public abstract CharBuffer compact();
public abstract boolean isDirect();
public int hashCode() {
int h = 1;
int p = position();
for (int i = limit() - 1; i >= p; i--)
h = 31 * h + (int)get(i);
return h;
}
public boolean equals(Object ob) {
if (this == ob)
return true;
if (!(ob instanceof CharBuffer))
return false;
CharBuffer that = (CharBuffer)ob;
if (this.remaining() != that.remaining())
return false;
int p = this.position();
for (int i = this.limit() - 1, j = that.limit() - 1; i >= p; i--, j--)
if (!equals(this.get(i), that.get(j)))
return false;
return true;
}
private static boolean equals(char x, char y) {
return x == y;
}
public int compareTo(CharBuffer that) {
int n = this.position() + Math.min(this.remaining(), that.remaining());
for (int i = this.position(), j = that.position(); i < n; i++, j++) {
int cmp = compare(this.get(i), that.get(j));
if (cmp != 0)
return cmp;
}
return this.remaining() - that.remaining();
}
private static int compare(char x, char y) {
return Character.compare(x, y);
}
// -- Other char stuff --
public String toString() {
return toString(position(), limit());
}
abstract String toString(int start, int end); // package-private
// --- Methods to support CharSequence ---
public final int length() {
return remaining();
}
public final char charAt(int index) {
return get(position() + checkIndex(index, 1));
}
public abstract CharBuffer subSequence(int start, int end);
public CharBuffer append(CharSequence csq) {
if (csq == null)
return put("null");
else
return put(csq.toString());
}
public CharBuffer append(CharSequence csq, int start, int end) {
CharSequence cs = (csq == null ? "null" : csq);
return put(cs.subSequence(start, end).toString());
}
public CharBuffer append(char c) {
return put(c);
}
public abstract ByteOrder order();
@Override
public IntStream chars() {
return StreamSupport.intStream(() -> new CharBufferSpliterator(this),
Buffer.SPLITERATOR_CHARACTERISTICS, false);
}
}
@Override
public IntStream chars() {
return StreamSupport.intStream(() -> new CharBufferSpliterator(this),
Buffer.SPLITERATOR_CHARACTERISTICS, false);
}
}
| Modifier and Type | Method and Description |
|---|---|
abstract Object | array() 返回支持此缓冲区的数组 (可选操作) 。 |
abstract int | arrayOffset() 返回该缓冲区的缓冲区的第一个元素的背衬数组中的偏移量 (可选操作) 。 |
int | capacity() 返回此缓冲区的容量。 |
Buffer | clear() 清除此缓冲区。 |
Buffer | flip() 翻转这个缓冲区。 |
abstract boolean | hasArray() 告诉这个缓冲区是否由可访问的数组支持。 |
boolean | hasRemaining() 告诉当前位置和极限之间是否存在任何元素。 |
abstract boolean | isDirect() 告诉这个缓冲区是否为 direct 。 |
abstract boolean | isReadOnly() 告知这个缓冲区是否是只读的。 |
int | limit() 返回此缓冲区的限制。 |
Buffer | limit(int newLimit) 设置此缓冲区的限制。 |
Buffer | mark() 将此缓冲区的标记设置在其位置。 |
int | position() 返回此缓冲区的位置。 |
Buffer | position(int newPosition) 设置这个缓冲区的位置。 |
int | remaining() 返回当前位置和限制之间的元素数。 |
Buffer | reset() 将此缓冲区的位置重置为先前标记的位置。 |
Buffer | rewind() 倒带这个缓冲区。 |
package java.nio;
import java.util.Spliterator;
public abstract class Buffer {
static final int SPLITERATOR_CHARACTERISTICS =
Spliterator.SIZED | Spliterator.SUBSIZED | Spliterator.ORDERED;
// Invariants: mark <= position <= limit <= capacity
private int mark = -1;
private int position = 0;
private int limit;
private int capacity;
// Used only by direct buffers
// NOTE: hoisted here for speed in JNI GetDirectBufferAddress
long address;
// Creates a new buffer with the given mark, position, limit, and capacity,
// after checking invariants.
//
Buffer(int mark, int pos, int lim, int cap) { // package-private
if (cap < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Negative capacity: " + cap);
this.capacity = cap;
limit(lim);
position(pos);
if (mark >= 0) {
if (mark > pos)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("mark > position: ("
+ mark + " > " + pos + ")");
this.mark = mark;
}
}
public final int capacity() {
return capacity;
}
public final int position() {
return position;
}
public final Buffer position(int newPosition) {
if ((newPosition > limit) || (newPosition < 0))
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
position = newPosition;
if (mark > position) mark = -1;
return this;
}
public final int limit() {
return limit;
}
public final Buffer limit(int newLimit) {
if ((newLimit > capacity) || (newLimit < 0))
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
limit = newLimit;
if (position > limit) position = limit;
if (mark > limit) mark = -1;
return this;
}
public final Buffer mark() {
mark = position;
return this;
}
public final Buffer reset() {
int m = mark;
if (m < 0)
throw new InvalidMarkException();
position = m;
return this;
}
public final Buffer clear() {
position = 0;
limit = capacity;
mark = -1;
return this;
}
public final Buffer flip() {
limit = position;
position = 0;
mark = -1;
return this;
}
public final Buffer rewind() {
position = 0;
mark = -1;
return this;
}
public final int remaining() {
return limit - position;
}
public final boolean hasRemaining() {
return position < limit;
}
public abstract boolean isReadOnly();
public abstract boolean hasArray();
public abstract Object array();
public abstract int arrayOffset();
public abstract boolean isDirect();
// -- Package-private methods for bounds checking, etc. --
final int nextGetIndex() { // package-private
if (position >= limit)
throw new BufferUnderflowException();
return position++;
}
final int nextGetIndex(int nb) { // package-private
if (limit - position < nb)
throw new BufferUnderflowException();
int p = position;
position += nb;
return p;
}
final int nextPutIndex() { // package-private
if (position >= limit)
throw new BufferOverflowException();
return position++;
}
final int nextPutIndex(int nb) { // package-private
if (limit - position < nb)
throw new BufferOverflowException();
int p = position;
position += nb;
return p;
}
final int checkIndex(int i) { // package-private
if ((i < 0) || (i >= limit))
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
return i;
}
final int checkIndex(int i, int nb) { // package-private
if ((i < 0) || (nb > limit - i))
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
return i;
}
final int markValue() { // package-private
return mark;
}
final void truncate() { // package-private
mark = -1;
position = 0;
limit = 0;
capacity = 0;
}
final void discardMark() { // package-private
mark = -1;
}
static void checkBounds(int off, int len, int size) { // package-private
if ((off | len | (off + len) | (size - (off + len))) < 0)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
}
| Modifier and Type | Method and Description |
|---|---|
char | charAt(int index) 返回 |
default IntStream | chars() 返回一个 |
default IntStream | codePoints() 从此序列返回码流值。 |
int | length() 返回此字符序列的长度。 |
CharSequence | subSequence(int start, int end) 返回一个 |
String | toString() 以与此顺序相同的顺序返回包含此序列中的字符的字符串。 |
package java.lang;
import java.util.NoSuchElementException;
import java.util.PrimitiveIterator;
import java.util.Spliterator;
import java.util.Spliterators;
import java.util.function.IntConsumer;
import java.util.stream.IntStream;
import java.util.stream.StreamSupport;
public interface CharSequence {
int length();
char charAt(int index);
CharSequence subSequence(int start, int end);
public String toString();
public default IntStream chars() {
class CharIterator implements PrimitiveIterator.OfInt {
int cur = 0;
public boolean hasNext() {
return cur < length();
}
public int nextInt() {
if (hasNext()) {
return charAt(cur++);
} else {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
}
@Override
public void forEachRemaining(IntConsumer block) {
for (; cur < length(); cur++) {
block.accept(charAt(cur));
}
}
}
return StreamSupport.intStream(() ->
Spliterators.spliterator(
new CharIterator(),
length(),
Spliterator.ORDERED),
Spliterator.SUBSIZED | Spliterator.SIZED | Spliterator.ORDERED,
false);
}
public default IntStream codePoints() {
class CodePointIterator implements PrimitiveIterator.OfInt {
int cur = 0;
@Override
public void forEachRemaining(IntConsumer block) {
final int length = length();
int i = cur;
try {
while (i < length) {
char c1 = charAt(i++);
if (!Character.isHighSurrogate(c1) || i >= length) {
block.accept(c1);
} else {
char c2 = charAt(i);
if (Character.isLowSurrogate(c2)) {
i++;
block.accept(Character.toCodePoint(c1, c2));
} else {
block.accept(c1);
}
}
}
} finally {
cur = i;
}
}
public boolean hasNext() {
return cur < length();
}
public int nextInt() {
final int length = length();
if (cur >= length) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
char c1 = charAt(cur++);
if (Character.isHighSurrogate(c1) && cur < length) {
char c2 = charAt(cur);
if (Character.isLowSurrogate(c2)) {
cur++;
return Character.toCodePoint(c1, c2);
}
}
return c1;
}
}
return StreamSupport.intStream(() ->
Spliterators.spliteratorUnknownSize(
new CodePointIterator(),
Spliterator.ORDERED),
Spliterator.ORDERED,
false);
}
}
package java.lang;
import java.util.*;
public interface Comparable<T> {
public int compareTo(T o);
}package java.lang;
import java.io.IOException;
public interface Readable {
public int read(java.nio.CharBuffer cb) throws IOException;
}
最后
以上就是健忘小蜜蜂最近收集整理的关于深入学习java源码之CharBuffer.append()与CharBuffer.slice()的全部内容,更多相关深入学习java源码之CharBuffer内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复