import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from sklearn.preprocessing import OneHotEncoder
import random
import os
from tensorflow.contrib import rnn
data_num=np.array([0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9])
data_num=data_num.reshape([-1,1])
data_num=OneHotEncoder().fit_transform(data_num).todense()
batch_size=100
#print(data)
def get_data(batch_size=100):
batch_in_data=[]
batch_out_data=[]
d1 = []
for i in range(batch_size):
a=random.randint(0,10000000)
b=random.randint(0,10000000)
c=[a,b]
d=a+b
d1.append(d)
data=[]
label=[]
out_data=[]
for j in c:
for i in range(8):
data.insert(i,j%10)
j=j//10
data=np.array(data)
data=data.reshape([2,8]).T
data=data.reshape([8,2])
for i in range(8):
out_data.insert(i,d%10)
d=d//10
for x in out_data:
label.append(data_num[x])
#print(out_data)
label=np.array(label)
label=label.reshape([8,10])
batch_out_data.append(label)
batch_in_data.append(data)
batch_in_data=np.array(batch_in_data)
batch_out_data=np.array(batch_out_data)
batch_in_data=batch_in_data.astype("float32")
batch_out_data=batch_out_data.astype("float32")
batch_in_data=batch_in_data.reshape([-1,8,2])
batch_out_data=batch_out_data.reshape([-1,8,10])
return batch_in_data,batch_out_data,d1
#输入:
x=tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,8,2])
y=tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,8,10])
#y=tf.placeholder(tf.int64,[8])
'''
weights = {
'out' : tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([8, 10])) #128*10
}
biases = {
'out' : tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([10])) #1*10
}
'''
weights = {'in':tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([2, 8])),
'out':tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([8, 10]))}
biases = {'in':tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1, shape=[8, ])),
'out':tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1, shape=[10, ]))}
def RNN(X, weights, biases):
#print(X)
#X=tf.transpose(X,[1,0,2])
#X=tf.reshape(X,[-1,2])
#X_in = tf.matmul(X, weights['in']) + biases['in']
#print(X_in)
#X_in = tf.reshape(X_in, [-1,8,16])
#X_in=tf.reshape(X_in,[-1,8,8])
X_in=tf.transpose(X,[1,0,2])
#X_in = tf.split(x,8,0)
print(X_in)
# 使用基本的LSTM循环网络单元
#lstm_cell = tf.contrib.rnn.BasicLSTMCell(16, forget_bias=1.0, state_is_tuple=True)
lstm_cell = tf.nn.rnn_cell.BasicLSTMCell(8, forget_bias=1.0, state_is_tuple=True)
#print(1)
# 初始化为0,LSTM单元由两部分构成(c_state, h_state)
init_state = lstm_cell.zero_state(100, dtype=tf.float32)
#print(2)
# dynamic_rnn接收张量要么为(batch, steps, inputs)或者(steps, batch, inputs)作为X_in
outputs, final_state = tf.nn.dynamic_rnn(lstm_cell, X_in, initial_state=init_state, time_major=True)
print("outputs:",outputs)
outputs = tf.reshape(outputs,[-1,8])
results = tf.matmul(outputs, weights["out"]) + biases["out"]
#outputs = tf.reshape(outputs, [-1, 16])
#results = tf.matmul(outputs, weights['out']) + biases['out']
#print("results:",results)
#results = tf.reshape(results, [-1, 8, 10])
print("results:",results)
results = tf.reshape(results,[8,-1,10])
print(results)
results = tf.transpose(results, [1, 0,2])
#os.system("pause")
return results
pred = RNN(x, weights, biases)
pre = tf.argmax(pred,2)
#pre = tf.argmax(pred,1)
#cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(pred-y))
#print(pre)
cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits_v2(logits=pred, labels=y))
#cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=pred, labels=y))
#optimizer = tf.train.AdagradOptimizer(1).minimize(cost)
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(0.01).minimize(cost)
correct_pred = tf.equal(tf.argmax(pred, 2), tf.argmax(y, 2))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_pred, tf.float32))
def train():
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
for i in range(2000000):
batch_xs,batch_ys,d=get_data(100)
#print(batch_xs.shape,batch_ys.shape)
sess.run(optimizer, feed_dict={x: batch_xs, y: batch_ys})
#print(5)
if i%100 ==0:
cc = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x: batch_xs, y: batch_ys})
loss = sess.run(cost, feed_dict={x: batch_xs, y: batch_ys})
print("cc:",cc," loss:",loss)
if i % 1000==0:
batch_xs,batch_ys,d=get_data(100)
#print(batch_xs)
#print(batch_ys)
#os.system("pause")
pree = sess.run(pre,feed_dict={x:batch_xs})
#cc = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x: batch_xs, y: batch_ys})
#loss = sess.run(cost, feed_dict={x: batch_xs, y: batch_ys})
for j in range(5):
print("true:",d[j])
print("pree:",pree[j][::-1][0:8])
print("________________")
#os.system("pause")
sess.close()
train()
以上就是实现的全过程,欢迎提问,有问必答,也欢迎指导贴一张训练后的图,说实话,自己敲一遍对这个东西的理解会深许多
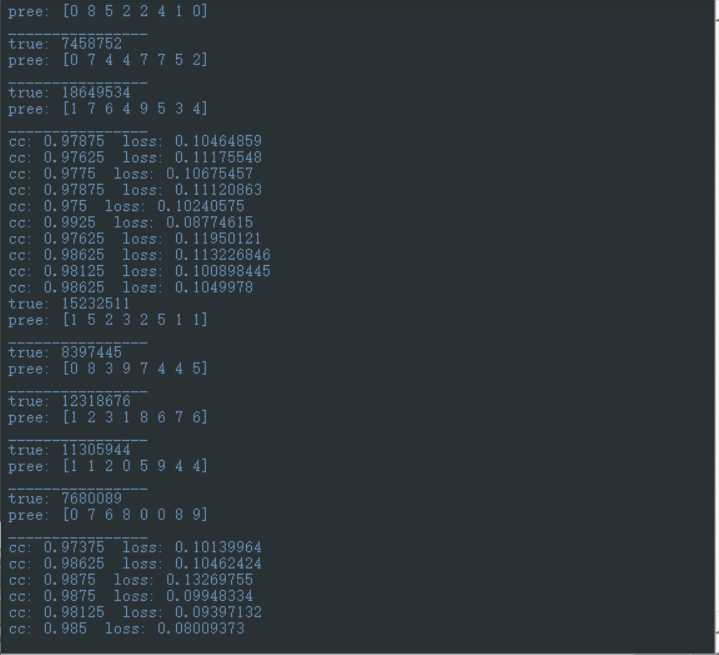
最后
以上就是秀丽花生最近收集整理的关于用lstm实现7位数以内的加法的全部内容,更多相关用lstm实现7位数以内内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复