LSTM
长的短时记忆网络。LSTM虽然只解决了短期依赖的问题,并且它通过刻意的设计来避免长期依赖问题,这样的做法在实际应用中被证明还是十分有效的,有很多人跟进相关的工作解决了很多实际的问题,所以现在LSTM 仍然被广泛地使用。
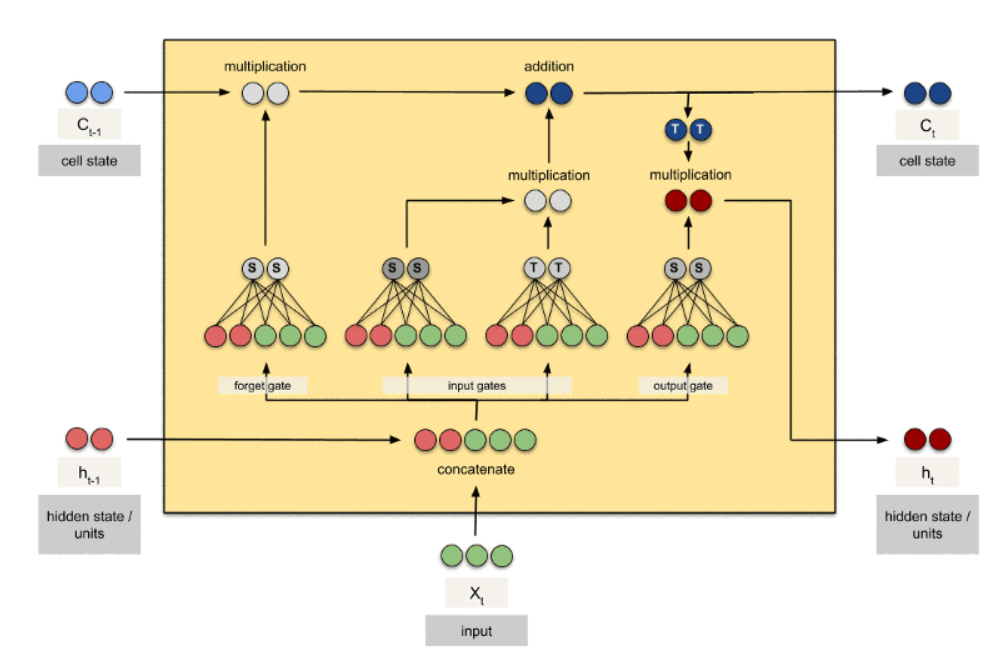
标准的循环神经网络内部只有一个简单的层结构,而 LSTM 内部有 4 个层结构:
-
第一层是个忘记层:决定状态中丢弃什么信息
-
第二层tanh层用来产生更新值的候选项,说明状态在某些维度上需要加强,在某些维度上需要减弱
-
第三层sigmoid层(输入门层),它的输出值要乘到tanh层的输出上,起到一个缩放的作用,极端情况下sigmoid输出0说明相应维度上的状态不需要更新
-
最后一层决定输出什么,输出值跟状态有关。候选项中的哪些部分最终会被输出由一个sigmoid层来决定。
每一层:input (X_t), Cell State(C_t-1), hidden state units(h_t-1), 得到Cell State(C_t-1),hidden state units(h_t);
最后一层,得到输出。
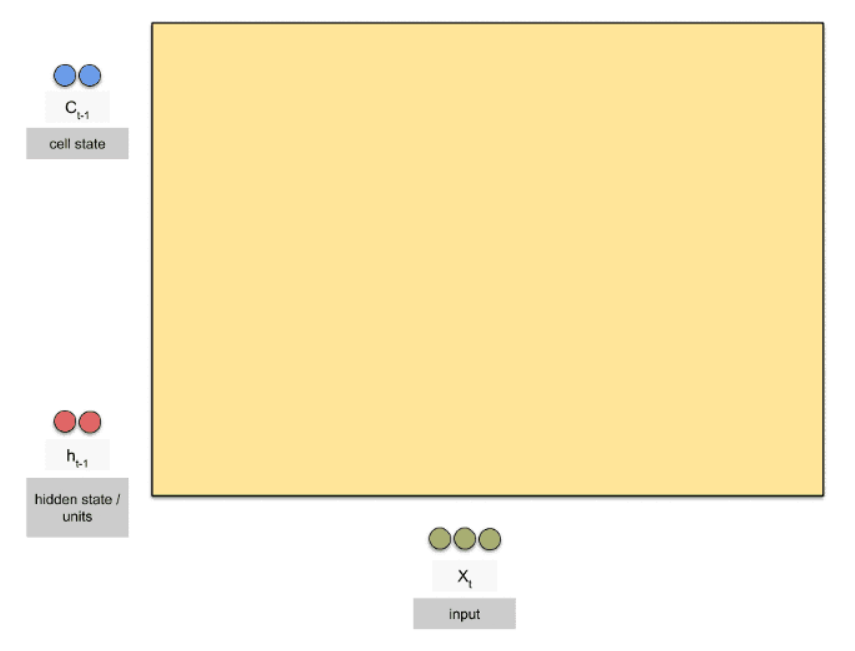
第一步:准备input (X_t), Cell State(C_t-1), hidden state units(h_t-1),
- 其中,第一层的Cell State(C_t-1), hidden state units(h_t-1)由初始化得到
- 其余层的Cell State(C_t-1), hidden state units(h_t-1)由上一层计算更新
def initHidden(self, batch_size):
Hidden_State = Variable(torch.zeros(batch_size, self.hidden_size))
Cell_State = Variable(torch.zeros(batch_size, self.hidden_size))
return Hidden_State, Cell_State
第二步:合并input (X_t), Cell State(C_t-1)
combined = torch.cat((input, Hidden_State), 1)

全部步骤:
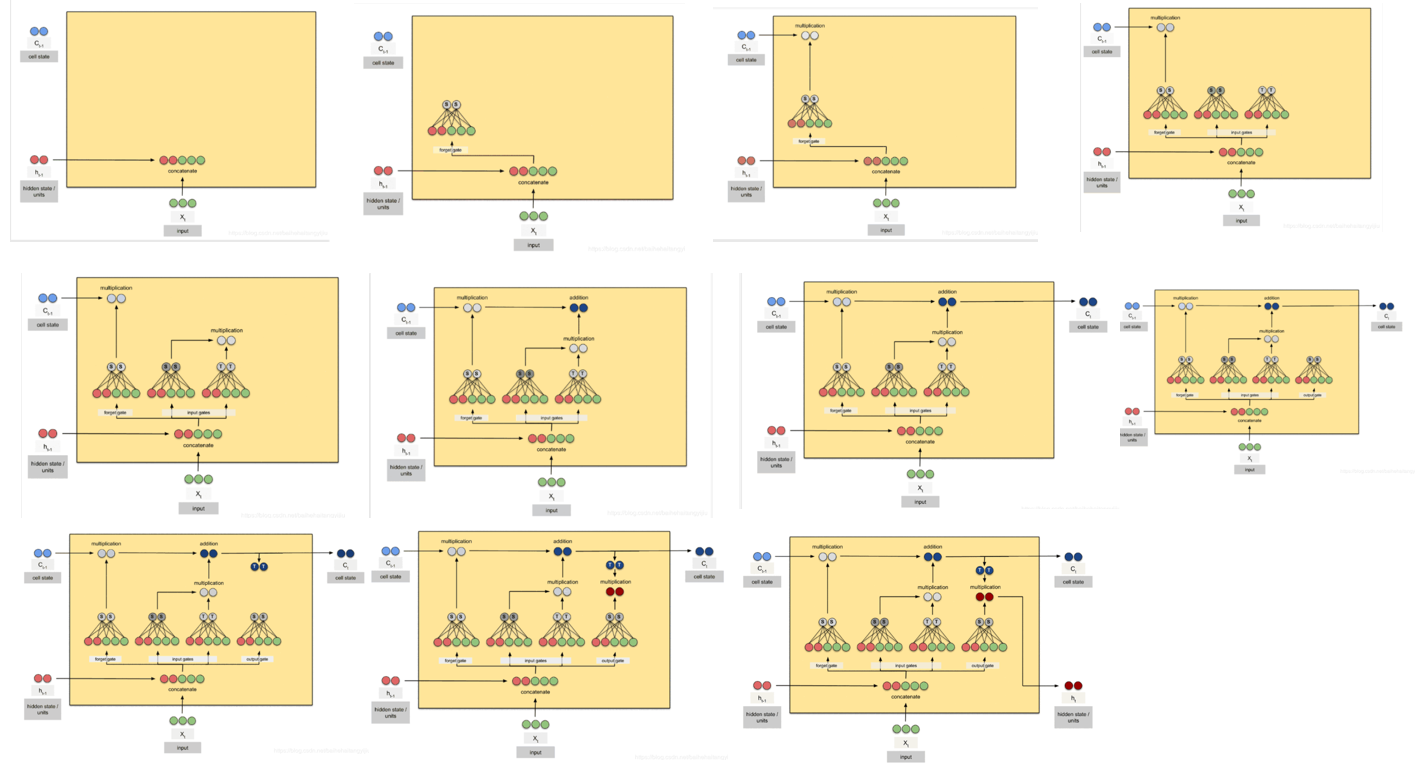
pytorch 中使用 nn.LSTM 类来搭建基于序列的循环神经网络
lstm = torch.nn.LSTM(10, 20,2) # (input_size, hidden_size,num_layers)
input = torch.randn(5, 3, 10) # (batch_size, num_loop, num_features)
h0 =torch.randn(2, 3, 20)
c0 = torch.randn(2, 3, 20)
output, hn = lstm(input, (h0, c0))
print(output.size(),hn[0].size(),hn[1].size())
torch.Size([5, 3, 20]) torch.Size([2, 3, 20]) torch.Size([2, 3, 20])
全部步骤代码
class LSTM(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, cell_size, hidden_size):
"""
cell_size is the size of cell_state.
hidden_size is the size of hidden_state, or say the output_state of each step
"""
super(LSTM, self).__init__()
self.cell_size = cell_size
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.fl = nn.Linear(input_size + hidden_size, hidden_size) # forget gate的线性因子
self.il = nn.Linear(input_size + hidden_size, hidden_size) # input gate的线性因子
self.ol = nn.Linear(input_size + hidden_size, hidden_size) # output gate的线性因子
self.Cl = nn.Linear(input_size + hidden_size, hidden_size) # Cell State的线性因子
def forward(self, input, Hidden_State, Cell_State):
combined = torch.cat((input, Hidden_State), 1) # 合并input (X_t), Cell State(C_t-1)
f = F.sigmoid(self.fl(combined)) # forget gate的激活函数
i = F.sigmoid(self.il(combined)) # input gate的激活函数
o = F.sigmoid(self.ol(combined)) # output gate的激活函数
C = F.tanh(self.Cl(combined)) # Cell State的激活函数
Cell_State = f * Cell_State + i * C # 更新Cell State
Hidden_State = o * F.tanh(Cell_State) # 更新Hidden_State
return Hidden_State, Cell_State
def loop(self, inputs):
batch_size = inputs.size(0)
time_step = inputs.size(1)
Hidden_State, Cell_State = self.initHidden(batch_size)
for i in range(time_step): # input:()LSTM循环函数的每一个
Hidden_State, Cell_State = self.forward(torch.squeeze(inputs[:,i:i+1,:]), Hidden_State, Cell_State)
return Hidden_State, Cell_State
def initHidden(self, batch_size):
use_gpu = torch.cuda.is_available()
if use_gpu:
Hidden_State = Variable(torch.zeros(batch_size, self.hidden_size).cuda())
Cell_State = Variable(torch.zeros(batch_size, self.hidden_size).cuda())
return Hidden_State, Cell_State
else:
Hidden_State = Variable(torch.zeros(batch_size, self.hidden_size))
Cell_State = Variable(torch.zeros(batch_size, self.hidden_size))
return Hidden_State, Cell_State
参考:https://github.com/zergtant/pytorch-handbook/blob/master/chapter2/2.5-rnn.ipynb
https://github.com/zhiyongc/Graph_Convolutional_LSTM/blob/master/Code_V1/Models.py#L82
最后
以上就是完美酒窝最近收集整理的关于pytorch_LSTM的全部内容,更多相关pytorch_LSTM内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复