实验报告内容
实验题目: Analyze TCP with Wireshark
实验目的:Understanding the application layer TCP protocol through wireshark packet capture.
实验要求:Complete the experiment according to the experimental steps provided by Wireshark Lab; 2. Answer the questions in the experiment
实验器材:omputer and wireshark runtime environment
实验步骤/程序源代码:
1.Capture a bulk TCP transfer from your computer to a remote server.
(1)Start up your web browser.Go the http://gaia.cs.umass.edu/wireshark-labs/alice.txt and retrieve an ASCII copy of Alice in Wonderland.Store this file somewhere on your computer.
(2)Next go to http://gaia.cs.umass.edu/wireshark-labs/TCP-wireshark-file1.html.
(3)Use the Browse button in this form to enter the name of the file(full path name)on your computer containing Alice in Wonderland(or do so manually).Don’t yet press the “Upload alice.txt file”button.
(4)Now start up Wireshark and begin packet capture(Capture->Start)and then press OK on the Wireshark Packet Capture Options screen(we’ll not need to select any options here).
(5)Returning to your browser,press the “Upload alice.txt file”button to upload the file to the gaia.cs.umass.edu server.Once the file has been uploaded,a short congratulations message will be displayed in your browser window.
(6)Stop Wireshark packet capture.Your Wireshark window should look similar to the window shown below.
2.A first look at the captured trace.
(1)First,filter the packets displayed in the Wireshark window by entering “tcp” into the display filter specification window towards the top of the Wireshark window.
(2)Answer the following questions,by opening the Wireshark captured packet file tcp-etheral-trace-1 in http://gaia.cs.umass.edu/wireshark-labs/wireshark-trace.zip
(3)To print a packet,use File->Print,choose Selected packet only,choose Packer summary line,and select the minimum amount of packet detail that you need to answer the question.
2.1 What is the IP address and TCP port number used by the client computer(source)that is transeferring the file to gaia.cs.edu?To answer this question,it’s probably easiest to select an HTTP message and explore the details of the TCP packet used to carry this HTTP message,using the ‘details of the selected packet header window’
2.2 What is the IP address of gaia.cs.umass.edu?On what port number is it sending and receiving TCP segments for this connection?
2.3 What is the IP address and TCP port number used by your client computer to transfer the file to gaia.cs.umass.edu?
3.TCP Basics
Answer the following questions for the TCP segments:
4.What is the sequence number of the TCP SYN segment that is used to initiate the TCP connection between the client computer and gaia.cs.umass.edu?What is it in the segment that identifies the segment as a SYN segment?
5.What is the sequence number of the SYNACK segment sent by gaia.cs.umass.edu Acknoledgement field in the SYNACK segment?How did gaia.cs.umass.edu determine that value?What is it in the segment that identifies the segment as a SYNACK segment?
6.What is the sequence number of the TCP segment containing the HTTP POST command?Note that in order to find the POST command,you’ll need to dig into the packet content field at the bottom of the Wireshark window,looking for a segment with a “POST” within its DATA field.
7.Consider the TCP segment containing the HTTP POST as the first segment in the TCP connection.What are the sequence numbers of the first six segments in the TCP connection?At what time was each segment sent?When was the ACK for each segment received?Given the difference between when each TCP segment was sent,and when its acknowledgement was received,what is the RTT value for each of the six segments?What is the EstimatedRTT value after the receipt of each ACK?Assume that the value of the EstimateRTT is equal to the measured RTT for the first segment,and then is computed using the EstimateRTT equation on page 242 for all subsequent segments.
8.What is the length of each of the first six TCP segments?
9.What is the minimum amount of available buffer space advertised at the received for the entire trace?Does the lack of receiver buffer space ever throttle the sender?
10.Are there any retransmitted segments in the trace file?What did you check for in order to answer this question?
11.How much data does the receiver typically acknowledge in an ACK?Can you identify cases where the receiver is ACKing every other received segment?
12.What is the throughput for the TCP connection?Explain how you calculated this value.
4.TCP congestion control in action
(1)Select a TCP segment in the Wireshark’s “listing of captured-packets”window.Then select the menu:Statistics->TCP Stream Graph->Time-Sequence-Graph.You should see a plot that look similar to the following plot,which was created from the captured packets in the packet trace tcp-etheral-trace-1 in http://gaia.cs.umass.edu/wireshark-labs/wireshark-traces.zip
13.Use the Time-Sequence-Graph plotting tool to view the sequence number versus time plot of segments being sent from the client to the gaia.cs.umass.server.Can you identify where TCP’s slowstart phase begins and ends,and where congestion avoidance takes over?Comment on ways in which the measured data differs from the idealized behavior of TCP that we’ve studied in the text.
实验结果分析:
一、Capture a bulk TCP transfer from your computer to a remote server.
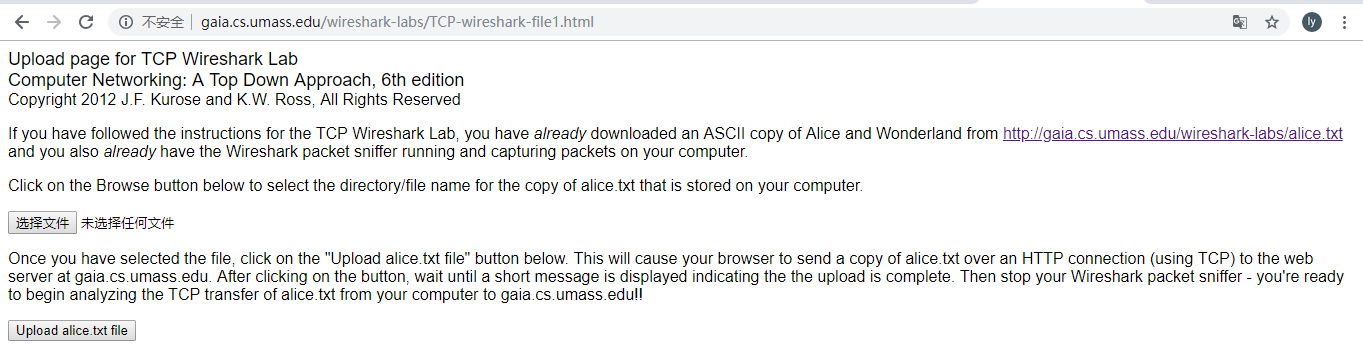
1.Startupyour web browser.Go the http://gaia.cs.umass.edu/wireshark-labs/alice.txt and retrieve an ASCII copy of Alice in Wonderland.Store this file somewhere on your computer.(如图1所示)

2. Next go to http://gaia.cs.umass.edu/wireshark-labs/TCP-wireshark-file1.html.
(如图2所示)
二、A first look at the captured trace
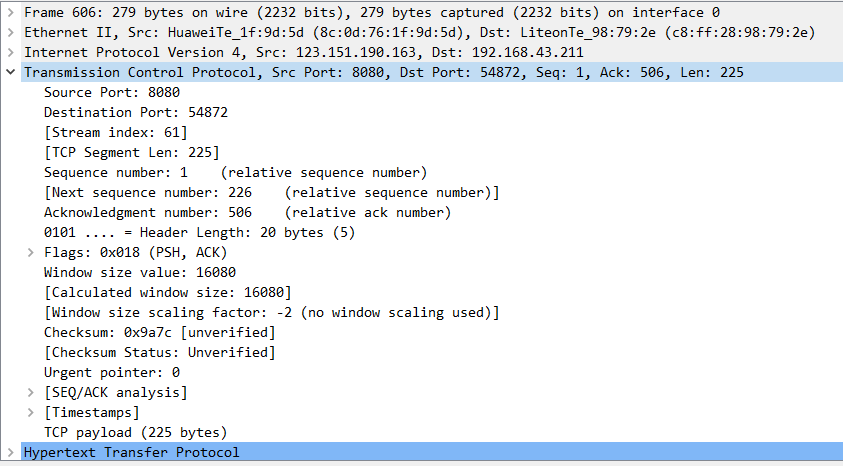
1、What is the IP address and TCP port number used by the client computer (source) that is transferring the file to gaia.cs.umass.edu? To answer this question, it’s probably easiest to select an HTTP message and explore the details of the TCP packet used to carry this HTTP message, using the “details of the selected packet header window” ?(如图3所示)
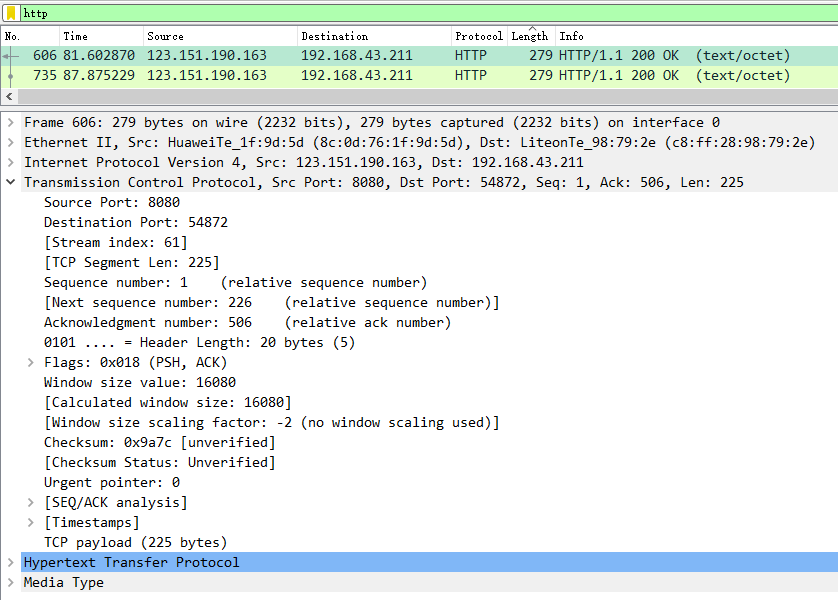
A:
Source IP address:123.151.190.163
Source Port: 8080
2、What is the IP address of gaia.cs.umass.edu? On what port number is it sending and receiving TCP segments for this connection?(如图4所示)
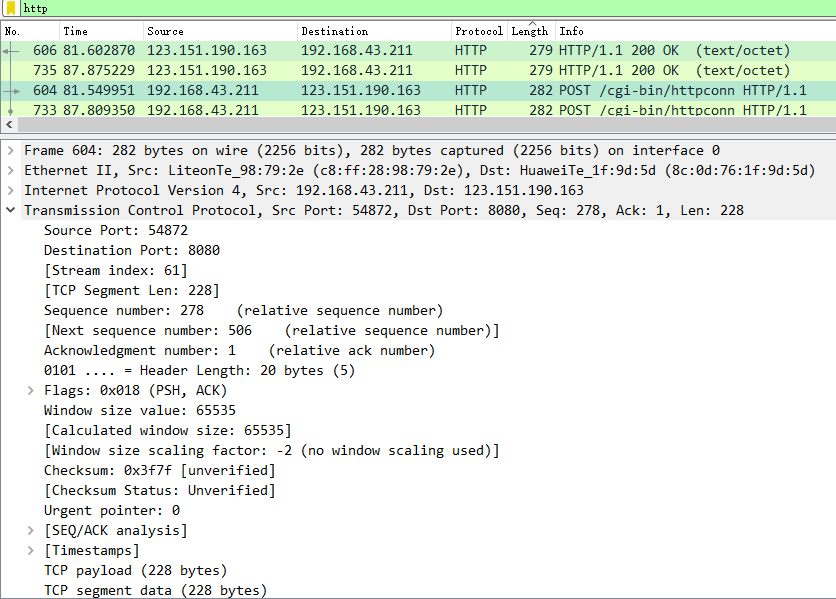
A:
Destination IP address:192.168.43.211
Destination Port: 8080
3、What is the IP address and TCP port number used by your client computer to transfer the file to gaia.cs.umass.edu? (如图5所示)

三、TCP Basics
4、(1)What is the sequence number of the TCP SYN segment that is used to initiate the TCP connection between the client computer and gaia.cs.umass.edu? (2)What is it in the segment that identifies the segment as a SYN segment?(如图6所示)
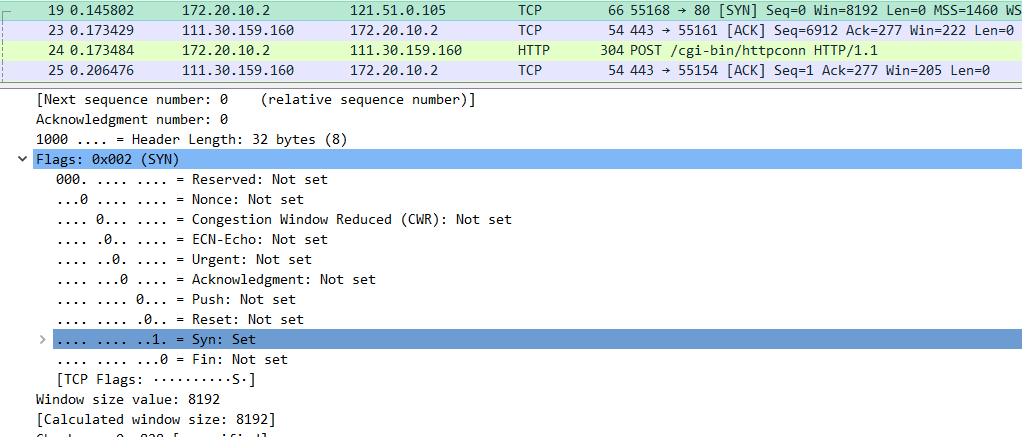
A:
(1) SYN sequence number =0
(2) … …1 … = Acknowledgment: Not Set
… … …1. = Syn: Set
5、(1)What is the sequence number of the SYNACK segment sent by gaia.cs.umass.edu to the client computer in reply to the SYN? What is the value of the ACKnowledgement field in the SYNACK segment? How did gaia.cs.umass.edu determine that value? What is it in the segment that identifies the segment as a SYNACK segment?(如图7所示)
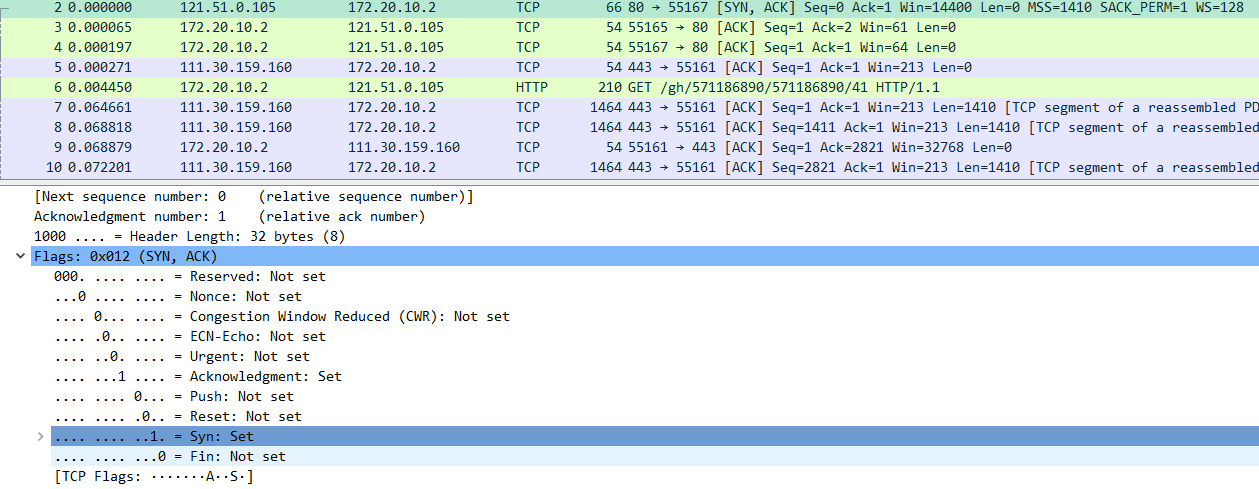
A:
(1)Sequence number: 0 (relative sequence number)
Acknowledgment number: 1 (relative ack number)
(2)ACKnowledgement value= initiate sequence number of the TCP SYN segment+1
(3)… …1 … = Acknowledgment: Set
… … …1. = Syn: Set
6、What is the sequence number of the TCP segment containing the HTTP POST command? Note that in order to find the POST command,you’ll need to dig into the packet content field at the bottom of the Wireshark window, looking for a segment with a “POST”
Within its DATA field?(如图8)
A:Sequence number: 1 (relative sequence number)
7、Consider the TCP segment containing the HTTP POST as the first segment in the TCP connection.What are the sequence numbers of the first six segments in the TCP connection?At what time was each segment sent?When was the ACK for each segment received?Given the difference between when each TCP segment was sent,and when its acknowledgement was received,what is the RTT value for each of the six segments?What is the EstimatedRTT value after the receipt of each ACK?Assume that the value of the EstimateRTT is equal to the measured RTT for the first segment,and then is computed using the EstimateRTT equation on page 242 for all subsequent segments.(如图9、10、11所示)
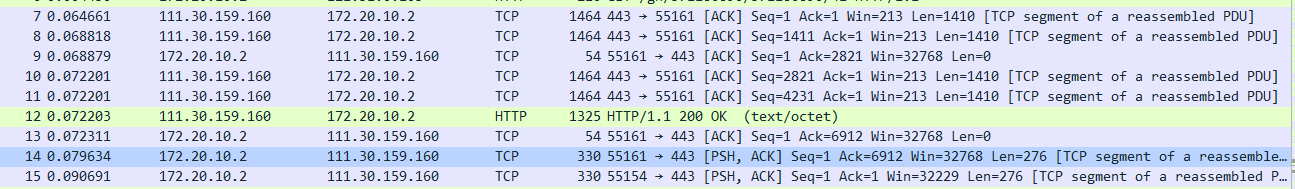
图9(包含HTTP POST前六个段)
A:(1)The sequence numbers of them respectively are 1、1411、2821、4231、1、1
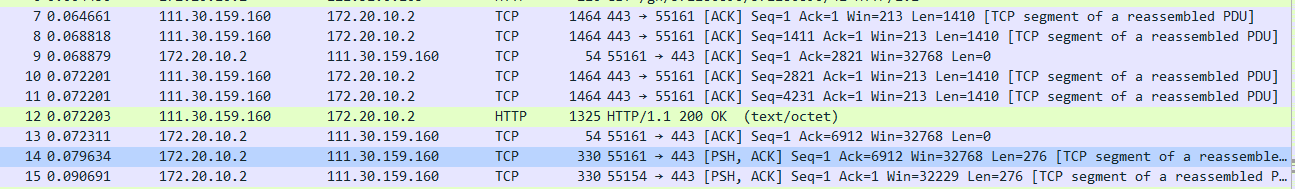
图10(HTTP POST前六个段)
(2)time:0.064661
0.068818
0.072201
0.072201
0.079634
0.090691
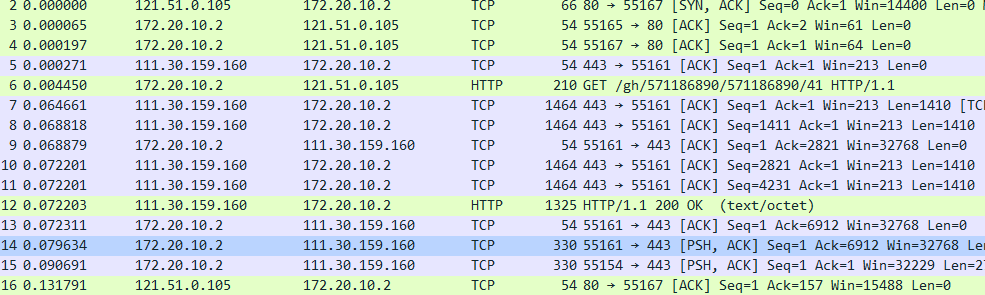
图11(包含HTTP POST中ACK的值)
(3)time:0.000065
0.000197
0.000271
0.068879
0.072311
0.131791
8、What is the length of each of the first six TCP segments?(如图12所示)
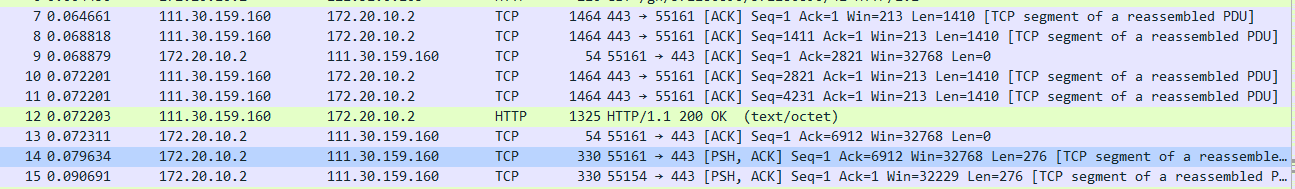
图12(TCP的长度)
A:Len:1410、1410、1410、1410、276、276
9、What is the minimum amount of available buffer space advertised at the received for the entire trace?Does the lack of receiver buffer space ever throttle the sender?(如图13所示)
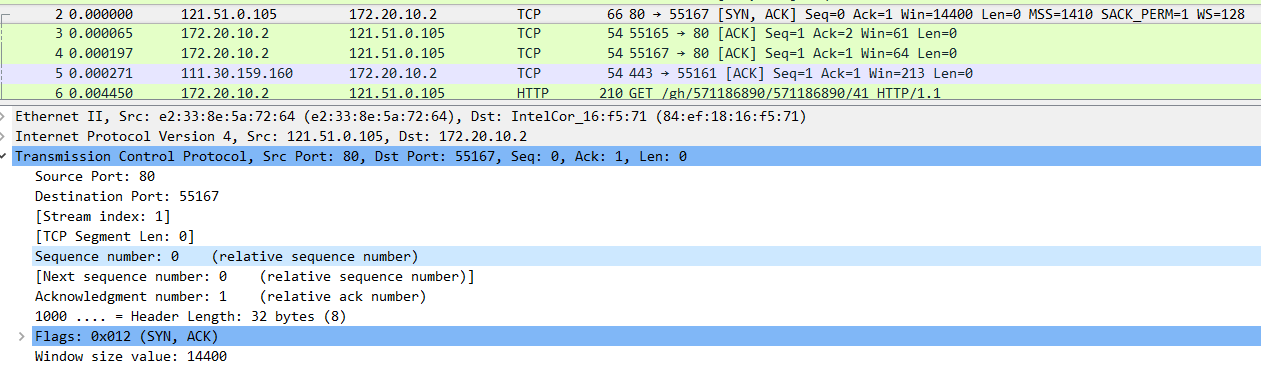
图13(Window的值)
A:Window size value: 14400
10、Are there any retransmitted segments in the trace file?What did you check for in order to answer this question?
A:There are no retransmitted segments in the trace file.We can verify this by checking the sequence numbers of the TCP segments in the trace file.In the Time-Sequence-Graph of this trace,all sequence numbers from the source to the destination are increasing monotonically with respect to time.If there is a retransmitted segment,the sequence number of this retransmitted segment should be smaller than those of its neighbouring segments.
11、How much data does the receiver typically acknowledge in an ACK?Can you identify cases where the receiver is ACKing every other received segment? (如表1所示)
表1
12、What is the throughput for the TCP connection?Explain how you calculated this value.
A:The TCP connection started to transmit data at segment 4,and end in segment 202.We can see from the figure below:
data1=1 byte t1=0.026477
data2=164091 bytes t2=5.455830
total data=164091-1=164090 bytes
It takes time:total time=5.455830-0.026477=5.429353 seconds
So the throughput for the TCP connection is the calculated as 164090/5.4294353=30.222 KByte/see
三、TCP congestion control in action
13、Use the Time-Sequence-Graph plotting tool to view the sequence number versus time plot of segments being sent from the client to the gaia.cs.umass.server.Can you identify where TCP’s slowstart phase begins and ends,and where congestion avoidance takes over?Comment on ways in which the measured data differs from the idealized behavior of TCP that we’ve studied in the text.
A:We can see from the figure above that TCP Slow Start begins at the start of the connection.The identification of the TCP slow start phase and congestion avoidance phase depends on the value of the congestion window size of this TCP sender,we can tell easily where TCP’s slow ends and where congestion avoidance takes over.
When answering the previous question,we can know that the TCP window size is larger than 8192 Bytes.But there is no data sent more than 8192 Bytes.It indicates before the end of the start phase,the application already stops transmitting.That is to say,the TCP’s slow ends and congesiton avoidance haven’t taken place.
最后
以上就是刻苦山水最近收集整理的关于陕西师范大学计网英文实验报告——TCP的全部内容,更多相关陕西师范大学计网英文实验报告——TCP内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复