提示:文章写完后,目录可以自动生成,如何生成可参考右边的帮助文档
FPGA信号处理系列文章——卷积编码与维特比译码
- 前言
- 卷积编码的概念和定义
- 卷积编码算法理解
- 卷积编码FPGA实现
- 维特比译码的说明
- 维特比译码算法理解
- 维特比译码的FPGA实现
前言
之前在北斗导航系统中的RDSS系统以及Galileo系统中接触到了其电文是有卷积编码的,这里我们就来回顾一下卷积编码和维特比译码的相关内容
卷积编码的概念和定义
通常以 (n, k, L) 来描述卷积编码
• k 表示编码器的 输入码元数
• n 表示编码器的 输出码元数
• L表示编码器的 约束长度
由输入的 k 个信息比特,得到 n 个编码结果,所以 编码效率 = k/n。约束长度 L 的意思是,编码结果不仅取决于当前输入的 k 比特信息,还取决于前 (L-1) 段时间内的信息位。在 k = 1 的条件下,编码器需要的 移位寄存器级数 m = L - 1。
Galileo中采用的卷积码参数为:
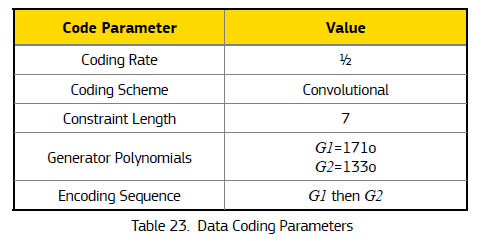
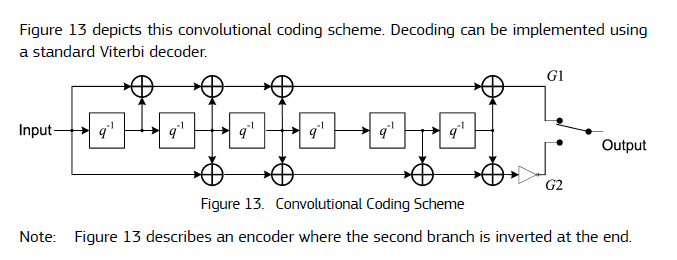
因此:Galileo 卷积编码 (n, k, L) 描述为(2,1,7)
这里有个特殊的地方:
第二分支出来的数据要反向,这是Galileo特有的
还有一个特点是,(2,1,7)卷积码的卷尾是6个0。
卷积编码算法理解
ICD的附录中有一个这样的例子
编码前: 244个bit
11111111 11110000 11001100 10101010 00000000 00001111 00110011 01010101
11100011 11101100 11011111 10001010 00011100 00010011 00100000 01110101
01010101 01100001 01100010 01100011 10101010 10011110 10011101 10011100
00011100 00100011 00001101 00111001 11011100 11101100 0000
编码后:
10001100 00011010 10101010 01110011 00110001 01011010 01101111 01011001
01111000 10010101 01010101 10001100 11001110 10100101 10010000 10100110
10000100 00000010 00000010 00011011 10011001 11101011 01011100 00011000
10111011 11111101 11111101 11100100 01100110 00010100 10100011 11100111
10100110 01100110 01101011 00010000 00011100 00011101 01010001 10101110
00111001 11101001 10010100 11101111 11100011 11100010 10101110 01010001
11111101 00111101 11110000 10101001 11011000 00110010 00111111 10000100
10010010 10010110 00100100 10101011 01001110
正好,我可以这个数据作为算法验证的数据
卷积编码的matlab程序,注意标红部分为额外取反处理
a = '1111111111110000110011001010101000000000000011110011001101010101111000111110110011011111100010100001110000010011001000000111010101010101011000010110001001100011101010101001111010011101100111000001110000100011000011010011100111011100111011000000';
for i = 1 : 244
msg(i)=str2num(a(i));
end
trel = poly2trellis(7,[171,133]); % Define trellis
code = convenc(msg,trel); % Encode
code(2:2:end) = not(code(2:2:end))
得出的结果与ICD上的一致。
卷积编码FPGA实现
卷积编码的verilog实现也非常简单,也就不多说了,直接上代码,与上面Galileo 卷积编码对应
module Convolutional_Coding_2_1_7(
input clk,
input encode_rst,
input data_in,
input nd,
output rdy,
output [1:0]data_out_v,
output data_out_s,
output rdy_s
);
wire [6:0]PolyA;
wire [6:0]PolyB;
reg [6:0]wA;
reg [6:0]wB;
reg [6:0]ShReg;
reg nd_d1;
reg nd_d2;
reg nd_d3;
assign PolyA = 7'b1_011_011;
assign PolyB = 7'b1_111_001;
always @(posedge clk)
if(encode_rst)
begin
ShReg <= 0;
end
else if(nd)
begin
ShReg[6] <= data_in;
ShReg[5:0] <= ShReg[6:1];
end
always @(posedge clk)
if(encode_rst)
begin
wA <= 0;
wB <= 0;
end
else
begin
wA <= PolyA & ShReg;
wB <= PolyB & ShReg;
end
assign data_out_v[0] = ^wA;
assign data_out_v[1] = ^wB;
always @(posedge clk)
if(encode_rst)
begin
nd_d1 <= 0;
nd_d2 <= 0;
nd_d3 <= 0;
end
else
begin
nd_d1 <= nd;
nd_d2 <= nd_d1;
nd_d3 <= nd_d2;
end
assign rdy = nd_d2;
assign rdy_s = nd_d2 | nd_d3;
assign data_out_s = nd_d2 ? data_out_v[0] : ~data_out_v[1];
维特比译码的说明
卷积编码解码的过程就是维特比译码,编码容易解码难。难道什么程度,难道xilinx 的viterbi ip都是要收费的就知道这个有多复杂了。
但我们可以先利用matlab提供的函数搞清楚先。
维特比解码分为硬判决和软判决
在无线通信系统中,编码后的数据经过调制由发射机发射出去,由接收机接收回来,一般来说接收机的ADC已经信号处理过程的中间数据都是有一定位宽的,将原始数据解调出来后送入译码器的数据保留了一定的幅度信息。硬判决只采用数据的符号为作为译码器的输入,而软判决将幅度信息也输入进去参与译码。
根据之前的经验,软判决一般采用3,4,5bit输入即可,再增加输入性能增加不明显,而且资源显著增加。性能软判决相比较硬判决灵敏度可能有个3-5dB的提升。(精确的理论分析见一些论文,实际工程与设计好坏也有关系)
维特比译码算法理解
维特比的matlab算法如下,注意几个地方
1、解码后的前42个为无效,与回溯深度tblen=42有关。
2、如果译码不是以数据流的形式进行,再数据结尾需要再补齐tblen*2个随机数据才行,不然会少输出tblen个解码数据
硬判决:
clc;clear all;close all;
a = '1111111111110000110011001010101000000000000011110011001101010101111000111110110011011111100010100001110000010011001000000111010101010101011000010110001001100011101010101001111010011101100111000001110000100011000011010011100111011100111011000000';
for i = 1 : 244
msg(i)=str2num(a(i));
end
%编码过程
trel = poly2trellis(7,[171,133]); % Define trellis
code = convenc(msg,trel); % Encode
code(488+1:488+42*2) = randi([0 1],42*2,1)';
code(2:2:end) = not(code(2:2:end))
%译码过程
tblen = 42;
code(2:2:end) = not(code(2:2:end))
decoded = vitdec(code,trel,tblen,'cont','hard');
plot(msg == decoded(43:end))
%decoded的前42个为无效,与tblen=42有关,所以输入需要多输入tblen*2个编码数据才行
软判决:
clc;clear all;close all;
a = '1111111111110000110011001010101000000000000011110011001101010101111000111110110011011111100010100001110000010011001000000111010101010101011000010110001001100011101010101001111010011101100111000001110000100011000011010011100111011100111011000000';
for i = 1 : 244
msg(i)=str2num(a(i));
end
tblen = 48;
trel = poly2trellis(7,[171,133]); % Define trellis
code = convenc(msg,trel); % Encode
code(488+1:488+tblen*2) = randi([0 1],tblen*2,1)';
%code(1:5) = 0;
%code(2:2:end) = not(code(2:2:end))
decoded1 = vitdec(code,trel,tblen,'cont','hard');
%decoded的前42个为无效,与tblen有关
% Map "0" bit to 1.0 and "1" bit to -1.0. Also add AWGN.
ucode = real(awgn(1-2*code, 2, 'measured'));
% Soft decision decoding with quantized inputs
[x,qcode] = quantiz(ucode,[1/(2^(8-1))-1:1/(2^(8-1)):1-1/(2^(8-1))],...
2^8-1:-1:0); % Values in qcode are between 0 and 2^8-1.
decoded2 = vitdec(qcode,trel,tblen,'cont','soft',8);
[n2,r2] = biterr(decoded2(tblen+1:end),msg(1:end));
disp(['The bit error rates are: ',num2str([r2])])
软判决,软判决对编码后的数据加噪声,来体现它的性能
clc;clear all;close all;
a = '1111111111110000110011001010101000000000000011110011001101010101111000111110110011011111100010100001110000010011001000000111010101010101011000010110001001100011101010101001111010011101100111000001110000100011000011010011100111011100111011000000';
for i = 1 : 244
msg(i)=str2num(a(i));
end
%编码过程
tblen = 48;
trel = poly2trellis(7,[171,133]); % Define trellis
code = convenc(msg,trel); % Encode
code(2:2:end) = not(code(2:2:end)) %galileo 定义独有
code(488+1:488+tblen*2) = randi([0 1],tblen*2,1)';
code(2:2:end) = not(code(2:2:end))
%硬判决
decoded1 = vitdec(code,trel,tblen,'cont','hard');
%decoded的前42个为无效,与tblen有关
% Map "0" bit to 1.0 and "1" bit to -1.0. Also add AWGN.
ucode = real(awgn(1-2*code, 3, 'measured'));
% Soft decision decoding with quantized inputs
[x,qcode] = quantiz(ucode,[1/(2^(8-1))-1:1/(2^(8-1)):1-1/(2^(8-1))],...
2^8-1:-1:0); % Values in qcode are between 0 and 2^8-1.
%软判决
decoded2 = vitdec(qcode,trel,tblen,'cont','soft',8);
[n2,r2] = biterr(decoded2(tblen+1:end),msg(1:end));
disp(['The bit error rates are: ',num2str([r2])])
维特比译码的FPGA实现
1、xilinx ip的维特比译码器
不交钱就不给你玩,不过幸好我以前玩过。我们可以看看里面的一些设置
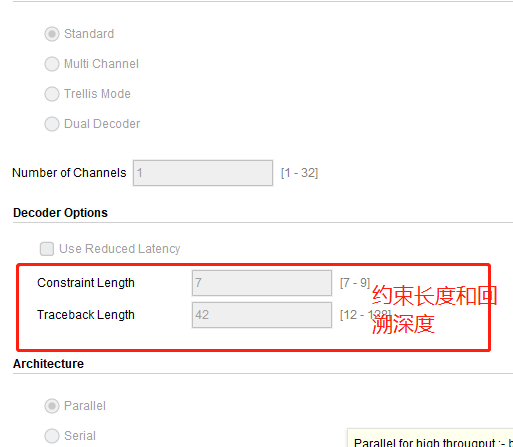
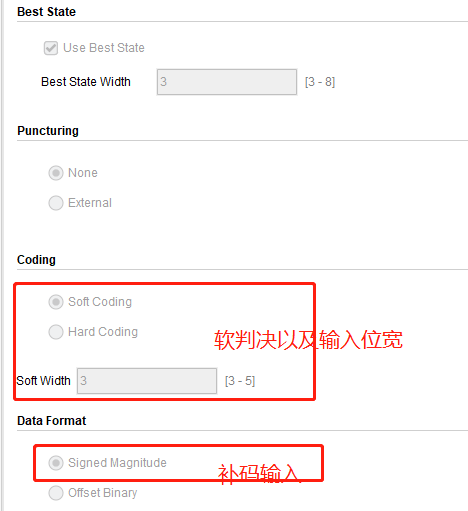
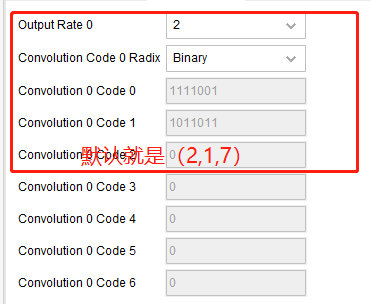
可以看到,也就这些参数的设置,所以如果能用ip的话就挺简单的
2、opencores网站上有一个开源项目

这个我也玩过,经过之前的验证,发现如果使用这个开源代码的话需要软判决位宽为6才能勉强和xilinx ip核的性能匹配上。有兴趣的小伙伴可以直接下载去验证下。
3、自己写
后面准备有空的时候,重新再去理解一下这个译码过程。当年虽然也花了些时间去理解,但始终云里雾里的感觉,忘的也差不多了,也许现在也不一定能看明白,到时候希望能搞明白点吧。有些东西可能过了几年回过头来看又有新的感悟呢
最后
以上就是健康云朵最近收集整理的关于FPGA信号处理系列文章——卷积编码与维特比译码前言卷积编码的概念和定义卷积编码算法理解卷积编码FPGA实现维特比译码的说明维特比译码算法理解维特比译码的FPGA实现的全部内容,更多相关FPGA信号处理系列文章——卷积编码与维特比译码前言卷积编码内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复