聚焦在 Twitter 上关于Apache Spark的数据, 这些是准备用于机器学习和流式处理应用的数据。 重点是如何通过分布式网络交换代码和数据,获得 串行化, 持久化 , 调度和缓存的实战经验 。 认真使用 Spark SQL, 交互性探索结构化和半结构化数据. Spark SQL 的基础数据结构是 Spark dataframe, Spark dataframe 受到了 Python Pandas dataframe 和R dataframe 的启发. 这是一个强大的数据结构, 有R 或Python 背景的数据科学家非常容易理解并喜欢上它.
主要关注以下几点:
• 连接 Twitter, 收集有关数据, 然后存储到各种格式中如 JSON ,CSV 以及 MongoDB这样的数据存储
• 使用Blaze and Odo分析数据, 一个Blaze的副产品库, 能够在各种源和目标之间建立连接并传输数据
• 引入 Spark dataframes 作为各个 Spark 模块交换数据的基础,同时使用 Spark SQL交互性探索数据
回顾数据密集型应用的架构
首先审视数据密集型应用架构,集中关注集成层以及获取、提炼和数据持久化迭代循环的基本运行. 这一循环命名为 5C. 5C 代表了connect, collect,correct, compose和consume. 这是集成层运行的基本过程以便于保证从Twitter 获取数据的质量和数量. 我们也将深入持久化层,建立如 MongoDB这样的数据存储方便后面数据的处理.
通过Blaze探索数据, 这是数据操控的一个Python 库, 通过Spark SQL使用 Spark dataframe, 完成交互性数据发现,感受一下三种 dataframe flavors 的细微差别。
下图指出了本章的重点, 集中在集成层和持久化层:
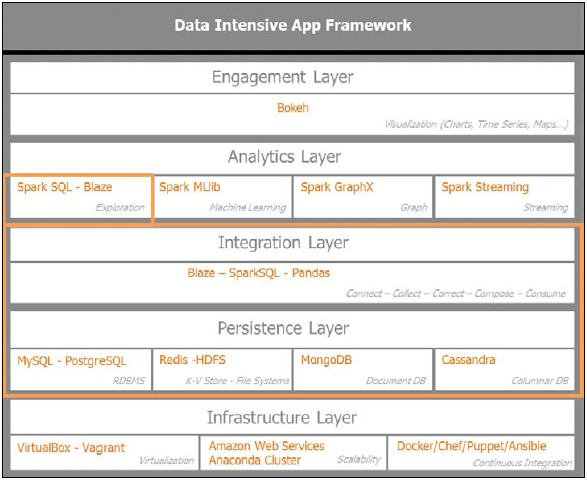
数据的序列化和反序列化
由于在通过API获取数据是的限制,我们需要数据存储. 数据在分布式集群上处理,我们需要一致的方式来保存状态以便于将来的提取使用。现在定义序列化, 持久化, 调度和缓存.
序列化一个Python对象是将它转换一个字节流. 该Python 对象在程序挂掉的时候能够通过反序列化提取.序列化后的 Python 对象在网络上传输或者存在持久化存储中. 反序列化是其逆运算将字节流转化为初始的 Python 对象所以程序能够从保存的状态中提取。 Python中最流行的序列化库是Pickle. 事实上,PySpark命令将pickled 的数据传输到多个工作节点.
持久化 将程序的状态数据保存到硬盘或内存,因而在离开或重启时继续使用。把一个Python 对象从内存保存到文件或数据库,在以后加载的时候拥有相同的状态。
调度 是在多核或者分布式系统中在网络TCP连接上发送 Python 代码和数据.
缓存 是将一个Python 对象转化为内存中的字符串可以作为字典中的关键字. Spark 支持将数据放入集群范围的内存缓冲区. 这在数据重复访问时非常有用,例如查询一个小引用的数据集或者象 Google PageRank那样的迭代算法.
缓存是Spark中非常关键的一个概念,允许我们将RDDs 存入内存或者溢出到硬盘 . 缓存策略的选择依赖于数据的线性程度或者RDD转换的DAG ,这样可以最小化 shuffle 或跨网络数据交换.Spark 为了获得更好的性能,需要注意数据shuffling. 一个好的分区策略和 RDD 缓存, 避免不必要的操作, 可以导致Spark更好的性能.
获取和存储数据
在深入如MongoDB这样的数据库存储之前,先看一下广泛使用的文件存储 : CSV和JSON文件存储. 这两种格式被广泛使用的主要原因: 可读性好, 简单, 轻度关联, 并容易使用.
在CSV中持久化数据
CSV 是轻量级可读易用的格式. 拥有已分隔的文本列和内在表格制式。Python提供了强健的csv库能将 cvs文件序列化为一个Python的字典. 为了我们的程序方便, 写了一个 python类来管理CSV格式中 数据的存储,和从CSV中读取数据. 看一下 IO_csv 类的代码. init 部分 实例化了文件路径,文件名和文件后缀(本例中, .csv):
class IO_csv(object):
def __init__(self, filepath, filename, filesuffix='csv'):
self.filepath = filepath # /path/to/file without the /'
at the end
self.filename = filename # FILE_NAME
self.filesuffix = filesuffix
该类的存储方法使用了tuple 和 csv 文件的头字段作为scheme来持久化数据。如果csv文件存在,则追加数据,否则创建:
def save(self, data, NTname, fields):
# NTname = Name of the NamedTuple
# fields = header of CSV - list of the fields name
NTuple = namedtuple(NTname, fields)
if os.path.isfile('{0}/{1}.{2}'.format(self.filepath, self.
filename, self.filesuffix)):
# Append existing file
with open('{0}/{1}.{2}'.format(self.filepath, self.
filename, self.filesuffix), 'ab') as f:
writer = csv.writer(f)
# writer.writerow(fields) # fields = header of CSV
writer.writerows([row for row in map(NTuple._make,
data)])
# list comprehension using map on the NamedTuple._
make() iterable and the data file to be saved
# Notice writer.writerows and not writer.writerow
(i.e. list of multiple rows sent to csv file
else:
# Create new file
with open('{0}/{1}.{2}'.format(self.filepath, self.
filename, self.filesuffix), 'wb') as f:
writer = csv.writer(f)
writer.writerow(fields) # fields = header of CSV -
list of the fields name
writer.writerows([row for row in map(NTuple._make,
data)])
# list comprehension using map on the NamedTuple._make() iterable and the data file to be saved
# Notice writer.writerows and not writer.writerow
(i.e. list of multiple rows sent to csv file该类的加载方法使用了tuple 和 csv 文件的头字段使用一致的schema来提取数据。 加载方法使用生成器来提高内存的有效性,使用yield 返回:
def load(self, NTname, fields):
# NTname = Name of the NamedTuple
# fields = header of CSV - list of the fields name
NTuple = namedtuple(NTname, fields)
with open('{0}/{1}.{2}'.format(self.filepath,self.filename,self.filesuffix),'rU') as f:
reader = csv.reader(f)
for row in map(NTuple._make, reader):
# Using map on the NamedTuple._make() iterable and the reader file to be loaded
yield row我们使用tuple解析tweet保存到csv或者从csv中提取数据:
fields01 = ['id', 'created_at', 'user_id', 'user_name', 'tweet_text','url']
Tweet01 = namedtuple('Tweet01',fields01)
def parse_tweet(data):
"""
Parse a ``tweet`` from the given response data.
"""
return Tweet01(
id=data.get('id', None),
created_at=data.get('created_at', None),
user_id=data.get('user_id', None),
user_name=data.get('user_name', None),
tweet_text=data.get('tweet_text', None),
url=data.get('url')
)
在 JSON中持久化
JSON 是互联网应用中使用最广泛的数据格式之一. 所有我们使用的API,Twitter, GitHub, 和Meetup, 都通过JSON格式发送数据. JSON 格式比 XML格式要轻,可读性好,在JSON 中内嵌模式. 对于CSV 格式, 所有记录遵从相同的表结构,而JSON 的结构能够变化,是半结构化的,一条JSON 记录能够映射成Python中的字典。 看一下 IO_json类的代码. init 部分例化了文件路径,文件名和文件后缀(本例中,.json):
class IO_json(object):
def __init__(self, filepath, filename, filesuffix='json'):
self.filepath = filepath # /path/to/file without the /'
at the end
self.filename = filename # FILE_NAME
self.filesuffix = filesuffix
# self.file_io = os.path.join(dir_name, .'.join((base_
filename, filename_suffix)))
该类的save方法使用utf-8编码来保证数据读写的兼容性。 如果JSON存在, 则追加数据否则创建:
def save(self, data):
if os.path.isfile('{0}/{1}.{2}'.format(self.filepath, self.
filename, self.filesuffix)):
# Append existing file
with io.open('{0}/{1}.{2}'.format(self.filepath, self.filename, self.filesuffix), 'a', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write(unicode(json.dumps(data, ensure_ascii=
False))) # In python 3, there is no "unicode" function
# f.write(json.dumps(data, ensure_ascii= False)) #
create a " escape char for " in the saved file
else:
# Create new file
with io.open('{0}/{1}.{2}'.format(self.filepath, self.filename, self.filesuffix), 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write(unicode(json.dumps(data, ensure_ascii=
False)))
# f.write(json.dumps(data, ensure_ascii= False))
这个类的load 方法返回了读取的文件 , 获取json数据需要调用 json.loads函数:
def load(self):
with io.open('{0}/{1}.{2}'.format(self.filepath, self.filename, self.filesuffix), encoding='utf-8') as f:
return f.read()
搭建MongoDB
鉴于存储所收集信息的重要性,搭建MongoDB 作为我们的文档存储数据库 . 所有采集的信息是 JSON 格式, MongoDB 以 BSON (short for Binary JSON)格式信息, 因此是一个自然的选择.
现在完成下列步骤:
• 安装MongoDB 服务器和客户端
• 运行MongoDB server
• 运行 Mongo client
• 安装PyMongo driver
• 创建 Python Mongo client
安装MongoDB服务器和客户端
执行如下步骤安装 MongoDB 包:
1. 使用包管理工具导入公钥(in our
case, Ubuntu’s apt),命令如下:
sudo apt-key adv --keyserver hkp://keyserver.ubuntu.com:80 --recv
7F0CEB10 - 创建 MongoDB 的文件列表,命令如下. :
echo "deb http://repo.mongodb.org/apt/ubuntu "$("lsb_release
-sc)"/ mongodb-org/3.0 multiverse" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.
list.d/mongodb-org-3.0.list
3.升级本地包的数据库:
sudo apt-get update4.安装MongoDB 的最新稳定版:
sudo apt-get install -y mongodb-org运行MongoDB服务器
启动MongoDB server:
1. 启动MongoDB server, 命令如下:
sudo service mongodb start
- 检查mongod 是否正常启动:
an@an-VB:/usr/bin$ ps -ef | grep mongo
mongodb
967 1 4 07:03 ? 00:02:02 /usr/bin/mongod
--config /etc/mongod.conf
an
3143 3085 0 07:45 pts/3 00:00:00 grep --color=auto
mongo
In 在本例中,mongodb 运行在967进程.
3. The mongod server 监听默认端口27017 可以在配置文件中修改.
4. 检查/var/log/mongod/mongod.log 日志文件的内容:
an@an-VB:/var/lib/mongodb$ ls -lru
total 81936
drwxr-xr-x 2 mongodb nogroup 4096 Apr 25 11:19 _tmp
-rw-r--r-- 1 mongodb nogroup 69 Apr 25 11:19 storage.bson
-rwxr-xr-x 1 mongodb nogroup 5 Apr 25 11:19 mongod.lock
-rw------- 1 mongodb nogroup 16777216 Apr 25 11:19 local.ns
-rw------- 1 mongodb nogroup 67108864 Apr 25 11:19 local.0
drwxr-xr-x 2 mongodb nogroup 4096 Apr 25 11:19 journal
5. 停止mongodb 的服务器, 命令如下:
sudo service mongodb stop运行Mongo客户端
在控制台运行Mongo client 很简单,命令如下:
an@an-VB:/usr/bin$ mongo
MongoDB shell version: 3.0.2
connecting to: test
Server has startup warnings:
2015-05-30T07:03:49.387+0200 I CONTROL [initandlisten]
2015-05-30T07:03:49.388+0200 I CONTROL [initandlisten]
在mongo client console 提示下, 查看数据库的命令如下:
> show dbs
local 0.078GB
test 0.078GB
选择 test数据库:
> use test
switched to db test
在数据库中显示 collections:
> show collections
restaurants
system.indexes
我们查看 restaurant collection 中的纪录:
> db.restaurants.find()
{ "_id" : ObjectId("553b70055e82e7b824ae0e6f"), "address : { "building
: "1007", "coord" : [ -73.856077, 40.848447 ], "street : "Morris Park
Ave", "zipcode : "10462 }, "borough : "Bronx", "cuisine : "Bakery",
"grades : [ { "grade : "A", "score" : 2, "date" : ISODate("2014-
03-03T00:00:00Z") }, { "date" : ISODate("2013-09-11T00:00:00Z"),
"grade : "A", "score" : 6 }, { "score" : 10, "date" : ISODate("2013-
01-24T00:00:00Z"), "grade : "A }, { "date" : ISODate("2011-11-
23T00:00:00Z"), "grade : "A", "score" : 9 }, { "date" : ISODate("2011-
03-10T00:00:00Z"), "grade : "B", "score" : 14 } ], "name : "Morris
Park Bake Shop", "restaurant_id : "30075445" }安装PyMongo driver
在anaconda 中安装mongodb的Python驱动也很简单:
conda install pymongo
创建 MongoDB的Python client
我们创建一个 IO_mongo 类用来收集数据 存储采集的数据 提取保存的数据. 为了创建mongo client, 需要import pymongo. 连接本地端口 27017命令如下:
from pymongo import MongoClient as MCli
class IO_mongo(object):
conn={'host':'localhost', 'ip':'27017'}我们的类初始化了客户端连接, 数据库 (本例中, twtr_db),和被访问连接的collection (本例中, twtr_coll):
def __init__(self, db='twtr_db', coll='twtr_coll', **conn ):
# Connects to the MongoDB server
self.client = MCli(**conn)
self.db = self.client[db]
self.coll = self.db[coll]save方法插入新的纪录:
def save(self, data):
#Insert to collection in db
return self.coll.insert(data) load 方法根据规则提取数据. 在数据量大的情况下 返回游标:
def load(self, return_cursor=False, criteria=None, projection=None):
if criteria is None:
criteria = {}
if projection is None:
cursor = self.coll.find(criteria)
else:
cursor = self.coll.find(criteria, projection)
# Return a cursor for large amounts of data
if return_cursor:
return cursor
else:
return [ item for item in cursor ]
从Twitter汲取数据
每个社交网络都有自己的限制和挑战, 一个主要的障碍就是强加的流量限制. 在长连接或重复执行时要有暂停, 必须要避免重复数据.我们重新设计了连接程序来关注流量限制。
TwitterAPI 类根据查询条件来搜索和采集,我们已经添加了如下操作:
•日志能力,使用 Python logging 库在程序失败时纪录错误和警告
• 使用MongoDB 的持久化能力,象使用 IO_json 操作JSON 文件那样操作 IO_mongo 类
• API 流量限制和错误管理能力 , 保证我们弹性调用 Twitter 而不会被认为是恶意攻击
步骤如下:
1. 通过证书初始化Twitter API 的实例:
class TwitterAPI(object):
"""
TwitterAPI class allows the Connection to Twitter via OAuth
once you have registered with Twitter and receive the
necessary credentials
"""
def __init__(self):
consumer_key = 'get_your_credentials'
consumer_secret = get your_credentials'
access_token = 'get_your_credentials'
access_secret = 'get your_credentials'
self.consumer_key = consumer_key
self.consumer_secret = consumer_secret
self.access_token = access_token
self.access_secret = access_secret
self.retries = 3
self.auth = twitter.oauth.OAuth(access_token, access_
secret, consumer_key, consumer_secret)
self.api = twitter.Twitter(auth=self.auth)2 设置日志等级,初始化 logger:
° logger.debug(debug message)
° logger.info(info message)
° logger.warn(warn message)
° logger.error(error message)
° logger.critical(critical message)3设置日志路径和内容格式:
# logger initialisation
appName = 'twt150530'
self.logger = logging.getLogger(appName)
#self.logger.setLevel(logging.DEBUG)
# create console handler and set level to debug
logPath = '/home/an/spark/spark-1.3.0-bin-hadoop2.4/examples/AN_Spark/data'
fileName = appName
fileHandler = logging.FileHandler("{0}/{1}.log".
format(logPath, fileName))
formatter = logging.Formatter('%(asctime)s - %(name)s -
%(levelname)s - %(message)s')
fileHandler.setFormatter(formatter)
self.logger.addHandler(fileHandler)
self.logger.setLevel(logging.DEBUG)4.初始化JSON文件的持久化指令:
# Save to JSON file initialisation
jsonFpath = '/home/an/spark/spark-1.3.0-bin-hadoop2.4/
examples/AN_Spark/data'
jsonFname = 'twtr15053001'
self.jsonSaver = IO_json(jsonFpath, jsonFname)5.初始化 MongoDB database 和 collection :
# Save to MongoDB Intitialisation
self.mongoSaver = IO_mongo(db='twtr01_db', coll='twtr01_
coll') 6.searchTwitter 方法 根据指定的查询条件搜索:
def searchTwitter(self, q, max_res=10,**kwargs):
search_results = self.api.search.tweets(q=q, count=10,
**kwargs)
statuses = search_results['statuses']
max_results = min(1000, max_res)
for _ in range(10):
try:
next_results = search_results['search_metadata']
['next_results']
# self.logger.info('info' in searchTwitter - next_
results:%s'% next_results[1:])
except KeyError as e:
self.logger.error('error' in searchTwitter: %s',%(e))
break
# next_results = urlparse.parse_qsl(next_results[1:])
# python 2.7
next_results = urllib.parse.parse_qsl(next_results[1:])
# self.logger.info('info' in searchTwitter - next_
results[max_id]:', next_results[0:])
kwargs = dict(next_results)
# self.logger.info('info' in searchTwitter - next_
results[max_id]:%s'% kwargs['max_id'])
search_results = self.api.search.tweets(**kwargs)
statuses += search_results['statuses']
self.saveTweets(search_results['statuses'])
if len(statuses) > max_results:
self.logger.info('info' in searchTwitter - got %i tweets - max: %i' %(len(statuses), max_results))
break
return statuses7.saveTweets 方法将所选的tweets 保存为JSON 存入MongoDB:
def saveTweets(self, statuses):
# Saving to JSON File
self.jsonSaver.save(statuses)
# Saving to MongoDB
for s in statuses:
self.mongoSaver.save(s)8.parseTweets 方法从Twitter API 提供的大量信息中提取关键的 tweet 信息:
def parseTweets(self, statuses):
return [ (status['id'],
status['created_at'],
status['user']['id'],
status['user']['name']
status['text''text'],
url['expanded_url'])
for status in statuses
for url in status['entities']['urls']
]9.getTweets 方法调用searchTwitter,保证API 调用的稳定性并重点关注速率限制。代码如下:
def getTweets(self, q, max_res=10):
"""
Make a Twitter API call whilst managing rate limit and errors.
"""
def handleError(e, wait_period=2, sleep_when_rate_
limited=True):
if wait_period > 3600: # Seconds
self.logger.error('Too many retries in getTweets:
%s', %(e))
raise e
if e.e.code == 401:
self.logger.error('error 401 * Not Authorised * in
getTweets: %s', %(e))
return None
elif e.e.code == 404:
self.logger.error('error 404 * Not Found * in
getTweets: %s', %(e))
return None
elif e.e.code == 429:
self.logger.error('error 429 * API Rate Limit
Exceeded * in getTweets: %s', %(e))
if sleep_when_rate_limited:
self.logger.error('error 429 * Retrying in 15
minutes * in getTweets: %s', %(e))
sys.stderr.flush()
time.sleep(60*15 + 5)
self.logger.info('error 429 * Retrying now *
in getTweets: %s', %(e))
return 2
else:
raise e # Caller must handle the rate limiting issue
elif e.e.code in (500, 502, 503, 504):
self.logger.info('Encountered %i Error. Retrying
in %i seconds' % (e.e.code, wait_period))
time.sleep(wait_period)
wait_period *= 1.5
return wait_period
else:
self.logger.error('Exit - aborting - %s', %(e))
raise e
10.根据指定的参数查询调用searchTwitter API . 如果遇到了任何错误, 由handleError 方法处理:
while True:
try:
self.searchTwitter( q, max_res=10)
except twitter.api.TwitterHTTPError as e:
error_count = 0
wait_period = handleError(e, wait_period)
if wait_period is None:
return使用Blaze探索数据
Blaze是个由Continuum.io,开发的 Python库 ,利用了 Python Numpy arrays 和 Pandas dataframe. Blaze 扩展到多核计算, 而Pandas 和 Numpy 是单核的.
Blaze 为各种后端提供了统一适配的一致性用户接口. Blaze 精心安排了:
• Data: 不同数据存储的无缝交换如 CSV, JSON, HDF5,
HDFS, 和 Bcolz 文件
• Computation: 对不同的后端采用同样的查询方式如 Spark, MongoDB, Pandas, or SQL Alchemy.
• Symbolic expressions: 在一定范围内使用了与Pandas类似的语法来抽象表达 join, group-by, filter,
selection, 和注入,参考R语言实现了
split-apply-combine 方法.
Blaze 表达式 和Spark RDD 数据转换一致,采用延迟计算.
深入 Blaze首先要引入所需的库: numpy, pandas, blaze 和 odo. Odo 是 Blaze的一个派生品保证了各种数据后端的数据移植,命令如下:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from blaze import Data, by, join, merge
from odo import odo
BokehJS successfully loaded.读取存储在CSV文件中解析过的tweets 生成Pandas Dataframe:
twts_csv:
twts_pd_df = pd.DataFrame(twts_csv_read, columns=Tweet01._fields)
twts_pd_df.head()
Out[65]:
id created_at user_id user_name tweet_text url
1 598831111406510082 2015-05-14 12:43:57 14755521
raulsaeztapia RT @pacoid: Great recap of @StrataConf EU in L...
http://www.mango-solutions.com/wp/2015/05/the-...
2 598831111406510082 2015-05-14 12:43:57 14755521
raulsaeztapia RT @pacoid: Great recap of @StrataConf EU in L...
http://www.mango-solutions.com/wp/2015/05/the-...
3 98808944719593472 2015-05-14 11:15:52 14755521
raulsaeztapia RT @alvaroagea: Simply @ApacheSpark http://t.c...
http://www.webex.com/ciscospark/
4 598808944719593472 2015-05-14 11:15:52 14755521
raulsaeztapia RT @alvaroagea: Simply @ApacheSpark http://t.c...
http://sparkjava.com/
运行Tweets Panda Dataframe 的 describe() 函数 获得数据集中的信心:
twts_pd_df.describe()
Out[66]:
id created_at user_id user_name tweet_text url
count 19 19 19 19 19 19
unique 7 7 6 6 6 7
top 598808944719593472 2015-05-14 11:15:52 14755521
raulsaeztapia RT @alvaroagea: Simply @ApacheSpark http://t.c...
http://bit.ly/1Hfd0Xm
freq 6 6 9 9 6 6简单的调用Data() 函数将Pandas dataframe 转化为一个 Blaze dataframe:
#
# Blaze dataframe
#
twts_bz_df = Data(twts_pd_df)通过传递schema 函数提取一个 Blaze dataframe 的schema 表达:
twts_bz_df.schema
Out[73]:
dshape("""{
id: ?string,
created_at: ?string,
user_id: ?string,
user_name: ?string,
tweet_text: ?string,
url: ?string
}""").dshape 函数给出一条记录和schema:
twts_bz_df.dshape
Out[74]:
dshape("""19 * {
id: ?string,
created_at: ?string,
user_id: ?string,
user_name: ?string,
tweet_text: ?string,
url: ?string
}""")打印Blaze dataframe 的内容:
twts_bz_df.data
Out[75]:
id created_at user_id user_name tweet_text url
1 598831111406510082 2015-05-14 12:43:57 14755521
raulsaeztapia RT @pacoid: Great recap of @StrataConf EU in L...
http://www.mango-solutions.com/wp/2015/05/the-...
2 598831111406510082 2015-05-14 12:43:57 14755521
raulsaeztapia RT @pacoid: Great recap of @StrataConf EU in L...
http://www.mango-solutions.com/wp/2015/05/the-...
...
18 598782970082807808 2015-05-14 09:32:39 1377652806
embeddedcomputer.nl RT @BigDataTechCon: Moving Rating
Prediction w... http://buff.ly/1QBpk8J
19 598777933730160640 2015-05-14 09:12:38 294862170 Ellen
Friedman I'm still on Euro time. If you are too check o...
http://bit.ly/1Hfd0Xm提取 tweet_text 字段,获得唯一的值:
twts_bz_df.tweet_text.distinct()
Out[76]:
tweet_text
0 RT @pacoid: Great recap of @StrataConf EU in L...
1 RT @alvaroagea: Simply @ApacheSpark http://t.c...
2 RT @PrabhaGana: What exactly is @ApacheSpark a...
3 RT @Ellen_Friedman: I'm still on Euro time. If...
4 RT @BigDataTechCon: Moving Rating Prediction w...
5 I'm still on Euro time. If you are too check o...从dataframe 中提取了多个字段 [‘id’, ‘user_name’,’tweet_text’] 并计算唯一的记录:
twts_bz_df[['id', 'user_name','tweet_text']].distinct()
Out[78]:
id user_name tweet_text
0 598831111406510082 raulsaeztapia RT @pacoid: Great recap of @
StrataConf EU in L...
1 598808944719593472 raulsaeztapia RT @alvaroagea: Simply @
ApacheSpark http://t.c...
2 598796205091500032 John Humphreys RT @PrabhaGana: What exactly
is @ApacheSpark a...
3 598788561127735296 Leonardo D'Ambrosi RT @Ellen_Friedman: I'm
still on Euro time. If...
4 598785545557438464 Alexey Kosenkov RT @Ellen_Friedman: I'm
still on Euro time. If...
5 598782970082807808 embeddedcomputer.nl RT @BigDataTechCon:
Moving Rating Prediction w...
6 598777933730160640 Ellen Friedman I'm still on Euro time. If
you are too check o...使用 Odo传输数据
Odo 是Blaze的一个衍生项目. 用于数据交换,保证了各种不同格式数据间的移植 (CSV, JSON, HDFS, and more) 并且跨越不同的数据库 (SQL 数据库, MongoDB, 等等) ,用法简单,Odo(source, target) 为了 传输到一个数据库,需要指定URL地址. 例如, MongoDB , 用法如下:
mongodb://username:password@hostname:port/database_name::collection_name
使用Odo 运行一些例子,这里通过读取CSV文件并创建一个 Blaze dataframe来展示Odo的用法:
filepath = csvFpath
filename = csvFname
filesuffix = csvSuffix
twts_odo_df = Data('{0}/{1}.{2}'.format(filepath, filename,
filesuffix))
计算 dataframe中的记录个数:
twts_odo_df.count()
Out[81]:
19
显示dataframe中最初的5条记录:
twts_odo_df.head(5)
Out[82]:
id created_at user_id user_name tweet_text url
0 598831111406510082 2015-05-14 12:43:57 14755521
raulsaeztapia RT @pacoid: Great recap of @StrataConf EU in L...
http://www.mango-solutions.com/wp/2015/05/the-...
2 598808944719593472 2015-05-14 11:15:52 14755521
raulsaeztapia RT @alvaroagea: Simply @ApacheSpark http://t.c... http://www.webex.com/ciscospark/
3 598808944719593472 2015-05-14 11:15:52 14755521
raulsaeztapia RT @alvaroagea: Simply @ApacheSpark http://t.c...
http://sparkjava.com/
4 598808944719593472 2015-05-14 11:15:52 14755521
raulsaeztapia RT @alvaroagea: Simply @ApacheSpark http://t.c...
https://www.sparkfun.com/从dataframe 中获得 dshape 的信息 , 这里得到记录的个数和 schema:
twts_odo_df.dshape
Out[83]:
dshape("var * {
id: int64,
created_at: ?datetime,
user_id: int64,
user_name: ?string,
tweet_text: ?string,
url: ?string
}""")将处理过的 Blaze dataframe 存入 JSON:
odo(twts_odo_distinct_df, '{0}/{1}.{2}'.format(jsonFpath, jsonFname,
jsonSuffix))
Out[92]:
<odo.backends.json.JSONLines at 0x7f77f0abfc50>转换JSON 文件为 CSV 文件:
odo('{0}/{1}.{2}'.format(jsonFpath, jsonFname, jsonSuffix), '{0}/{1}.{2}'.format(csvFpath, csvFname, csvSuffix))
Out[94]:
<odo.backends.csv.CSV at 0x7f77f0abfe10>使用Spark SQL探索数据
Spark SQL 是建立在Spark 核心之上的关系型查询引擎. Spark SQL 使用的查询优化叫 Catalyst.
关系型查询使用 SQL 或HiveQL 表达,在 JSON, CSV, 和各种数据库中查询. Spark SQL 为 RDD 函数式编程之上的Spark dataframes 提供了完整的声明式表达.
理解 Spark dataframe
从 @bigdata 而来的一个tweet 意味着 Spark SQL和 dataframes都可以使用了,参见图中下方的各种数据源. 在顶部, R作为一个新的语言在Scala, Java和Python之后将逐步被支持. 最终, Data Frame 机理遍布在 R, Python, 和 Spark 中.
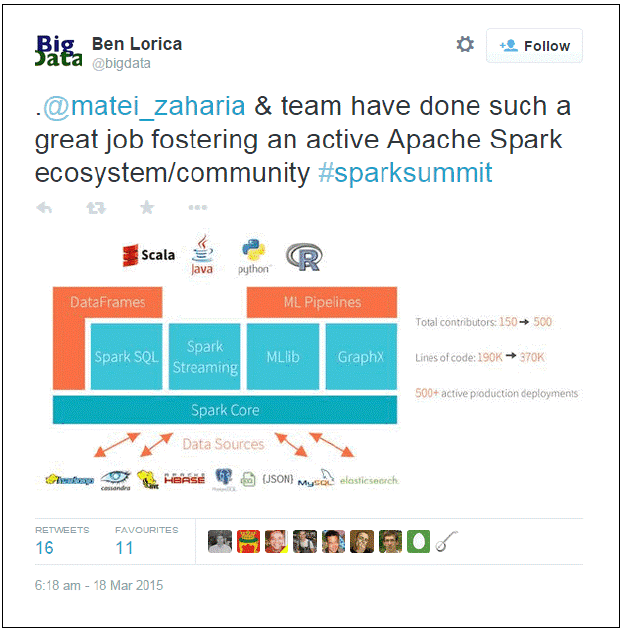
Spark dataframes 从 SchemaRDDs 中产生. 它结合了 RDD 和可以被Spark 推导 schema, 注册过的dataframe 才能被请求,允许通过直白的SQL 完成复杂嵌套的JSON 数据查询,同时支持 延迟计算, lineage,分区,和持久化.
通过 Spark SQL 查询数据, 首先要导入 SparkContext 和SQLContex:
from pyspark import SparkConf, SparkContext
from pyspark.sql import SQLContext, Row
In [95]:
sc
Out[95]:
<pyspark.context.SparkContext at 0x7f7829581890>
In [96]:
sc.master
Out[96]:
u'local[*]'
''In [98]:
# Instantiate Spark SQL context
sqlc = SQLContext(sc) 读取存储在 Odo中的JSON文件:
twts_sql_df_01 = sqlc.jsonFile ("/home/an/spark/spark-1.3.0-bin-
hadoop2.4/examples/AN_Spark/data/twtr15051401_distinct.json")
In [101]:
twts_sql_df_01.show()
created_at id tweet_text user_id
user_name
2015-05-14T12:43:57Z 598831111406510082 RT @pacoid: Great... 14755521
raulsaeztapia
2015-05-14T11:15:52Z 598808944719593472 RT @alvaroagea: S... 14755521
raulsaeztapia
2015-05-14T10:25:15Z 598796205091500032 RT @PrabhaGana: W... 48695135
John Humphreys
2015-05-14T09:54:52Z 598788561127735296 RT @Ellen_Friedma...
2385931712 Leonardo D'Ambrosi
2015-05-14T09:42:53Z 598785545557438464 RT @Ellen_Friedma... 461020977
Alexey Kosenkov
2015-05-14T09:32:39Z 598782970082807808 RT @BigDataTechCo...
1377652806 embeddedcomputer.nl
2015-05-14T09:12:38Z 598777933730160640 I'm still on Euro... 294862170
Ellen Friedman打印 Spark dataframe 的schema:
twts_sql_df_01.printSchema()
root
|-- created_at: string (nullable = true)
|-- id: long (nullable = true)
|-- tweet_text: string (nullable = true)
|-- user_id: long (nullable = true)
|-- user_name: string (nullable = true)从dataframe中选择 user_name 字段:
twts_sql_df_01.select('user_name').show()
user_name
raulsaeztapia
raulsaeztapia
John Humphreys
Leonardo D'Ambrosi
Alexey Kosenkov
embeddedcomputer.nl
Ellen Friedman将 dataframe 注册成一个表 ,在上执行一个 SQL 查询:
twts_sql_df_01.registerAsTable('tweets_01')可以处理更复杂的 JSON; 读取原始的 Twitter JSON 文件:
twts_sql_df_01_selection = sqlc.sql("SELECT * FROM tweets_01 WHERE
user_name = 'raulsaeztapia'")
In [109]:
twts_sql_df_01_selection.show()
created_at id tweet_text user_id
user_name
2015-05-14T12:43:57Z 598831111406510082 RT @pacoid: Great... 14755521
raulsaeztapia
2015-05-14T11:15:52Z 598808944719593472 RT @alvaroagea: S... 14755521
raulsaeztapia
Let's process some more complex JSON; we read the original Twitter JSON file:
tweets_sqlc_inf = sqlc.jsonFile(infile)
Spark SQL is able to infer the schema of a complex nested JSON file:
tweets_sqlc_inf.printSchema()
root
|-- contributors: string (nullable = true)
|-- coordinates: string (nullable = true)
|-- created_at: string (nullable = true)
|-- entities: struct (nullable = true)
| |-- hashtags: array (nullable = true)
| | |-- element: struct (containsNull = true)
| | | |-- indices: array (nullable = true)
| | | | |-- element: long (containsNull = true)
| | | |-- text: string (nullable = true)
| |-- media: array (nullable = true)
| | |-- element: struct (containsNull = true)
| | | |-- display_url: string (nullable = true)
| | | |-- expanded_url: string (nullable = true)
| | | |-- id: long (nullable = true)
| | | |-- id_str: string (nullable = true)
| | | |-- indices: array (nullable = true)
... (snip) ...
| |-- statuses_count: long (nullable = true)
| |-- time_zone: string (nullable = true)
| |-- url: string (nullable = true)
| |-- utc_offset: long (nullable = true)
| |-- verified: boolean (nullable = true)从dataframe 选定列中读取感兴趣的关键信息 (本例中, [‘created_at’, ‘id’, ‘text’, ‘user.id’, ‘user.name’, ‘entities.urls.expanded_url’]):
tweets_extract_sqlc = tweets_sqlc_inf[['created_at', 'id', 'text',
'user.id', 'user.name', 'entities.urls.expanded_url']].distinct()
In [145]:
tweets_extract_sqlc.show()
created_at id text id
name expanded_url
Thu May 14 09:32:... 598782970082807808 RT @BigDataTechCo...
1377652806 embeddedcomputer.nl ArrayBuffer(http:...
Thu May 14 12:43:... 598831111406510082 RT @pacoid: Great... 14755521
raulsaeztapia ArrayBuffer(http:...
Thu May 14 12:18:... 598824733086523393 @rabbitonweb spea...
...
Thu May 14 12:28:... 598827171168264192 RT @baandrzejczak... 20909005
Paweł Szulc ArrayBuffer()理解Spark SQL query optimizer
在 dataframe 中执行SQL 语句:
tweets_extract_sqlc_sel = sqlc.sql("SELECT * from Tweets_xtr_001 WHERE
name='raulsaeztapia'")看一下Spark SQL 执行查询计划的细节:
• 解析
• 分析
• 优化
• 物理查询
查询计划使用了 Spark SQL’s Catalyst 优化器. 为了冲查询部分生成编译过的字节码, Catalyst 优化器在物理计划评估后根据成本执行解析和优化.
在tweet中的解释:
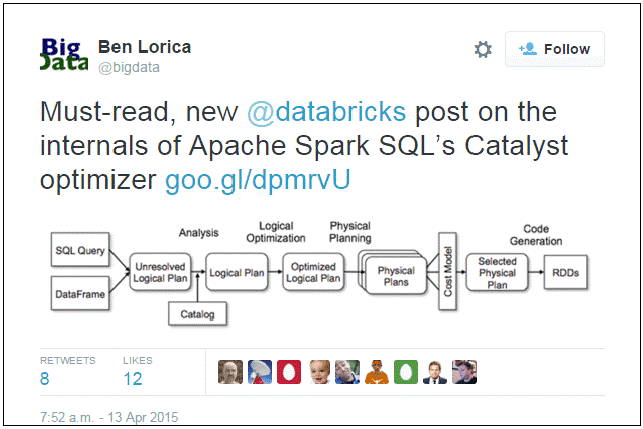
回顾一下代码, 在执行Spark SQL 查询时调用 .explain 函数, 给出了 Catalyst optimizer之行时的全部细节:
tweets_extract_sqlc_sel.explain(extended = True)
== Parsed Logical Plan ==
'Project [*]
'Filter ('name = raulsaeztapia)'name' 'UnresolvedRelation' [Tweets_
xtr_001], None
== Analyzed Logical Plan ==
Project [created_at#7,id#12L,text#27,id#80L,name#81,expanded_url#82]
Filter (name#81 = raulsaeztapia)
Distinct
Project [created_at#7,id#12L,text#27,user#29.id AS id#80L,user#29.
name AS name#81,entities#8.urls.expanded_url AS expanded_url#82]
Relation[contributors#5,coordinates#6,created_
at#7,entities#8,favorite_count#9L,favorited#10,geo#11,id#12L,id_
str#13,in_reply_to_screen_name#14,in_reply_to_status_id#15,in_reply_
to_status_id_str#16,in_reply_to_user_id#17L,in_reply_to_user_id_str#
18,lang#19,metadata#20,place#21,possibly_sensitive#22,retweet_count#2
3L,retweeted#24,retweeted_status#25,source#26,text#27,truncated#28,us
er#29] JSONRelation(/home/an/spark/spark-1.3.0-bin-hadoop2.4/examples/
AN_Spark/data/twtr15051401.json,1.0,None)
== Optimized Logical Plan ==
Filter (name#81 = raulsaeztapia)
Distinct
Project [created_at#7,id#12L,text#27,user#29.id AS id#80L,user#29.
name AS name#81,entities#8.urls.expanded_url AS expanded_url#82]
Relation[contributors#5,coordinates#6,created_
at#7,entities#8,favorite_count#9L,favorited#10,geo#11,id#12L,id_
str#13,in_reply_to_screen_name#14,in_reply_to_status_id#15,in_reply_
to_status_id_str#16,in_reply_to_user_id#17L,in_reply_to_user_id_str#
18,lang#19,metadata#20,place#21,possibly_sensitive#22,retweet_count#2
3L,retweeted#24,retweeted_status#25,source#26,text#27,truncated#28,us
er#29] JSONRelation(/home/an/spark/spark-1.3.0-bin-hadoop2.4/examples/
AN_Spark/data/twtr15051401.json,1.0,None)
== Physical Plan ==
Filter (name#81 = raulsaeztapia)
Distinct false
Exchange (HashPartitioning [created_at#7,id#12L,text#27,id#80L,name#
81,expanded_url#82], 200)
Distinct true
Project [created_at#7,id#12L,text#27,user#29.id AS id#80L,user#29.
name AS name#81,entities#8.urls.expanded_url AS expanded_url#82]
PhysicalRDD [contributors#5,coordinates#6,created_
at#7,entities#8,favorite_count#9L,favorited#10,geo#11,id#12L,id_str#13,in_reply_to_screen_name#14,in_reply_to_status_id#15,in_reply_to_status_id_str#16,in_reply_to_user_id#17L,in_reply_to_user_id_str#
18,lang#19,metadata#20,place#21,possibly_sensitive#22,retweet_count#2
3L,retweeted#24,retweeted_status#25,source#26,text#27,truncated#28,us
er#29], MapPartitionsRDD[165] at map at JsonRDD.scala:41
Code Generation: false
== RDD ==最后, 这里是查询的结果:
tweets_extract_sqlc_sel.show()
created_at id text id
name expanded_url
Thu May 14 12:43:... 598831111406510082 RT @pacoid: Great... 14755521
raulsaeztapia ArrayBuffer(http:...
Thu May 14 11:15:... 598808944719593472 RT @alvaroagea: S... 14755521
raulsaeztapia ArrayBuffer(http:...
In [148]:用Spark SQL 加载和处理 CSV files with Spark
使用 Spark 的 spark-csv_2.11:1.2.0 包. 在IPython Notebook 启动PySpark 需要准确地通过 –packages 指定 spark-csv 的包名:
$ IPYTHON_OPTS='notebook' /home/an/spark/spark-1.5.0-bin-hadoop2.6/bin/
pyspark --packages com.databricks:spark-csv_2.11:1.2.0
这触发了下面的输出; 可以看到 spark-csv 包使用的所有依赖:
an@an-VB:~/spark/spark-1.5.0-bin-hadoop2.6/examples/AN_Spark$ IPYTHON_
OPTS='notebook' /home/an/spark/spark-1.5.0-bin-hadoop2.6/bin/pyspark
--packages com.databricks:spark-csv_2.11:1.2.0
... (snip) ...
Ivy Default Cache set to: /home/an/.ivy2/cache
The jars for the packages stored in: /home/an/.ivy2/jars
:: loading settings :: url = jar:file:/home/an/spark/spark-1.5.0-bin-
hadoop2.6/lib/spark-assembly-1.5.0-hadoop2.6.0.jar!/org/apache/ivy/
core/settings/ivysettings.xml
com.databricks#spark-csv_2.11 added as a dependency
:: resolving dependencies :: org.apache.spark#spark-submit-parent;1.0
confs: [default]
found com.databricks#spark-csv_2.11;1.2.0 in central
found org.apache.commons#commons-csv;1.1 in central
found com.univocity#univocity-parsers;1.5.1 in central
:: resolution report :: resolve 835ms :: artifacts dl 48ms
:: modules in use:
com.databricks#spark-csv_2.11;1.2.0 from central in [default]
com.univocity#univocity-parsers;1.5.1 from central in [default]
org.apache.commons#commons-csv;1.1 from central in [default]
----------------------------------------------------------------
| | modules || artifacts |
| conf | number| search|dwnlded|evicted|| number|dwnlded|
----------------------------------------------------------------
| default | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 || 3 | 0
----------------------------------------------------------------
:: retrieving :: org.apache.spark#spark-submit-parent
confs: [default]
0 artifacts copied, 3 already retrieved (0kB/45ms)We are now ready to load our csv file and process it. Let’s first import the
SQLContext:
#
# Read csv in a Spark DF
#
sqlContext = SQLContext(sc)
spdf_in = sqlContext.read.format('com.databricks.spark.csv')
.options(delimiter=";").
options(header="true")
.options(header='true').load(csv_
in)访问从加载的CSV中创建的 dataframe 的schema:
In [10]:
spdf_in.printSchema()
root
|-- : string (nullable = true)
|-- id: string (nullable = true)
|-- created_at: string (nullable = true)
|-- user_id: string (nullable = true)
|-- user_name: string (nullable = true)
|-- tweet_text: string (nullable = true)检查 dataframe的列:
In [12]:
spdf_in.columns
Out[12]:
['', 'id', 'created_at', 'user_id', 'user_name', 'tweet_text']审视一下 dataframe 的内容:
In [13]:
spdf_in.show()
+---+------------------+--------------------+----------+--------------
----+--------------------+
| | id| created_at| user_id| user_
name| tweet_text|
+---+------------------+--------------------+----------+--------------
----+--------------------+
| 0|638830426971181057|Tue Sep 01 21:46:...|3276255125| True
Equality|ernestsgantt: Bey...|
| 1|638830426727911424|Tue Sep 01 21:46:...|3276255125| True
Equality|ernestsgantt: Bey...|
| 2|638830425402556417|Tue Sep 01 21:46:...|3276255125| True
Equality|ernestsgantt: Bey...|
... (snip) ...
| 41|638830280988426250|Tue Sep 01 21:46:...| 951081582| Jack
Baldwin|RT @cloudaus: We ...|
| 42|638830276626399232|Tue Sep 01 21:46:...| 6525302|Masayoshi
Nakamura|PynamoDB使使使使使使使 |
+---+------------------+--------------------+----------+--------------
----+--------------------+
only showing top 20 rows通过Spark SQL查询MangoDB
有两个方法完成MongoDB 和Spark的交互: 首先是通过 Hadoop MongoDB connector, 第二种的直接访问.
第一种方法需要搭建一个 Hadoop 环境才能从
Hadoop MongoDB connector中完成查询. onnector
托管在GitHub 上 https://github.com/mongodb/mongo-hadoop/
wiki/Spark-Usage.
MongoDB 发表了一系列的官方博客描述了真实的使用场景:
• Using MongoDB with Hadoop & Spark: Part 1 - Introduction & Setup (https://
www.mongodb.com/blog/post/using-mongodb-hadoop-spark-part-1-
introduction-setup)
• Using MongoDB with Hadoop and Spark: Part 2 - Hive Example (https://www.
mongodb.com/blog/post/using-mongodb-hadoop-spark-part-2-hive-
example)
• Using MongoDB with Hadoop & Spark: Part 3 - Spark Example & Key Takeaways
(https://www.mongodb.com/blog/post/using-mongodb-hadoop-spark-
part-3-spark-example-key-takeaways)
搭建一个完整的 Hadoop 环境是个力气活. 使用第二种方法,利用Stratio开发并维护的spark-mongodb ,这是托管在Spark.packages.org.上的 Stratio spark-mongodb 包. 该包的版本和相关信息可以从 spark.packages.org :
Releases
Version: 0.10.1 ( 8263c8 | zip | jar ) / Date: 2015-11-18 / License:
Apache-2.0 / Scala version: 2.10
(http://spark-packages.org/package/Stratio/spark-mongodb)
在IPython Notebook 中启动PySpark, 同时准确指定spark-mongodb 的包名:
$ IPYTHON_OPTS='notebook' /home/an/spark/spark-1.5.0-bin-hadoop2.6/bin/
pyspark --packages com.stratio.datasource:spark-mongodb_2.10:0.10.1这将触发下面的输出; 可以看到 spark-mongodb 包的所有依赖:
an@an-VB:~/spark/spark-1.5.0-bin-hadoop2.6/examples/AN_Spark$ IPYTHON_
OPTS='notebook' /home/an/spark/spark-1.5.0-bin-hadoop2.6/bin/pyspark
--packages com.stratio.datasource:spark-mongodb_2.10:0.10.1
... (snip) ...
Ivy Default Cache set to: /home/an/.ivy2/cache
The jars for the packages stored in: /home/an/.ivy2/jars
:: loading settings :: url = jar:file:/home/an/spark/spark-1.5.0-bin-
hadoop2.6/lib/spark-assembly-1.5.0-hadoop2.6.0.jar!/org/apache/ivy/
core/settings/ivysettings.xml
com.stratio.datasource#spark-mongodb_2.10 added as a dependency
:: resolving dependencies :: org.apache.spark#spark-submit-parent;1.0
confs: [default]
found com.stratio.datasource#spark-mongodb_2.10;0.10.1 in central
[W 22:10:50.910 NotebookApp] Timeout waiting for kernel_info reply
from 764081d3-baf9-4978-ad89-7735e6323cb6
found org.mongodb#casbah-commons_2.10;2.8.0 in central
found com.github.nscala-time#nscala-time_2.10;1.0.0 in central
found joda-time#joda-time;2.3 in central
found org.joda#joda-convert;1.2 in central
found org.slf4j#slf4j-api;1.6.0 in central
found org.mongodb#mongo-java-driver;2.13.0 in central
found org.mongodb#casbah-query_2.10;2.8.0 in central
found org.mongodb#casbah-core_2.10;2.8.0 in central
downloading https://repo1.maven.org/maven2/com/stratio/datasource/
park-mongodb_2.10/0.10.1/spark-mongodb_2.10-0.10.1.jar...
[SUCCESSFUL ] com.stratio.datasource#spark-
mongodb_2.10;0.10.1!spark-mongodb_2.10.jar (3130ms)
downloading https://repo1.maven.org/maven2/org/mongodb/casbah-
ommons_2.10/2.8.0/casbah-commons_2.10-2.8.0.jar...
[SUCCESSFUL ] org.mongodb#casbah-commons_2.10;2.8.0!casbah-
commons_2.10.jar (2812ms)
downloading https://repo1.maven.org/maven2/org/mongodb/casbah-
uery_2.10/2.8.0/casbah-query_2.10-2.8.0.jar...
[SUCCESSFUL ] org.mongodb#casbah-query_2.10;2.8.0!casbah-query_2.10.
jar (1432ms)
downloading https://repo1.maven.org/maven2/org/mongodb/casbah-
ore_2.10/2.8.0/casbah-core_2.10-2.8.0.jar...
[SUCCESSFUL ] org.mongodb#casbah-core_2.10;2.8.0!casbah-core_2.10.
jar (2785ms)
downloading https://repo1.maven.org/maven2/com/github/nscala-time/
scala-time_2.10/1.0.0/nscala-time_2.10-1.0.0.jar...
[SUCCESSFUL ] com.github.nscala-time#nscala-time_2.10;1.0.0!nscala-
time_2.10.jar (2725ms)
downloading https://repo1.maven.org/maven2/org/slf4j/slf4j-api/1.6.0/
slf4j-api-1.6.0.jar ...
[SUCCESSFUL ] org.slf4j#slf4j-api;1.6.0!slf4j-api.jar (371ms)
downloading https://repo1.maven.org/maven2/org/mongodb/mongo-java-
driver/2.13.0/mongo-java-driver-2.13.0.jar ...
[SUCCESSFUL ] org.mongodb#mongo-java-driver;2.13.0!mongo-java-
driver.jar (5259ms)
downloading https://repo1.maven.org/maven2/joda-time/joda-time/2.3/
joda-time-2.3.jar ...
[SUCCESSFUL ] joda-time#joda-time;2.3!joda-time.jar (6949ms)
downloading https://repo1.maven.org/maven2/org/joda/joda-convert/1.2/
joda-convert-1.2.jar ...
[SUCCESSFUL ] org.joda#joda-convert;1.2!joda-convert.jar (548ms)
:: resolution report :: resolve 11850ms :: artifacts dl 26075ms
:: modules in use:
com.github.nscala-time#nscala-time_2.10;1.0.0 from central in
[default]
com.stratio.datasource#spark-mongodb_2.10;0.10.1 from central in
[default]
joda-time#joda-time;2.3 from central in [default]
org.joda#joda-convert;1.2 from central in [default]
org.mongodb#casbah-commons_2.10;2.8.0 from central in [default]
org.mongodb#casbah-core_2.10;2.8.0 from central in [default]
org.mongodb#casbah-query_2.10;2.8.0 from central in [default]
org.mongodb#mongo-java-driver;2.13.0 from central in [default]
org.slf4j#slf4j-api;1.6.0 from central in [default]
-----------------------------------------------------------------
| | modules || artifacts
|
| conf | number| search|dwnlded|evicted||
number|dwnlded|
-------------------------------------------------------------------
--
| default | 9 | 9 | 9 | 0 || 9 | 9
|
-------------------------------------------------------------------
--
:: retrieving :: org.apache.spark#spark-submit-parent
confs: [default]
9 artifacts copied, 0 already retrieved (2335kB/51ms)
... (snip) ...
查询MongDB的27017端口,从twtr01_db中的collection twtr01_coll读取数据。
首先import SQLContext:
In [5]:
from pyspark.sql import SQLContext
sqlContext.sql("CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE tweet_table USING com.stratio.datasource.mongodb OPTIONS (host 'localhost:27017', database 'twtr01_
db', collection 'twtr01_coll')")
sqlContext.sql("SELECT * FROM tweet_table where id=598830778269769728
").collect()这里是查询输出:
Out[5]:
[Row(text=u'@spark_io is now @particle - awesome news - now I can enjoy my Particle Cores/Photons + @sparkfun sensors + @ApacheSpark analytics :-)', _id=u'55aa640fd770871cba74cb88', contributors=None,
retweeted=False, user=Row(contributors_enabled=False, created_at=u'Mon Aug 25 14:01:26 +0000 2008', default_profile=True, default_profile_image=False, description=u'Building open source tools for and teaching
enterprise software developers', entities=Row(description=Row(urls=[]), url=Row(urls=[Row(url=u'http://t.co/TSHp13EWeu', indices=[0,22],
... (snip) ...
9], name=u'Spark is Particle', screen_name=u'spark_io'),
Row(id=487010011, id_str=u'487010011', indices=[17, 26],
name=u'Particle', screen_name=u'particle'), Row(id=17877351,
id_str=u'17877351', indices=[88, 97], name=u'SparkFun
Electronics', screen_name=u'sparkfun'), Row(id=1551361069, id_
str=u'1551361069', indices=[108, 120], name=u'Apache Spark', screen_name=u'ApacheSpark')]), is_quote_status=None, lang=u'en', quoted_status_id_str=None, quoted_status_id=None, created_at=u'Thu May 14 12:42:37 +0000 2015', retweeted_status=None, truncated=False,
place=None, id=598830778269769728, in_reply_to_user_id=3187046084,
retweet_count=0, in_reply_to_status_id=None, in_reply_to_screen_name=u'spark_io', in_reply_to_user_id_str=u'3187046084', source=u'<a href="http://twitter.com" rel="nofollow">Twitter Web Client</a>',
id_str=u'598830778269769728', coordinates=None, metadata=Row(iso_language_code=u'en', result_type=u'recent'), quoted_status=None)]
#最后
以上就是现实大白最近收集整理的关于地铁译:Spark for python developers ---Spark的数据戏法回顾数据密集型应用的架构数据的序列化和反序列化获取和存储数据搭建MongoDB使用Blaze探索数据使用 Odo传输数据使用Spark SQL探索数据的全部内容,更多相关地铁译:Spark内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复