我是靠谱客的博主 干净长颈鹿,这篇文章主要介绍老卫带你学---faster-rcnn源码剖析(generate_anchor.py运算解读2)【深度学习:目标检测】 faster rcnn RPN之anchor(generate_anchors)源码解析,现在分享给大家,希望可以做个参考。
【深度学习:目标检测】 faster rcnn RPN之anchor(generate_anchors)源码解析
转载:http://blog.csdn.net/xzzppp/article/details/52317863
英文原文:faste rcnn。其中生成RPN(Regional proposal network)的Python代码解析
本代码主要用于:生成尺度为:128,256,512; 宽高比为:1:2,1:1,2:1的anchor
-
<span style=“font-size:24px;”>#功能描述:生成多尺度、多宽高比的anchors。 -
# 尺度为:128,256,512; 宽高比为:1:2,1:1,2:1 -
-
import numpy as np #提供矩阵运算功能的库 -
-
#生成anchors总函数:ratios为一个列表,表示宽高比为:1:2,1:1,2:1 -
#2**x表示:2^x,scales:[2^3 2^4 2^5],即:[8 16 32] -
def generate_anchors(base_size=16, ratios=[0.5, 1, 2], -
scales=2**np.arange(3, 6)): -
”“” -
Generate anchor (reference) windows by enumerating aspect ratios X -
scales wrt a reference (0, 0, 15, 15) window. -
”“” -
base_anchor = np.array([1, 1, base_size, base_size]) - 1 #新建一个数组:base_anchor:[0 0 15 15] -
ratio_anchors = _ratio_enum(base_anchor, ratios) #枚举各种宽高比 -
anchors = np.vstack([_scale_enum(ratio_anchors[i, :], scales) #枚举各种尺度,vstack:竖向合并数组 -
for i in xrange(ratio_anchors.shape[0])]) #shape[0]:读取矩阵第一维长度,其值为3 -
return anchors -
-
#用于返回width,height,(x,y)中心坐标(对于一个anchor窗口) -
def _whctrs(anchor): -
”“” -
Return width, height, x center, and y center for an anchor (window). -
”“” -
#anchor:存储了窗口左上角,右下角的坐标 -
w = anchor[2] - anchor[0] + 1 -
h = anchor[3] - anchor[1] + 1 -
x_ctr = anchor[0] + 0.5 * (w - 1) #anchor中心点坐标 -
y_ctr = anchor[1] + 0.5 * (h - 1) -
return w, h, x_ctr, y_ctr -
-
#给定一组宽高向量,输出各个anchor,即预测窗口,输出anchor的面积相等,只是宽高比不同 -
def _mkanchors(ws, hs, x_ctr, y_ctr): -
#ws:[23 16 11],hs:[12 16 22],ws和hs一一对应。 -
”“” -
Given a vector of widths (ws) and heights (hs) around a center -
(x_ctr, y_ctr), output a set of anchors (windows). -
”“” -
ws = ws[:, np.newaxis] #newaxis:将数组转置 -
hs = hs[:, np.newaxis] -
anchors = np.hstack((x_ctr - 0.5 * (ws - 1), #hstack、vstack:合并数组 -
y_ctr - 0.5 * (hs - 1), #anchor:[[-3.5 2 18.5 13] -
x_ctr + 0.5 * (ws - 1), # [0 0 15 15] -
y_ctr + 0.5 * (hs - 1))) # [2.5 -3 12.5 18]] -
return anchors -
-
#枚举一个anchor的各种宽高比,anchor[0 0 15 15],ratios[0.5,1,2] -
def _ratio_enum(anchor, ratios): -
”“” 列举关于一个anchor的三种宽高比 1:2,1:1,2:1 -
Enumerate a set of anchors for each aspect ratio wrt an anchor. -
”“” -
-
w, h, x_ctr, y_ctr = _whctrs(anchor) #返回宽高和中心坐标,w:16,h:16,x_ctr:7.5,y_ctr:7.5 -
size = w * h #size:16*16=256 -
size_ratios = size / ratios #256/ratios[0.5,1,2]=[512,256,128] -
#round()方法返回x的四舍五入的数字,sqrt()方法返回数字x的平方根 -
ws = np.round(np.sqrt(size_ratios)) #ws:[23 16 11] -
hs = np.round(ws * ratios) #hs:[12 16 22],ws和hs一一对应。as:23&12 -
anchors = _mkanchors(ws, hs, x_ctr, y_ctr) #给定一组宽高向量,输出各个预测窗口 -
return anchors -
-
#枚举一个anchor的各种尺度,以anchor[0 0 15 15]为例,scales[8 16 32] -
def _scale_enum(anchor, scales): -
”“” 列举关于一个anchor的三种尺度 128*128,256*256,512*512 -
Enumerate a set of anchors for each scale wrt an anchor. -
”“” -
w, h, x_ctr, y_ctr = _whctrs(anchor) #返回宽高和中心坐标,w:16,h:16,x_ctr:7.5,y_ctr:7.5 -
ws = w * scales #[128 256 512] -
hs = h * scales #[128 256 512] -
anchors = _mkanchors(ws, hs, x_ctr, y_ctr) #[[-56 -56 71 71] [-120 -120 135 135] [-248 -248 263 263]] -
return anchors -
-
if name == ’main’: #主函数 -
import time -
t = time.time() -
a = generate_anchors() #生成anchor(窗口) -
print time.time() - t #显示时间 -
print a -
from IPython import embed; embed() -
</span>
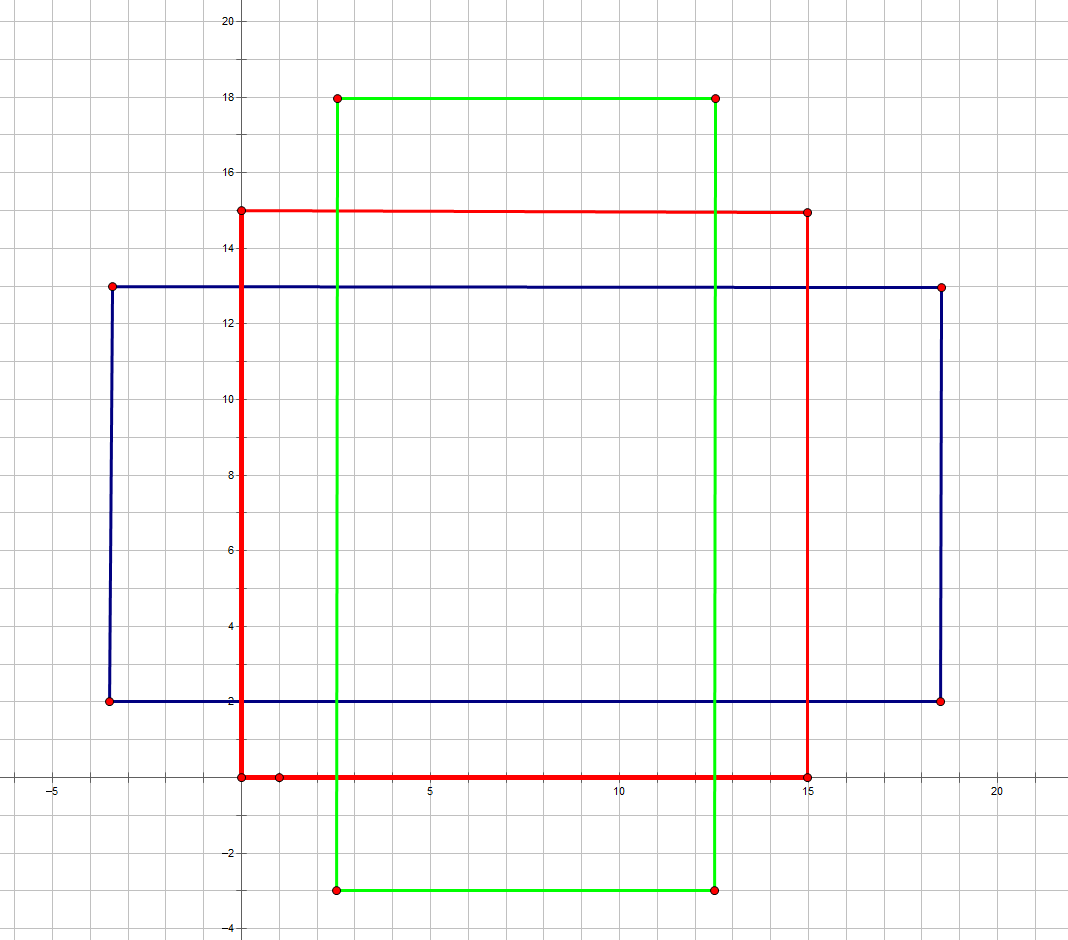
其中,_ratio_enum()部分生成三种宽高比 1:2,1:1,2:1的anchor如下图所示:
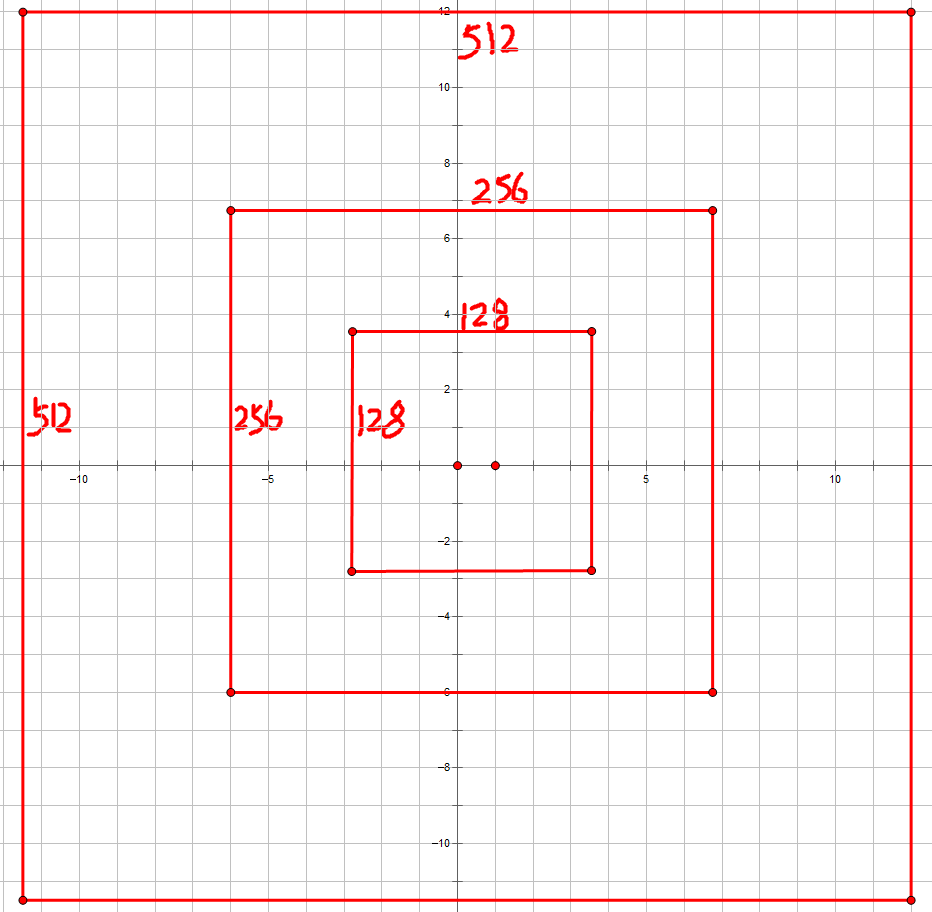
其中,_scale_enum()部分,生成三种尺寸的anchor,以_ratio_enum()部分生成的anchor[0 0 15 15]为例,扩展了三种尺度 128*128,256*256,512*512,如下图所示:
最后
以上就是干净长颈鹿最近收集整理的关于老卫带你学---faster-rcnn源码剖析(generate_anchor.py运算解读2)【深度学习:目标检测】 faster rcnn RPN之anchor(generate_anchors)源码解析的全部内容,更多相关老卫带你学---faster-rcnn源码剖析(generate_anchor.py运算解读2)【深度学习:目标检测】内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复