文章目录
- 基础知识
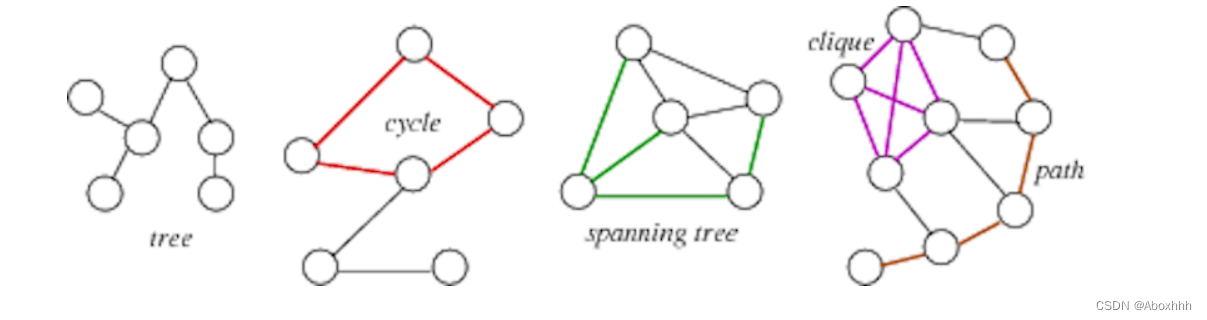
- Path
- Simple path
- Cycle
- Connected graph
- Complete graph Kv
- Tree
- Spanning tree
- Spanning forest
- Clique
- Undirected graph
- Directed graph
- Weighted graph
- Multi-graph
- 三种表示图的数据结构
- Array of edges
- Adjacency matrix
- Adjacency list
- 三种方法的内存空间
基础知识
- 顶点(有穷)和边
vertices and edges - V个顶点的图最多有V(V-1)/2个边,根据数目可以判断出这个图是dense or spars.
- For an edge e that connects vertices v and w
-
- v and w are adjacent (neighbours)
-
- e is incident on both v and w
- Degree of a vertex 就是有几条边连入这个v。
Path
一串顶点的序列,
a sequence of vertices where each vertex has an edge to its predecessor
Simple path
A path that repeats no vertex, except that the first and last may be the same vertex.
一个没有重复顶点的路径,除了第一个和最后一个可能是同一个顶点。
Cycle
a path that is simple except last vertex = first vertex
Connected graph
there is a path from each vertex to every other vertex
if a graph is not connected, it has ≥2 connected components
一个节点到其余任何一个节点都有一个路径
Complete graph Kv
there is an edge from each vertex to every other vertex
in a complete graph, E = V(V-1)/2
每个节点 和 其他任何节点都有路径
Tree
connected (sub)graph with no cycles
Spanning tree
tree containing all vertices
- A spanning tree of connected graph G = (V,E)
-
- is a subgraph of G containing all of V
-
- and is a single tree (connected, no cycles)
Spanning forest
- A spanning forest of non-connected graph G = (V,E) is a subgraph of G containing all of V
-
- and is a set of trees (not connected, no cycles), with one tree for each connected component
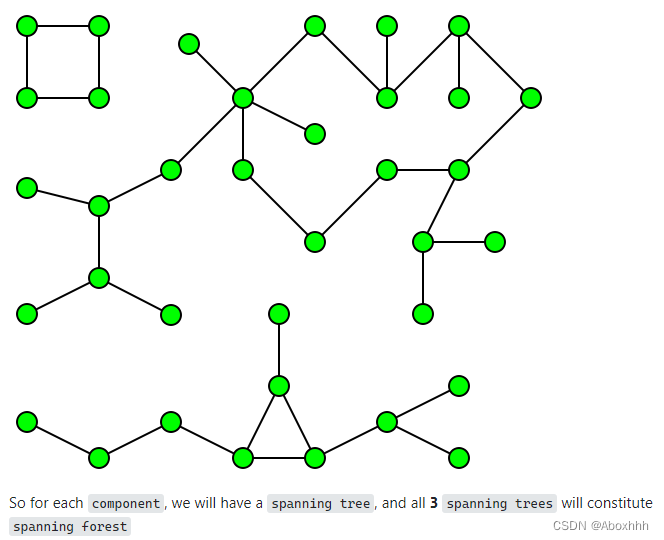
- and is a set of trees (not connected, no cycles), with one tree for each connected component
Clique
complete subgraph
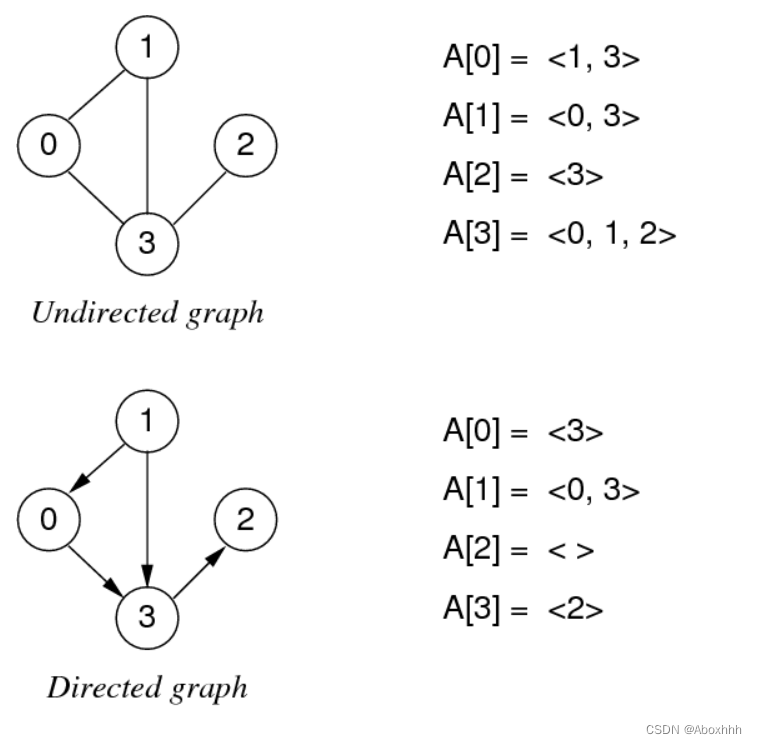
Undirected graph
edge(u,v) = edge(v,u), no self-loops (i.e. no edge(v,v))
Directed graph
edge(u,v) ≠ edge(v,u), can have self-loops (i.e. edge(v,v))
Weighted graph
each edge has an associated value (weight)
e.g. road map (weights on edges are distances between cities)
Multi-graph
allow multiple edges between two vertices
e.g. f() calls g() in several places
三种表示图的数据结构
Array of edges
通过一对顶点表示一条边。
- 添加删除边稍显复杂;
- 节省空间的表示
- 可以表示有方向的图和无方向的
插入和删除边
insertEdge(g,(v,w)):
| Input graph g, edge (v,w) // assumption: (v,w) not in g
|
| g.edges[g.nE]=(v,w)
| g.nE=g.nE+1
removeEdge(g,(v,w)):
| Input graph g, edge (v,w) // assumption: (v,w) in g
|
| i=0
| while (v,w)≠g.edges[i] do
| i=i+1
| end while
| g.edges[i]=g.edges[g.nE-1] // replace (v,w) by last edge in array
| g.nE=g.nE-1
show(g):
| Input graph g
|
| for all i=0 to g.nE-1 do
| print g.edges[i]
| end for
O(E)
Storage cost: O(E)
Cost of operations:
initialisation: O(1)
insert edge: O(1) (assuming edge array has space)
find/delete edge: O(E) (need to find edge in edge array)
If array is full on insert
allocate space for a bigger array, copy edges across ⇒ O(E)
If we maintain edges in order
use binary search to insert/find edge ⇒ O(log E)
Adjacency matrix
二维数组表示一条边
Advantages:
- can represent graphs, digraphs and weighted graphs
-
- graphs: symmetric boolean matrix
-
- digraphs: non-symmetric boolean matrix
-
- weighted: non-symmetric matrix of weight values
Disadvantages:
if few edges (sparse) ⇒ memory-inefficient
- weighted: non-symmetric matrix of weight values
Graph initialisation
newGraph(V):
| Input number of nodes V
| Output new empty graph
|
| g.nV = V // #vertices (numbered 0..V-1)
| g.nE = 0 // #edges
| allocate memory for g.edges[][]
| for all i,j=0..V-1 do
| g.edges[i][j]=0 // false
| end for
| return g
Edge insertion
insertEdge(g,(v,w)):
| Input graph g, edge (v,w)
|
| if g.edges[v][w]=0 then // (v,w) not in graph
| g.edges[v][w]=1 // set to true
| g.edges[w][v]=1
| g.nE=g.nE+1
| end if
Edge removal
removeEdge(g,(v,w)):
| Input graph g, edge (v,w)
|
| if g.edges[v][w]≠0 then // (v,w) in graph
| g.edges[v][w]=0 // set to false
| g.edges[w][v]=0
| g.nE=g.nE-1
| end if
show(g):
| Input graph g
|
| for all i=0 to g.nV-2 do
| | for all j=i+1 to g.nV-1 do
| | if g.edges[i][j] then
| | print i"—"j
| | end if
| | end for
| end for
Time complexity: O(V2)
Storage cost: O(V2)
If the graph is sparse, most storage is wasted.
Cost of operations:
initialisation: O(V2) (initialise V×V matrix)
insert edge: O(1) (set two cells in matrix)
delete edge: O(1) (unset two cells in matrix)
Adjacency list
For each vertex, store linked list of adjacent vertices:
- Advantages
relatively easy to implement in languages like C
can represent graphs and digraphs
memory efficient if E:V relatively small(为啥) - Disadvantages:
one graph has many possible representations
(unless lists are ordered by same criterion e.g. ascending)
Graph initialisation
newGraph(V):
| Input number of nodes V
| Output new empty graph
|
| g.nV = V // #vertices (numbered 0..V-1)
| g.nE = 0 // #edges
| allocate memory for g.edges[]
| for all i=0..V-1 do
| g.edges[i]=NULL // empty list
| end for
| return g
Edge insertion:
insertEdge(g,(v,w)):
| Input graph g, edge (v,w)
|
| insertLL(g.edges[v],w)
| insertLL(g.edges[w],v)
| g.nE=g.nE+1
Edge removal:
removeEdge(g,(v,w)):
| Input graph g, edge (v,w)
|
| deleteLL(g.edges[v],w)
| deleteLL(g.edges[w],v)
| g.nE=g.nE-1
Storage cost: O(V+E) (V list pointers, total of 2·E list elements)
the larger of V,E determines the complexity
Cost of operations
initialisation: O(V) (initialise V lists)
insert edge: O(1) (insert one vertex into list)
if you don’t check for duplicates
find/delete edge: O(V) (need to find vertex in list)
If vertex lists are sorted
insert requires search of list ⇒ O(V)
delete always requires a search, regardless of list order
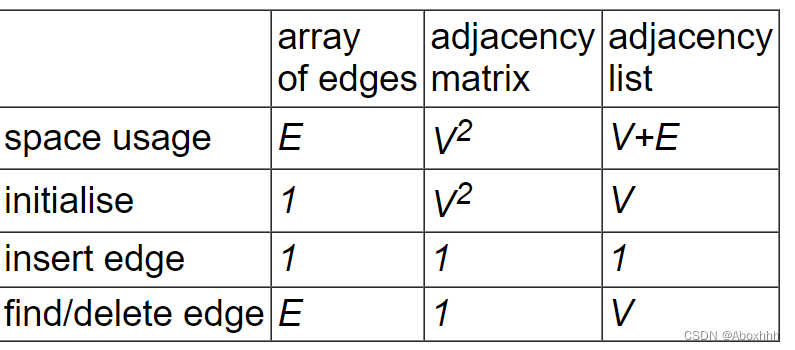
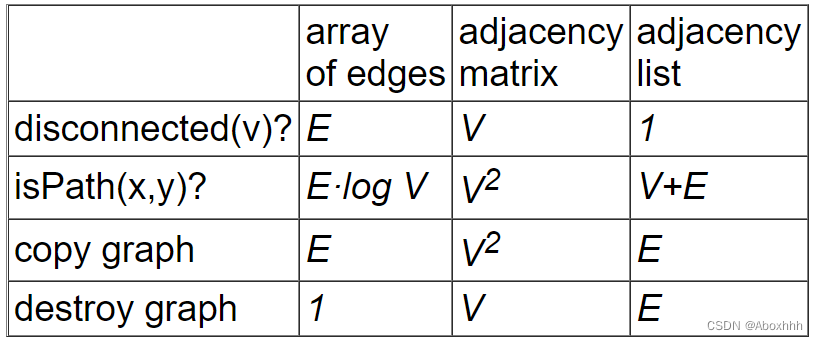
三种方法的内存空间
- array of edges :边的数目 * 8 (即为8E)如果求最大边就是E=V*(V-1)/2
- adjacency matrix:将矩阵中的数值看作bool型,则总体大小为,指针大小乘定点个数加指针平方的个数 8*V+V2
- adjacency list: 每个节点就是顶点+内容+指针->4+4+8=16 ,每个顶点出现两次,所以总体大小就是2* 16 * E=32E,再加上前面的头指针,8*V+32E。
最后
以上就是动人耳机最近收集整理的关于20221005 数据结构之图基础知识的全部内容,更多相关20221005内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复