在上一篇,我们搭建了开发环境。本篇,使用C++代码真正实现功能。我们使用UDP协议从手机上指定发送的目的地、端口。效果如下图,完整工程参考https://gitcode.net/coloreaglestdio/qtcpp_demo/-/tree/master/android/sensors2pc:
| 移动端1 | 移动端2 | 桌面 |
|---|---|---|
 |  |  |
1. 在PC端实现程序并调试
我们建立一个Qt的Widgets程序,添加 position, sensors模块。
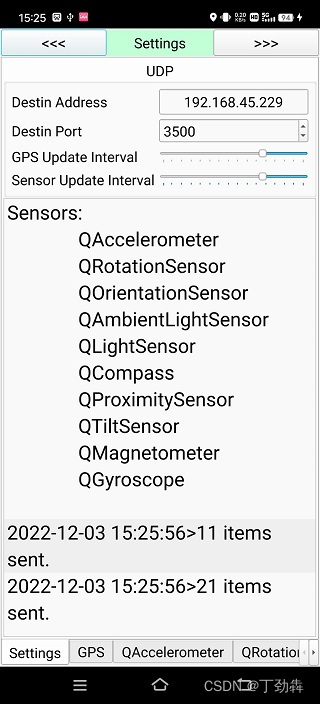
- 界面里支持设置目的地址、端口。
- 界面里可以设置GPS与各个传感器的刷新速度。
- 传感器使用Qt枚举,并创建刷新函数。
传感器的主对话框类如下:
#ifndef DLGSTP_H
#define DLGSTP_H
#include <QDialog>
#include <QGeoPositionInfoSource>
#include <QStandardItemModel>
#include <QUdpSocket>
#include <QSensor>
#include <functional>
QT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE
namespace Ui { class DlgSTP; }
QT_END_NAMESPACE
class DlgSTP : public QDialog
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
DlgSTP(QWidget *parent = nullptr);
~DlgSTP();
void EnumSensors();
void openGPS();
protected:
void timerEvent(QTimerEvent * evt) override;
private:
Ui::DlgSTP *ui;
QStandardItemModel * m_pMsgMod = 0;
int m_nTimer = -1;
protected:
//Sensors Update Lambdas
QList<std::function<void (void)> > m_sensorUpdaters;
protected:
//GPS
QGeoPositionInfoSource *m_pos_source = 0;
protected:
//Net Send
QUdpSocket * m_psock = 0;
QStringList m_listInfo;
};
#endif // DLGSTP_H
//cpp
DlgSTP::DlgSTP(QWidget *parent)
: QDialog(parent)
, ui(new Ui::DlgSTP)
, m_pMsgMod(new QStandardItemModel(this))
, m_psock(new QUdpSocket(this))
{
ui->setupUi(this);
ui->listView_msg->setModel(m_pMsgMod);
showMaximized();
//Open GPS Device
openGPS();
//Enum all sensors
EnumSensors();
loadSettings();
m_nTimer = startTimer(20);
}
1.1 枚举传感器并建立界面
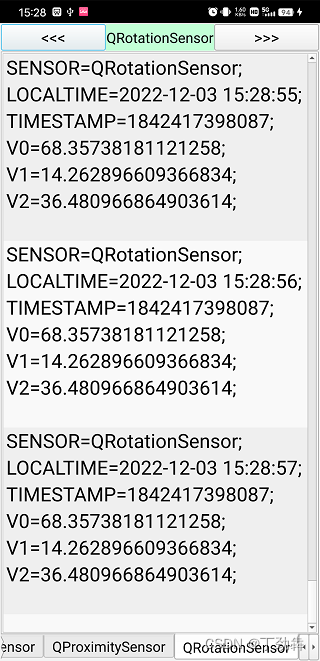
通过Qt的Sensors可以枚举到传感器的取值。
void DlgSTP::EnumSensors()
{
QList<QByteArray> sensors = QSensor::sensorTypes();
QString strSensors = "Sensors:n";
for (QByteArray stp : sensors)
{
QSensor * sensor = new QSensor(stp);
sensor->start();
//添加界面刷新
QListView * lstView = new QListView(this);
QStandardItemModel * m_pMod = new QStandardItemModel(this);
lstView->setModel(m_pMod);
QString name = stp;
ui->tabWidget->addTab(lstView,name);
//设置刷新函数(供定时器调用),使用Lamdba后期调用,省的建立函数了。
m_sensorUpdaters<<[sensor,m_pMod,this,lstView,name](void)->void
{
QSensorReading *reading = sensor->reading();
QString str = "SENSOR="+name + ";n";
//获取当前传感器有多少数值
int n = reading->valueCount();
for (int i=0;i<n;++i)
{
QVariant vt = reading->value(i);
str += QString("%1").arg(vt.toString());
}
//消息写入m_listInfo,后续发送
m_listInfo << str;
m_pMod->appendRow(new QStandardItem(str));
lstView->scrollToBottom();
};
}
}
值得注意的是,上面的代码是在实际代码中进行了简化。实际代码里为了避免频繁刷新界面的同时,迅速吞吐传感器数据,进行了一些处理。可参考实际源码。
1.2 初始化GPS
GPS是手机的一个重要功能。通过初始化GPS,可以实时获取位置、时刻。
void DlgSTP::openGPS()
{
m_pos_source = QGeoPositionInfoSource::createDefaultSource(0);
if (m_pos_source)
{
//Add Tab
QListView * lstView = new QListView(this);
QStandardItemModel * m_pMod = new QStandardItemModel(this);
lstView->setModel(m_pMod);
ui->tabWidget->addTab(lstView,"GPS");
//直接把GPS刷新信号绑定到Lambda
connect (m_pos_source,
&QGeoPositionInfoSource::positionUpdated,
[lstView,m_pMod,this](const QGeoPositionInfo &update)->void
{
double lat = update.coordinate().latitude();
double lon = update.coordinate().longitude();
QDateTime dtm = update.timestamp();
QString str = QString("SENSOR=GPS;nGMT_TIME=%1;nLAT=%2;nLON=%3;n")
.arg(dtm.toString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"))
.arg(lat,0,'f',7)
.arg(lon,0,'f',7);
//消息写入m_listInfo,后续发送
m_listInfo << str;
m_pMod->appendRow(new QStandardItem(str));
lstView->scrollToBottom();
});
//即使出错了,也继续开始,把出错的信息绑定到Lambda
connect (m_pos_source,
&QGeoPositionInfoSource::errorOccurred,
[this](QGeoPositionInfoSource::Error pe)->void{
m_pos_source->startUpdates();
m_pMsgMod->appendRow(new QStandardItem(QString("GPS Err Code %1.").arg(int(pe))));
});
//开启GPS
m_pos_source->setUpdateInterval(ui->horizontalSlider_gps->value());
m_pos_source->startUpdates();
}
else
m_pMsgMod->appendRow(new QStandardItem("No GPS Found!"));
}
1.3 发送UDP
设置一个定时器,进行UDP发射。定时器的尺度是20ms的整数倍,可以调整。
void DlgSTP::timerEvent(QTimerEvent * evt)
{
if (evt->timerId()==m_nTimer)
{
++m_clk;
//UDP Send
const int updateITV = ui->horizontalSlider_freq->value();
const int updateGUI = (50 / (updateITV>50?50:updateITV) )* updateITV;
if (m_clk % updateITV ==0 )
{
//调用各个Lambda刷新传感器,消息写入m_listInfo
foreach(auto fn, m_sensorUpdaters)
fn();
//发送
QHostAddress addr (ui->lineEdit_ip->text());
int port = ui->spinBox_port->value();
foreach(QString i, m_listInfo)
m_psock->writeDatagram(i.toLocal8Bit(),addr,port);
m_nTotalSent += m_listInfo.size();
m_listInfo.clear();
//适时更新界面
if (m_clk % updateGUI==0)
{
m_pMsgMod->appendRow(new QStandardItem(QString("%1>%2 items sent.")
.arg(QDateTime::currentDateTime().toString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"))
.arg(m_nTotalSent)));
if (m_pMsgMod->rowCount()>MAX_ROWS_LSTV)
m_pMsgMod->removeRows(0,m_pMsgMod->rowCount()-MAX_ROWS_LSTV);
ui->listView_msg->scrollToBottom();
}
}
}
}
我们在PC上可以先调试,发现PC上竟然也有很多传感器。
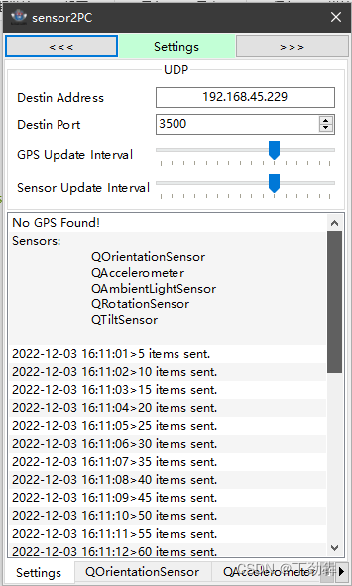
2 部署到Android 手机
我们在手机上打开调试模式,一般是连续击打系统版本号,即可打开。打开后,手机会提示允不允许USB调试,点击允许即可。
如果编译Debug版本,是不需要证书签名的。如果是Release,需要签名。
2.1 设置应用程序的名字和图标
在项目设置里,直接创建app的manifest
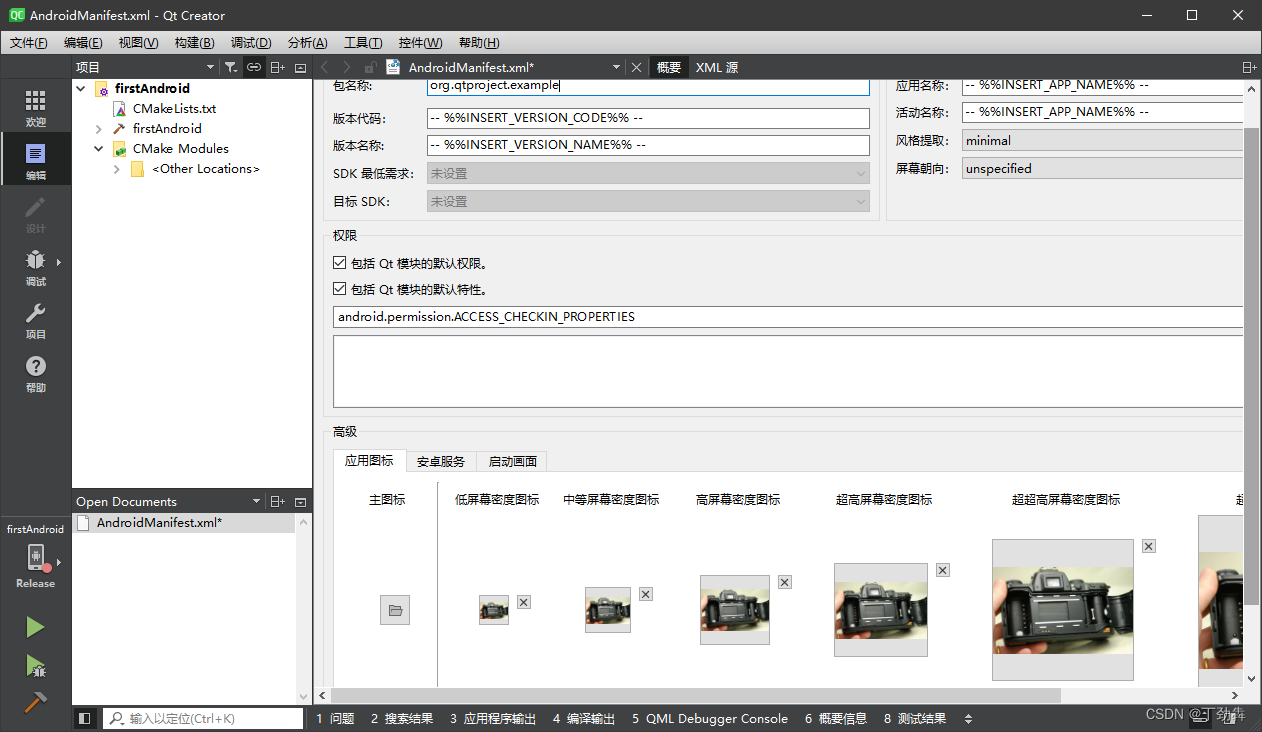
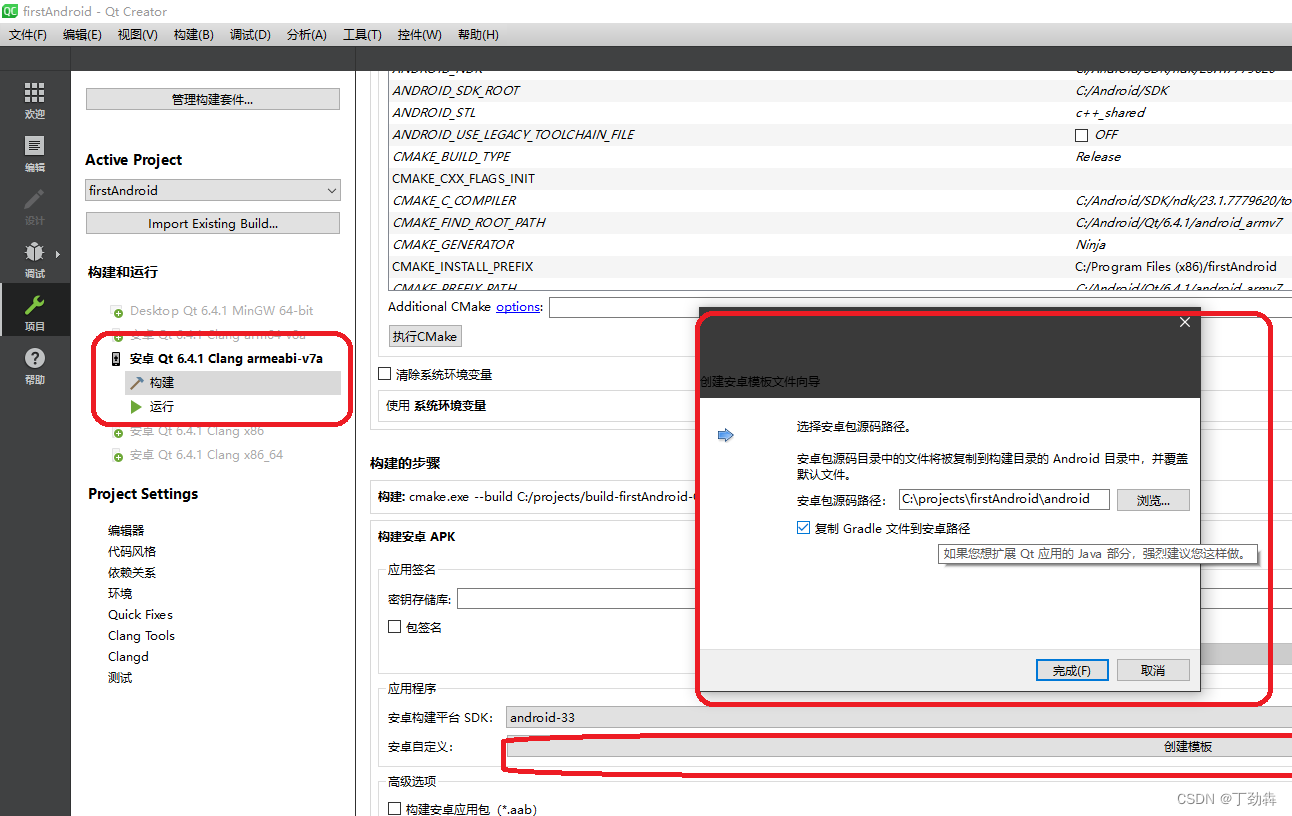 创建后,即可编辑名字、图标:
创建后,即可编辑名字、图标:
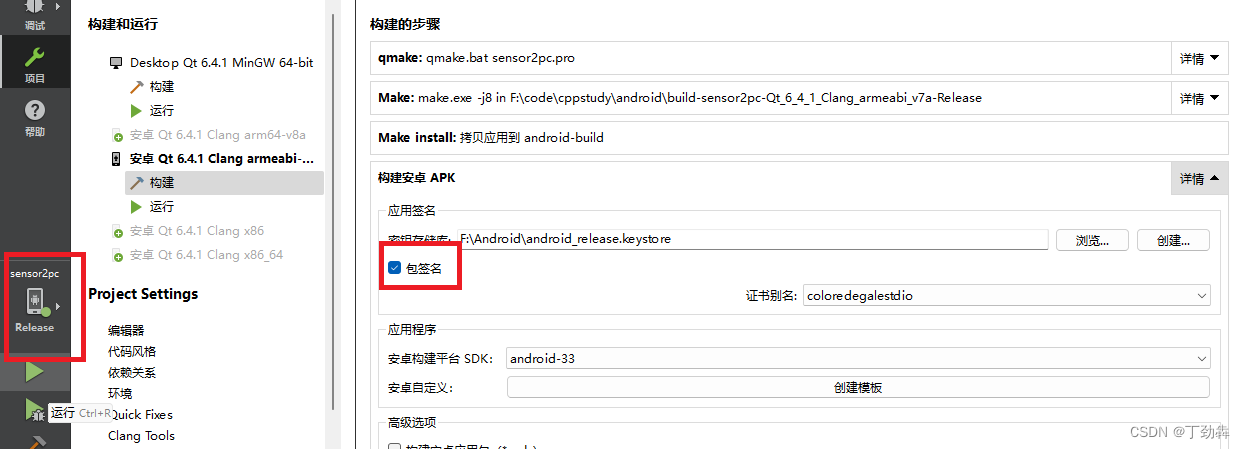
2.2 创建证书
在构建选项里,选择创建证书,输入必要信息后完成创建。注意,Release版本如果构建不成功,就要重新开启一下签名。为了安全,QtCreator会确保是你本人在烧写程序。
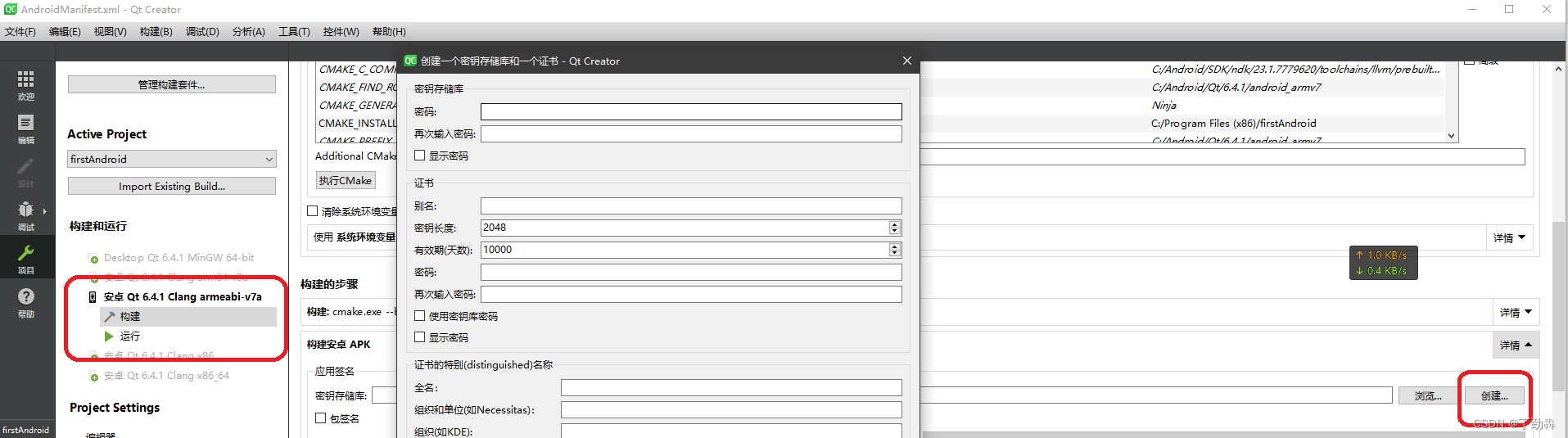 创建后,选择“”包签名“”即可开启签名。注意,Release版本如果构建不成功,就要重新开启一下签名。为了安全,QtCreator会确保是你本人在烧写程序,会经常清除这个选项,以便您再次输入密码。
创建后,选择“”包签名“”即可开启签名。注意,Release版本如果构建不成功,就要重新开启一下签名。为了安全,QtCreator会确保是你本人在烧写程序,会经常清除这个选项,以便您再次输入密码。
2.3 部署并运行程序
确保在Qt的编译栏选取了适当的设备(API版本一致),且绿色按钮出现(而非红色)
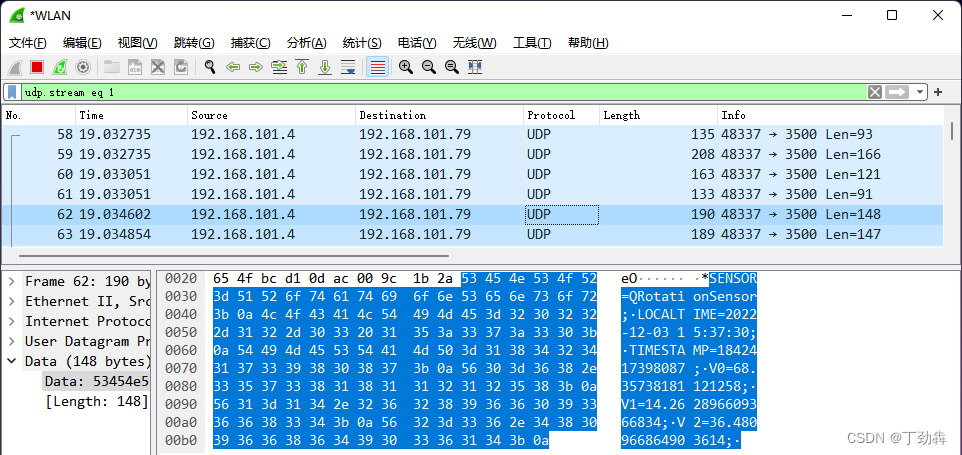
3 在PC上接收数据
当计算机、手机处于一个局域网,或者是处于IP可达的网络时,在PC端就可以接收到消息了。

最后
以上就是明亮热狗最近收集整理的关于使用 Qt for Android 获取并利用手机传感器数据(下篇)使用C++实现功能1. 在PC端实现程序并调试2 部署到Android 手机2.1 设置应用程序的名字和图标3 在PC上接收数据的全部内容,更多相关使用内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
![[Android6.0][MTK6737] UVC Camera (MJPEG) 移植[Android6.0][MTK6737] UVC Camera (MJPEG) 移植](https://www.shuijiaxian.com/files_image/reation/bcimg11.png)







发表评论 取消回复