文章目录
- 一、前言
- 二、Filter 分类
- 三、代码解析
- 1. CacheFilter
- 2. ValidationFilter
- 3. EchoFilter
- 4. GenericFilter & GenericImplFilter
- 5. TokenFilter
- 6. AccessLogFilter
- 7. ActiveLimitFilter & ExecuteLimitFilter
- 7.1 ActiveLimitFilter
- 7.2 ExecuteLimitFilter
- 8. ClassLoaderFilter
- 9. ContextFilter & ConsumerContextFilter
- 10. ExceptionFilter
- 11. DeprecatedFilter
- 12. CompatibleFilter
- 13. TimeoutFilter
- 14. TraceFilter
- 15. FutureFilter
- 16. MonitorFilter
一、前言
本系列为个人Dubbo学习笔记,内容基于《深度剖析Apache Dubbo 核心技术内幕》, 过程参考官方源码分析文章,仅用于个人笔记记录。本文分析基于Dubbo2.7.0版本,由于个人理解的局限性,若文中不免出现错误,感谢指正。
Dubbo通过 ProtocolFilterWrapper 完成了 Dubbo Filter 的功能。
在 Dubbo笔记衍生篇③:ProtocolWrapper 中我们讲到 ProtocolFilterWrapper 是怎么实现的 Filter的 功能。
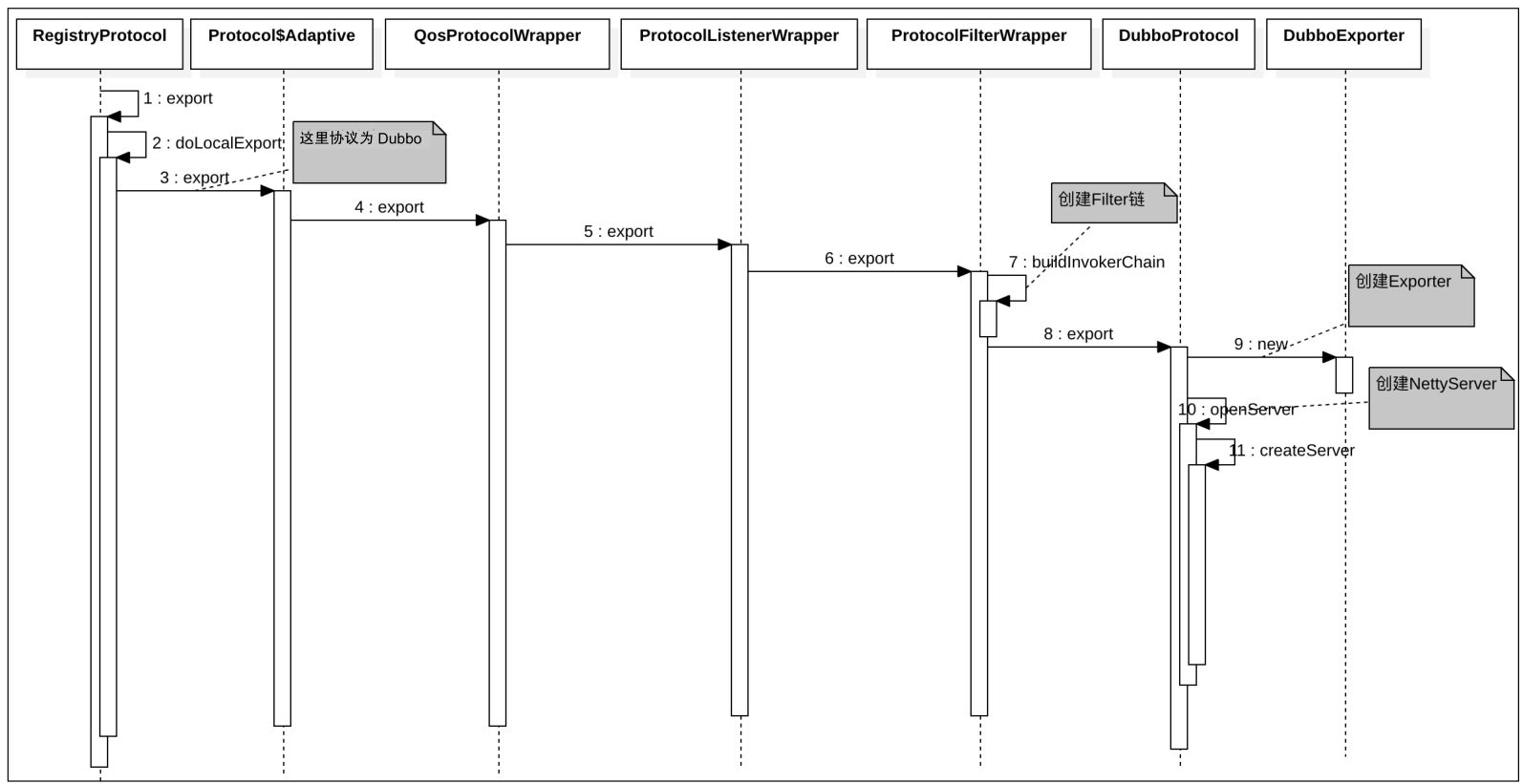
- 对于服务提供者,在其服务发布时会调用 Protocol#export 生成对应 Exporter,其中会调用 ProtocolFilterWrapper#export 完成了Invoker 的 Filter 包装。
提供者暴露服务时序图如下:
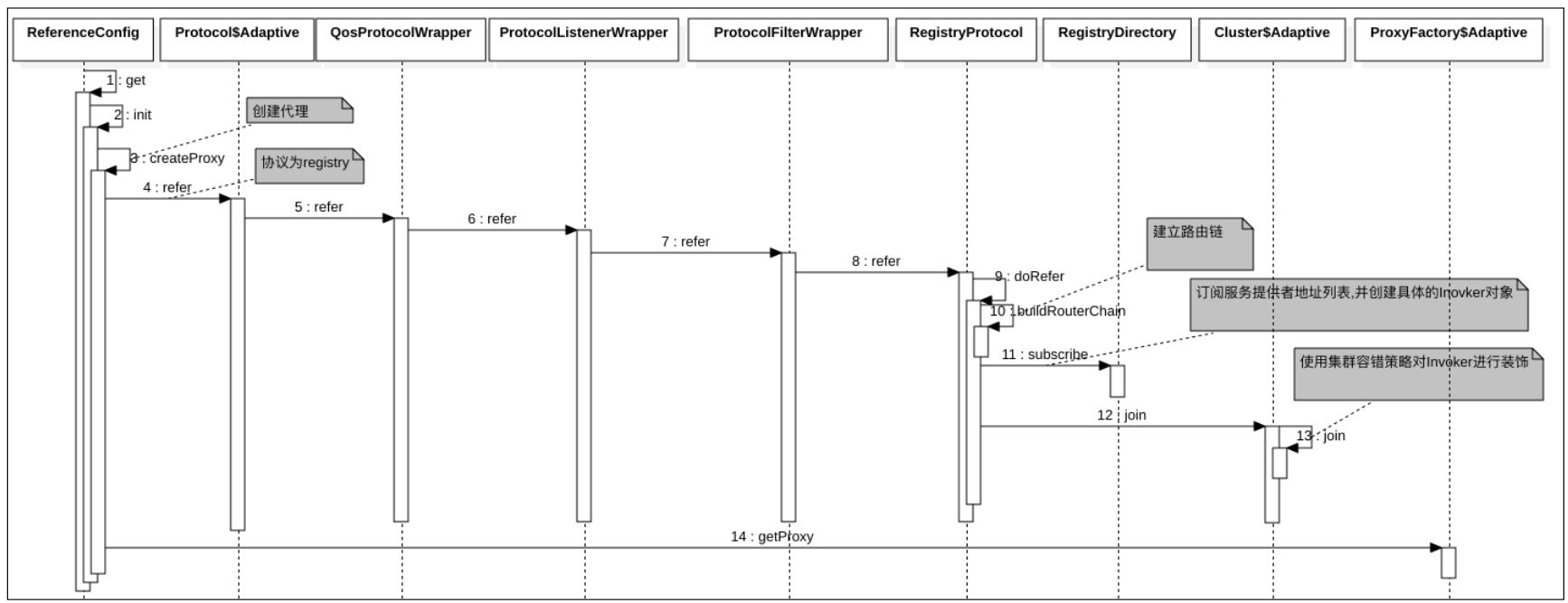
- 对于服务消费者,在其创建服务引用的代理时则会通过 Protocol#refer 来创建 Invoker。其中会调用ProtocolFilterWrapper#refer 完成了Invoker 的 Filter 包装。
消费者发起服务时序图如下:
二、Filter 分类
本文来看看 Dubbo默认提供的 Filter的详细实现。在 META-INF/dubbo/internal 目录下的 org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Filter 文件内容如下:
cache=org.apache.dubbo.cache.filter.CacheFilter
validation=org.apache.dubbo.validation.filter.ValidationFilter
echo=org.apache.dubbo.rpc.filter.EchoFilter
generic=org.apache.dubbo.rpc.filter.GenericFilter
genericimpl=org.apache.dubbo.rpc.filter.GenericImplFilter
token=org.apache.dubbo.rpc.filter.TokenFilter
accesslog=org.apache.dubbo.rpc.filter.AccessLogFilter
activelimit=org.apache.dubbo.rpc.filter.ActiveLimitFilter
classloader=org.apache.dubbo.rpc.filter.ClassLoaderFilter
context=org.apache.dubbo.rpc.filter.ContextFilter
consumercontext=org.apache.dubbo.rpc.filter.ConsumerContextFilter
exception=org.apache.dubbo.rpc.filter.ExceptionFilter
executelimit=org.apache.dubbo.rpc.filter.ExecuteLimitFilter
deprecated=org.apache.dubbo.rpc.filter.DeprecatedFilter
compatible=org.apache.dubbo.rpc.filter.CompatibleFilter
timeout=org.apache.dubbo.rpc.filter.TimeoutFilter
trace=org.apache.dubbo.rpc.protocol.dubbo.filter.TraceFilter
future=org.apache.dubbo.rpc.protocol.dubbo.filter.FutureFilter
monitor=org.apache.dubbo.monitor.support.MonitorFilter
这里需要注意,并非所有的Filter都可作用于提供者和消费者,有的 Filter 只需要作用于消费者,有的则只需要作用于提供者。这里则是通过@Activate 注解来根据情况激活 Filter。如下(如有需要,详参Dubbo笔记衍生篇②:Dubbo SPI 原理):
- Dubbo 在创建 SPI 接口的 适配器类 Spi$Adapive 时,会扫描指定文件,获取到SPI 实现类的全路径名,在利用反射获取Class 时会判断Class 是否被 @Activate修饰,如果被修饰则缓存到
ExtensionLoader#cachedActivates中。 - 当通过
getActivateExtension(URL url, String key, String group)调用时,会遍历ExtensionLoader#cachedActivates并从中获取到Class, 并根据 参数中的key,group 信息进行匹配,如果匹配,则创建对应实例。
每个Filter 提供的作用如下:
| Filter | 作用方 | 作用 |
|---|---|---|
| CacheFilter | 消费者和提供者 | 缓存调用的结果。可通过cache 属性开启或指定缓存策略 |
| ValidationFilter | 消费者和提供者 | 提供参数验证功能。详参 https://dubbo.apache.org/zh/docs/v2.7/user/examples/parameter-validation/ |
| EchoFilter | 提供者 | 回声过滤器,用于消费者校验服务是否可用 , 并不执行处理逻辑。详参https://dubbo.apache.org/zh/docs/v2.7/user/examples/echo-service/ |
| GenericFilter | 提供者 | 用于处理提供者的泛化调用逻辑 |
| GenericImplFilter | 消费者 | 用于处理消费者的泛化调用逻辑 |
| TokenFilter | 提供者 | 完成token验证功能 |
| AccessLogFilter | 提供者 | 记录服务的访问日志 |
| ActiveLimitFilter | 消费者 | 完成了限制消费端最大并发的功能 |
| ExecuteLimitFilter | 提供者 | 完成了限制服务端最大并发的功能 |
| ClassLoaderFilter | 提供者 | 将当前执行线程类加载器设置为服务接口的类加载器 |
| ContextFilter | 提供者 | 完成了服务端上下文参数的隐式参数传递的功能 |
| ConsumerContextFilter | 消费者 | 完成了消费端上下文参数的隐式参数传递的功能 |
| ExceptionFilter | 提供者 | 对提供者调用时出现异常时的规范化处理 |
| DeprecatedFilter | 消费者 | 如果方法已经被弃用(被设置了 deprecated 参数),则 DeprecatedFilter 会记录弃用日志,但并不会阻止此次调用 |
| CompatibleFilter | 无修饰 | 兼容过滤器。使远程方法的返回值与调用者的对象版本兼容 |
| TimeoutFilter | 提供者 | 如果调用超时,则会记录超时日志 ,但不会阻止后续步骤 |
| TraceFilter | 提供者 | 跟踪过滤器。dubbo telnet 的实现 |
| FutureFilter | 消费者 | 实现了消费者的事件回调,在调用之前、调用之后、出现异常时,会触发 oninvoke、onreturn、onthrow 三个事件,可以配置当事件发生时,通知哪个类的哪个方法。 |
| MonitorFilter | 提供者和消费者 | 完成与监控中心的交互,向监控中心传递信息 |
三、代码解析
下面我们来看这些过滤器的详细分析:
1. CacheFilter
CacheFilter 为 缓存过滤器,作用于消费者和提供者,通过 cache 属性激活。在启用的情况下,会缓存调用的结果,下次调用直接从缓存中获取。
可通过如下方式指定缓存策略
@Service(cache = "lru")
或
@Reference(cache = "lru")
缓存方法有如下方案:
org.apache.dubbo.cache.support.lru.LruCache : 默认使用该策略,最近最少使用
org.apache.dubbo.cache.support.jcache.JCache
org.apache.dubbo.cache.support.expiring.ExpiringCache
org.apache.dubbo.cache.support.threadlocal.ThreadLocalCache
CacheFilter#invoke 实现如下,逻辑比较清楚,这里不再赘述
@Override
public Result invoke(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
if (cacheFactory != null && ConfigUtils.isNotEmpty(invoker.getUrl().getMethodParameter(invocation.getMethodName(), Constants.CACHE_KEY))) {
// 根据指定的缓存策略获取缓存类。cacheFactory 为 缓存策略工厂类,SPI 接口,可以通过实现该接口定义 缓存策略
Cache cache = cacheFactory.getCache(invoker.getUrl(), invocation);
if (cache != null) {
String key = StringUtils.toArgumentString(invocation.getArguments());
Object value = cache.get(key);
if (value != null) {
if (value instanceof ValueWrapper) {
return new RpcResult(((ValueWrapper)value).get());
} else {
return new RpcResult(value);
}
}
Result result = invoker.invoke(invocation);
if (!result.hasException()) {
cache.put(key, new ValueWrapper(result.getValue()));
}
return result;
}
}
return invoker.invoke(invocation);
}
2. ValidationFilter
ValidationFilter 完成了参数校验的功能,作用于提供者和消费者, 通过 validation 属性激活。对于 Dubbo 的Rpc 请求来说,有时候也需要参数验证,而ValidationFilter则完成了对 JSR303 标准的验证 annotation,并通过声明 filter 来实现验证。
详细使用参考https://dubbo.apache.org/zh/docs/v2.7/user/examples/parameter-validation/
ValidationFilter#invoke 实现如下:
@Override
public Result invoke(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
// validation 为 SPI 接口 Validation。默认实现为 JValidation
if (validation != null && !invocation.getMethodName().startsWith("$")
&& ConfigUtils.isNotEmpty(invoker.getUrl().getMethodParameter(invocation.getMethodName(), Constants.VALIDATION_KEY))) {
try {
// 获取 Validation 实例
Validator validator = validation.getValidator(invoker.getUrl());
if (validator != null) {
// 进行参数校验。在该方法中将参数校验委托给 javax.validation.Validator 来完成
validator.validate(invocation.getMethodName(), invocation.getParameterTypes(), invocation.getArguments());
}
} catch (RpcException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Throwable t) {
return new RpcResult(t);
}
}
return invoker.invoke(invocation);
}
3. EchoFilter
官方描述:
回声测试用于检测服务是否可用,回声测试按照正常请求流程执行,能够测试整个调用是否通畅,可用于监控。作用于提供者,默认激活状态
所有服务自动实现 EchoService 接口,只需将任意服务引用强制转型为 EchoService,即可使用。。
使用细节如下:
- Spring的配置
<dubbo:reference id="memberService" interface="com.xxx.MemberService" /> - 代码
// 远程服务引用 MemberService memberService = ctx.getBean("memberService"); EchoService echoService = (EchoService) memberService; // 强制转型为EchoService // 回声测试可用性 String status = echoService.$echo("OK"); assert(status.equals("OK"));
这里解释一下 所有服务自动实现 EchoService 接口,只需将任意服务引用强制转型为 EchoService,即可使用。 说白了,就是所有的接口可以强转成 EchoService,并调用EchoService#$echo 方法来进行回声测试。
下面解释一下为什么接口可以直接强转成 EchoService,以上面代码为例:
- 对于消费者来说,消费者持有的 MemberService 并非真的是 MemberService 实例,而是一个代理类 ProxyService。当调用 ProxService#method 时,会通过网络将调用信息传递给服务提供者,由提供者找到对应的方法执行并返回,所以对消费者来说调用什么方法并没有什么区别。如:消费者调用MemberService#sayHello,发送给提供者时的信息是
类名 xxx.xxx.MemberService ,方法名 sayHello 等信息。至于是否MemberService#sayHello 方法,并不需要消费者端来判断。 - 对于提供者来说,当接收到请求后,在经历真正调用前,会先经过 Dubbo Filter 链。而在 EchoFilter 中当调用的方法满足
方法名为 $echo && 参数只有一个的条件时就会认为是回声测试,则会在EchoFilter 中直接将结果返回,而并不会真正调用提供者的某个方法。
EchoFilter#invoke 实现如下
@Override
public Result invoke(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation inv) throws RpcException {
// 方法名为 $echo && 参数只有一个
if (inv.getMethodName().equals(Constants.$ECHO) && inv.getArguments() != null && inv.getArguments().length == 1) {
return new RpcResult(inv.getArguments()[0]);
}
return invoker.invoke(inv);
}
4. GenericFilter & GenericImplFilter
GenericFilter 和 GenericImplFilter 完成了 Dubbo 泛化调用的功能。
详参:Dubbo笔记 ⑱ :泛化调用 & 泛化实现
5. TokenFilter
TokenFilter 仅供服务提供者使用。实现了token 校验的功能。作用域提供者,通过 token 属性激活。
服务提供者接收到请求后执行到TokenFilter#invoke 会获取自身的token并与远端调用的token 比对,如果不一致则认为是非法调用。Token的可以防止跨注册中心调用的产生。
使用方式详参:
https://dubbo.apache.org/zh/docs/v2.7/user/examples/token-authorization/
TokenFilter#invoke 的实现如下:
@Override
public Result invoke(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation inv)
throws RpcException {
// 获取 服务提供者的 token 值
String token = invoker.getUrl().getParameter(Constants.TOKEN_KEY);
if (ConfigUtils.isNotEmpty(token)) {
// 获取消费者远程调用的token值
Class<?> serviceType = invoker.getInterface();
Map<String, String> attachments = inv.getAttachments();
String remoteToken = attachments == null ? null : attachments.get(Constants.TOKEN_KEY);
// 进行token比较。
if (!token.equals(remoteToken)) {
throw new RpcException("Invalid token! Forbid invoke remote service " + serviceType + " method " + inv.getMethodName() + "() from consumer " + RpcContext.getContext().getRemoteHost() + " to provider " + RpcContext.getContext().getLocalHost());
}
}
return invoker.invoke(inv);
}
6. AccessLogFilter
AccessLogFilter 的作用是将调用记录追加到日志中。作用于提供者,通过 accesslog 属性激活。
- 对于 accesslog = true || default 的情况,直接调用日志框架进行写日志
- 对于其他情况,则认为 accesslog 为日志文件路径。会将其保存到 logQueue中,其中key为 accesslog ,value 为日志内容。同时会启动一个定时任务,每隔 5s 将 logQueue 中的内容写入到日志文件中。
AccessLogFilter#invoke 实现如下:
private final ConcurrentMap<String, Set<String>> logQueue = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Set<String>>();
@Override
public Result invoke(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation inv) throws RpcException {
try {
String accesslog = invoker.getUrl().getParameter(Constants.ACCESS_LOG_KEY);
if (ConfigUtils.isNotEmpty(accesslog)) {
RpcContext context = RpcContext.getContext();
String serviceName = invoker.getInterface().getName();
String version = invoker.getUrl().getParameter(Constants.VERSION_KEY);
String group = invoker.getUrl().getParameter(Constants.GROUP_KEY);
StringBuilder sn = new StringBuilder();
// ... 拼接 sn 日志
String msg = sn.toString();
// 如果 accesslog 是默认情况 : accesslog = true || default
if (ConfigUtils.isDefault(accesslog)) {
// 默认情况 直接调用日志框架进行写日志
LoggerFactory.getLogger(ACCESS_LOG_KEY + "." + invoker.getInterface().getName()).info(msg);
} else {
// 否则认为 accesslog 指定了写入的日志文件。将其保存到logQueue 中。
// 会开启定时任务将 logQueue 的内容写入到日志文件中
log(accesslog, msg);
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.warn("Exception in AcessLogFilter of service(" + invoker + " -> " + inv + ")", t);
}
return invoker.invoke(inv);
}
private void init() {
if (logFuture == null) {
synchronized (logScheduled) {
if (logFuture == null) {
// 开启定时任务,5s 执行一次。其中 LogTask 的作用即是将logQueue 中的内容写入到对应的日志文件中。这里篇幅所限,不再贴出LogTask 的实现。
logFuture = logScheduled.scheduleWithFixedDelay(new LogTask(), LOG_OUTPUT_INTERVAL, LOG_OUTPUT_INTERVAL, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
}
}
}
// 将日志保存到 logQueue 中
private void log(String accesslog, String logmessage) {
init();
Set<String> logSet = logQueue.get(accesslog);
if (logSet == null) {
logQueue.putIfAbsent(accesslog, new ConcurrentHashSet<String>());
logSet = logQueue.get(accesslog);
}
if (logSet.size() < LOG_MAX_BUFFER) {
logSet.add(logmessage);
}
}
7. ActiveLimitFilter & ExecuteLimitFilter
ActiveLimitFilter & ExecuteLimitFilter 完成了Dubbo 并发调用的次数限制。
- ActiveLimitFilter 控制了消费者端最大并发,作用于消费者, 通过 actives 属性激活。ActiveLimitFilter 限制的次数作用的是同一个提供者的同一个接口的同一个方法。
- ExecuteLimitFilter 控制了提供者端最大并发,作用于提供者,通过 executes 属性激活。ExecuteLimitFilter 限制的次数作用的是当前提供者的某个方法最大可以支持多少并发访问。
7.1 ActiveLimitFilter
ActiveLimitFilter#invoke 实现如下:
@Override
public Result invoke(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
URL url = invoker.getUrl();
String methodName = invocation.getMethodName();
// 获取最大调用次数
int max = invoker.getUrl().getMethodParameter(methodName, Constants.ACTIVES_KEY, 0);
// 获取当前消费者对 当前方法的调用统计状态 RpcStatus
RpcStatus count = RpcStatus.getStatus(invoker.getUrl(), invocation.getMethodName());
// 判断是否达到最大限制,如果到达次数限制则进入 if分支
if (!RpcStatus.beginCount(url, methodName, max)) {
// 获取超时时间
long timeout = invoker.getUrl().getMethodParameter(invocation.getMethodName(), Constants.TIMEOUT_KEY, 0);
// 获取当前时间作为开始时间
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 最大等待时间。为 超时时间
long remain = timeout;
synchronized (count) {
// while 循环,直到活跃调用次数小于 max时才会跳出
while (!RpcStatus.beginCount(url, methodName, max)) {
try {
// 等待,最大等待时间为 remain
count.wait(remain);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// ignore
}
// 获取等待时间差
long elapsed = System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
// 如果等待阶段已经超时则抛出异常
remain = timeout - elapsed;
if (remain <= 0) {
//... 抛出异常
}
}
}
}
// 到达这里说明当前活跃访问数量小于 最大限制数 max,可以进行正常调用
boolean isSuccess = true;
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
// 进行服务调用
return invoker.invoke(invocation);
} catch (RuntimeException t) {
isSuccess = false;
throw t;
} finally {
// 减少一个活跃调用次数
RpcStatus.endCount(url, methodName, System.currentTimeMillis() - begin, isSuccess);
if (max > 0) {
synchronized (count) {
// 唤醒其他等待者
count.notifyAll();
}
}
}
}
7.2 ExecuteLimitFilter
ExecuteLimitFilter#invoke 提供端的活跃调用限制 。逻辑和 ActiveLimitFilter 基本相同。其实现如下:
@Override
public Result invoke(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
URL url = invoker.getUrl();
String methodName = invocation.getMethodName();
// 获取服务端针对 methodName 的最大并发调用次数
int max = url.getMethodParameter(methodName, Constants.EXECUTES_KEY, 0);
// 如果当前并发超过了最大并发次数限制。直接抛出异常
if (!RpcStatus.beginCount(url, methodName, max)) {
throw new RpcException("Failed to invoke method " + invocation.getMethodName() + " in provider " +
url + ", cause: The service using threads greater than <dubbo:service executes="" + max +
"" /> limited.");
}
// 开始常规调用
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
boolean isSuccess = true;
try {
return invoker.invoke(invocation);
} catch (Throwable t) {
isSuccess = false;
if (t instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) t;
} else {
throw new RpcException("unexpected exception when ExecuteLimitFilter", t);
}
} finally {
// 调用结束,并发量减一
RpcStatus.endCount(url, methodName, System.currentTimeMillis() - begin, isSuccess);
}
注意:
- ExecuteLimitFilter在超过限制的数量后会直接返回,而ActiveLimitFilter会等待,直到超时。
- RpcStatus 中缓存了每个方法的正在调用的次数等信息。并且通过原子类(AtomicXxx) 来控制线程安全。
8. ClassLoaderFilter
切换线程上下文类加载器,作用于消费者。默认激活状态。作用是在设计目的中,切换到加载了接口定义的类加载器,以便实现与相同的类加载器上下文一起工作。
@Override
public Result invoke(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
ClassLoader ocl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
// 切换类加载器为借口的类加载器
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(invoker.getInterface().getClassLoader());
try {
return invoker.invoke(invocation);
} finally {
// 切换回类加载器
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(ocl);
}
}
目前理解深度不够理解其作用场景,怀疑是为了解决双亲委派模式,但感觉不像
9. ContextFilter & ConsumerContextFilter
ContextFilter 和 ConsumerContextFilter 完成了 Dubbo参数隐式传递。
详参:Dubbo笔记 ⑲ :隐式参数传递
10. ExceptionFilter
ExceptionFilter 作用即是对服务端的调用异常做规范化处理。作用于服务提供者,默认激活状态。将所有不满足条件的异常封装成 RuntimeException 返回给客户端。
ExceptionFilter#invoke 实现如下:
@Override
public Result invoke(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
try {
return invoker.invoke(invocation);
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
// 运行时异常打印 error 日志后抛出
logger.error("Got unchecked and undeclared exception which called by " + RpcContext.getContext().getRemoteHost()
+ ". service: " + invoker.getInterface().getName() + ", method: " + invocation.getMethodName()
+ ", exception: " + e.getClass().getName() + ": " + e.getMessage(), e);
throw e;
}
}
@Override
public Result onResponse(Result result, Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) {
// 非泛化调用时出现了异常
if (result.hasException() && GenericService.class != invoker.getInterface()) {
try {
Throwable exception = result.getException();
// directly throw if it's checked exception
// 受检异常(编译时异常)直接抛出
if (!(exception instanceof RuntimeException) && (exception instanceof Exception)) {
return result;
}
// directly throw if the exception appears in the signature
try {
// 如果该方法声明了该异常,则直接抛出
Method method = invoker.getInterface().getMethod(invocation.getMethodName(), invocation.getParameterTypes());
Class<?>[] exceptionClassses = method.getExceptionTypes();
for (Class<?> exceptionClass : exceptionClassses) {
if (exception.getClass().equals(exceptionClass)) {
return result;
}
}
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
return result;
}
// 未在方法签名上定义的异常,在服务器端打印ERROR日志
// for the exception not found in method's signature, print ERROR message in server's log.
logger.error("Got unchecked and undeclared exception which called by " + RpcContext.getContext().getRemoteHost()
+ ". service: " + invoker.getInterface().getName() + ", method: " + invocation.getMethodName()
+ ", exception: " + exception.getClass().getName() + ": " + exception.getMessage(), exception);
// directly throw if exception class and interface class are in the same jar file.
// 如果异常类和接口类在同一个jar文件中,则直接抛出。
String serviceFile = ReflectUtils.getCodeBase(invoker.getInterface());
String exceptionFile = ReflectUtils.getCodeBase(exception.getClass());
if (serviceFile == null || exceptionFile == null || serviceFile.equals(exceptionFile)) {
return result;
}
// directly throw if it's JDK exception
// 如果是 JDK 异常直接抛出
String className = exception.getClass().getName();
if (className.startsWith("java.") || className.startsWith("javax.")) {
return result;
}
// directly throw if it's dubbo exception
// 如果是 Dubbo的 RpcException 异常直接抛出
if (exception instanceof RpcException) {
return result;
}
// otherwise, wrap with RuntimeException and throw back to the client
// 否则封装成 RuntimeException 异常返回给客户端
return new RpcResult(new RuntimeException(StringUtils.toString(exception)));
} catch (Throwable e) {
logger.warn("Fail to ExceptionFilter when called by " + RpcContext.getContext().getRemoteHost()
+ ". service: " + invoker.getInterface().getName() + ", method: " + invocation.getMethodName()
+ ", exception: " + e.getClass().getName() + ": " + e.getMessage(), e);
return result;
}
}
return result;
}
11. DeprecatedFilter
DeprecatedFilter 作用是日志记录调用废弃方法的过程,但并非阻断调用,作用于服务消费者,通过 deprecated 属性激活。
DeprecatedFilter#invoke 实现如下:
@Override
public Result invoke(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
String key = invoker.getInterface().getName() + "." + invocation.getMethodName();
if (!logged.contains(key)) {
logged.add(key);
// 如果方法标记已经废弃,则打印 error 日志。但并不阻止本地调用
if (invoker.getUrl().getMethodParameter(invocation.getMethodName(), Constants.DEPRECATED_KEY, false)) {
LOGGER.error("The service method " + invoker.getInterface().getName() + "." + getMethodSignature(invocation) + " is DEPRECATED! Declare from " + invoker.getUrl());
}
}
return invoker.invoke(invocation);
}
12. CompatibleFilter
兼容过滤器, 用于兼容不同的Dubbo之间的相互调用
CompatibleFilter#invoke 实现如下:
@Override
public Result invoke(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
Result result = invoker.invoke(invocation);
// 如果方法不以 $ 开头 && 调用没有出现异常
if (!invocation.getMethodName().startsWith("$") && !result.hasException()) {
// 获取返回值
Object value = result.getValue();
if (value != null) {
try {
// 获取方法实例
Method method = invoker.getInterface().getMethod(invocation.getMethodName(), invocation.getParameterTypes());
// 获取f昂发返回值
Class<?> type = method.getReturnType();
Object newValue;
// 获取序列化方式
String serialization = invoker.getUrl().getParameter(Constants.SERIALIZATION_KEY);
// 如果是 json 或 fastjson 序列化方式则
if ("json".equals(serialization)
|| "fastjson".equals(serialization)) {
// If the serialization key is json or fastjson
Type gtype = method.getGenericReturnType();
newValue = PojoUtils.realize(value, type, gtype);
} else if (!type.isInstance(value)) {
//if local service interface's method's return type is not instance of return value
// 如果本地服务接口的方法的返回类型不是返回值的实例。进行类型装换
newValue = PojoUtils.isPojo(type)
? PojoUtils.realize(value, type)
: CompatibleTypeUtils.compatibleTypeConvert(value, type);
} else {
newValue = value;
}
if (newValue != value) {
result = new RpcResult(newValue);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.warn(t.getMessage(), t);
}
}
}
return result;
}
13. TimeoutFilter
TimeoutFilter 作用即日志记录超时调用的过程,作用于服务提供者,默认激活状态
TimeoutFilter#invoke 实现如下:
@Override
public Result invoke(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Result result = invoker.invoke(invocation);
long elapsed = System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
// 超时则日志记录
if (invoker.getUrl() != null
&& elapsed > invoker.getUrl().getMethodParameter(invocation.getMethodName(),
"timeout", Integer.MAX_VALUE)) {
// 使用程序默认日志框架记录
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("invoke time out. method: " + invocation.getMethodName()
+ " arguments: " + Arrays.toString(invocation.getArguments()) + " , url is "
+ invoker.getUrl() + ", invoke elapsed " + elapsed + " ms.");
}
}
return result;
}
14. TraceFilter
TraceFilter 完成了 Dubbo telent 的功能,作用于服务提供者,默认激活状态。
从 2.0.5 版本开始,dubbo 开始支持通过 telnet 命令来进行服务治理。
关于 dubbo telnet 使用详参: https://dubbo.apache.org/zh/docs/v2.7/user/references/telnet/
关于 TraceFilter 逻辑详参:https://blog.csdn.net/yuanshangshenghuo/article/details/107794082
这里参考上述参考文章简单总结 :telnet 命令会被 dubbo handler 读取处理,将 trace 命令解析出来后交由 TraceTelnetHandler。TraceTelnetHandler 找到对应的 Invoker 后调用 TraceFilter#addTracer 方法添加追踪监控任务。之后当服务提供者被调用时,在 TraceFilter#invoke 方法中会判断是否是追踪方法,如果是,则进行追踪并将信息写回 telnet 通道。
public static void addTracer(Class<?> type, String method, Channel channel, int max) {
channel.setAttribute(TRACE_MAX, max);
channel.setAttribute(TRACE_COUNT, new AtomicInteger());
String key = method != null && method.length() > 0 ? type.getName() + "." + method : type.getName();
Set<Channel> channels = tracers.get(key);
if (channels == null) {
tracers.putIfAbsent(key, new ConcurrentHashSet<Channel>());
channels = tracers.get(key);
}
channels.add(channel);
}
public static void removeTracer(Class<?> type, String method, Channel channel) {
channel.removeAttribute(TRACE_MAX);
channel.removeAttribute(TRACE_COUNT);
String key = method != null && method.length() > 0 ? type.getName() + "." + method : type.getName();
Set<Channel> channels = tracers.get(key);
if (channels != null) {
channels.remove(channel);
}
}
TraceFilter#invoke 实现如下:
@Override
public Result invoke(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Result result = invoker.invoke(invocation);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 如果 tracers 不为空,则说明当前有服务跟踪
if (tracers.size() > 0) {
// 获取当前接口 或方法的 telnet 通道
String key = invoker.getInterface().getName() + "." + invocation.getMethodName();
Set<Channel> channels = tracers.get(key);
if (channels == null || channels.isEmpty()) {
key = invoker.getInterface().getName();
channels = tracers.get(key);
}
if (channels != null && !channels.isEmpty()) {
for (Channel channel : new ArrayList<Channel>(channels)) {
// 当前通道保持连接
if (channel.isConnected()) {
try {
int max = 1;
// 获取追踪次数
Integer m = (Integer) channel.getAttribute(TRACE_MAX);
if (m != null) {
max = (int) m;
}
int count = 0;
// 获取已经追踪的次数
AtomicInteger c = (AtomicInteger) channel.getAttribute(TRACE_COUNT);
if (c == null) {
c = new AtomicInteger();
channel.setAttribute(TRACE_COUNT, c);
}
// i++
count = c.getAndIncrement();
// 如果追踪次数没达到上限,将调用信息写回 telnet 通道
if (count < max) {
String prompt = channel.getUrl().getParameter(Constants.PROMPT_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_PROMPT);
channel.send("rn" + RpcContext.getContext().getRemoteAddress() + " -> "
+ invoker.getInterface().getName()
+ "." + invocation.getMethodName()
+ "(" + JSON.toJSONString(invocation.getArguments()) + ")" + " -> " + JSON.toJSONString(result.getValue())
+ "rnelapsed: " + (end - start) + " ms."
+ "rnrn" + prompt);
}
// 到达追踪次数上限,移除该通道
if (count >= max - 1) {
channels.remove(channel);
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
channels.remove(channel);
logger.warn(e.getMessage(), e);
}
} else {
channels.remove(channel);
}
}
}
}
return result;
}
15. FutureFilter
用于完成 Dubbo的事件回调。作用于消费者,默认激活状态。实现了在调用之前、调用之后、出现异常时,会触发 oninvoke、onreturn、onthrow 三个事件,可以配置当事件发生时,通知哪个类的哪个方法。
详参:Dubbo笔记衍生篇⑧:事件通知 FutureFilter
16. MonitorFilter
作用于消费者和提供者。
@Override
public Result invoke(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
// 如果指定了监控中心
if (invoker.getUrl().hasParameter(Constants.MONITOR_KEY)) {
RpcContext context = RpcContext.getContext(); // provider must fetch context before invoke() gets called
String remoteHost = context.getRemoteHost();
long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); // record start timestamp
// 增加活跃调用次数
getConcurrent(invoker, invocation).incrementAndGet(); // count up
try {
// 服务调用
Result result = invoker.invoke(invocation); // proceed invocation chain
collect(invoker, invocation, result, remoteHost, start, false);
return result;
} catch (RpcException e) {
collect(invoker, invocation, null, remoteHost, start, true);
throw e;
} finally {
// 减少活跃调用次数
getConcurrent(invoker, invocation).decrementAndGet(); // count down
}
} else {
return invoker.invoke(invocation);
}
}
// 汇总监控指标
private void collect(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation, Result result, String remoteHost, long start, boolean error) {
try {
// 获取监控中心实例
URL monitorUrl = invoker.getUrl().getUrlParameter(Constants.MONITOR_KEY);
// 这里的监控中心实例为代理类。
Monitor monitor = monitorFactory.getMonitor(monitorUrl);
if (monitor == null) {
return;
}
// 创建 统计 URL。URL作为信息承载
URL statisticsURL = createStatisticsUrl(invoker, invocation, result, remoteHost, start, error);
// 数据汇
monitor.collect(statisticsURL);
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.warn("Failed to monitor count service " + invoker.getUrl() + ", cause: " + t.getMessage(), t);
}
}
以上:内容部分参考
《深度剖析Apache Dubbo 核心技术内幕》
https://dubbo.apache.org/zh/docs/v2.7/dev/source/
https://blog.csdn.net/yuanshangshenghuo/article/details/107794082
https://blog.csdn.net/XiaoHanZuoFengZhou/article/details/100264651
如有侵扰,联系删除。 内容仅用于自我记录学习使用。如有错误,欢迎指正
最后
以上就是聪明大米最近收集整理的关于Dubbo笔记 ⑰ :Dubbo Filter 详解一、前言二、Filter 分类三、代码解析的全部内容,更多相关Dubbo笔记内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复