1.一个整数以8、10、16进制输出:
一个布尔类型:
#include <iostream> //输入输出头文件
#include <stdlib.h> //标准库头文件
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout << "int:" << endl;
int x = 0;
cin >> x;
cout << oct << x << endl;
cout << dec << x << endl;
cout << hex << x << endl;
cout << "bool:" << endl;
bool flag = false;
cin >> flag;
cout << boolalpha << flag << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}//命名空间关键子 namespace
namespace A {
int x = 0;
void f1();
void f2();
}
namespace B {
int x = 2;
void f1();
void f3();
}
cout << A::x << endl;
B::f1();#include <iostream>
#include <stdlib.h>
namespace A
{
int X = 0;
void fun()
{
std::cout << "A" << std::endl;
}
void fun1()
{
std::cout << "1A" << std::endl;
}
}
namespace B
{
int X = 2;
void fun()
{
std::cout << "B" << std::endl;
}
void fun2()
{
std::cout << "2B" << std::endl;
}
}
using namespace B;
int main()
{
std::cout << A::X << std::endl;
A::fun();
fun();
A::fun1();
B::fun2();
fun2();
system("pause");
return 0;
}2.通过栈实例化对象和通过堆实例化对象:
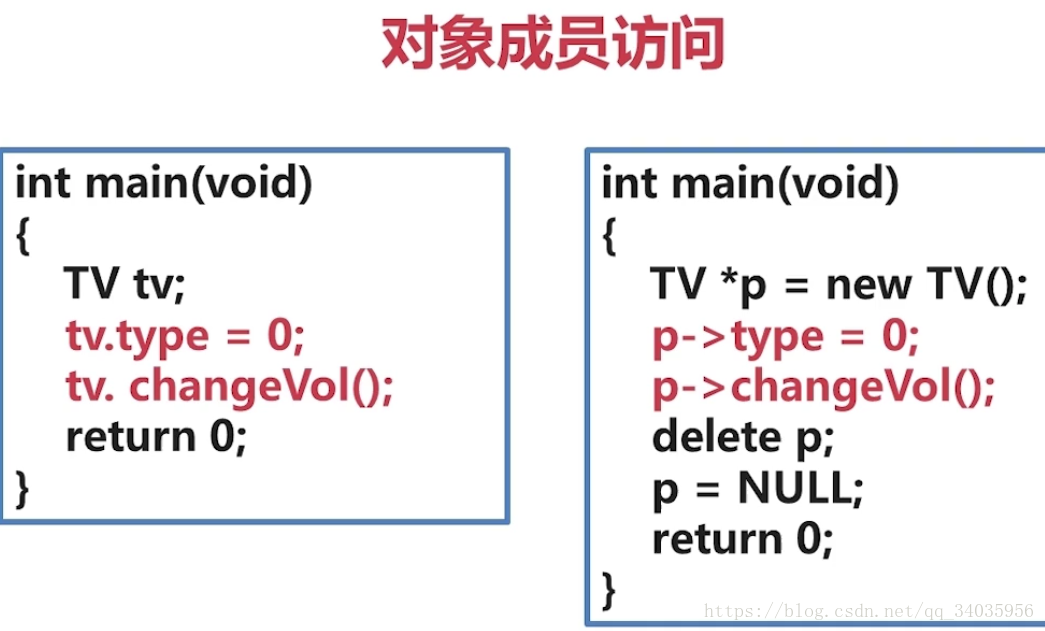
通过栈实例化对象代码:
通过堆实例化对象代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <stdlib.h>
using namespace std;
class Coordinate
{
public:
int x = 1, y = 2;
void PrintX()
{
cout << x << endl;
}
void PrintY()
{
cout << y << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
Coordinate coor;//使用栈实例化对象
coor.x = 10;
coor.y = 20;
coor.PrintX();
coor.PrintY();
Coordinate *p=new Coordinate();//使用堆实例化对象
if (NULL == p)
{
return 0;
}
p->x = 100;
p->y = 200;
p->PrintX();
p->PrintY();
delete p;
p = NULL;
system("pause");
return 0;
}3.C++获取字符串输入:
cout << "请输入姓名:";
string name;
getline(cin, name);4.为什么c++类的定义中成员名习惯加"m_"?
m是member的缩写,表示这是成员名。
2dx里大量使用了这个 不过3.0里取消了 现在直接是 _xxx
满屏幕的m_ 看着真恶心那
5.内联函数
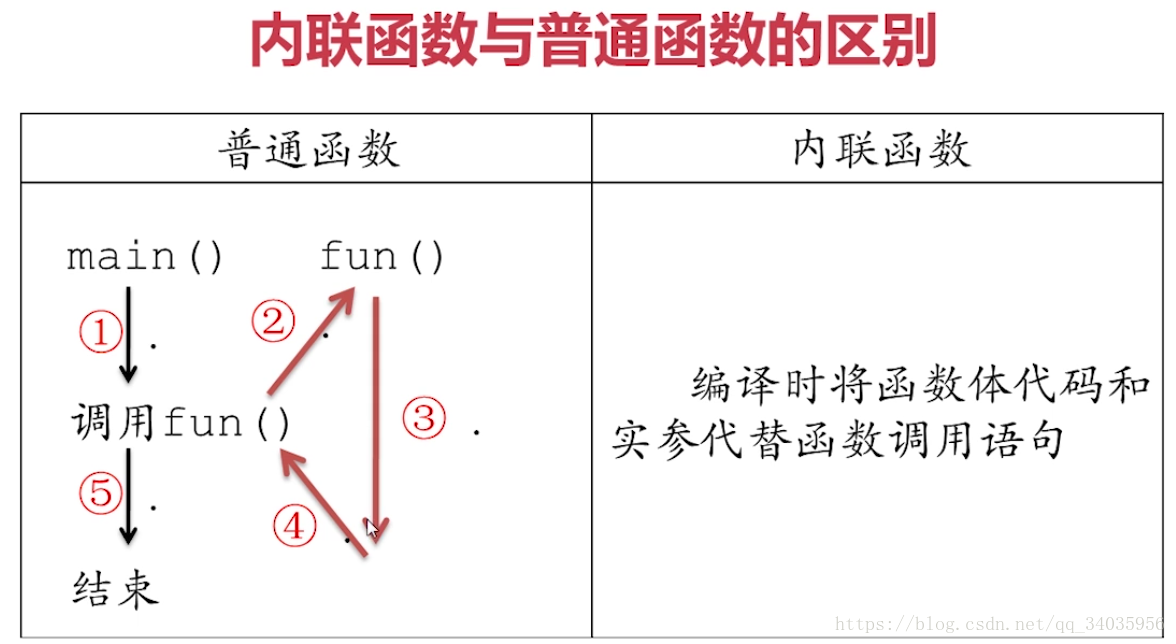
同文件类外定义:
//同文件类外定义
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <stdlib.h>
using namespace std;
class Teacher
{
public:
void SetName(string);
string GetName();
void SetAge(int _age);
int GetAge();
void SetGender(string _gender);
string GetGender();
void Teach();
private:
string strName;
int iAge;
string strGender;
};
void Teacher::SetName(string _name)
{
strName = _name;
}
string Teacher::GetName()
{
return strName;
}
void Teacher::SetAge(int _age)
{
iAge = _age;
}
int Teacher::GetAge()
{
return iAge;
}
void Teacher::SetGender(string _gender)
{
strGender = _gender;
}
string Teacher::GetGender()
{
return strGender;
}
void Teacher::Teach()
{
cout << "正在上课" << endl;
}
int main()
{
Teacher *teacher = new Teacher();
teacher->SetName("kerven");
teacher->SetAge(23);
teacher->SetGender("男");
cout << "姓名:" + teacher->GetName() << endl;
cout << "年龄:" << teacher->GetAge() << endl;
cout << "性别:" + teacher->GetGender() << endl;
teacher->Teach();
delete teacher;
teacher = NULL;
system("pause");
return 0;
}分文件类外定义:
Teacher.h
//分文件类外定义
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Teacher
{
public:
void SetName(string _name);
string GetName();
void SetAge(int _age);
int GetAge();
void SetGender(string _gender);
string GetGender();
void Teach();
private:
string strName;
int iAge;
string strGender;
};Teacher.cpp
//分文件类外定义
#include "Teacher.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void Teacher::SetName(string _name)
{
strName = _name;
}
string Teacher::GetName()
{
return strName;
}
void Teacher::SetAge(int _age)
{
iAge = _age;
}
int Teacher::GetAge()
{
return iAge;
}
void Teacher::SetGender(string _gender)
{
strGender = _gender;
}
string Teacher::GetGender()
{
return strGender;
}
void Teacher::Teach()
{
cout << "正在上课" << endl;
}//分文件类外定义
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include "Teacher.h"
#include <stdlib.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
Teacher *teacher = new Teacher();
teacher->SetName("kerven");
teacher->SetAge(23);
teacher->SetGender("男");
cout << "姓名:" + teacher->GetName() << endl;
cout << "年龄:" << teacher->GetAge() << endl;
cout << "性别:" + teacher->GetGender() << endl;
teacher->Teach();
delete teacher;
teacher = NULL;
system("pause");
return 0;
}6.内存分区
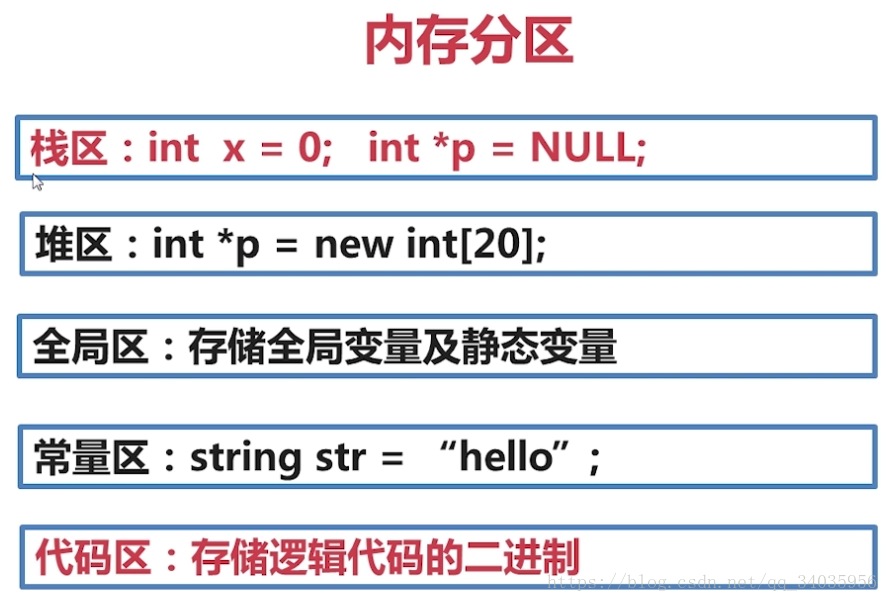
7.C++构造函数初始化列表初始化列表的特性:--效率高、速度快
(1).初始化列表先于构造函数执行
(2).初始化列表只能用于构造函数
(3).初始化列表可以同时初始化多个数据成员
//初始化列表存在的必要性
class Circle
{
public:
Circle():dPi(3.14){}
private:
const double dPi;
};8.C++拷贝构造函数--拷贝构造函数不能被重载

Teacher t1;
Teacher t2 = t1;
Teacher t3(t1);
9.析构函数

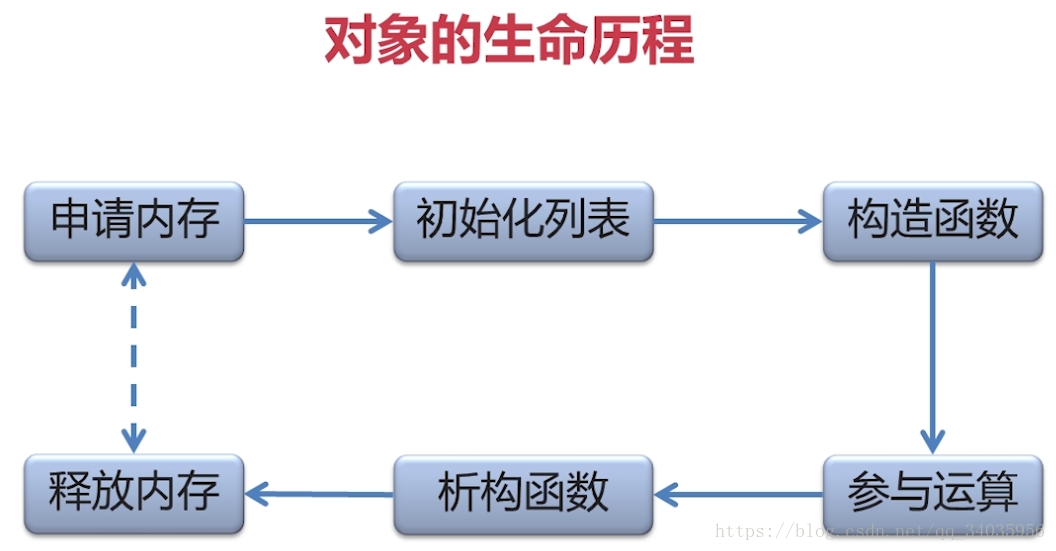
10.C++引用(别名)
11.C++语言-const(常量)
常指针、指针常量、常量常指针
12.

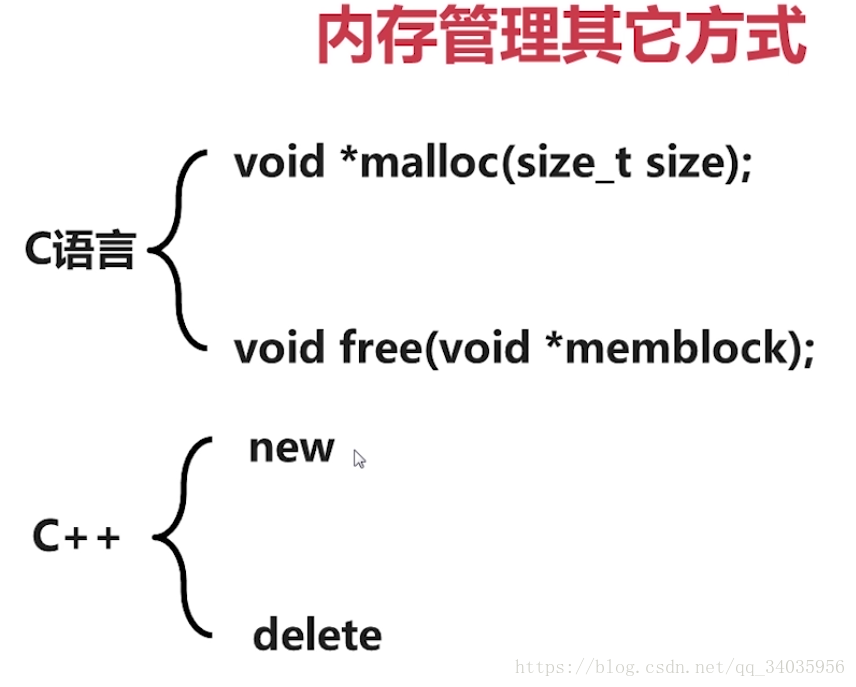
13.C++ 忽略警告的写法:
#pragma warning(disable:4305)
14.对象含有对象成员时各构造函数与析构函数的执行顺序:
例子:当线段Line含有坐标A和B时,
构造函数:A、B、Line
析构函数:Line、B、A
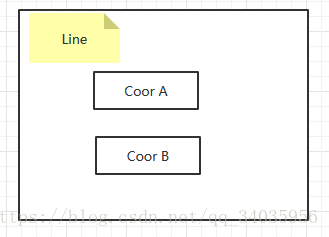
15.[C++]深拷贝与浅拷贝
16.C++ sort函数
#include <algorithm>
sort(a1, a1 + size);
17.C++动态数组
#include <iostream>
int main() {
// 1. initialize
vector<int> v0;
vector<int> v1(5, 0);
// 2. make a copy
vector<int> v2(v1.begin(), v1.end());
vector<int> v3(v2);
// 2. cast an array to a vector
int a[5] = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4};
vector<int> v4(a, *(&a + 1));
// 3. get length
cout << "The size of v4 is: " << v4.size() << endl;
// 4. access element
cout << "The first element in v4 is: " << v4[0] << endl;
// 5. iterate the vector
cout << "[Version 1] The contents of v4 are:";
for (int i = 0; i < v4.size(); ++i) {
cout << " " << v4[i];
}
cout << endl;
cout << "[Version 2] The contents of v4 are:";
for (int& item : v4) {
cout << " " << item;
}
cout << endl;
cout << "[Version 3] The contents of v4 are:";
for (auto item = v4.begin(); item != v4.end(); ++item) {
cout << " " << *item;
}
cout << endl;
// 6. modify element
v4[0] = 5;
// 7. sort
sort(v4.begin(), v4.end());
// 8. add new element at the end of the vector
v4.push_back(-1);
// 9. delete the last element
v4.pop_back();
}18.C++虚继承
19.
#ifndef PERSON_H
#define PERSON_H
#endif
20.来一次完整的:
//Person.h
#ifndef PERSON_H
#define PERSON_H
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Person
{
public:
Person(string name);
virtual ~Person() {}
virtual void work() = 0;
private:
string strName;
};
#endif//Person.cpp
#include "Person.h"
Person::Person(string name)
{
strName = name;
}//Worker.h
#ifndef WORKER_H
#define WORKER_H
#include "Person.h"
class Worker : public Person
{
public:
Worker(string name, int age);
virtual void work();
private:
int iAge;
};
#endif
//Worker.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "Worker.h"
using namespace std;
Worker::Worker(string name, int age) : Person(name)
{
iAge = age;
}
void Worker::work()
{
cout << "work" << endl;
}//Dustman.h
#ifndef DUSTMAN_H
#define DUSTMAN_H
#include "Worker.h"
class Dustman:public Worker
{
public:
Dustman(string name, int age);
virtual void work();
};
#endif
//Dustman.cpp
#include "Dustman.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
Dustman::Dustman(string name, int age) :Worker(name, age)
{
}
void Dustman::work()
{
cout << "扫地" << endl;
}//Demo.cpp
#include "Person.h"
#include "Worker.h"
#include "Dustman.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
Dustman *d = new Dustman("kerven", 18);
d->work();
Worker worker("xiaowen", 20);
worker.work();
delete d;
d = NULL;
system("pause");
return 0;
}NEW
========C++常用标准库:vector、map、list
vector向量:对数组的封装
特点:读取能在常数时间内完成
vector<T> v1; --vector<int> ivec1; --vector<string> svec1;
vector<T> v2(v1); --vector<int> ivec2(ivec1); --vector<string> svec2(svec1);
vector<T> v3(n,i); //v3包含n个值为i的元素 --vector<int> ivec4(10, -1);
vector<T> v4(n); //v4包含n个值 --vector<string> scec(10, "hi");
vector常用函数
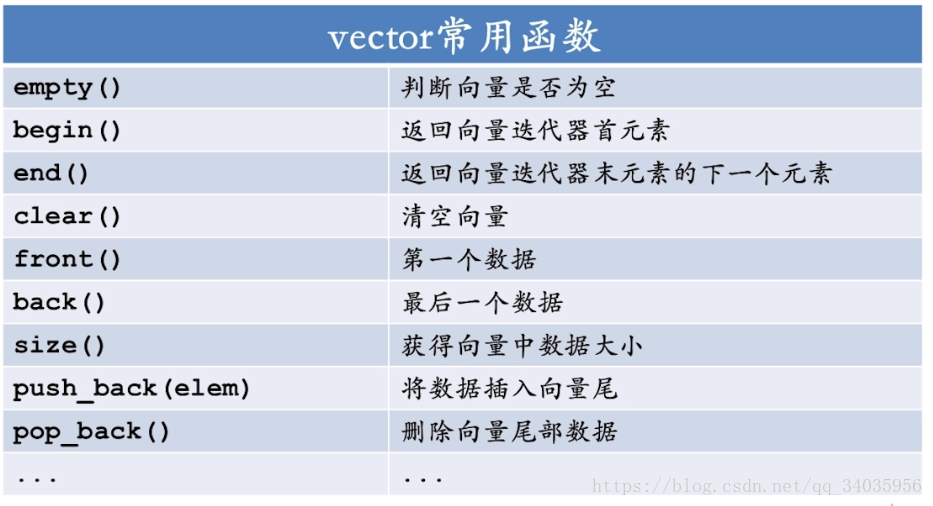
迭代器:iterator
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<string> vec;
vec.push_back("001");
vector<string>::iterator citer = vec.begin();
for(;citer!=vec.end();citer++)
{
cout << *citer << endl;
}
return 0;
}list:链表(头节点、链表与数组的插入对比、数据域、指针域)--双链表
特点:数据插入速度快
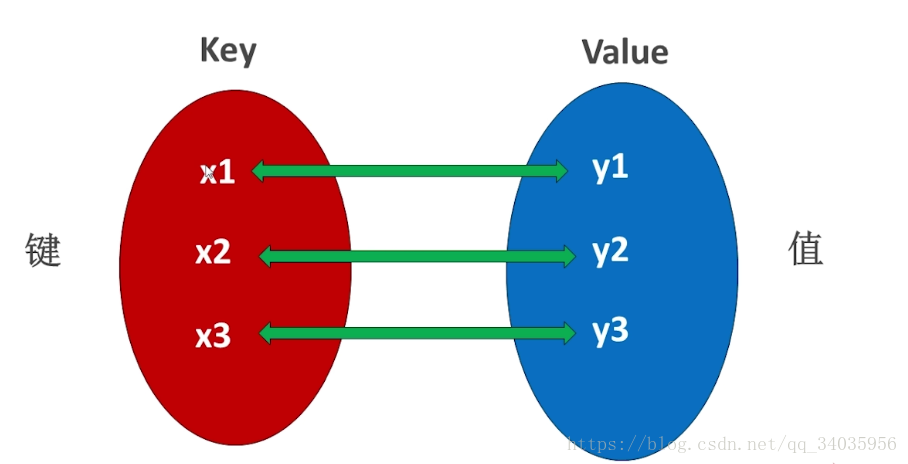
map:映射
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
map<int, string> m;
pair<int, string> p1(10, "shanghai");
pair<int, string> p2(20, "beijing");
m.insert(p1);
m.insert(p2);
cout << m[10] <<endl;
cout << m[20] <<endl;
return 0;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <string>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
map<string, string> sTosMap;
pair<string, string> p1("S", "Shanghai");
pair<string, string> p2("B", "Beijing");
sTosMap.insert(p1);
sTosMap.insert(p2);
cout << sTosMap["S"] << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}数据结构:是指相互之间存在一种或者多种特定关系的数据元素的集合。
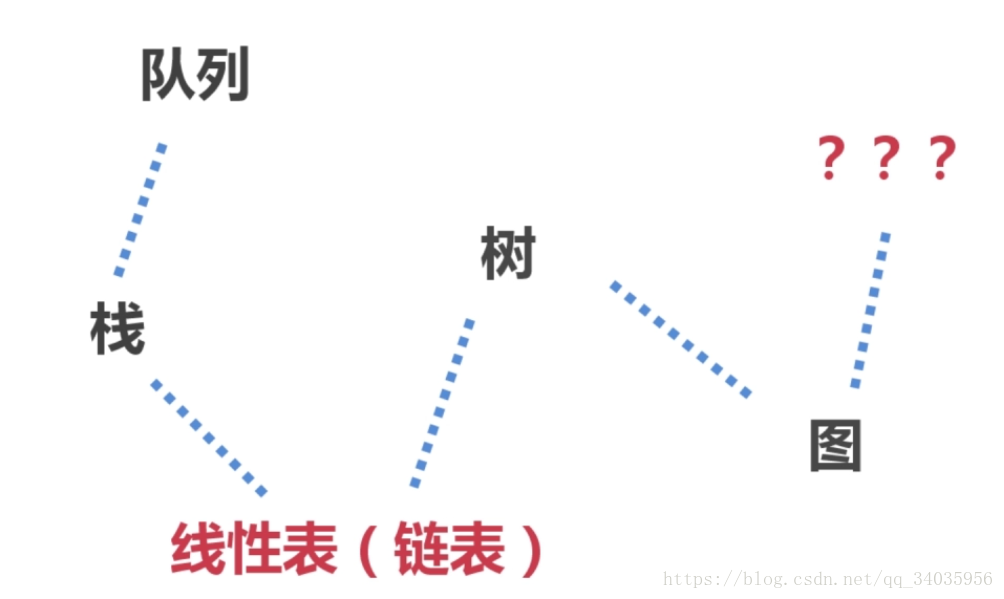 队列:先进先出:FIFO:first in first out
队列:先进先出:FIFO:first in first out
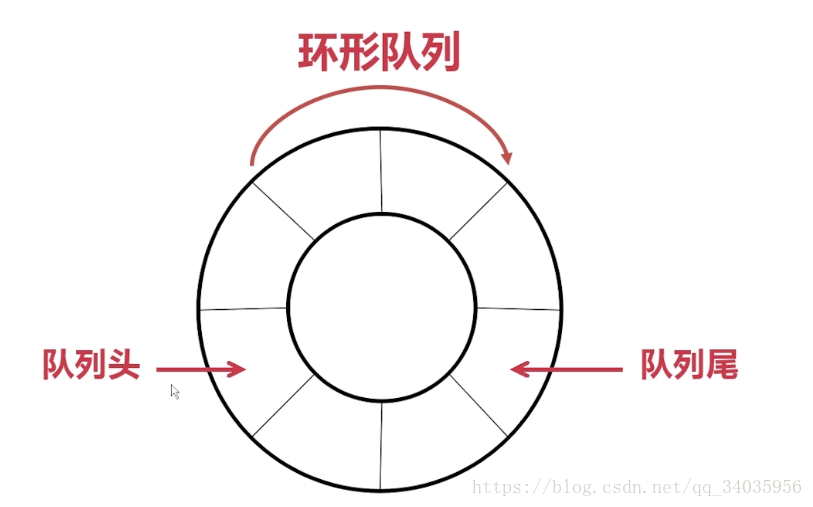
普通队列、环形队列
//MyQueue.h
#pragma once
class MyQueue
{
public:
MyQueue(int queueCapacity); //InitQueue(&Q) 创建队列
virtual ~MyQueue(); //DestoryQueue(&Q) 销毁队列
void ClearQueue(); //ClearQueue(&Q) 清空队列
bool QueueEmpty() const; //QueueEmpty(Q) 判空队列
bool QueueFull() const; //判断队列是否为满
int QueueLength() const; //QueueLength(Q) 队列长度
bool EnQueue(int element); //EnQueue(&Q, element) 新元素入队
bool DeQueue(int &element); //DeQueue(&Q, &element) 首元素出队
void QueueTraverse(); //QueueTraverse(Q, visit()) 遍历队列
private:
int *m_pQueue; //队列数组指针
int m_iQueueLen; //队列元素个数
int m_iQueueCapacity; //队列数组容量
int m_iHead;
int m_iTail;
};//MyQueue.cpp
#include "MyQueue.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
MyQueue::MyQueue(int queueCapacity)
{
m_iQueueCapacity = queueCapacity;
m_pQueue = new int[m_iQueueCapacity];
ClearQueue();
}
MyQueue::~MyQueue()
{
delete[] m_pQueue;
m_pQueue = NULL;
}
void MyQueue::ClearQueue()
{
m_iHead = 0;
m_iTail = 0;
m_iQueueLen = 0;
}
bool MyQueue::QueueEmpty() const
{
return m_iQueueLen == 0 ? true : false;
}
int MyQueue::QueueLength() const
{
return m_iQueueLen;
}
bool MyQueue::QueueFull() const
{
return m_iQueueLen == m_iQueueCapacity ? true : false;
}
bool MyQueue::EnQueue(int element)
{
if (QueueFull())
{
return false;
}
else
{
m_pQueue[m_iTail] = element;
m_iTail++;
m_iTail = m_iTail % m_iQueueCapacity;
m_iQueueLen++;
return true;
}
}
bool MyQueue::DeQueue(int &element)
{
if (QueueEmpty())
{
return false;
}
else
{
element = m_pQueue[m_iHead];
m_iHead++;
m_iHead = m_iHead % m_iQueueCapacity;
m_iQueueLen--;
return true;
}
}
void MyQueue::QueueTraverse()
{
for (int i = m_iHead; i < m_iQueueLen + m_iHead; i++)
{
cout << m_pQueue[i % m_iQueueCapacity] << endl;
}
}//Main.h
//环形队列C++实现
#include <iostream>
#include "MyQueue.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
MyQueue *p = new MyQueue(4);
p->EnQueue(10);
p->EnQueue(13);
p->EnQueue(15);
p->EnQueue(17);
p->EnQueue(21);
p->QueueTraverse();
int e = 0;
p->DeQueue(e);
cout << endl;
cout << e << endl;
p->DeQueue(e);
cout << endl;
cout << e << endl;
cout << endl;
p->QueueTraverse();
p->ClearQueue();
p->QueueTraverse();
cout << endl;
p->EnQueue(17);
p->EnQueue(21);
p->QueueTraverse();
delete p;
system("pause");
return 0;
}例子:用环形队列,以雇员的类为例子的代码:
//Customer.h
#ifndef CUSTOMER_H
#define CUSTOMER_H
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Customer
{
public:
Customer(string name = "", int age = 0);
void printInfo() const;
private:
string m_strName;
int m_iAge;
};
#endif
//Customer.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "Customer.h"
using namespace std;
Customer::Customer(string name, int age)
{
m_strName = name;
m_iAge = age;
}
void Customer::printInfo() const
{
cout << "xingming:" << m_strName << endl;
cout << "nianlin:" << m_iAge << endl;
cout << endl;
}//MyQueue.h
#pragma once
#include "Customer.h"
class MyQueue
{
public:
MyQueue(int queueCapacity); //InitQueue(&Q) 创建队列
virtual ~MyQueue(); //DestoryQueue(&Q) 销毁队列
void ClearQueue(); //ClearQueue(&Q) 清空队列
bool QueueEmpty() const; //QueueEmpty(Q) 判空队列
bool QueueFull() const; //判断队列是否为满
int QueueLength() const; //QueueLength(Q) 队列长度
bool EnQueue(Customer element); //EnQueue(&Q, element) 新元素入队
bool DeQueue(Customer &element); //DeQueue(&Q, &element) 首元素出队
void QueueTraverse(); //QueueTraverse(Q, visit()) 遍历队列
private:
Customer *m_pQueue; //队列数组指针
int m_iQueueLen; //队列元素个数
int m_iQueueCapacity; //队列数组容量
int m_iHead;
int m_iTail;
};//MyQueue.cpp
#include "MyQueue.h"
#include "Customer.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
MyQueue::MyQueue(int queueCapacity)
{
m_iQueueCapacity = queueCapacity;
m_pQueue = new Customer[m_iQueueCapacity];
ClearQueue();
}
MyQueue::~MyQueue()
{
delete[] m_pQueue;
m_pQueue = NULL;
}
void MyQueue::ClearQueue()
{
m_iHead = 0;
m_iTail = 0;
m_iQueueLen = 0;
}
bool MyQueue::QueueEmpty() const
{
return m_iQueueLen == 0 ? true : false;
}
int MyQueue::QueueLength() const
{
return m_iQueueLen;
}
bool MyQueue::QueueFull() const
{
return m_iQueueLen == m_iQueueCapacity ? true : false;
}
bool MyQueue::EnQueue(Customer element)
{
if (QueueFull())
{
return false;
}
else
{
m_pQueue[m_iTail] = element;
m_iTail++;
m_iTail = m_iTail % m_iQueueCapacity;
m_iQueueLen++;
return true;
}
}
bool MyQueue::DeQueue(Customer &element)
{
if (QueueEmpty())
{
return false;
}
else
{
element = m_pQueue[m_iHead];
m_iHead++;
m_iHead = m_iHead % m_iQueueCapacity;
m_iQueueLen--;
return true;
}
}
void MyQueue::QueueTraverse()
{
for (int i = m_iHead; i < m_iQueueLen + m_iHead; i++)
{
m_pQueue[i % m_iQueueCapacity].printInfo();
}
}//Main.cpp
//环形队列C++实现
#include <iostream>
#include "MyQueue.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
Customer c1("123", 10);
Customer c2("456", 20);
MyQueue *p = new MyQueue(4);
p->EnQueue(c1);
p->EnQueue(c2);
p->EnQueue(c1);
p->EnQueue(c2);
p->QueueTraverse();
Customer cc;
p->DeQueue(cc);
p->QueueTraverse();
delete p;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
最后
以上就是甜美流沙最近收集整理的关于C++基础知识的全部内容,更多相关C++基础知识内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复