软件结构分类
C/S结构 :全称为Client/Server结构,是指客户端和服务器结构。常见程序有QQ、迅雷等软件
B/S结构 :全称为Browser/Server结构,是指浏览器和服务器结构。常见浏览器有谷歌、火狐等
网络编程三要素
- IP地址
- 端口号
- 协议
IP地址
- 设备在网络中的地址, 是唯一的标识
- 全称”互联网协议地址”,也称IP地址。是分配给上网设备的数字标签。常见的IP分类为:ipv4和ipv6
简单来说 : 就是设备在网络中的唯一标识 , 想要连接哪一台电脑 , 就找到此电脑在网络中的ip地址
ipv4是由4个字节组成, 通常使用点分十进制表示法
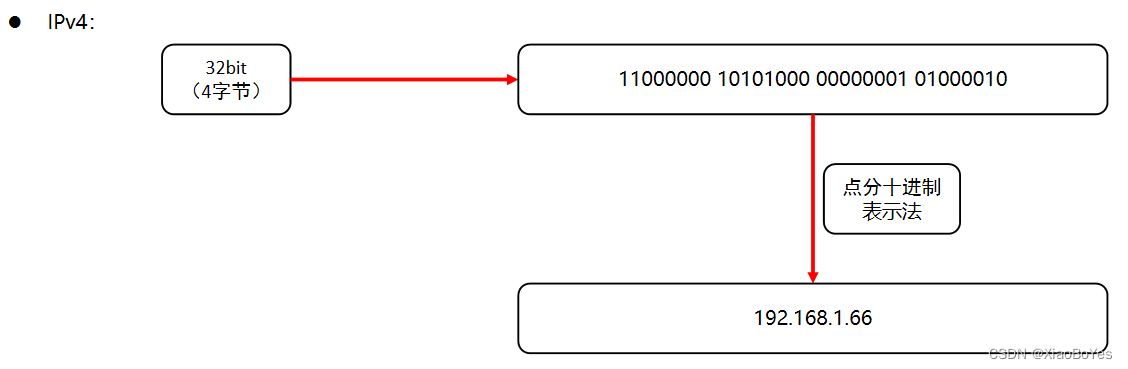
ipv6是由16个字节组成, 每两个字节为一组, 通常使用冒分十六进制表示法
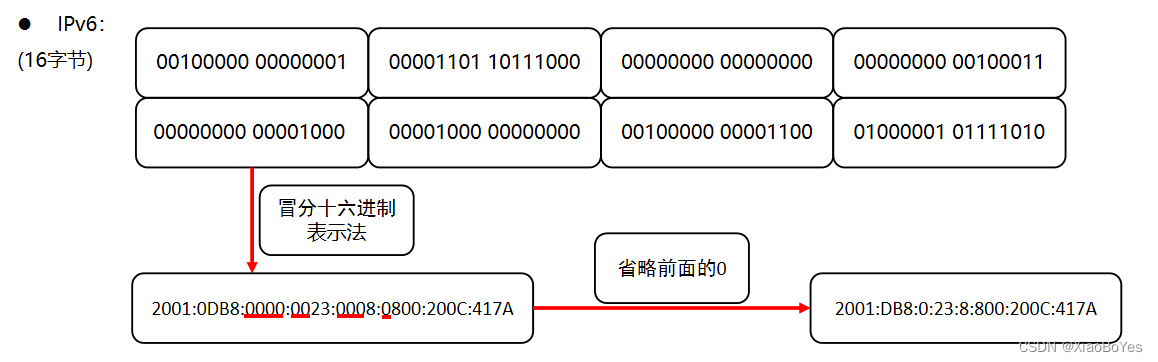
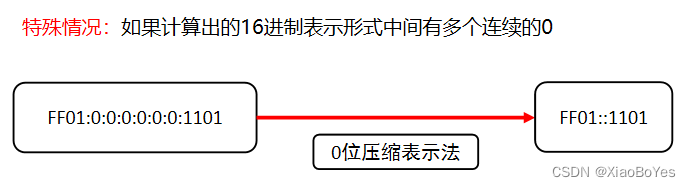
ipv6表示的特殊情况
命令行窗口中的IP操作
- 常用命令:
- ipconfig:查看本机IP地址
- ping IP地址:检查网络是否连通
- 特殊IP地址:
- 127.0.0.1:是回送地址也称本地回环地址,可以代表本机的IP地址,一般用来测试使用
Java中的IP操作
为了方便我们对IP地址的获取和操作,Java提供了一个类InetAddress 供我们使用
InetAddress:此类表示Internet协议(IP)地址
static InetAddress getByName(String host) 在给定主机名的情况下获取InetAddress类的对象
String getHostName() 获取此 IP 地址的主机名
String getHostAddress() 返回 IP 地址字符串(以文本表现形式)
端口
- 应用程序在设备中的唯一标识
- 端口号:应用程序的唯一标识方式 , 用两个字节表示的整数值,它的取值范围是0~65535。
其中0~1023之间的端口号用于一些知名的网络服务或者应用。
我们自己使用1024以上的端口号就可以了。
协议
- 数据在网络中传输的规则, 常见的协议有UDP协议和TCP协议
- UDP协议
- 用户数据报协议(User Datagram Protocol)
- UDP是面向无连接通信协议
- 速度快,有大小限制一次最多发送64K,数据不安全,易丢失数据。
- TCP协议
- 传输控制协议 (Transmission Control Protocol)
- TCP协议是面向连接的通信协议
- 速度慢,没有大小限制,数据安全
TCP通信原理
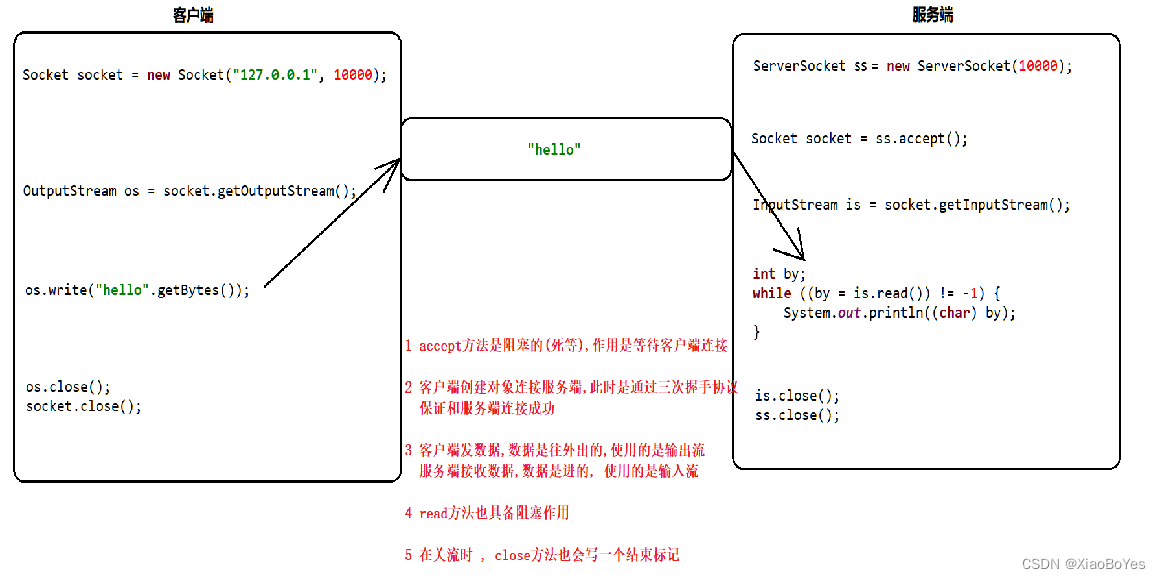
- TCP通信协议是一种可靠的网络协议,它在通信的两端各建立一个Socket对象
- 通信之前要保证连接已经建立
- 通过Socket产生IO流来进行网络通信
TCP发送数据的步骤(客户端)
public class ClientDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1 创建客户端的Socket对象 Socket(String host, int port) 与指定服务端连接
Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 10086);
// 2 通过Socket对象获取网络中的输出流 写数据
OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();
os.write("hello world".getBytes());
os.flush();
// 没有手动写结束标记
// 3 释放资源
os.close(); // 关闭输出流会自动添加结束标记
socket.close();
}
}
TCP接收数据的步骤(服务端)
public class ServerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1 创建服务端的Socket对象 : ServerSocket类
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(10086);
// 2 监听客户端连接, 并接受连接, 返回一个Socket对象
System.out.println("阻塞之前...");
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept(); // accept函数会阻塞, 除非接受到客户端连接
System.out.println("阻塞之后...");
// 3 获取网络中的输入流, 用来读取客户端发来的数据
InputStream is = socket.getInputStream();
byte[] bys = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len = is.read(bys)) != -1) { // read函数会阻塞, 除非读到结束标记
System.out.print(new String(bys, 0, len));
}
// 4 释放资源 : 服务端一般不会关闭
is.close();
socket.close();
serverSocket.close();
}
}
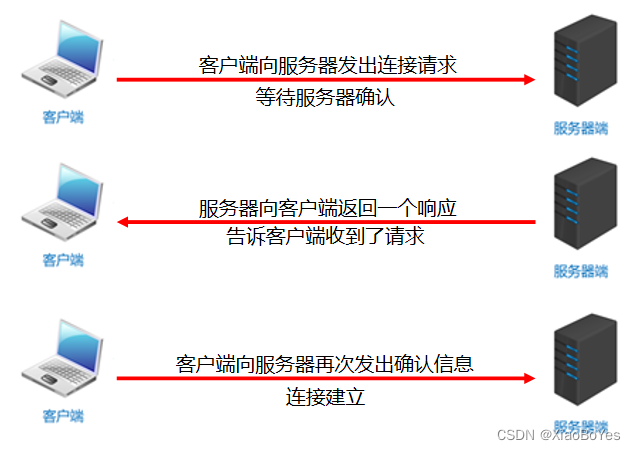
TCP的三次握手(建立连接)
TCP案例一 客户端向服务端发送图片
- 客户端:
public class ClientDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1 创建Socket对象
Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 10000);
// 把本地文件中的图片读到内存中
// 创建高效的字节输入流
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("F:\p1.jpg"));
// 把网络中字节输出流封装成高效的字节输出流
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream());
// 从本地中读一个字节 再把字节发送到服务端
byte[] bys = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len = bis.read(bys)) != -1) { // 读到结束标记后停止, 但不写入结束标记
bos.write(bys, 0, len);
bos.flush();
}
socket.shutdownOutput(); // 写入结束标记
// =====================等待服务端的反馈============================
// 把网络中的字节输入流封装成高效的字符输入流
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream()));
String s = br.readLine();
System.out.println(s);
br.close();
bos.close();
bis.close();
socket.close();
}
}
- 服务端
public class ServerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1 创建ServerSocket对象
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(10000);
// 2 监听客户端的连接
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
// 3 把网络中的字节输入流封装成高效的字节输入流
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(socket.getInputStream());
// 4 创建本地的高效字节输出流
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("day12\p1.jpg"));
// 5 使用网络字节输入流接收一个字节 再通过本地的字节输出流把字节写到本地文件中去
byte[] bys = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len = bis.read(bys)) != -1) {
bos.write(bys, 0, len);
bos.flush();
}
// =====================给客户端反馈==========================
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(socket.getOutputStream()));
bw.write("感谢, 很好看");
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
// 释放资源
bw.close();
bos.close();
bis.close();
socket.close();
serverSocket.close();
}
}
TCP案例二 客户端从服务端下载图片
- 客户端:
public class ClientDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 10010);
// 高效的网络字节输入流
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(socket.getInputStream());
// 高效的本地字节输出流
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("day12\src\com\xiaobo\homework04\p1.jpg"));
byte[] bys = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = bis.read(bys)) != -1) {
bos.write(bys, 0, len);
bos.flush();
}
//=====================给予服务端反馈=====================
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(socket.getOutputStream()));
bw.write("下载成功!");
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
//=====================关闭资源=====================
bw.close();
bos.close();
bis.close();
socket.close();
}
}
- 服务端:
public class ServerDemo {
// 定义有3个线程的线程池
private static ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(10010);
while (true) {
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept(); // 接收客户端连接
threadPool.submit(new ServerThread(socket));
}
}
}
public class ServerThread implements Runnable {
private Socket socket;
public ServerThread(Socket socket) {
this.socket = socket;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
// 高效的网络字节输出流
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream());
// 高效的本地字节输入流
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("F:test1\p2.jpg"));
byte[] bys = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = bis.read(bys)) != -1) {
bos.write(bys, 0, len);
bos.flush();
}
socket.shutdownOutput(); // 结束标记
// 高效的网络字符输入流
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream()));
String s = br.readLine();
System.out.println(s);
//=====================无资源的关闭=====================
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
最后
以上就是鲜艳小笼包最近收集整理的关于网络编程-TCP的全部内容,更多相关网络编程-TCP内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复