1、Springboot整合mybatis
1.1导入mybatis整合依赖
<!-- mybatis整合 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.1.4</version>
</dependency>
<!-- lombok -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>
1.2连接完数据库就去applicaton.yml配置一下数据库
spring:
datasource:
username: root
password: 123456
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?serverTimezone=UTC&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
1.3编写与数据库对应的实体类
package com.example.pojo;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
@Data //生成get、set方法
@AllArgsConstructor //生成所有参数构造器
@NoArgsConstructor //生成无参构造器
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private String pwd;
}
1.4.编写mapper
package com.example.mapper;
import com.example.pojo.User;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import java.util.List;
@Mapper
@Repository
public interface UserMapper {
//查询用户的全部信息
List<User> getUserList();
//select 找出id=1的用户
User getUserById(int id);
//insert 增加一个用户
int insertUser(User user);
//delete 删除id=4的用户
int deleteUser(int id);
//update 将id=2的用户名字改为小龙
int updateUser(User user);
}
@maper注解
@Mapper是mybatis自身带的注解。在spring程序中,mybatis需要找到对应的mapper,在编译时生成动态代理类,与数据库进行交互,这时需要用到@Mapper注解
1.5.编写mapper.xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.example.mapper.UserMapper">
<select id="getUserList" resultType="user">
select *
from mybatis.user
</select>
<select id="getUserById" resultType="user" parameterType="int">
select *
from mybatis.user
where id = #{id};
</select>
<insert id="insertUser" parameterType="user">
insert into mybatis.user (id, name, pwd)
values (#{id}, #{name}, #{pwd});
</insert>
<delete id="deleteUser" parameterType="int">
delete
from mybatis.user
where id = #{id};
</delete>
<update id="updateUser" parameterType="user">
update mybatis.user
set name = #{name},
pwd = #{pwd}
where id = #{id};
</update>
</mapper>
这里我们用了别名而且我们把这个mapper.xml文件放在了resources目录下,所以我们要去application.yml配置一下
mybatis:
type-aliases-package: com.example.pojo
mapper-locations: classpath:mybatis/mapper/*.xml
1.6编写controller
package com.example.controller;
import com.example.mapper.UserMapper;
import com.example.pojo.User;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@GetMapping("/getUserList")
public List<User> getUserList(){
return userMapper.getUserList();
}
@GetMapping("/getUserById/{id}")
public User getUserById(@PathVariable("id") int id){
return userMapper.getUserById(id);
}
@GetMapping("/insertUser")
public String insertUser(){
userMapper.insertUser(new User(5,"xiaoming","111"));
return "ok";
}
@GetMapping("/deleteUser")
public String deleteUser(){
userMapper.deleteUser(5);
return "ok";
}
@GetMapping("/updateUser")
public String updateUser(){
userMapper.updateUser(new User(5,"xx","111"));
return "ok";
}
}
Mybatis常用知识点
1:自动生成主键
1) 若数据库支持自动生成主键的字段(比如 MySQL 和 SQL Server),则可以设置 useGeneratedKeys=”true”,然后再把 keyProperty 设置到目标属性上
<insert id="insertEmployee" parameterType="com.mybatis.beans.Employee"
databaseId="mysql"
useGeneratedKeys="true"
keyProperty="id">
insert into tbl_employee(last_name,email,gender) values(#{lastName},#{email},#{gender})
</insert>
2:参数传递的种方法
1) 单个普通类型参数
可以接受基本类型,包装类型,字符串类型等。这种情况MyBatis可直接使用这个参数,不需要经过任何处理。
直接使用#{参数名称},直接取就可以了
2) 多个参数
任意多个参数,都会被MyBatis重新包装成一个Map传入。Map的key是param1,param2,或者0,1…,值就是参数的值
mapper中
List<Employee> selectByGenderAndAge(Short gender,String age );
xml中错误的参数传递
<select id="selectByGenderAndAge" resultMap="BaseResultMap" >
select * from employee where gender = #{gender} and age = #{age}
</select>
注意这里按参数名去引用的话会报如下错误,mybatis错误提示很细致,这里明确给我们提示,匿名参数只能使用arg1, arg0, param1, param2 类似的形式这种传参方式的缺点是不够灵活,必须严格按照参数顺序来引用
<!--BindingException: Parameter 'gender' not found. Available parameters are [arg1, arg0, param1, param2]-->
<!--所以正确的引用方式如下-->
<select id="selectByGenderAndAge" resultMap="BaseResultMap" >
select * from employee where gender = #{param1} and age = #{param2}
</select>
3) 命名参数
为参数使用@Param起一个名字,MyBatis就会将这些参数封装进map中,key就是我们自己指定的名字
mapper
List<Employee> selectByGenderAndAge( @Param("gender") Shortgender,@Param("age") String age );
xml中
<select id="selectByGenderAndAge" resultMap="BaseResultMap" >
select * from employee where gender = #{gender} and age = #{age}
</select>
4) POJO
当这些参数属于我们业务POJO时,我们直接传递POJO
mapper
List <Employee> selectByBeans(Employee employee);
xml
<select id="selectByBeans" resultMap="BaseResultMap" parameterType="com.Employee">
select
*
from employee where gender = #{gender} and age = #{age}
</select>
5) Map
我们也可以封装多个参数为map,直接传递
mapper
List<Employee> selectByMapParams(Map params);
<select id="selectByMapParams" resultMap="BaseResultMap" parameterType="map">
select * from employee where gender = #{gender} and age = #{age}
</select>
6) Collection/Array
mapper
List <Employee> findByList(List list);
<select id="findByList" resultMap="BaseResultMap" >
SELECT * from employee where age in
<foreach collection="list" open="(" separator="," close=")" item="age">
#{age}
</foreach>
</select>
7:直接使用JSON传递参数
mapper
List <Employee> findByJSONObject(JSONObject params);
<select id="findByJSONObject" resultMap="BaseResultMap" parameterType="com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject">
select
*
from employee where gender = #{gender} and age = #{age}
</select>
8:.参数类型为对象+集合
@Data
public class Department {
private Long id;
private String deptName;
private String descr;
private Date createTime;
List<Employee> employees;
}
mapper
List <Employee> findByDepartment(@Param("department")Department department);
xml
<select id="findByDepartment" resultMap="BaseResultMap" parameterType="com.wg.demo.po.Department">
SELECT * from employee where dept_id =#{department.id} and age in
<foreach collection="department.employees" open="(" separator="," close=")" item="employee">
#{employee.age}
</foreach>
</select>
3${}与#{}的区别
3.1、符号类型
(1)#{}:参数占位符,即预编译
(2)${} :字符串替换符,即SQL拼接
3.2、防注入问题
(1)#{}:很大程度上能防止sql 注入
(2)${}:不能防止sql 注入
1)#{}:将传入的数据都当成一个字符串,会对传入的变量自动加一个单引号。如:user_id = #{userId},如果传入的值是111,那么解析成sql时的值为user_id = ‘111’,如果传入的值是id,则解析成的sql为user_id = ‘id’。
(2)${}:将传入的参数直接显示生成在sql中,且不加任何引号。如:user_id = ${userId},如果传入的值是111,那么解析成sql时的值为user_id = 111 , 如果传入的值是id,则解析成的sql为user_id = id。
3.2、用$的情况
在某些特殊场合下只能用${},不能用#{}。例如:在使用排序时ORDER BY ${id}, 如果使用#{id},则会被解析成ORDER BY “id”,这显然是一种错误的写法。
2)
方
式
一
般
用
于
传
入
数
据
库
对
象
,
例
如
传
入
表
名
用
{}方式一般用于传入数据库对象,例如传入表名 用
方式一般用于传入数据库对象,例如传入表名用 会快一些。
Select * from ${tableName} where user_id = #{userId}
4resultMap自定义映射
resultMap中的属性定义
1) 自定义resultMap,实现高级结果集映射
2) id :用于完成主键值的映射
3) result :用于完成普通列的映射
4) association :一个复杂的类型关联;许多结果将包成这种类型
5) collection : 复杂类型的集

<select id="getEmployeeById" resultMap="myEmp">
select id, last_name,email, gender from tbl_employee where id =#{id}
</select>
<resultMap type="com.mybatis.beans.Employee" id="myEmp">
<id column="id" property="id" />
<result column="last_name" property="lastName"/>
<result column="email" property="email"/>
<result column="gender" property="gender"/>
</resultMap>
Association
1)POJO中的属性可能会是一个对象,我们可以使用联合查询,并以级联属性的方式封装对象.使用association标签定义对象的封装规则
public class Department {
private Integer id ;
private String departmentName ;
// 省略 get/set方法
}
public class Employee {
private Integer id ;
private String lastName;
private String email ;
private String gender ;
private Department dept ;
// 省略 get/set方法
}
xml
<resultMap type="com.atguigu.mybatis.beans.Employee" id="myEmpAndDept">
<id column="eid" property="id"/>
<result column="last_name" property="lastName"/>
<result column="email" property="email"/>
<result column="gender" property="gender"/>
<association property="dept" javaType="com.atguigu.mybatis.beans.Department">
<id column="did" property="id"/>
<result column="dept_name" property="departmentName"/>
</association>
</resultMap>
<resultMap type="com.mybatis.beans.Employee" id="myEmpAndDept">
<id column="eid" property="id"/>
<result column="last_name" property="lastName"/>
<result column="email" property="email"/>
<result column="gender" property="gender"/>
<association property="dept" javaType="com.mybatis.beans.Department">
<id column="did" property="id"/>
<result column="dept_name" property="departmentName"/>
</association>
</resultMap>
collection
1)OJO中的属性可能会是一个集合对象,我们可以使用联合查询,并以级联属性的方式封装对象.使用collection标签定义对象的封装规则
public class Department {
private Integer id ;
private String departmentName ;
private List<Employee> emps ;
}
XML
<select id="getDeptAndEmpsById" resultMap="myDeptAndEmps">
SELECT d.id did, d.dept_name ,e.id eid ,e.last_name ,e.email,e.gender
FROM tbl_dept d LEFT OUTER JOIN tbl_employee e ON d.id = e.d_id
WHERE d.id = #{id}
</select>
<resultMap type="com.mybatis.beans.Department" id="myDeptAndEmps">
<id column="did" property="id"/>
<result column="dept_name" property="departmentName"/>
<!--
property: 关联的属性名
ofType: 集合中元素的类型
-->
<collection property="emps" ofType="com.mybatis.beans.Employee">
<id column="eid" property="id"/>
<result column="last_name" property="lastName"/>
<result column="email" property="email"/>
<result column="gender" property="gender"/>
</collection>
</resultMap>
拓展
javaType和ofType的区别
javaType用来指定对象所属的java数据类型,也就是private List<Employee>Employees 的ArrayList类型,用在association
ofType用来指定对象的所属javaBean类,也就是尖括号的泛型private List<Employee>Employees,用在collection
5MyBatis动态SQL
if where
1) If用于完成简单的判断.
Where用于解决SQL语句中where关键字以及条件中第一个and或者or的问题
<select id="getEmpsByConditionIf" resultType="com.atguigu.mybatis.beans.Employee">
select id , last_name ,email , gender
from tbl_employee
<where>
<if test="id!=null">
and id = #{id}
</if>
<if test="lastName!=null && lastName!=""">
and last_name = #{lastName}
</if>
<if test="email!=null and email.trim()!=''">
and email = #{email}
</if>
<if test=""m".equals(gender) or "f".equals(gender)">
and gender = #{gender}
</if>
</where>
</select>
trim
1) Trim 可以在条件判断完的SQL语句前后添加或者去掉指定的字符
prefix: 添加前缀
prefixOverrides: 去掉前缀
suffix: 添加后缀
suffixOverrides: 去掉后缀
select id="/、getEmpsByConditionTrim" resultType="com.atguigu.mybatis.beans.Employee">
select id , last_name ,email , gender
from tbl_employee
<trim prefix="where" suffixOverrides="and">
<if test="id!=null">
id = #{id} and
</if>
<if test="lastName!=null && lastName!=""">
last_name = #{lastName} and
</if>
<if test="email!=null and email.trim()!=''">
email = #{email} and
</if>
<if test=""m".equals(gender) or "f".equals(gender)">
gender = #{gender}
</if>
</trim>
</select>
set
1) set 主要是用于解决修改操作中SQL语句中可能多出逗号的问题
<update id="updateEmpByConditionSet">
update tbl_employee
<set>
<if test="lastName!=null && lastName!=""">
last_name = #{lastName},
</if>
<if test="email!=null and email.trim()!=''">
email = #{email} ,
</if>
<if test=""m".equals(gender) or "f".equals(gender)">
gender = #{gender}
</if>
</set>
where id =#{id}
</update>
choose
choose 主要是用于分支判断,类似于java中的switch case,只会满足所有分支中的一个
<select id="getEmpsByConditionChoose" resultType="com.atguigu.mybatis.beans.Employee">
select id ,last_name, email,gender from tbl_employee
<where>
<choose>
<when test="id!=null">
id = #{id}
</when>
<when test="lastName!=null">
last_name = #{lastName}
</when>
<when test="email!=null">
email = #{email}
</when>
<otherwise>
gender = 'm'
</otherwise>
</choose>
</where>
</select>
foreach
1) foreach 主要用于循环迭代
collection: 要迭代的集合
item: 当前从集合中迭代出的元素
open: 开始字符
close:结束字符
separator: 元素与元素之间的分隔符
index:
迭代的是List集合: index表示的当前元素的下标
迭代的Map集合: index表示的当前元素的key
<select id="getEmpsByConditionForeach" resultType="com.atguigu.mybatis.beans.Employee">
select id , last_name, email ,gender from tbl_employee where id in
<foreach collection="ids" item="curr_id" open="(" close=")" separator="," >
#{curr_id}
</foreach>
</select>
sql
1) sql 标签是用于抽取可重用的sql片段,将相同的,使用频繁的SQL片段抽取出来,单独定义,方便多次引用.
2) 抽取SQL:
<sql id="selectSQL">
select id , last_name, email ,gender from tbl_employee
</sql>
引用SQL:
<include refid="selectSQL"></include>
扩展-PageHelper分页插件
1) 导入相关包pagehelper-x.x.x.jar 和 jsqlparser-0.9.5.jar
2) 在MyBatis全局配置文件中配置分页插件
<plugins>
<plugin interceptor="com.github.pagehelper.PageInterceptor"></plugin>
</plugins>
3) 使用PageHelper提供的方法进行分页
可以使用更强大的PageInfo封装返回结果
Page对象的使用
1) 在查询之前通过PageHelper.startPage(页码,条数)设置分页信息,该方法返回Page对象
@Test
public void testPageHelper() throws Exception{
SqlSessionFactory ssf = getSqlSessionFactory();
SqlSession session = ssf.openSession();
try {
EmployeeMapper mapper =
session.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class);
//设置分页信息
Page<Object> page = PageHelper.startPage(9, 1);
List<Employee> emps = mapper.getAllEmps();
for (Employee employee : emps) {
System.out.println(employee);
}
System.out.println("=============获取分页相关的信息=================");
System.out.println("当前页: " + page.getPageNum());
System.out.println("总页码: " + page.getPages());
System.out.println("总条数: " + page.getTotal());
System.out.println("每页显示的条数: " + page.getPageSize());
} finally {
session.close();
}
}
原理
首先是在Mybatis里面配置了分页拦截器(PageInterceptor),即在执行相关Sql之前会拦截做一点事情;
这里通过setLocalPage()方法,将分页信息保存在当前线程中。查询方法与之处于同一个线程中,共享ThreadLocal中的数据。
selectlist查询之后赋值给的List list。这个list是Page 类型。
再将list放到PageInfo<>中即可。
1) 在查询完数据后,使用PageInfo对象封装查询结果,可以获取更详细的分页信息以及
可以完成分页逻辑
@Test
public void testPageHelper1() throws Exception{
SqlSessionFactory ssf = getSqlSessionFactory();
SqlSession session = ssf.openSession();
try {
EmployeeMapper mapper = session.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class);
//设置分页信息
Page<Object> page = PageHelper.startPage(9, 1);
List<Employee> emps = mapper.getAllEmps();
//
PageInfo<Employee> info = new PageInfo<>(emps,5);
for (Employee employee : emps) {
System.out.println(employee);
}
System.out.println("=============获取详细分页相关的信息=================");
System.out.println("当前页: " + info.getPageNum());
System.out.println("总页码: " + info.getPages());
System.out.println("总条数: " + info.getTotal());
System.out.println("每页显示的条数: " + info.getPageSize());
System.out.println("是否是第一页: " + info.isIsFirstPage());
System.out.println("是否是最后一页: " + info.isIsLastPage());
System.out.println("是否有上一页: " + info.isHasPreviousPage());
System.out.println("是否有下一页: " + info.isHasNextPage());
System.out.println("============分页逻辑===============");
int [] nums = info.getNavigatepageNums();
for (int i : nums) {
System.out.print(i +" " );
}
} finally {
session.close();
}
}
PageInfo包含的信息
private int pageNum;//当前页码
private int pageSize;//设置每页多少条数据
private int size;//当前页有多少条数据
private int startRow;//当前页码第一条数据的
private int endRow;//当前页码的开始条
private int pages;//当前页码结束条
private int prePage;//上一页(页面链接使用)
private int nextPage;//下一页(页面链接使用)
private boolean isFirstPage;//是否为第一页
private boolean isLastPage;//是否为最后一页
private boolean hasPreviousPage;//是否有前一页
private boolean hasNextPage;//是否有下一页
private int navigatePages;//导航页码数(就是总共有多少页)
private int[] navigatepageNums;//导航页码数(就是总共有多少页),可以用来遍历
private int navigateFirstPage;//首页号
private int navigateLastPage;//尾页号
Springboot 集成pagehelper
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.pagehelper</groupId>
<artifactId>pagehelper-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.2.13</version>
</dependency>
配置文件
pagehelper:
helperDialect: mysql
reasonable: true
supportMethodsArguments: true
params: count=countSql
pagehelper配置参数参考
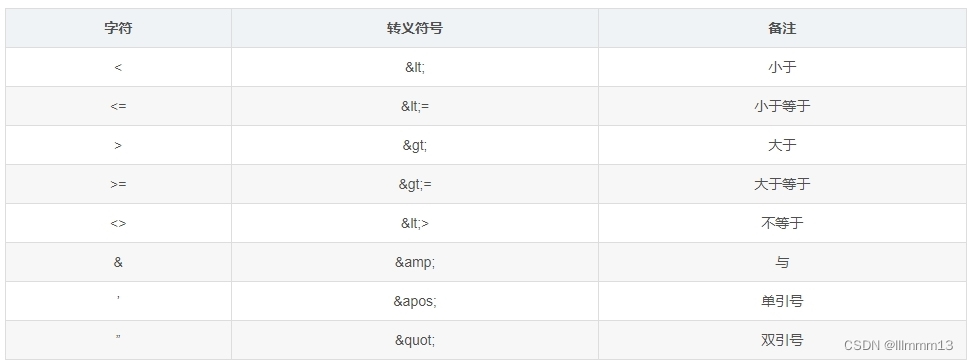
补充,mybatis中转译字符
最后
以上就是清爽抽屉最近收集整理的关于Springboot集成Mybatis和Mybatis常用知识点总结的全部内容,更多相关Springboot集成Mybatis和Mybatis常用知识点总结内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复