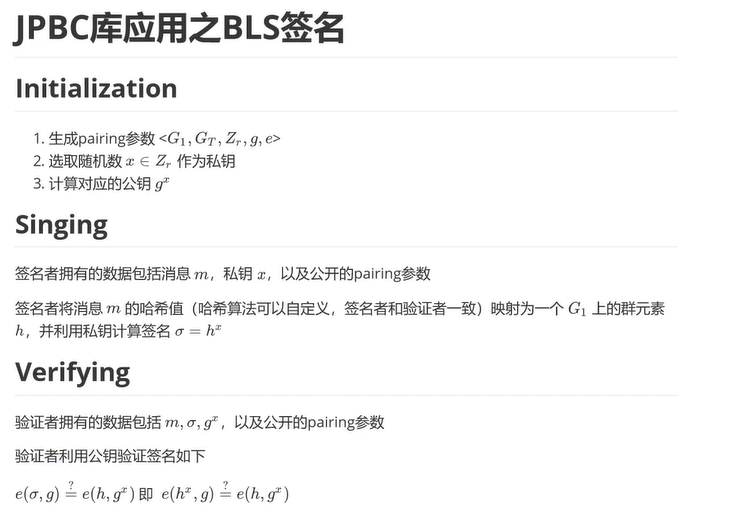
各种签密算法链接
BF签密算法Java实现(JPBC)
BF加密
Ident.java
package com.xyl.yes;
public interface Ident {
void buildSystem();
void extractSecretKey();
void encrypt();
void decrypt();
}
BasicIdent2.java
package com.xyl.yes;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import it.unisa.dia.gas.jpbc.Element;
import it.unisa.dia.gas.jpbc.Field;
import it.unisa.dia.gas.jpbc.Pairing;
import it.unisa.dia.gas.plaf.jpbc.pairing.PairingFactory;
public class BasicIdent2 implements Ident{
private Element s, r, P, Ppub, Su, Qu, V, T1, T2;
private Field G1, Zr;
private Pairing pairing;
public BasicIdent2() {
init();
}
/**
* 初始化
*/
private void init() {
PairingFactory.getInstance().setUsePBCWhenPossible(true);
pairing = PairingFactory.getPairing("a.properties");//
checkSymmetric(pairing);
//将变量r初始化为Zr中的元素
Zr = pairing.getZr();//
r = Zr.newElement();//阶
//将变量Ppub,Qu,Su,V初始化为G1中的元素,G1是加法群
G1 = pairing.getG1();//
Ppub = G1.newElement(); //主公钥
Qu = G1.newElement();
Su = G1.newElement();
V = G1.newElement();
//将变量T1,T2V初始化为GT中的元素,GT是乘法群
Field GT = pairing.getGT();//
T1 = GT.newElement();
T2 = GT.newElement();
}
/**
* 判断配对是否为对称配对,不对称则输出错误信息
*
* @param pairing
*/
private void checkSymmetric(Pairing pairing) {
if (!pairing.isSymmetric()) {
throw new RuntimeException("密钥不对称!");
}
}
@Override
public void buildSystem() {
System.out.println("-------------------系统建立阶段----------------------");
s = Zr.newRandomElement().getImmutable();// //随机生成主密钥s
P = G1.newRandomElement().getImmutable();// 生成G1的生成元P
Ppub = P.mulZn(s);// 计算Ppub=sP,注意顺序
System.out.println("P=" + P);
System.out.println("s=" + s);
System.out.println("Ppub=" + Ppub);
}
@Override
public void extractSecretKey() {
System.out.println("-------------------密钥提取阶段----------------------");
Qu = pairing.getG1().newElement().setFromHash("IDggjjhjkkku".getBytes(), 0, 3)
.getImmutable();// //从长度为3的Hash值IDu确定用户U产生的公钥Qu
Su = Qu.mulZn(s).getImmutable();
System.out.println("Qu=" + Qu);
System.out.println("Su=" + Su);
}
@Override
public void encrypt() {
System.out.println("-------------------加密阶段----------------------");
r = Zr.newRandomElement().getImmutable();
V = P.mulZn(r);
T1 = pairing.pairing(Ppub, Qu).getImmutable();// 计算e(Ppub,Qu)
T1 = T1.powZn(r).getImmutable();
System.out.println("r=" + r);
System.out.println("V=" + V);
System.out.println("T1=e(Ppub,Qu)^r=" + T1);
}
@Override
public void decrypt() {
System.out.println("-------------------解密阶段----------------------");
T2 = pairing.pairing(V, Su).getImmutable();
System.out.println("e(V,Su)=" + T2);
int byt = V.getLengthInBytes();// 求V的字节长度,假设消息长度为128字节
System.out.println("文本长度" + (byt + 128));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BasicIdent2 ident = new BasicIdent2();
// 动态代理,统计各个方法耗时
Ident identProxy = (Ident) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
BasicIdent2.class.getClassLoader(),
new Class[] { Ident.class }, new TimeCountProxyHandle(ident));
identProxy.buildSystem();
identProxy.extractSecretKey();
identProxy.encrypt();
identProxy.decrypt();
}
}
TimeCountProxyHandle.java
package com.xyl.yes;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class TimeCountProxyHandle implements InvocationHandler {
private Object proxied;
public TimeCountProxyHandle(Object obj) {
proxied = obj;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
Object result = method.invoke(proxied, args);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(method.getName() + "耗时:" + (end - begin) + "ms");
return result;
}
}
验证双线性
package com.xyl.jpbctest;
import it.unisa.dia.gas.jpbc.Element;
import it.unisa.dia.gas.jpbc.Field;
import it.unisa.dia.gas.jpbc.Pairing;
import it.unisa.dia.gas.plaf.jpbc.pairing.PairingFactory;
public class JPBCTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Pairing bp = PairingFactory.getPairing("a.properties");
Field G1 = bp.getG1();
Field Zr = bp.getZr();
Element g = G1.newRandomElement();
Element a = Zr.newRandomElement();
Element b = Zr.newRandomElement();
Element g_a = g.duplicate().powZn(a);
Element g_b = g.duplicate().powZn(b);
Element egg1 = bp.pairing(g_a, g_b);
Element egg2 = bp.pairing(g, g);
Element ab = a.duplicate().mul(b);
Element egg3 = egg2.duplicate().powZn(ab);
if(egg1.isEqual(egg3)){
System.out.println(true);
}else{
throw new RuntimeException("双线性验证不成功");
}
}
}
BLS签名
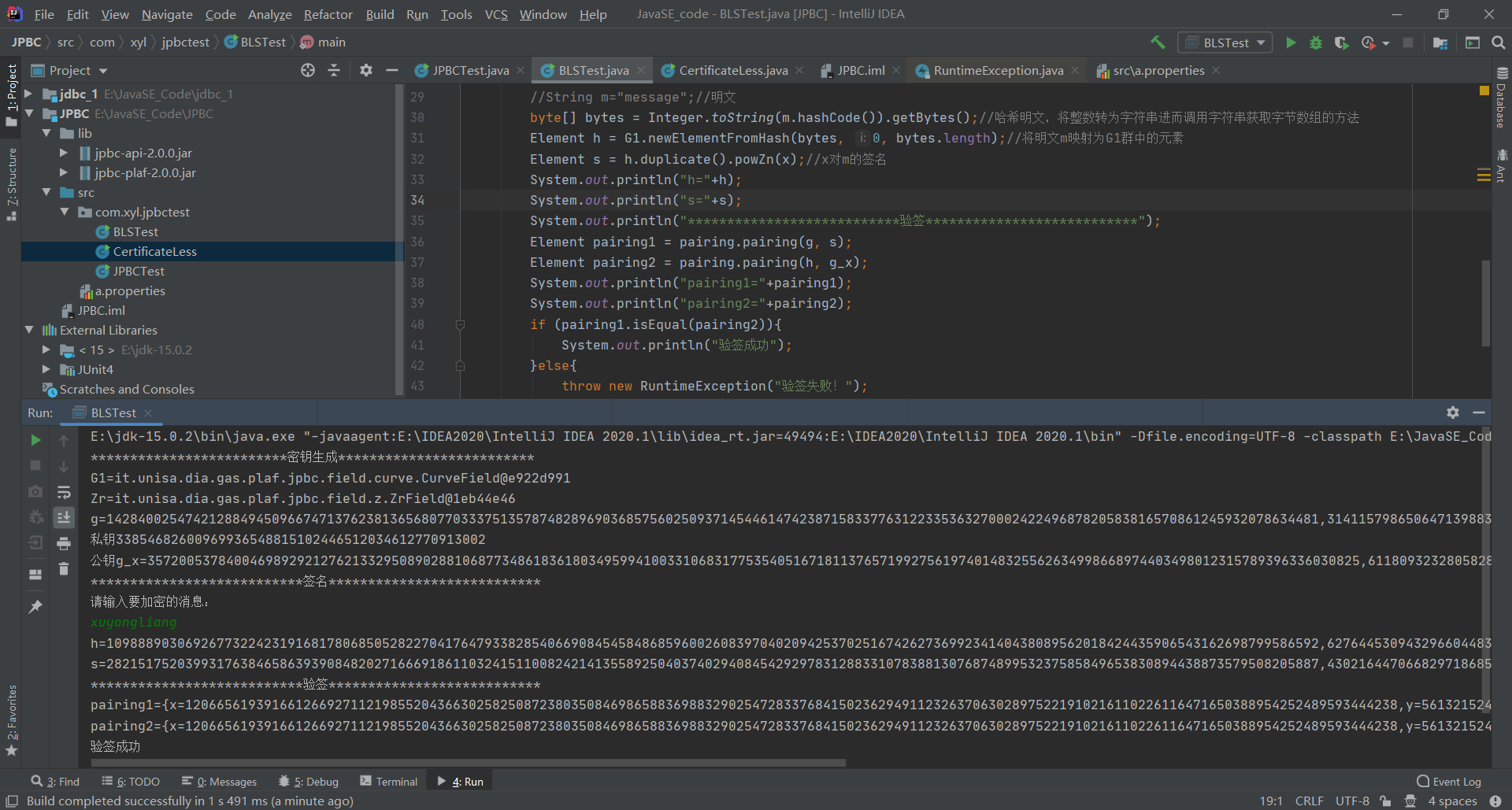
package com.xyl.jpbctest;
import it.unisa.dia.gas.jpbc.Element;
import it.unisa.dia.gas.jpbc.Field;
import it.unisa.dia.gas.jpbc.Pairing;
import it.unisa.dia.gas.plaf.jpbc.pairing.PairingFactory;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class BLSTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("*************************密钥生成*************************");
Pairing pairing = PairingFactory.getPairing("a.properties");//由工厂类生成Pairing对象
Field G1 = pairing.getG1();//Pairing对象获取G1循环加法群
Field Zr = pairing.getZr();//Pairing对象获取Zr群,用于随机选取私钥
Element g = G1.newRandomElement();//G1随机生成G1的生成元
Element x = Zr.newRandomElement();//Zr群中随机选取一个元素作为生成元x
Element g_x = g.duplicate().powZn(x);//公钥
System.out.println("G1="+G1);
System.out.println("Zr="+Zr);
System.out.println("g="+g);
System.out.println("私钥"+x);
System.out.println("公钥g_x="+g_x);
System.out.println("***************************签名***************************");
System.out.println("请输入要加密的消息:");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String m = scanner.next();
//String m="message";//明文
byte[] bytes = Integer.toString(m.hashCode()).getBytes();//哈希明文,将整数转为字符串进而调用字符串获取字节数组的方法
Element h = G1.newElementFromHash(bytes, 0, bytes.length);//将明文m映射为G1群中的元素
Element s = h.duplicate().powZn(x);//x对m的签名
System.out.println("h="+h);
System.out.println("s="+s);
System.out.println("***************************验签***************************");
Element pairing1 = pairing.pairing(g, s);
Element pairing2 = pairing.pairing(h, g_x);
System.out.println("pairing1="+pairing1);
System.out.println("pairing2="+pairing2);
if (pairing1.isEqual(pairing2)){
System.out.println("验签成功");
}else{
throw new RuntimeException("验签失败!");
}
/*
// Initialization
Pairing bp = PairingFactory.getPairing("a.properties");
Field G1 = bp.getG1();
Field Zr = bp.getZr();
Element g = G1.newRandomElement();
Element x = Zr.newRandomElement();
Element g_x = g.duplicate().powZn(x);
System.out.println("G1="+G1);
System.out.println("Zr="+Zr);
System.out.println("g="+g);
System.out.println("x="+x);
System.out.println("g_x="+g_x);
//Signing
String m = "message";
byte[] m_hash = Integer.toString(m.hashCode()).getBytes();
Element h = G1.newElementFromHash(m_hash, 0, m_hash.length);
Element sig = h.duplicate().powZn(x);
System.out.println("h="+h);
System.out.println("sig="+sig);
//Verification
Element pl = bp.pairing(g, sig);
Element pr = bp.pairing(h, g_x);
System.out.println("pl="+pl);
System.out.println("pr="+pr);
if (pl.isEqual(pr))
System.out.println("Yes");
else
System.out.println("No");
*/
}
}
持续更新ing
最后
以上就是懵懂路灯最近收集整理的关于数字签密算法JPBC实现各种签密算法链接BF签密算法Java实现(JPBC)BF加密验证双线性BLS签名持续更新ing的全部内容,更多相关数字签密算法JPBC实现各种签密算法链接BF签密算法Java实现(JPBC)BF加密验证双线性BLS签名持续更新ing内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复