前言:无奈研究了一下CodePush,遇到了很多坑~~ 但是原理呢不是很难理解,就是配置有点多,原理可以简单的参考一下我之前的一篇博客React-Native 热更新尝试(Android),下面说一下期间遇到的坑~
大家可以看一下官网:https://github.com/Microsoft/react-native-code-push,
如果觉得自己英文不太好的话可以看一下这哥们的博客:
React Native热更新部署/热更新-CodePush最新集成总结(新)
下面带大家一步一步实现一下传说中的rn热更新:
首先我们创建一个rn项目叫UpdateDemo,然后运行android:
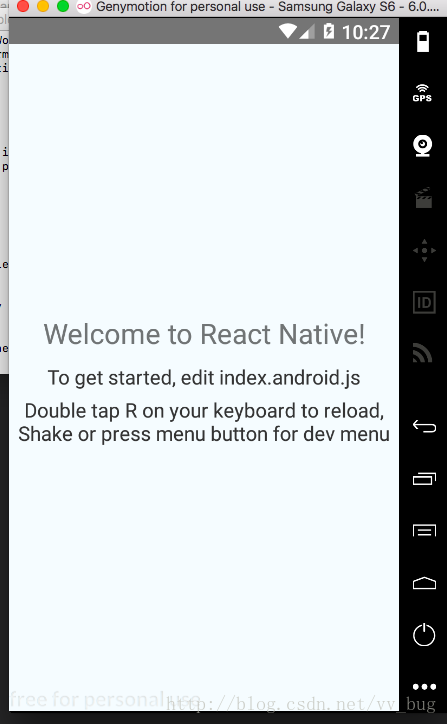
好啦! 很干净的一个app(不要在问我怎么创建和运行rn了)~~
开始之前小伙伴可以自己去看看CodePush做一个简单的了解,然后你需要的是一台mac电脑~
一、安装 CodePush
进入命令栏执行:
npm install -g code-push-cli然后短暂等待一会:
二、创建一个CodePush账号, 并登入
执行在命令栏里执行:
code-push register然后会弹出一个注册页面,我们直接github登入,登入成功后会显示你的access-key,我们直接copy一下:
然后复制到命令栏中:
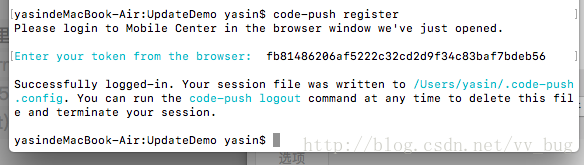
可以看到,我们已经成功的登入了~~
三、在CodePush注册一个我们的app
我们在终端输入:
code-push app add <appname> android react-native
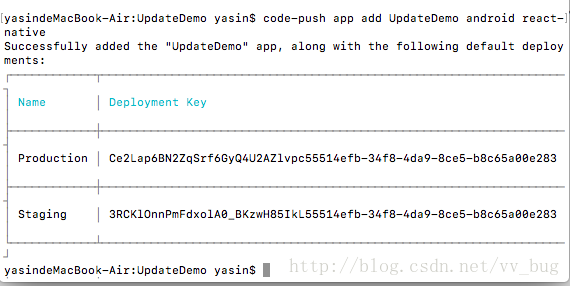
我们这里是以android为例子的~~
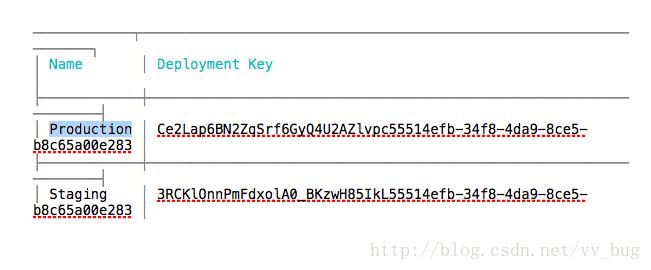
然后我们把Production和Staging对应的可以copy一下,后面需要用到~~
四、集成Android开发环境
1、进入到项目个根目录然后执行:
npm install --save react-native-code-push
然后短暂停留几秒~~~
2、进到android目录,然后执行:
npm i -g rnpm
3、回到项目根目录,直接命令集成android环境:
rnpm link react-native-code-push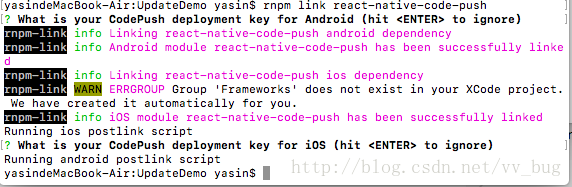
一路回车~~~~
然后用 AndroidStudio 打开android项目,找到/xxxx/UpdateDemo/android/app/build.gradle,你会发现多了几行代码:
compile project(':react-native-code-push')
apply from: "../../node_modules/react-native-code-push/android/codepush.gradle"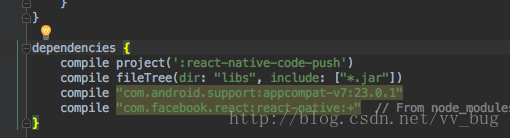
这就是脚本文件为我们自动生成的,然后/xxx/UpdateDemo/android/settings.gradle这个文件也多了几行代码:
include ':react-native-code-push'
project(':react-native-code-push').projectDir = new File(rootProject.projectDir, '../node_modules/react-native-code-push/android/app')
最后我们点击重新编译app:
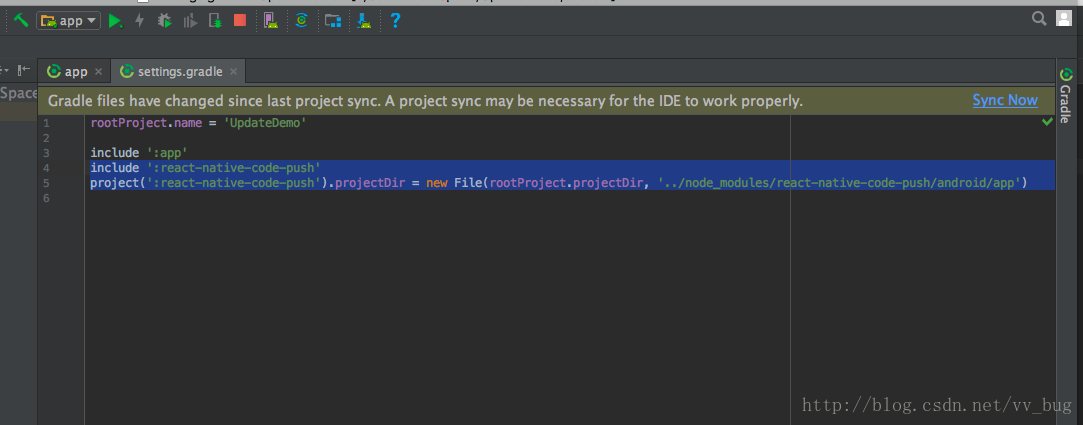
点击”Sync Now”~~
然后我们试着运行app,你会发现报了一个不明的错误,我们继续找到/xxx/UpdateDemo/android/app/src/main/java/com/updatedemo/MainApplication.java文件:
package com.updatedemo;
import android.app.Application;
import com.facebook.react.ReactApplication;
import com.facebook.react.ReactNativeHost;
import com.facebook.react.ReactPackage;
import com.facebook.react.shell.MainReactPackage;
import com.facebook.soloader.SoLoader;
import com.microsoft.codepush.react.CodePush;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
public class MainApplication extends Application implements ReactApplication {
private final ReactNativeHost mReactNativeHost = new ReactNativeHost(this) {
@Override
protected String getJSBundleFile() {
return CodePush.getJSBundleFile();
}
@Override
public boolean getUseDeveloperSupport() {
return BuildConfig.DEBUG;
}
@Override
protected List<ReactPackage> getPackages() {
return Arrays.<ReactPackage>asList(
new MainReactPackage(),
new CodePush("deployment-key-here", MainApplication.this, BuildConfig.DEBUG)
);
}
};
@Override
public ReactNativeHost getReactNativeHost() {
return mReactNativeHost;
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
SoLoader.init(this, /* native exopackage */ false);
}
}
如果为了偷懒一下的话,直接把“deployment-key-here”用我们之前获取的Production的key替换就可以了
当然,我们是需要切换Production跟Staging的,所以我们得动态的配置我们的key,我们需要变成这样:
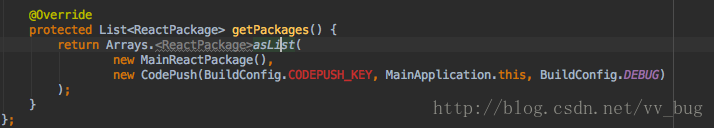
你会看到CODEPUSH_KEY变红色了,那么这个变量我们怎么配置呢?
我们找到xxxx/UpdateDemo/android/app/build.gradle文件,
改成:
buildTypes {
release {
minifyEnabled enableProguardInReleaseBuilds
proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile("proguard-android.txt"), "proguard-rules.pro"
buildConfigField "String", "CODEPUSH_KEY", '"Ce2Lap6BN2ZqSrf6GyQ4U2AZlvpc55514efb-34f8-4da9-8ce5-b8c65a00e283"'
}
debug {
buildConfigField "String", "CODEPUSH_KEY", '"3RCKlOnnPmFdxolA0_BKzwH85IkL55514efb-34f8-4da9-8ce5-b8c65a00e283"'
}
releaseStaging {
minifyEnabled enableProguardInReleaseBuilds
buildConfigField "String", "CODEPUSH_KEY", '"3RCKlOnnPmFdxolA0_BKzwH85IkL55514efb-34f8-4da9-8ce5-b8c65a00e283"'
}
}里面的CODEPUSH_KEY即为我们之前获取的Deployment Key ,
release对应的Production
releaseStaging跟debug对应的Staging
然后重新编译一下as,会发现之前的地方不报红色了:
new CodePush(BuildConfig.CODEPUSH_KEY, MainApplication.this, BuildConfig.DEBUG)package com.updatedemo;
import android.app.Application;
import com.facebook.react.ReactApplication;
import com.facebook.react.ReactNativeHost;
import com.facebook.react.ReactPackage;
import com.facebook.react.shell.MainReactPackage;
import com.facebook.soloader.SoLoader;
import com.microsoft.codepush.react.CodePush;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
public class MainApplication extends Application implements ReactApplication {
private final ReactNativeHost mReactNativeHost = new ReactNativeHost(this) {
@Override
protected String getJSBundleFile() {
return CodePush.getJSBundleFile();
}
@Override
public boolean getUseDeveloperSupport() {
return BuildConfig.DEBUG;
}
@Override
protected List<ReactPackage> getPackages() {
return Arrays.<ReactPackage>asList(
new MainReactPackage(),
new CodePush(BuildConfig.CODEPUSH_KEY, MainApplication.this, BuildConfig.DEBUG)
);
}
};
@Override
public ReactNativeHost getReactNativeHost() {
return mReactNativeHost;
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
SoLoader.init(this, /* native exopackage */ false);
}
}
然后我们顺便把我们的keystore打包key配置一下:
不懂的小伙伴可以去看我之前的一篇博客:
React-Native打包发布(Android)
然后配置好keystore之后,然后我们的/xxxx/UpdateDemo/android/app/build.gradle文件就变成了这样:
apply plugin: "com.android.application"
import com.android.build.OutputFile
/**
* The react.gradle file registers a task for each build variant (e.g. bundleDebugJsAndAssets
* and bundleReleaseJsAndAssets).
* These basically call `react-native bundle` with the correct arguments during the Android build
* cycle. By default, bundleDebugJsAndAssets is skipped, as in debug/dev mode we prefer to load the
* bundle directly from the development server. Below you can see all the possible configurations
* and their defaults. If you decide to add a configuration block, make sure to add it before the
* `apply from: "../../node_modules/react-native/react.gradle"` line.
*
* project.ext.react = [
* // the name of the generated asset file containing your JS bundle
* bundleAssetName: "index.android.bundle",
*
* // the entry file for bundle generation
* entryFile: "index.android.js",
*
* // whether to bundle JS and assets in debug mode
* bundleInDebug: false,
*
* // whether to bundle JS and assets in release mode
* bundleInRelease: true,
*
* // whether to bundle JS and assets in another build variant (if configured).
* // See http://tools.android.com/tech-docs/new-build-system/user-guide#TOC-Build-Variants
* // The configuration property can be in the following formats
* // 'bundleIn${productFlavor}${buildType}'
* // 'bundleIn${buildType}'
* // bundleInFreeDebug: true,
* // bundleInPaidRelease: true,
* // bundleInBeta: true,
*
* // whether to disable dev mode in custom build variants (by default only disabled in release)
* // for example: to disable dev mode in the staging build type (if configured)
* devDisabledInStaging: true,
* // The configuration property can be in the following formats
* // 'devDisabledIn${productFlavor}${buildType}'
* // 'devDisabledIn${buildType}'
*
* // the root of your project, i.e. where "package.json" lives
* root: "../../",
*
* // where to put the JS bundle asset in debug mode
* jsBundleDirDebug: "$buildDir/intermediates/assets/debug",
*
* // where to put the JS bundle asset in release mode
* jsBundleDirRelease: "$buildDir/intermediates/assets/release",
*
* // where to put drawable resources / React Native assets, e.g. the ones you use via
* // require('./image.png')), in debug mode
* resourcesDirDebug: "$buildDir/intermediates/res/merged/debug",
*
* // where to put drawable resources / React Native assets, e.g. the ones you use via
* // require('./image.png')), in release mode
* resourcesDirRelease: "$buildDir/intermediates/res/merged/release",
*
* // by default the gradle tasks are skipped if none of the JS files or assets change; this means
* // that we don't look at files in android/ or ios/ to determine whether the tasks are up to
* // date; if you have any other folders that you want to ignore for performance reasons (gradle
* // indexes the entire tree), add them here. Alternatively, if you have JS files in android/
* // for example, you might want to remove it from here.
* inputExcludes: ["android/**", "ios/**"],
*
* // override which node gets called and with what additional arguments
* nodeExecutableAndArgs: ["node"],
*
* // supply additional arguments to the packager
* extraPackagerArgs: []
* ]
*/
apply from: "../../node_modules/react-native/react.gradle"
apply from: "../../node_modules/react-native-code-push/android/codepush.gradle"
/**
* Set this to true to create two separate APKs instead of one:
* - An APK that only works on ARM devices
* - An APK that only works on x86 devices
* The advantage is the size of the APK is reduced by about 4MB.
* Upload all the APKs to the Play Store and people will download
* the correct one based on the CPU architecture of their device.
*/
def enableSeparateBuildPerCPUArchitecture = false
/**
* Run Proguard to shrink the Java bytecode in release builds.
*/
def enableProguardInReleaseBuilds = false
android {
signingConfigs {
release {
keyAlias 'update'
keyPassword '123456'
storeFile file('/Users/yasin/SelfRnWorkSpace/UpdateDemo/android/update.keystore')
storePassword '123456'
}
}
compileSdkVersion 23
buildToolsVersion "23.0.1"
defaultConfig {
applicationId "com.updatedemo"
minSdkVersion 16
targetSdkVersion 22
versionCode 1
versionName "1.0"
ndk {
abiFilters "armeabi-v7a", "x86"
}
}
splits {
abi {
reset()
enable enableSeparateBuildPerCPUArchitecture
universalApk false // If true, also generate a universal APK
include "armeabi-v7a", "x86"
}
}
buildTypes {
release {
minifyEnabled enableProguardInReleaseBuilds
proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile("proguard-android.txt"), "proguard-rules.pro"
buildConfigField "String", "CODEPUSH_KEY", '"Ce2Lap6BN2ZqSrf6GyQ4U2AZlvpc55514efb-34f8-4da9-8ce5-b8c65a00e283"'
signingConfig signingConfigs.release
}
debug {
buildConfigField "String", "CODEPUSH_KEY", '"3RCKlOnnPmFdxolA0_BKzwH85IkL55514efb-34f8-4da9-8ce5-b8c65a00e283"'
}
releaseStaging {
minifyEnabled enableProguardInReleaseBuilds
buildConfigField "String", "CODEPUSH_KEY", '"3RCKlOnnPmFdxolA0_BKzwH85IkL55514efb-34f8-4da9-8ce5-b8c65a00e283"'
signingConfig signingConfigs.release
}
}
// applicationVariants are e.g. debug, release
applicationVariants.all { variant ->
variant.outputs.each { output ->
// For each separate APK per architecture, set a unique version code as described here:
// http://tools.android.com/tech-docs/new-build-system/user-guide/apk-splits
def versionCodes = ["armeabi-v7a": 1, "x86": 2]
def abi = output.getFilter(OutputFile.ABI)
if (abi != null) { // null for the universal-debug, universal-release variants
output.versionCodeOverride =
versionCodes.get(abi) * 1048576 + defaultConfig.versionCode
}
}
}
}
dependencies {
compile project(':react-native-code-push')
compile fileTree(include: ['*.jar'], dir: 'libs')
compile 'com.android.support:appcompat-v7:23.0.1'
compile 'com.facebook.react:react-native:+'
// From node_modules
}
// Run this once to be able to run the application with BUCK
// puts all compile dependencies into folder libs for BUCK to use
task copyDownloadableDepsToLibs(type: Copy) {
from configurations.compile
into 'libs'
}
好啦~~~ 有点偏题了哈~ 配置完key后,我们的android配置到这就结束了
五、配置React Native环境
我们什么时候更新我们的app呢? 我们为了简单一点就直接在rn的第一个页面中作更新了,我们直接在我们的index.android.js文件的componentDidMount方法:
componentDidMount() {
AppState.addEventListener("change", (newState) => {
newState === "active" && CodePush.sync();
});
}全部内容:
/**
* Sample React Native App
* https://github.com/facebook/react-native
* @flow
*/
import React, {Component} from 'react';
import {
AppRegistry,
StyleSheet,
Text,
View,
AppState,
} from 'react-native';
import CodePush from 'react-native-code-push';
const VERSION = '1.0.0';
export default class UpdateDemo extends Component {
render() {
return (
<View style={styles.container}>
<Text>{'当前版本:' + VERSION}</Text>
<Text style={styles.welcome}>
Welcome to React Native!
</Text>
<Text style={styles.instructions}>
To get started, edit index.android.js
</Text>
<Text style={styles.instructions}>
Double tap R on your keyboard to reload,{'n'}
Shake or press menu button for dev menu
</Text>
</View>
);
}
componentDidMount() {
AppState.addEventListener("change", (newState) => {
newState === "active" && CodePush.sync();
});
}
}
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
flex: 1,
justifyContent: 'center',
alignItems: 'center',
backgroundColor: '#F5FCFF',
},
welcome: {
fontSize: 20,
textAlign: 'center',
margin: 10,
},
instructions: {
textAlign: 'center',
color: '#333333',
marginBottom: 5,
},
});
AppRegistry.registerComponent('UpdateDemo', () => UpdateDemo);
然后我们打个生产包运行一下,我们直接在根目录执行:
React-native bundle --entry-file index.android.js --bundle-output ./android/app/src/main/assets/index.android.bundle --platform android --assets-dest ./android/app/src/main/res/ --dev false
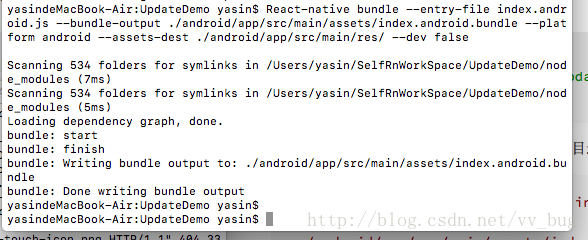
然后到我们android studio中把 buildtype改为release:
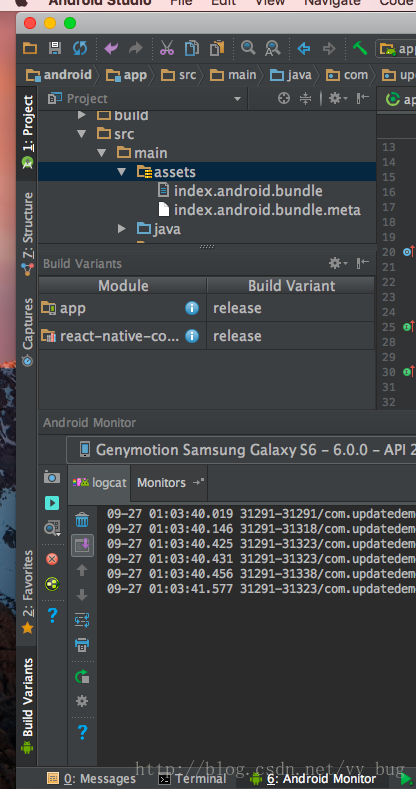
然后直接运行我们的app:
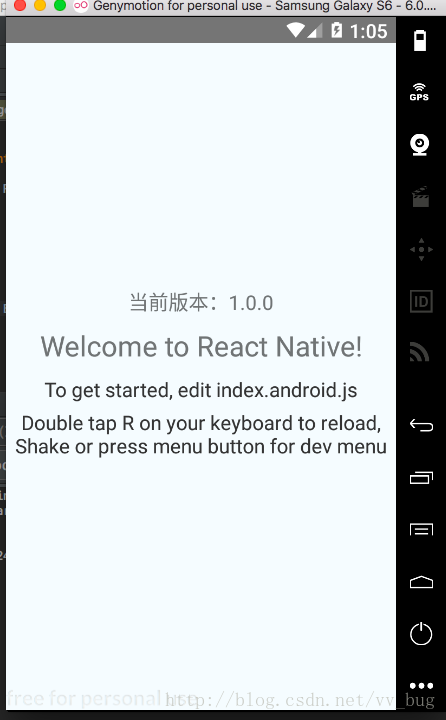
可以看到,我们的app出现了,我们加了一个版本控制为:1.0.0,
然后我们怎么发布我们的jsbundle让它热更新呢?
六、发布jsbundle到codepush
比如我们现在要升级了,我们模拟一下,把rn页面的当前版本1.0.0的提示改为1.0.1:
const VERSION = '1.0.1';
export default class UpdateDemo extends Component {
render() {
return (
<View style={styles.container}>
<Text>{'当前版本:' + VERSION}</Text>然后我们在项目根目录创建一个bundles文件夹:
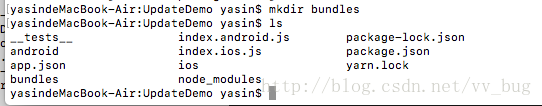
然后打一个jsbundle包到bundles文件夹中:
react-native bundle --platform android --entry-file index.android.js --bundle-output ./bundles/index.android.bundle --dev false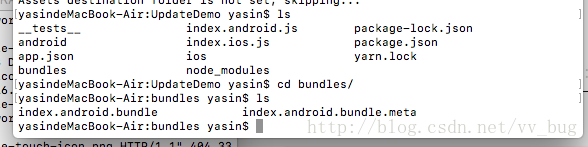
index.android.bundle即为我们需要上传到codepush的文件~~
最后到codepush
code-push release UpdateDemo ./bundles/index.android.bundle 1.0.0 --deploymentName Production --description "更改版本为1.0.1" --mandatory true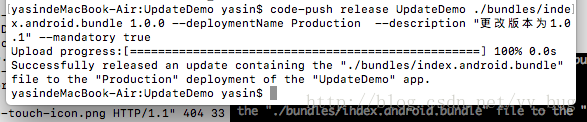
然后查看一下我们的发布情况:
code-push deployment ls UpdateDemo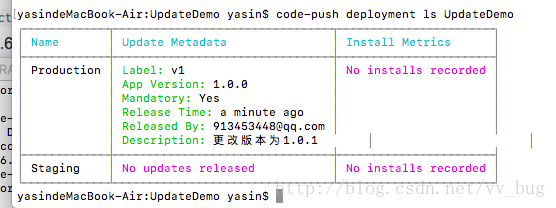
好啦~~~ 我们改变一下我们android中的版本为1.0.0,因为要跟我们codepush上的版本对应起来,所以我们找到andoid的/xxx/UpdateDemo/android/app/build.gradle文件,然后把版本号改为:1.0.0:
defaultConfig {
applicationId "com.updatedemo"
minSdkVersion 16
targetSdkVersion 22
versionCode 1
versionName "1.0.0"
ndk {
abiFilters "armeabi-v7a", "x86"
}
}然后重新编译运行一下:
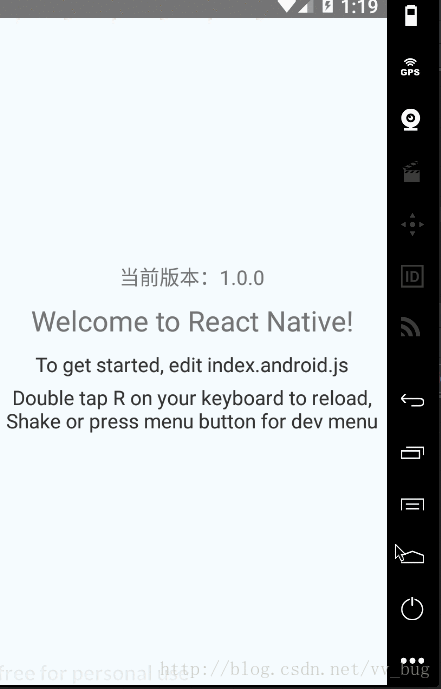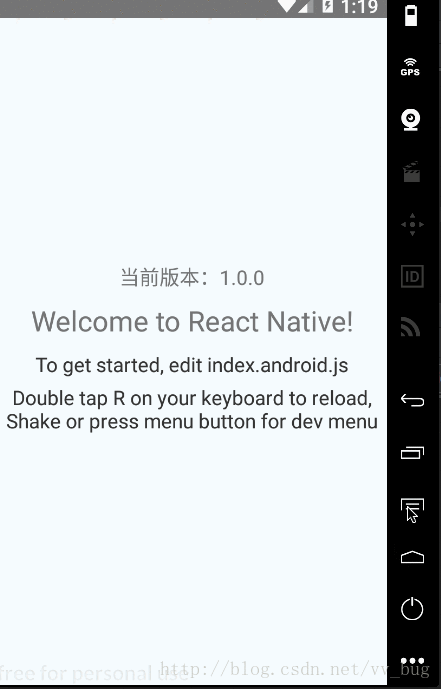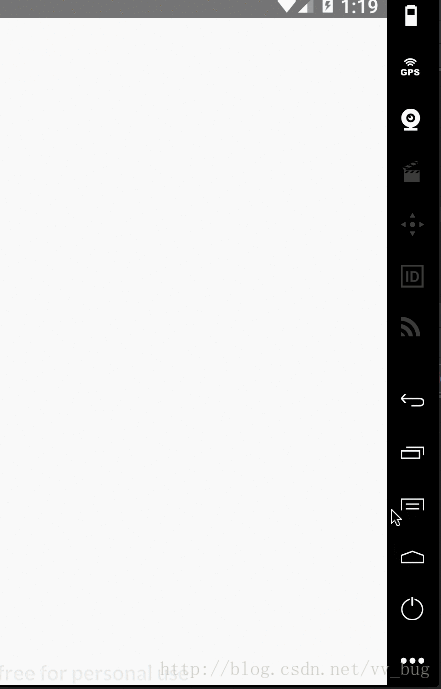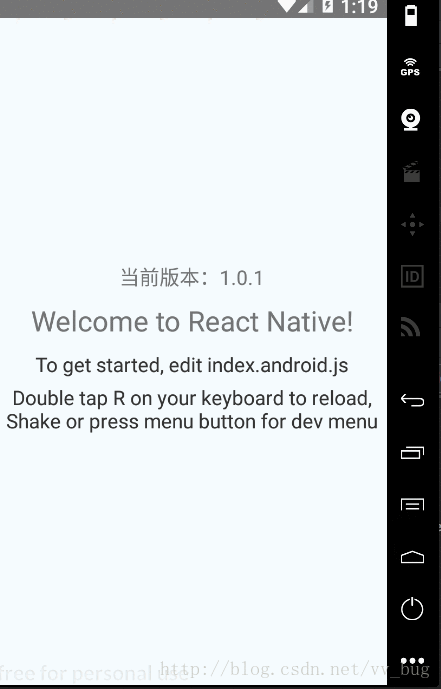
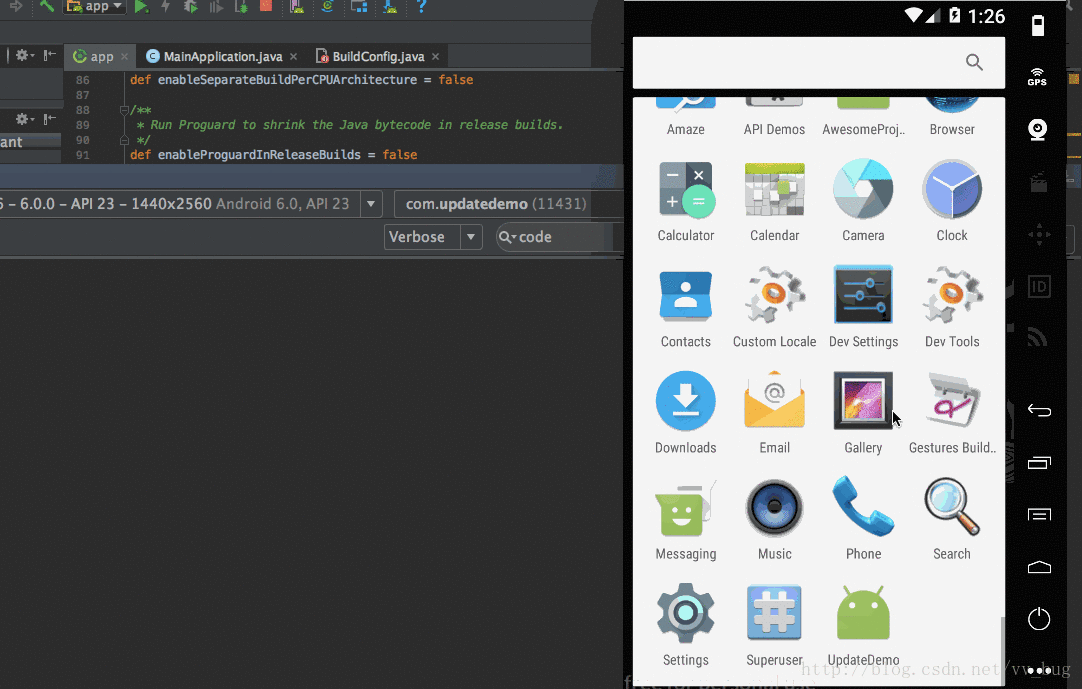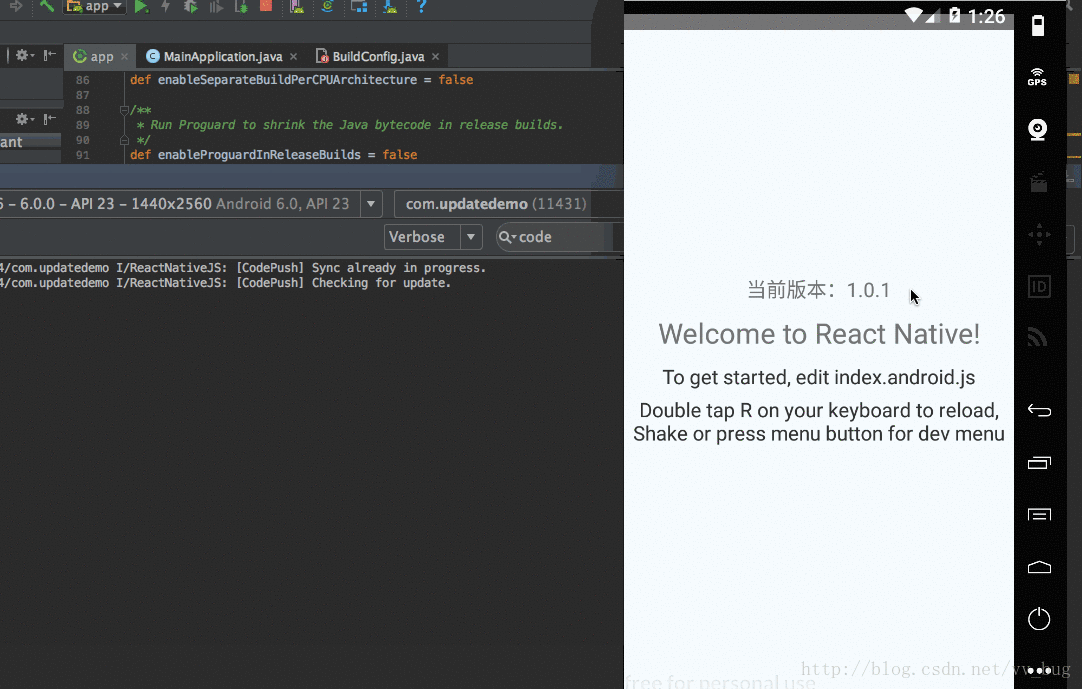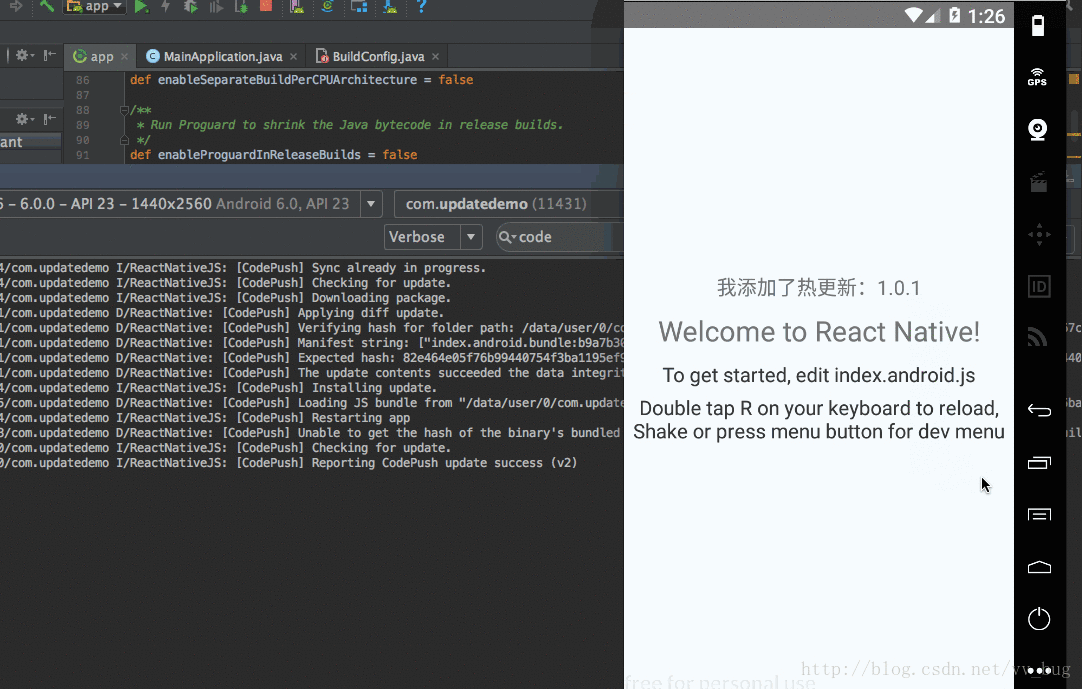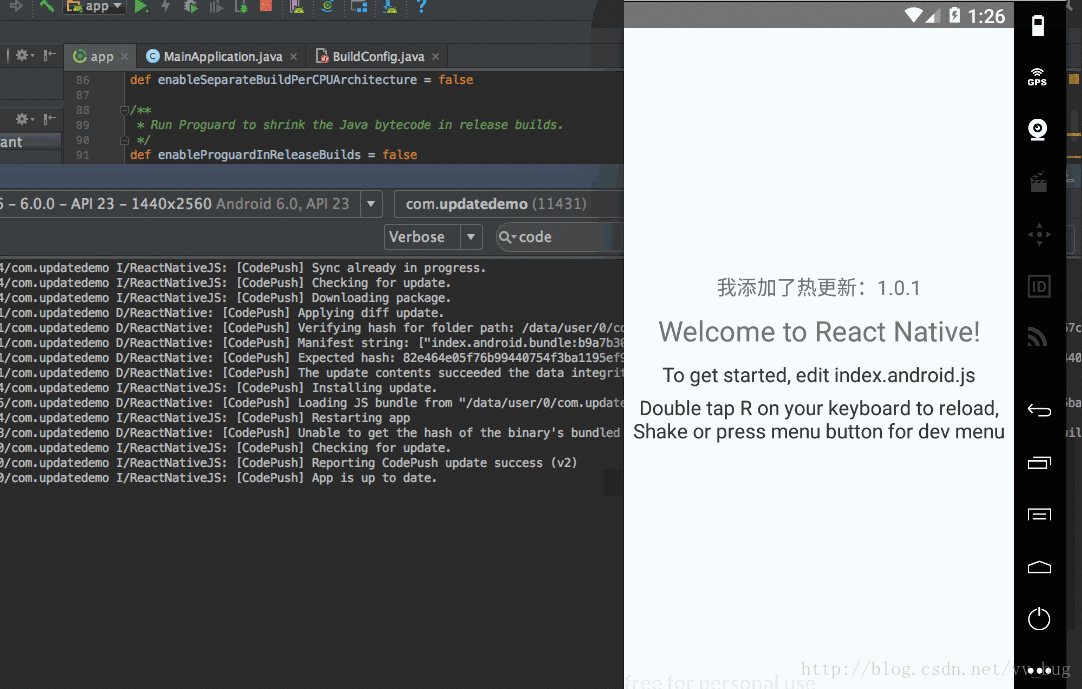
可以看到,我们运行后当前版本先是1.0.0,然后过了一会变成了1.0.1,也就是我们的热更新已经集成好了~~
注意:android中的versionName一定要跟codepush中的version一样,我就是这里卡了很久~~~
那如果我们要针对1.0.0再做一次升级呢?
我们继续操作一下~~
const VERSION = '1.0.1';
export default class UpdateDemo extends Component {
render() {
return (
<View style={styles.container}>
<Text>{'我添加了热更新:' + VERSION}</Text>
可以看到,我改了几个文字,然后我们重新打包:
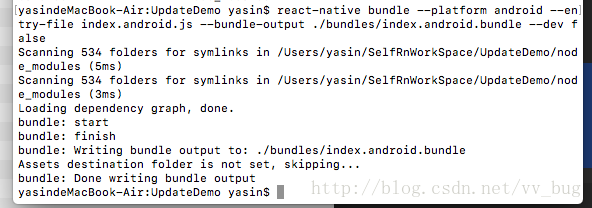
然后重新上传codepush:
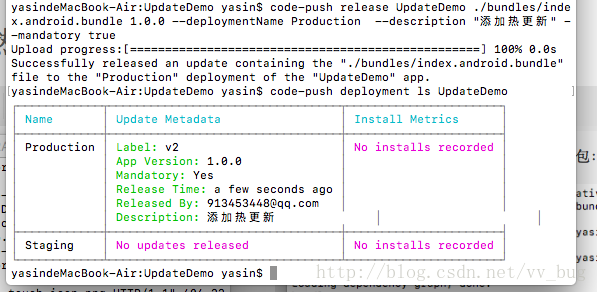
我们重新打开我们的app,顺便看一下as的log:
好啦~到这里我们的热更新就全部完毕了
小伙伴正在项目的情况可能是这样的:进入app请求后台接口–>根据后台接口判断是否需要更新—>弹出dialog提示用户—>点击更新—>执行CodePush.sync();
具体我就不掩饰了~~~
不懂的童鞋可以进群联系我,欢迎交流~~
qq交流群:

参考:
http://www.jianshu.com/p/9e3b4a133bcc
https://github.com/Microsoft/react-native-code-push,
最后
以上就是拼搏高跟鞋最近收集整理的关于React Native带你一步步实现热更新(CodePush-Android)的全部内容,更多相关React内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复