需要源码请点赞关注收藏后评论区留下QQ并且私信~~~
一、模型、学习、规划简介
1:模型
Agent可以通过模型来预测环境并做出反应,这里所说的模型通常指模拟模型,即在给定一个状态和动作时,通过模型可以对下一状态和奖赏做出预测
模型通常可以分为分布模型和样本模型两种类型
分布模型:该模型可以生成所有可能的结果及其对应的概率分布
样本模型:该模型能够从所有可能的情况中产生一个确定的结果
从功能上讲,模型是用于模拟环境和产生模拟经验的。与样本模型相比,分布模型包含更多的信息,只是现实任务中难以获得所有的状态转移概率
2:学习
学习过程是从环境产生的真实经验中进行学习,根据经验的使用方法,学习过程可以分为直接强化学习和模型学习两种类型
直接强化学习:在真实环境中采集真实经验,根据真实经验直接更新值函数或策略,不受模型偏差的影响
模型学习:在真实环境中采集真实经验,根据真实经验来构建和改进模拟模型,提供模拟模型精度,使其更接近真实环境
3:规划
规划过程是基于模拟环境或经验模型,从模拟经验中更新值函数,实现改进策略的目的,学习和规划的核心都是通过回溯操作来评估值函数,不同之处在于:在规划过程中,Agent并没有与真实环境交互
规划通常可分为状态空间规划和方案空间规划,状态空间规划是在状态空间中寻找最优策略,值函数的计算都是基于状态的,通常该规划方法视为搜索方法,其基本思想如下
1:所有规划算法都以计算值函数作为策略改进的中间关键步骤
2:所有规划算法都可以通过基于模型产生的模拟经验来计算值函数
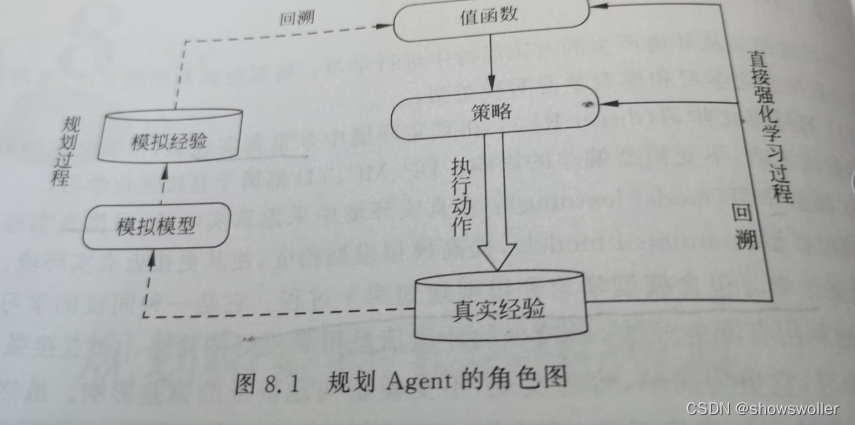
二、Dyna-Q结构及其算法
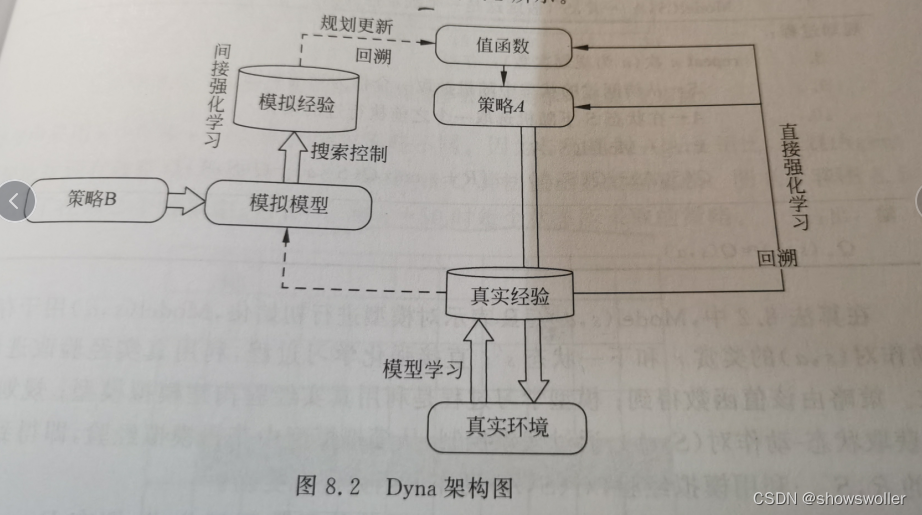
Dyna-Q架构包含了在线规划Agent所需要的主要功能,该架构讲学习和规划有机地结合在一起,是有模型和无模型方法的融合,其数据来源包括基于真实环境采样的真实经验以及基于模拟模型采样的模拟经验,通过直接强化学习或间接强化学习来更新值函数或者策略
架构图如下
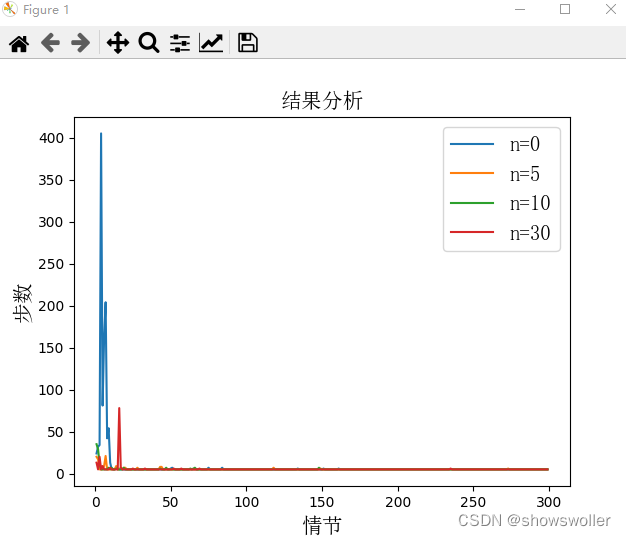
三、Dyna-Q不同规划对学习步数的影响
机器人环境搭建以及背景可点击如下链接了解
机器人环境
此处比较不同规划步数对实验效果的影响,当机器人离开边界或者撞到障碍物则得到-10的奖赏,到达充电桩获得+1的奖赏,其他情况奖赏均为0,不同需要不同情节数,可视化结果如下

代码如下
import gym
from gym import spaces
from gym.utils import seeding
from random import random, choice
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
class Grid(object):
def __init__(self, x:int = None,
y:int = None,
type:int = 0,
reward:float = 0.0):
self.x = x # 坐标x
self.y = y
self.type = type # 类别值(0:空;1:障碍或边界)
self.reward = reward # 该格子的即时奖励
self.name = None # 该格子的名称
self._update_name()
def _update_name(self):
self.name = "X{0}-Y{1}".format(self.x, self.y)
def __str__(self):
return "name:{3}, x:{0}, y:{1}, type:{2}".format(self.x,
self.y,
self.type,
self.name
)
class GridMatrix(object):
def __init__(self, n_width:int, # 水平方向格子数
n_height:int, # 竖直方向格子数
default_type:int = 0, # 默认类型
default_reward:float = 0.0, # 默认即时奖励值
):
self.grids = None
self.n_height = n_height
self.n_width = n_width
self.len = n_width * n_height
self.default_reward = default_reward
self.default_type = default_type
self.reset()
def reset(self):
self.grids = []
for x in range(self.n_height):
for y in range(self.n_width):
self.grids.append(Grid(x,
y,
self.default_type,
self.default_reward))
def get_grid(self, x, y=None):
'''获取一个格子信息
args:坐标信息,由x,y表示或仅有一个类型为tuple的x表示
return:grid object
'''
xx, yy = None, None
if isinstance(x, int):
xx, yy = x, y
elif isinstance(x, tuple):
xx, yy = x[0], x[1]
assert(xx >= 0 and yy >= 0 and xx < self.n_width and yy < self.n_height), "任意坐标值应在合理区间"
index = yy * self.n_width + xx
return self.grids[index]
def set_reward(self, x, y, reward):
grid = self.get_grid(x, y)
if grid is not None:
grid.reward = reward
else:
raise("grid doesn't exist")
def set_type(self, x, y, type):
grid = self.get_grid(x, y)
if grid is not None:
grid.type = type
else:
raise("grid doesn't exist")
def get_reward(self, x, y):
grid = self.get_grid(x, y)
if grid is None:
return None
return grid.reward
def get_type(self, x, y):
grid = self.get_grid(x, y)
if grid is None:
return None
return grid.type
# 格子世界环境
class GridWorldEnv(gym.Env):
metadata = {
'render.modes': ['human', 'rgb_array'],
'video.frames_per_second': 30
}
def __init__(self, n_width: int=5,
n_height: int = 5,
u_size=40,
default_reward: float = 0.0,
default_type=0):
self.u_size = u_size # 当前格子绘制尺寸
self.n_width = n_width # 格子世界宽度(以格子数计)
self.n_height = n_height # 高度
self.width = u_size * n_width # 场景宽度 screen width
self.height = u_size * n_height # 场景长度
self.default_reward = default_reward
self.default_type = default_type
self.grids = GridMatrix(n_width=self.n_width,
n_height=self.n_height,
default_reward=self.default_reward,
default_type=self.default_type)
self.reward = 0 # for rendering
self.action = None # for rendering
# 0,1,2,3 represent up, down, left, right
self.action_space = spaces.Discrete(4)
# 观察空间由low和high决定
self.observation_space = spaces.Discrete(self.n_height * self.n_width)
self.ends = [(0, 0)] # 终止格子坐标,可以有多个
self.start = (0, 4) # 起始格子坐标,只有一个
self.types = [(2, 2, 1)]
self.rewards = []
self.refresh_setting()
self.viewer = None # 图形接口对象
self.seed() # 产生一个随机子
self.reset()
def seed(self, seed=None):
# 产生一个随机化时需要的种子,同时返回一个np_random对象,支持后续的随机化生成操作
self.np_random, seed = seeding.np_random(seed)
return [seed]
def step(self, action):
assert self.action_space.contains(action), "%r (%s) invalid" % (action, type(action))
self.action = action # action for rendering
old_x, old_y = self._state_to_xy(self.state)
new_x, new_y = old_x, old_y
if action == 0: new_y += 1 # up
elif action == 1: new_y -= 1 # down
elif action == 2: new_x -= 1 # left
elif action == 3: new_x += 1 # right
# boundary effect
if new_x < 0: new_x = 0
if new_x >= self.n_width: new_x = self.n_width - 1
if new_y < 0: new_y = 0
if new_y >= self.n_height: new_y = self.n_height - 1
# wall effect:
# 类型为1的格子为障碍格子,不可进入
if self.grids.get_type(new_x, new_y) == 1:
new_x, new_y = old_x, old_y
self.reward = self.grids.get_reward(new_x, new_y)
done = self._is_end_state(new_x, new_y)
self.state = self._xy_to_state(new_x, new_y)
# 提供格子世界所有的信息在info内
info = {"x": new_x, "y": new_y, "grids": self.grids}
return self.state, self.reward, done, info
# 将状态变为横纵坐标
def _state_to_xy(self, s):
x = s % self.n_width
y = int((s - x) / self.n_width)
return x, y
def _xy_to_state(self, x, y=None):
if isinstance(x, int):
assert (isinstance(y, int)), "incomplete Position info"
return x + self.n_width * y
elif isinstance(x, tuple):
return x[0] + self.n_width * x[1]
return -1 # 未知状态
def refresh_setting(self):
'''用户在使用该类创建格子世界后可能会修改格子世界某些格子类型或奖励值
的设置,修改设置后通过调用该方法使得设置生效。
'''
for x, y, r in self.rewards:
self.grids.set_reward(x, y, r)
for x, y, t in self.types:
self.grids.set_type(x, y, t)
def reset(self):
self.state = self._xy_to_state(self.start)
return self.state
# 判断是否是终止状态
def _is_end_state(self, x, y=None):
if y is not None:
xx, yy = x, y
elif isinstance(x, int):
xx, yy = self._state_to_xy(x)
else:
assert (isinstance(x, tuple)), "坐标数据不完整"
xx, yy = x[0], x[1]
for end in self.ends:
if xx == end[0] and yy == end[1]:
return True
return False
# 图形化界面
def render(self, mode='human', close=False):
if close:
if self.viewer is not None:
self.viewer.close()
self.viewer = None
return
zero = (0, 0)
u_size = self.u_size
m = 2 # 格子之间的间隙尺寸
# 如果还没有设定屏幕对象,则初始化整个屏幕具备的元素。
if self.viewer is None:
from gym.envs.classic_control import rendering
self.viewer = rendering.Viewer(self.width, self.height)
# 绘制格子
for x in range(self.n_width):
for y in range(self.n_height):
v = [(x * u_size + m, y * u_size + m),
((x + 1) * u_size - m, y * u_size + m),
((x + 1) * u_size - m, (y + 1) * u_size - m),
(x * u_size + m, (y + 1) * u_size - m)]
rect = rendering.FilledPolygon(v)
r = self.grids.get_reward(x, y) / 10
if r < 0:
rect.set_color(0.9 - r, 0.9 + r, 0.9 + r)
elif r > 0:
rect.set_color(0.3, 0.5 + r, 0.3)
else:
rect.set_color(0.9, 0.9, 0.9)
self.viewer.add_geom(rect)
# 绘制边框
v_outline = [(x * u_size + m, y * u_size + m),
((x + 1) * u_size - m, y * u_size + m),
((x + 1) * u_size - m, (y + 1) * u_size - m),
(x * u_size + m, (y + 1) * u_size - m)]
outline = rendering.make_polygon(v_outline, False)
outline.set_linewidth(3)
if self._is_end_state(x, y):
# 给终点方格添加金黄色边框
outline.set_color(0.9, 0.9, 0)
self.viewer.add_geom(outline)
if self.start[0] == x and self.start[1] == y:
outline.set_color(0.5, 0.5, 0.8)
self.viewer.add_geom(outline)
if self.grids.get_type(x, y) == 1: # 障碍格子用深灰色表示
rect.set_color(0.3, 0.3, 0.3)
else:
pass
# 绘制个体
self.agent = rendering.make_circle(u_size / 4, 30, True)
self.agent.set_color(1.0, 1.0, 0.0)
self.viewer.add_geom(self.agent)
self.agent_trans = rendering.Transform()
self.agent.add_attr(self.agent_trans)
# 更新个体位置
x, y = self._state_to_xy(self.state)
self.agent_trans.set_translation((x + 0.5) * u_size, (y + 0.5) * u_size)
return self.viewer.render(return_rgb_array= mode == 'rgb_array')
# 环境参数设定
class Agent():
def __init__(self, env):
self.episode = 1
self.Q = {}
self.actions = [0, 1, 2, 3]
self.position = env.start
self.model = {}
# 建立模型
def make_model(self, pos, act, reward, next_state):
self.model["{0},{1}".format(pos, act)] = "{0},{1}".format(reward, next_state)
# 模型规划
def q_planning(self,n):
for i in range(0,n):
a = [i for i in self.model.keys()]
done = False
if a != []:
str = choice(a)
pos = str.split(",")[0]+","+str.split(",")[1]
act = int(str.split(",")[2])
reward = float(self.model[str].split(",")[0])
next_state = self.model[str].split(",")[1]+","+self.model[str].split(",")[2]
if next_state == "(0,0)" or next_state == "(4,3)":
done = True
self.updateQ(pos, act, next_state, reward, done)
def chaxunQ(self, pos, act):
judge = False
for i in self.Q:
if i == "{0},{1}".format(pos, act):
judge = True
break
if judge == True:
return True
else:
self.Q["{0},{1}".format(pos, act)] = float(format(random()/10000, '.3f'))
return
# 更新状态动作值Q函数
def updateQ(self, pos, action, next_pos, reward, done):
if done == False:
self.chaxunQ(pos, action)
old_q = self.Q["{0},{1}".format(pos, action)]
action1 = self.performmax(next_pos)
# self.chaxunQ(next_pos, action1)
new_q = self.Q["{0},{1}".format(next_pos, action1)]
old_q = old_q + 0.1 * (reward+0.9 * new_q - old_q)
self.Q["{0},{1}".format(pos, action)] = float(format(old_q, '.3f'))
else:
self.chaxunQ(pos, action)
self.Q["{0},{1}".format(pos, action)] = float(format(reward, '.3f'))
# print(pos, action,reward)
# 动作选取策略
def perform(self, pos):
eplison = random()
self.chaxunQ(pos, choice([0, 1, 2, 3]))
if eplison > 1/self.episode:
maxq = -1000
act = ""
for i in self.Q:
list = i.split(",")
state = list[0] + "," + list[1]
if state == str(pos):
if self.Q[i] > maxq:
maxq = self.Q[i]
act = list[2]
return int(act)
else:
return choice([0, 1, 2, 3])
# argmaxQ
def performmax(self, pos):
maxq = -1000
str1 = ""
self.chaxunQ(pos,choice([0,1,2,3]))
for i in self.Q:
list = i.split(",")
state = list[0]+","+list[1]
if state == str(pos):
if self.Q[i] > maxq:
maxq = self.Q[i]
str1 = list[2]
return int(str1)
def run(n):
agent = Agent(env)
total_j = 0
total_r = 0
a = []
b = []
env.refresh_setting()
for i in range(0, 300):
done = False
env.reset()
r = 0
j = 0
while done == False:
state = env._state_to_xy(env.state)
action = agent.perform(state)
next_state, reward, done, info = env.step(action)
next_state = env._state_to_xy(next_state)
# 更新Q值
agent.updateQ(state, action, next_state, reward,done)
# 更新模型
agent.make_model(state, action, reward, next_state)
r += reward
# 模型规划
agent.q_planning(n)
j = j+1
tpend(total_r)
agent.episode += 1
# print(agent.Q)
total_j += j
if i != 0:
b.append(j)
print("回合={0},步数={1},奖赏={2}".format(i, j, '%.3f' % r))
# return (np.array(a)/np.array(total_j)).tolist()
# return a
return b
if __name__ == "__main__":
n_width = 5
n_height = 5
default_reward = 0
env = GridWorldEnv(n_width, n_height, default_reward=default_reward)
env.types = [(2, 2, 1)]
env.rewards = [(0, 0, 1), (4, 3, 1)] # 奖赏值设定
env.start = (0, 4)
env.ends = [(0, 0), (4, 3)]
env.refresh_setting()
x = range(1, 300)
ln1, = plt.plot(x, run(0), label=u"n=0")
ln2, = plt.plot(x, run(5), label=u"n=5")
ln3, = plt.plot(x, run(10), label=u"n=10")
ln4, = plt.plot(x, run(30), label=u"n=30")
font1 = FontProperties(fname=r"c:windowsfontssimsun.ttc", size=15)
ontproperties=font1)
plt.ylabel(u'步数', fontproperties=font1)
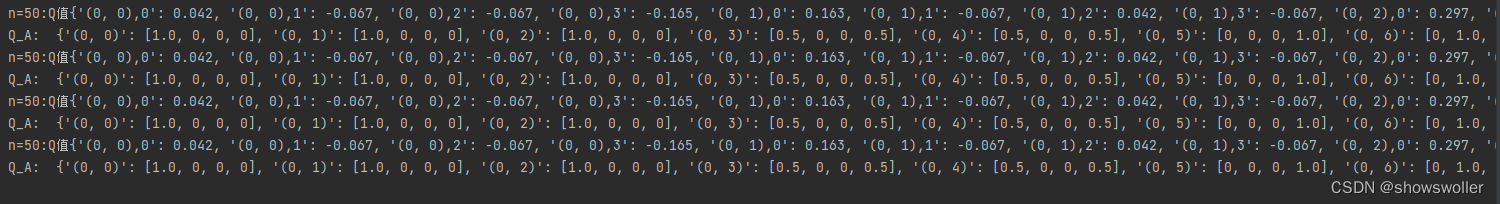
plt.show()四、Dyan-Q算法对策略的影响
同样Agent在不同的情节中采用不同的n获得的策略也不一样,当n=50的时候明显快,而且策略更加广泛
代码如下
from random import random, choice
import gym
from gym import spaces
from gym.utils import seeding
class Grid(object):
def __init__(self, x:int = None,
y:int = None,
type:int = 0,
reward:float = 0.0):
self.x = x # 坐标x
self.y = y
self.type = type # 类别值(0:空;1:障碍或边界)
self.reward = reward # 该格子的即时奖励
self.name = None # 该格子的名称
self._update_name()
def _update_name(self):
self.name = "X{0}-Y{1}".format(self.x, self.y)
def __str__(self):
return "name:{3}, x:{0}, y:{1}, type:{2}".format(self.x,
self.y,
self.type,
self.name
)
class GridMatrix(object):
def __init__(self, n_width:int, # 水平方向格子数
n_height:int, # 竖直方向格子数
default_type:int = 0, # 默认类型
default_reward:float = 0.0, # 默认即时奖励值
):
self.grids = None
self.n_height = n_height
self.n_width = n_width
self.len = n_width * n_height
self.default_reward = default_reward
self.default_type = default_type
self.reset()
def reset(self):
self.grids = []
for x in range(self.n_height):
for y in range(self.n_width):
self.grids.append(Grid(x,
y,
self.default_type,
self.default_reward))
def get_grid(self, x, y=None):
'''获取一个格子信息
args:坐标信息,由x,y表示或仅有一个类型为tuple的x表示
return:grid object
'''
xx, yy = None, None
if isinstance(x, int):
xx, yy = x, y
elif isinstance(x, tuple):
xx, yy = x[0], x[1]
assert(xx >= 0 and yy >= 0 and xx < self.n_width and yy < self.n_height), "任意坐标值应在合理区间"
index = yy * self.n_width + xx
return self.grids[index]
def set_reward(self, x, y, reward):
grid = self.get_grid(x, y)
if grid is not None:
grid.reward = reward
else:
raise("grid doesn't exist")
def set_type(self, x, y, type):
grid = self.get_grid(x, y)
if grid is not None:
grid.type = type
else:
raise("grid doesn't exist")
def get_reward(self, x, y):
grid = self.get_grid(x, y)
if grid is None:
return None
return grid.reward
def get_type(self, x, y):
grid = self.get_grid(x, y)
if grid is None:
return None
return grid.type
class GridWorldEnv(gym.Env):
metadata = {
'render.modes': ['human', 'rgb_array'],
'video.frames_per_second': 30
}
def __init__(self, n_width: int=5,
n_height: int = 5,
u_size=40,
default_reward: float = 0.0,
default_type=0):
self.u_size = u_size # 当前格子绘制尺寸
self.n_width = n_width # 格子世界宽度(以格子数计)
self.n_height = n_height # 高度
self.width = u_size * n_width # 场景宽度 screen width
self.height = u_size * n_height # 场景长度
self.default_reward = default_reward
self.default_type = default_type
self.grids = GridMatrix(n_width=self.n_width,
n_height=self.n_height,
default_reward=self.default_reward,
default_type=self.default_type)
self.reward = 0 # for rendering
self.action = None # for rendering
# 0,1,2,3 represent up, down, left, right
self.action_space = spaces.Discrete(4)
# 观察空间由low和high决定
self.observation_space = spaces.Discrete(self.n_height * self.n_width)
self.ends = [(0, 0)] # 终止格子坐标,可以有多个
self.start = (0, 4) # 起始格子坐标,只有一个
self.types = [(2, 2, 1)]
self.rewards = []
self.refresh_setting()
self.viewer = None # 图形接口对象
self.seed() # 产生一个随机子
self.reset()
def seed(self, seed=None):
# 产生一个随机化时需要的种子,同时返回一个np_random对象,支持后续的随机化生成操作
self.np_random, seed = seeding.np_random(seed)
return [seed]
def step(self, action):
assert self.action_space.contains(action), "%r (%s) invalid" % (action, type(action))
self.action = action # action for rendering
old_x, old_y = self._state_to_xy(self.state)
new_x, new_y = old_x, old_y
if action == 0: new_y += 1 # up
elif action == 1: new_y -= 1 # down
elif action == 2: new_x -= 1 # left
elif action == 3: new_x += 1 # right
# boundary effect
if new_x < 0: new_x = 0
if new_x >= self.n_width: new_x = self.n_width - 1
if new_y < 0: new_y = 0
if new_y >= self.n_height: new_y = self.n_height - 1
# wall effect:
# 类型为1的格子为障碍格子,不可进入
if self.grids.get_type(new_x, new_y) == 1:
new_x, new_y = old_x, old_y
self.reward = self.grids.get_reward(new_x, new_y)
done = self._is_end_state(new_x, new_y)
self.state = self._xy_to_state(new_x, new_y)
# 提供格子世界所有的信息在info内
info = {"x": new_x, "y": new_y, "grids": self.grids}
return self.state, self.reward, done, info
# 将状态变为横纵坐标
def _state_to_xy(self, s):
x = s % self.n_width
y = int((s - x) / self.n_width)
return x, y
def _xy_to_state(self, x, y=None):
if isinstance(x, int):
assert (isinstance(y, int)), "incomplete Position info"
return x + self.n_width * y
elif isinstance(x, tuple):
return x[0] + self.n_width * x[1]
return -1 # 未知状态
def refresh_setting(self):
'''用户在使用该类创建格子世界后可能会修改格子世界某些格子类型或奖励值
的设置,修改设置后通过调用该方法使得设置生效。
'''
for x, y, r in self.rewards:
self.grids.set_reward(x, y, r)
for x, y, t in self.types:
self.grids.set_type(x, y, t)
def reset(self):
self.state = self._xy_to_state(self.start)
return self.state
# 判断是否是终止状态
def _is_end_state(self, x, y=None):
if y is not None:
xx, yy = x, y
elif isinstance(x, int):
xx, yy = self._state_to_xy(x)
else:
assert (isinstance(x, tuple)), "坐标数据不完整"
xx, yy = x[0], x[1]
for end in self.ends:
if xx == end[0] and yy == end[1]:
return True
return False
# 图形化界面
def render(self, mode='human', close=False):
if close:
if self.viewer is not None:
self.viewer.close()
self.viewer = None
return
zero = (0, 0)
u_size = self.u_size
m = 2 # 格子之间的间隙尺寸
# 如果还没有设定屏幕对象,则初始化整个屏幕具备的元素。
if self.viewer is None:
from gym.envs.classic_control import rendering
self.viewer = rendering.Viewer(self.width, self.height)
# 绘制格子
for x in range(self.n_width):
for y in range(self.n_height):
v = [(x * u_size + m, y * u_size + m),
((x + 1) * u_size - m, y * u_size + m),
((x + 1) * u_size - m, (y + 1) * u_size - m),
(x * u_size + m, (y + 1) * u_size - m)]
rect = rendering.FilledPolygon(v)
r = self.grids.get_reward(x, y) / 10
if r < 0:
rect.set_color(0.9 - r, 0.9 + r, 0.9 + r)
elif r > 0:
rect.set_color(0.3, 0.5 + r, 0.3)
else:
rect.set_color(0.9, 0.9, 0.9)
self.viewer.add_geom(rect)
# 绘制边框
v_outline = [(x * u_size + m, y * u_size + m),
((x + 1) * u_size - m, y * u_size + m),
((x + 1) * u_size - m, (y + 1) * u_size - m),
(x * u_size + m, (y + 1) * u_size - m)]
outline = rendering.make_polygon(v_outline, False)
outline.set_linewidth(3)
if self._is_end_state(x, y):
# 给终点方格添加金黄色边框
outline.set_color(0.9, 0.9, 0)
self.viewer.add_geom(outline)
if self.start[0] == x and self.start[1] == y:
outline.set_color(0.5, 0.5, 0.8)
self.viewer.add_geom(outline)
if self.grids.get_type(x, y) == 1: # 障碍格子用深灰色表示
rect.set_color(0.3, 0.3, 0.3)
else:
pass
# 绘制个体
self.agent = rendering.make_circle(u_size / 4, 30, True)
self.agent.set_color(1.0, 1.0, 0.0)
self.viewer.add_geom(self.agent)
self.agent_trans = rendering.Transform()
self.agent.add_attr(self.agent_trans)
# 更新个体位置
x, y = self._state_to_xy(self.state)
self.agent_trans.set_translation((x + 0.5) * u_size, (y + 0.5) * u_size)
return self.viewer.render(return_rgb_array= mode == 'rgb_array')
# 环境参数设定
class Agent():
def __init__(self, env):
self.episode = 1
self.Q = {}
self.actions = [0, 1, 2, 3]
self.position = env.start
self.model = {}
def make_model(self, pos, act, reward, next_state):
self.model["{0},{1}".format(pos, act)] = "{0},{1}".format(reward, next_state)
def q_planning(self,n):
for i in range(0, n):
a = [i for i in self.model.keys()]
done=False
if a != []:
str = choice(a)
pos = str.split(",")[0]+","+str.split(",")[1]
act = int(str.split(",")[2])
reward = float(self.model[str].split(",")[0])
next_state = self.model[str].split(",")[1]+","+self.model[str].split(",")[2]
if next_state == "(8,5)" or next_state == "(1,6)":
done = True
self.updateQ(pos,act,next_state,reward,done)
def chaxunQ(self, pos, act):
judge = False
for i in self.Q:
if i == "{0},{1}".format(pos, act):
judge = True
break
if judge == True:
return True
else:
self.Q["{0},{1}".format(pos, act)] = float(format(random()/10000, '.3f'))
return
# 更新状态动作值Q函数
def updateQ(self, pos,action,next_pos,reward,done):
if done == False:
self.chaxunQ(pos, action)
old_q = self.Q["{0},{1}".format(pos, action)]
action1 = self.performmax(next_pos)
new_q = self.Q["{0},{1}".format(next_pos, action1)]
old_q = old_q + 0.1 * (reward+0.9 * new_q - old_q)
self.Q["{0},{1}".format(pos, action)] = float(format(old_q, '.3f'))
else:
self.chaxunQ(pos, action)
self.Q["{0},{1}".format(pos, action)] = float(format(reward, '.3f'))
# 动作选取策略
def perform(self, pos):
eplison = random()
self.chaxunQ(pos, choice([0, 1, 2, 3]))
if eplison > 1/self.episode:
maxq = -1000
act = ""
for i in self.Q:
list = i.split(",")
state = list[0] + "," + list[1]
if state == str(pos):
if self.Q[i] > maxq:
maxq = self.Q[i]
act = list[2]
return int(act)
else:
return choice([0, 1, 2, 3])
# argmaxQ
def performmax(self, pos):
maxq = -1000
str1 = ""
self.chaxunQ(pos,choice([0,1,2,3]))
for i in self.Q:
list = i.split(",")
state = list[0]+","+list[1]
if state == str(pos):
if self.Q[i] > maxq:
maxq = self.Q[i]
str1 = list[2]
return int(str1)
def run(n):
agent = Agent(env)
total_j = 0
total_r = 0
a = []
b = []
env.refresh_setting()
for i in range(0, 300):
done = False
env.reset()
r = 0
j = 0
while done == False and j < 50:
j = j + 1
state = env._state_to_xy(env.state)
action = agent.perform(state)
next_state, reward, done, info = env.step(action)
next_state = env._state_to_xy(next_state)
# 更新模型
agent.make_model(state, action, reward, next_state)
# 更新Q值
agent.updateQ(state, action, next_state, reward, done)
r += reward
# 模型规划
agent.q_planning(n)
if i >= 2:
total_r += r
a.append(total_r)
agent.episode += 1
action_Q = {}
for i in sorted(list(agent.Q.keys()), key=lambda x: [x[1], x[4], x[5], x[-1]]):
action_Q[i] = agent.Q[i]
print("n={0}:Q值{1}".format(n, action_Q))
# P_A:状态采取策略
P_A = {}
Q_keys = list(action_Q.keys())
for i in range(0, len(Q_keys)-4, 4):
temp_action_list = []
max_a_value = max(action_Q[Q_keys[j]] for j in range(i, i+4))
# temp_num:标记四个动作最大值
temp_num = [0, 0, 0, 0]
# PA:四个动作概率
PA = [0, 0, 0, 0]
for k in range(i, i+4):
if action_Q[Q_keys[k]] == max_a_value:
temp_action_list.append(Q_keys[k])
temp_num[k-i] = 1
valid_action_p = round(1/len(temp_action_list), 2)
for m in range(4):
if temp_num[m] == 1:
PA[m] = valid_action_p
P_A[Q_keys[i][0:-2]] = PA
print("Q_A: ", P_A)
total_j += j
b.append(j)
return a
if __name__ == "__main__":
n_width = 11
n_height = 7
default_reward = -0.1
env = GridWorldEnv(n_width, n_height, default_reward=default_reward)
env.types = [(1, 2, 1), (2, 2, 1), (3, 2, 1), (4, 2, 1), (5, 2, 1), (6, 2, 1), (7, 2, 1), (8, 2, 1), (9, 2, 1),
(10, 2, 1)]
env.rewards = [(8, 5, 1), (1, 6, 1)] # 奖赏值设定
env.start = (4, 0) # 机器人出发点坐标
env.ends = [(8, 5), (1, 6)] # 吸入状态坐标
env.refresh_setting()
for i in range(0, 2):
print("episode=", i+1)
run(0)
for i in range(0, 2):
print("episode=", i+1)
run(50)
创作不易 觉得有帮助请点赞关注收藏~~~
最后
以上就是激动薯片最近收集整理的关于强化深度学习中使用Dyna-Q算法确定机器人问题中不同规划的学习和策略实战(超详细 附源码)一、模型、学习、规划简介 二、Dyna-Q结构及其算法 三、Dyna-Q不同规划对学习步数的影响四、Dyan-Q算法对策略的影响的全部内容,更多相关强化深度学习中使用Dyna-Q算法确定机器人问题中不同规划的学习和策略实战(超详细内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复