实例要求:
- 编写一个 Netty 心跳检测机制案例, 当服务器超过 3 秒没有读时,就提示读空闲
- 当服务器超过 5 秒没有写操作时,就提示写空闲
- 实现当服务器超过 7 秒没有读或者写操作时,就提示读写空闲
服务端代码实现
Myserver类代码
package com.netty.heartBeat;
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.*;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LogLevel;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler;
import io.netty.handler.timeout.IdleStateHandler;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class MyServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//创建两个线程池组
NioEventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
NioEventLoopGroup workGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
//创建Netty启动类
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap=new ServerBootstrap();
try {
serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup,workGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO))//在bossGroup中加入一个handler
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {//在workGroup中加入handler
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
//加入一个netty 提供IdleStateHandler
/*
文档说明
* 1、IdleStateHandler 是netty 提供的处理空闲状态的处理器
2、long readerIdleTime :表示多长时间没有读,就会发送一个心跳检测包 检测是否连接
3、long writeIdleTime :表示多长时间没有写,就会发送一个心跳检测包 检测是否连接
4、long allIdleTime: 表示多长时间没有读写,就会发送一个心跳检测包 检测是否连接
5、当IdleStateEvent触发后,就会传递给管道(pipeline)的下一个handler去处理
通过调用(触发)下一个handler的userEventTiggered,在该方法中去处理(读空闲、写空闲、读写空闲)
*/
pipeline.addLast(new IdleStateHandler(3, 5, 7, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
//加入一个对空闲检测进一步处理的handler(自定义)
pipeline.addLast(new MyServerHandler());
}
});
//启动服务器
ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(7000).sync();
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}finally {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
MyServerHandler类代码
package com.netty.heartBeat;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.handler.timeout.IdleStateEvent;
public class MyServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
/**
*
* @param ctx 上下文
* @param evt 事件
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void userEventTriggered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object evt) throws Exception {
if(evt instanceof IdleStateEvent){
//將evt向下转型 IdleStateEvent
IdleStateEvent event = (IdleStateEvent) evt;
String eventType=null;
switch (event.state()){
case READER_IDLE:
eventType="读空闲";
break;
case WRITER_IDLE:
eventType = "写空闲";
break;
case ALL_IDLE:
eventType = "读写空闲";
break;
}
//当管道发生空闲事件时,关闭通道
ctx.channel().close().sync();
System.out.println(ctx.channel().remoteAddress() + "--超时事件--" + eventType);
System.out.println("服务器做相应处理..");
}
}
}
客户端代码实现
MyServerHandler 类代码
package com.netty.heartBeat;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.handler.timeout.IdleStateEvent;
public class MyServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
/**
*
* @param ctx 上下文
* @param evt 事件
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void userEventTriggered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object evt) throws Exception {
if(evt instanceof IdleStateEvent){
//將evt向下转型 IdleStateEvent
IdleStateEvent event = (IdleStateEvent) evt;
String eventType=null;
switch (event.state()){
case READER_IDLE:
eventType="读空闲";
break;
case WRITER_IDLE:
eventType = "写空闲";
break;
case ALL_IDLE:
eventType = "读写空闲";
break;
}
//当管道发生空闲事件时,关闭通道
ctx.channel().close().sync();
System.out.println(ctx.channel().remoteAddress() + "--超时事件--" + eventType);
System.out.println("服务器做相应处理..");
}
}
}
NettyClientHandler代码
package com.netty.heartBeat;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.util.CharsetUtil;
public class NettyClientHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
//当通道就绪就会触发该方法
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println("client" + ctx);
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("hello,Server:小沙弥", CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
}
//当通道有读取事件是,会触发
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;
System.out.println("服务器回复的消息:" + buf.toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
System.out.println("服务器地址是:"+ctx.channel().remoteAddress());
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
}
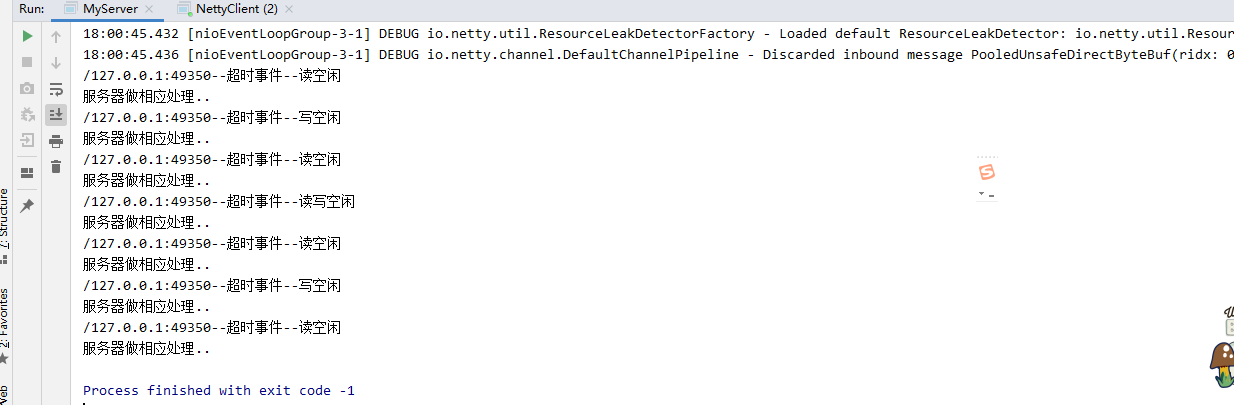
结果
????推荐阅读????
上一篇:九、Netty核心技术之模块分析
下一篇:十一、Netty 通过 WebSocket 编程实现服务器和客户端长连接
最后
以上就是酷炫画板最近收集整理的关于十、Netty核心技术之Netty心跳机制服务端代码实现客户端代码实现结果的全部内容,更多相关十、Netty核心技术之Netty心跳机制服务端代码实现客户端代码实现结果内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复