天池入门赛-心跳信号分类预测-PyTorch CNN模型
- 天池赛-心跳信号分类预测
- 赛题简介
- 评测标准
- 数据分析
- CNN模型
- 损失函数
- 主要代码
- 结语
- 代码
天池赛-心跳信号分类预测
赛题简介
赛题以预测心电图心跳信号类别为任务,数据集报名后可见并可下载,该数据来自某平台心电图数据记录,总数据量超过20万,主要为1列心跳信号序列数据,其中每个样本的信号序列采样频次一致,长度相等。为了保证比赛的公平性,将会从中抽取10万条作为训练集,2万条作为测试集A,2万条作为测试集B,同时会对心跳信号类别(label)信息进行脱敏。
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| id | 为心跳信号分配的唯一标识 |
| heartbeat_signals | 心跳信号序列 |
| label | 心跳信号类别(0、1、2、3) |
评测标准
选手需提交4种不同心跳信号预测的概率,选手提交结果与实际心跳类型结果进行对比,求预测的概率与真实值差值的绝对值(越小越好)。
具体计算公式如下:
针对某一个信号,若真实值为[
y
1
y_1
y1,
y
2
y_2
y2,
y
3
y_3
y3,
y
4
y_4
y4], 模型预测概率值为[
a
1
a_1
a1,
a
2
a_2
a2,
a
3
a_3
a3,
a
4
a_4
a4], 那么该模型的平均指标
a
b
s
−
s
u
m
abs-sum
abs−sum为
a
b
s
−
s
u
m
abs-sum
abs−sum =
∑
y
=
1
n
∑
i
=
1
4
∣
y
i
−
a
i
∣
displaystylesum_{y=1}^{n}displaystylesum_{i=1}^{4} |y_i -a_i|
y=1∑ni=1∑4∣yi−ai∣
例如,心跳信号为1, 会通过编码转成[0, 1, 0, 0], 预测不同心跳信号概率为[0.1, 0.7, 0.1, 0.1], 那么这个预测结果的
a
b
s
−
s
u
m
abs-sum
abs−sum为
a
b
s
−
s
u
m
abs-sum
abs−sum = ∣0.1−0∣+∣0.7−1∣+∣0.1−0∣+∣0.1−0∣=0.6
数据分析
这一部分在天池nootbook上已有作者提供代码示例,在此引用。链接如下:
Task 2 数据分析
CNN模型
这个CNN模型是用PyTorch框架实现的。
大概思路如下:
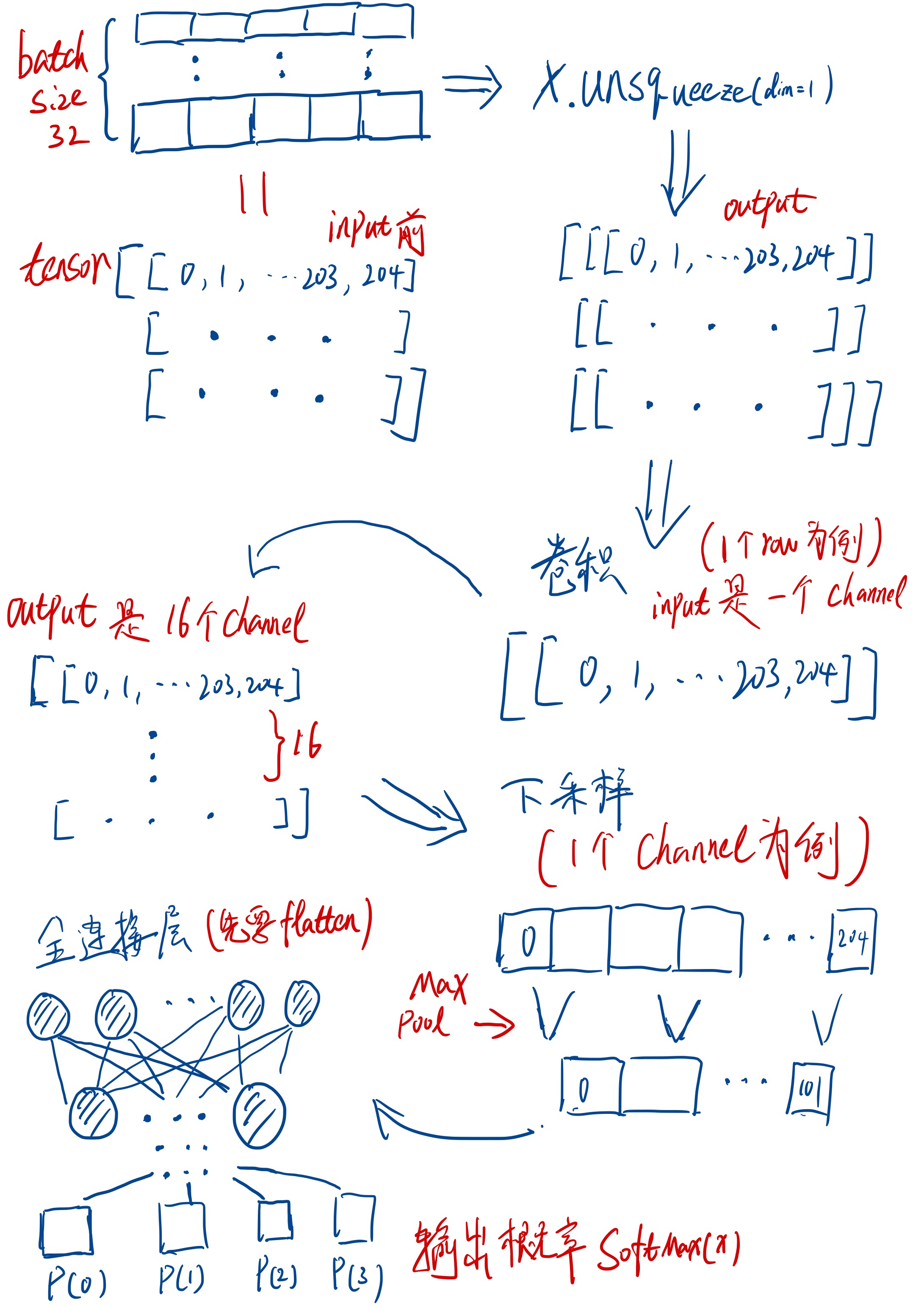
希望上图能够帮助新手理解卷积层和采样层是个什么意思,图片大小有限没能画出kernel和kernel怎么移动的。对于每一层输入的shape可以结合笔者代码中的注释进行推算。
也可参考PyTorch的文档和Source code进行理解,链接如下:
nn.Conv1d
class Model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
"""
CNN模型构造
"""
super(Model, self).__init__()
self.conv_layer1 = nn.Sequential(
# input shape(32, 1, 205) -> [batch_size, channel, features]
# 参考->https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.Conv1d.html#torch.nn.Conv1d
nn.Conv1d(in_channels=1, out_channels=16, kernel_size=3, padding=1), # 卷积后(16, 1, 205)
nn.BatchNorm1d(16),
nn.ReLU()
)
# 下采样down-sampling
self.sampling_layer1 = nn.Sequential(
# input shape(32, 16, 205)
nn.Conv1d(in_channels=16, out_channels=32, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm1d(32),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool1d(kernel_size=2, stride=2), # size随便选的, 这里output应该是(32, 32, 102)
)
self.conv_layer2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv1d(in_channels=32, out_channels=64, kernel_size=3, padding=1), # 输出(32, 64, 102)
nn.BatchNorm1d(64),
nn.ReLU()
)
self.sampling_layer2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv1d(in_channels=64, out_channels=128, kernel_size=3, padding=1), # 输出(32, 128, 102)
nn.BatchNorm1d(128),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool1d(kernel_size=2, stride=2), # 输出(32, 64, 51)
)
self.conv_layer3 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv1d(in_channels=128, out_channels=256, kernel_size=3, padding=1), # 输出(32, 256, 51)
nn.BatchNorm1d(256),
nn.ReLU()
)
self.sampling_layer3 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv1d(in_channels=256, out_channels=512, kernel_size=3, padding=1), # 输出(32, 512, 51)
nn.BatchNorm1d(512),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool1d(kernel_size=2, stride=2), # 输出(32, 512, 25)
)
# 全连接层
self.full_layer = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(in_features=512*25, out_features=256*25),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(in_features=256*25, out_features=128*25),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(in_features=128*25, out_features=64*25),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(in_features=64*25, out_features=4)
)
# 这个是输出label预测概率, 不知道这写法对不对
self.pred_layer = nn.Softmax(dim=1)
def forward(self, x):
"""
前向传播
:param x: batch
:return: training == Ture 返回的是全连接层输出, training == False 加上一个Softmax(), 返回各个label概率.
"""
x = x.unsqueeze(dim=1) # 升维. input shape(32, 205), output shape(32, 1, 205)
x = self.conv_layer1(x)
x = self.sampling_layer1(x)
x = self.conv_layer2(x)
x = self.sampling_layer2(x)
x = self.conv_layer3(x)
x = self.sampling_layer3(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1) # output(32, 12800)
x = self.full_layer(x)
if self.training:
return x # CrossEntropyLoss自带LogSoftmax, 所以训练的时候不用输出概率(我也不知道这个写法对不对, 我是试错出来的.)
else:
return self.pred_layer(x)
损失函数
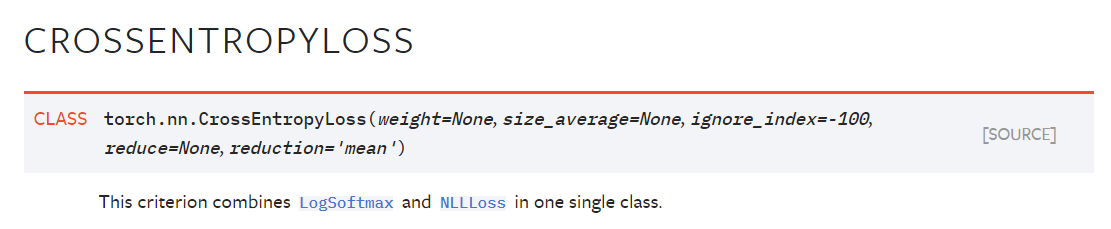
Cross Entropy Loss:
这个损失函数是多分类问题经常使用的, 需要注意的是Cross Entropy Loss结合了LogSoftmax和NLLLoss, 如果你在输出层使用了Softmax可能会导致你的模型无法拟合.
参考链接: Cross Entropy Loss
L1 Loss:
在评分标准中有题提到这个比赛采用的是
a
b
s
−
s
u
m
abs-sum
abs−sum =
∑
y
=
1
n
∑
i
=
1
4
∣
y
i
−
a
i
∣
displaystylesum_{y=1}^{n}displaystylesum_{i=1}^{4} |y_i -a_i|
y=1∑ni=1∑4∣yi−ai∣
这个其实就是PyTorch中的nn.L1Loss()或者F.l1_loss(). PyTorch默认的是mean absolute error (MAE), 但根据文档你只要将reduction设置为 reduction=‘sum’ 就可以了. 这不就成了sum absolute error(SAE)了.
L1 Loss的参考链接: nn.L1Loss

主要代码
一下是主要代码供大家参考.
def train_loop(dataloader, model, loss_fn, optimizer):
"""
模型训练部分
:param dataloader: 训练数据集
:param model: 训练用到的模型
:param loss_fn: 评估用的损失函数
:param optimizer: 优化器
:return: None
"""
for batch, x_y in enumerate(dataloader):
X, y = x_y[:, :205].type(torch.float64), torch.tensor(x_y[:, 205], dtype=torch.long, device='cuda:0')
# 开启梯度
with torch.set_grad_enabled(True):
# Compute prediction and loss
pred = model(X.float())
loss = loss_fn(pred, y)
optimizer.zero_grad()
# Backpropagation
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
def test_loop(dataloader, model, loss_fn):
"""
模型测试部分
:param dataloader: 测试数据集
:param model: 测试模型
:param loss_fn: 损失函数
:return: None
"""
size = len(dataloader.dataset)
test_loss, correct, l1_loss = 0, 0, 0
# 用来计算abs-sum. 等于PyTorch L1Loss-->
# https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.L1Loss.html#torch.nn.L1Loss
l1loss_fn = AbsSumLoss()
with torch.no_grad(): # 关掉梯度
model.eval()
for x_y in dataloader:
X, y = x_y[:, :205].type(torch.float64), torch.tensor(x_y[:, 205], dtype=torch.long, device='cuda:0')
# 注意Y和y的区别, Y用来计算L1 loss, y是CrossEntropy loss.
Y = torch.zeros(size=(len(y), 4), device='cuda:0')
for i in range(len(Y)):
Y[i][y[i]] = 1
pred = model(X.float())
test_loss += loss_fn(pred, y).item() # 这个是CrossEntropy loss
l1_loss += l1loss_fn(pred, Y).item() # 这个是abs-sum/L1 loss
correct += (pred.argmax(1) == y).type(torch.float).sum().item() # 这个是计算准确率的, 取概率最大值的下标.
test_loss /= size # 等于CrossEntropy的reduction='mean', 这里有些多此一举可删掉.
correct /= size
print(f"Test Results:nAccuracy: {(100*correct):>0.1f}% abs-sum loss: {l1_loss:>8f} CroEtr loss: {test_loss:>8f}")
def prediction(net, loss):
"""
对数据进行预测
:param net: 训练好的模型
:param loss: 模型的测试误差值, 不是损失函数. 可以去掉, 这里是用来给预测数据命名方便区分.
:return: None
"""
with torch.no_grad():
net.eval()
pred_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset=pred_data)
res = []
for x in pred_loader:
x = torch.tensor(x, device='cuda:0', dtype=torch.float64)
output = net(x.float())
res.append(output.cpu().numpy().tolist())
res = [i[0] for i in res]
res_df = pd.DataFrame(res, columns=['label_0', 'label_1', 'label_2', 'label_3'])
res_df.insert(0, 'id', value=range(100000, 120000))
res_df.to_csv('res-loss '+str(loss)+'.csv', index=False)
class Model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
"""
CNN模型构造
"""
super(Model, self).__init__()
self.conv_layer1 = nn.Sequential(
# input shape(32, 1, 205) -> [batch_size, channel, features]
# 参考->https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.Conv1d.html#torch.nn.Conv1d
nn.Conv1d(in_channels=1, out_channels=16, kernel_size=3, padding=1), # 卷积后(32, 16, 205)
nn.BatchNorm1d(16),
nn.ReLU()
)
# 下采样down-sampling
self.sampling_layer1 = nn.Sequential(
# input shape(32, 16, 205)
nn.Conv1d(in_channels=16, out_channels=32, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm1d(32),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool1d(kernel_size=2, stride=2), # size随便选的, 这里output应该是(32, 32, 102)
)
self.conv_layer2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv1d(in_channels=32, out_channels=64, kernel_size=3, padding=1), # 输出(32, 64, 102)
nn.BatchNorm1d(64),
nn.ReLU()
)
self.sampling_layer2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv1d(in_channels=64, out_channels=128, kernel_size=3, padding=1), # 输出(32, 128, 102)
nn.BatchNorm1d(128),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool1d(kernel_size=2, stride=2), # 输出(32, 64, 51)
)
self.conv_layer3 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv1d(in_channels=128, out_channels=256, kernel_size=3, padding=1), # 输出(32, 256, 51)
nn.BatchNorm1d(256),
nn.ReLU()
)
self.sampling_layer3 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv1d(in_channels=256, out_channels=512, kernel_size=3, padding=1), # 输出(32, 512, 51)
nn.BatchNorm1d(512),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool1d(kernel_size=2, stride=2), # 输出(32, 512, 25)
)
# 全连接层
self.full_layer = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(in_features=512*25, out_features=256*25),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(in_features=256*25, out_features=128*25),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(in_features=128*25, out_features=64*25),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(in_features=64*25, out_features=4)
)
# 这个是输出label预测概率, 不知道这写法对不对
self.pred_layer = nn.Softmax(dim=1)
def forward(self, x):
"""
前向传播
:param x: batch
:return: training == Ture 返回的是全连接层输出, training == False 加上一个Softmax(), 返回各个label概率.
"""
x = x.unsqueeze(dim=1) # 升维. input shape(32, 205), output shape(32, 1, 205)
x = self.conv_layer1(x)
x = self.sampling_layer1(x)
x = self.conv_layer2(x)
x = self.sampling_layer2(x)
x = self.conv_layer3(x)
x = self.sampling_layer3(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1) # output(32, 12800)
x = self.full_layer(x)
if self.training:
return x # CrossEntropyLoss自带LogSoftmax, 训练的时候不用输出概率(我也不知道这个写法对不对, 我是试错出来的.)
else:
return self.pred_layer(x)
class AbsSumLoss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
"""
可以直接用PyTorch的nn.L1Loss, 这个我写的时候不知道。
"""
super(AbsSumLoss, self).__init__()
def forward(self, output, target):
loss = F.l1_loss(target, output, reduction='sum')
return loss
if __name__ == '__main__':
set_random_seed(1996) # 设定随机种子
# 加载数据集
data = pd.read_csv('train.csv')
data = process_data(data)
pred_data = pd.read_csv('testA.csv')
pred_data = get_pred_x(pred_data)
# 初始化模型
lr_rate = 1e-5
w_decay = 1e-6
n_epoch = 100
b_size = 32
device = torch.device('cuda:0' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
net = Model()
net.to(device)
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(params=net.parameters(), lr=lr_rate, weight_decay=w_decay)
loss_fn = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(reduction='sum')
# 拆分训练测试集
train, test = train_test_split(data, test_size=0.2)
train, test = torch.cuda.FloatTensor(train), torch.cuda.FloatTensor(test)
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset=train, batch_size=b_size)
test_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset=test, batch_size=b_size)
for epoch in range(n_epoch):
start = time.time()
print(f"n----------Epoch {epoch + 1}----------")
train_loop(train_loader, net, loss_fn, optimizer)
test_loop(test_loader, net, loss_fn)
end = time.time()
print('training time: ', end-start)
# predict
结语
我也是个新手, 没什么经验, 难免存在错误和纰漏还请各位大佬指正. 比赛还在进行中, 如有新的发现和经验会在后续和大家继续分享.
代码
上传了代码,CNN最后B榜的表现是16名。
模型代码
最后
以上就是深情灯泡最近收集整理的关于天池入门赛-心跳信号分类预测-PyTorch CNN模型天池赛-心跳信号分类预测的全部内容,更多相关天池入门赛-心跳信号分类预测-PyTorch内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复