使用algorithm头文件,需要在头文件下加一行“using namespace std”。
1.max()、min()、abs()
max(x,y)和min(x,y)分别返回x和y中的最大值和最小值,且参数必须是两个(可以是浮点数)。如果想要返回三个数x、y、z的最大值,可以使用max(x,max(y,z)的写法。
abs(x)返回x的绝对值。注意:x必须是整数,浮点型的绝对值请用math头文件下的fabs。
程序代码:
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int x=1,y=-2;
printf("%d %dn",max(x,y),min(x,y));
printf("%d %dn",abs(x),abs(y));
return 0;
}
运行结果:

2.swap()
swap(x,y)用来交换x和y的值。
程序代码:
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main(){
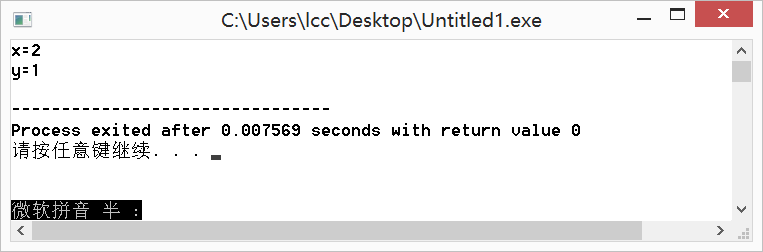
int x=1,y=2;
swap(x,y);
printf("x=%dn",x);
printf("y=%dn",y);
return 0;
} 运行结果:
3.reverse()
reverse(it,it2)可以将数组指针在[it,it2)之间的元素或容器的迭代器在[it,it2)范围内的元素进行反转。
(1)对指针数组:
程序代码:
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main(){
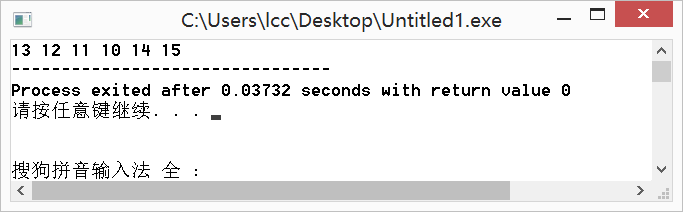
int a[10]={10,11,12,13,14,15};
reverse(a,a+4);//将a[0]~[3]反转
for(int i=0;i<6;i++) {
printf("%d ",a[i]);
}
return 0;
} 运行结果:
(2)对容器:
程序代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main(){
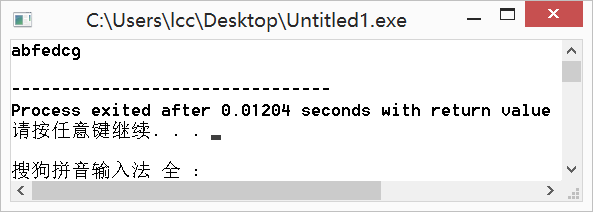
string str = "abcdefg";
reverse(str.begin()+2,str.begin()+6);//对str[2]~str[5]反转
cout<<str<<endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
4.next_permutation()
next_permutation()给出一个序列在全排列中的下一个序列。
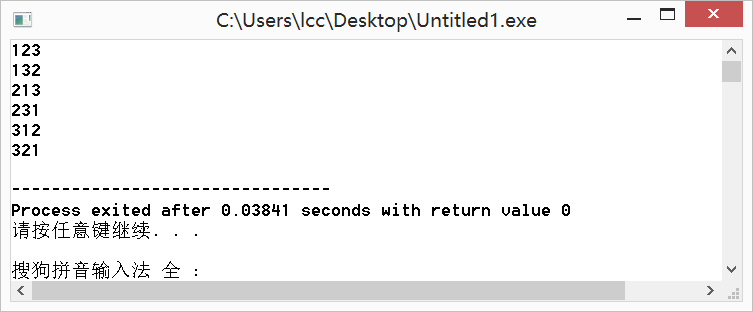
例如,当n==3时全排列是:
123
132
213
231
312
321这样231的下一个序列就是312。
程序代码:
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a[10] = {1,2,3};
//a[0]~a[2]之间的序列需要求解next_permutation
do{
printf("%d%d%dn",a[0],a[1],a[2]);
} while(next_permutation(a,a+3));
return 0;
} 运行结果:
在上述代码中,使用循环是因为next_permutation在已经到达全排列的最后一个时会返回false,这样会方便退出循环。而使用do… while语句而不使用while语句是因为序列123本身也需要输出,如果使用while会直接跳到下一个序列再输出,这样结果会少一个123。
普通的全排列解决方法:全排列
5.fill()
fill()可以把数组或者容器中的某一段区间赋为某个相同的值。和memset不同,这里的赋值可以是数组类型对应范围内的任意值。
程序代码:
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a[5] = {1,2,3,4,5};
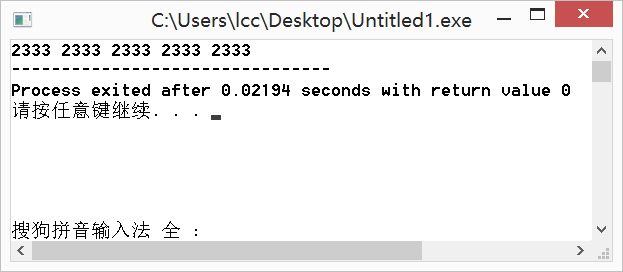
fill(a,a+5,2333);//将a[0]~a[4]均赋值为2333
for(int i=0;i<5;i++) {
printf("%d ",a[i]);
}
return 0;
} 运行结果:
最后
以上就是自由便当最近收集整理的关于algorithm头文件下的常用函数之max()、min()、abs()、swap()、reverse()、next_permutation()、fill()1.max()、min()、abs()2.swap()3.reverse()4.next_permutation()5.fill()的全部内容,更多相关algorithm头文件下内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复