UD什么时网络协议栈?
我们知道,数据流从网络到用户态应用程序,需要经历的阶段,如下图黑色线部分
就是从网卡拷贝到内核,再从内核拷贝到用户态程序,这其中会经历两次拷贝。如果时大量客户端C10M时,就会造成性能的瓶颈。
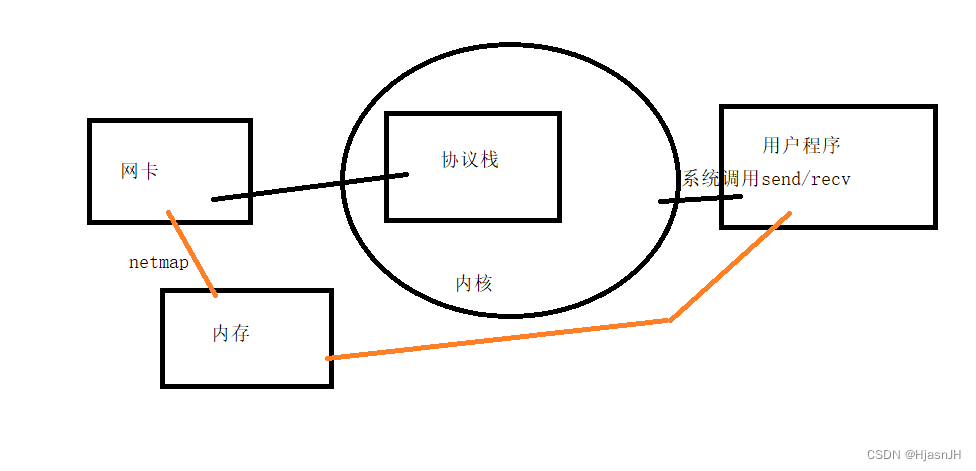 所以,就有了用户态协议栈的诞生,也就是说,原本内核完成了协议栈的功能,被移动到用户程序,那此时,用户程序如何从网卡取数据呢?
所以,就有了用户态协议栈的诞生,也就是说,原本内核完成了协议栈的功能,被移动到用户程序,那此时,用户程序如何从网卡取数据呢?
有很多种实现方式,比如通过netmap,将网卡的数据映射到内存,则用户态协议栈只需要从内存中解析并实现协议栈的功能,则可以实现用户态的协议栈的应用程序。减少了两次拷贝的开销。
这也就是实现了零拷贝,因为网卡到内存的数据,是直接通过DMA技术来实现,绕过了CPU。
如何将网卡数据映射到内存?
这里使用netmap的开源软件,https://github.com/luigirizzo/netmap
如何安装和编译,这个软件依赖了内核,所以,首先要找到自己的系统内核版本:
https://github.com/luigirizzo/netmap比如我的 3.10.0-1160.62.1.el7.x86_64,上谷歌搜索,找到下面的这个包,然后安装对应的内核的rpm包kernel-devel-3.10.0-1160.62.1.el7.x86_64.rpm,然后通过.configure,再make和make install
就能成功安装netmap,这里只是大概的讲解,基本上网上都能搜索到,还有最好把网卡改名位eth0
编译完成后,就能发现有netmap.ko 的文件。
启动内核模块,insmod netmap.ko
netmap的代码实现
首先,我们先要了解一包网络数据是怎么组成的。
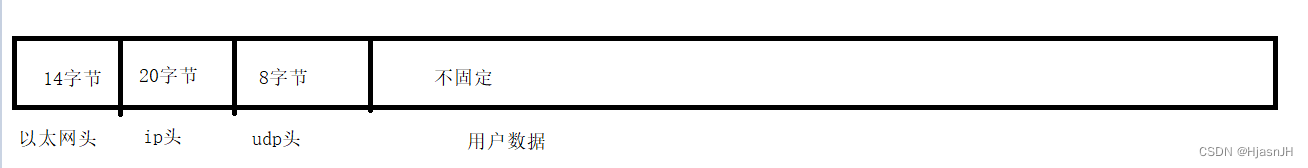
以太网头的组成:
 对应的数据结构定义:
对应的数据结构定义:
#define ETH_ALEN 6
struct ethhdr {
unsigned char h_dest[ETH_ALEN];
unsigned char h_source[ETH_ALEN];
unsigned short h_proto;
};IP头定义
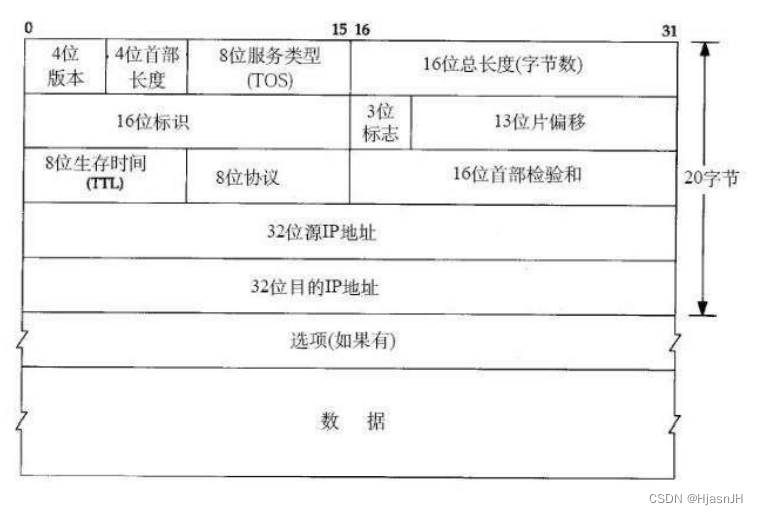
代码实现:
struct iphdr {
unsigned char version;
unsigned char tos;
unsigned short tot_len;
unsigned short id;
unsigned short flag_off;
unsigned char ttl;
unsigned char protocol;
unsigned short check;
unsigned int saddr;
unsigned int daddr;
};UDP头
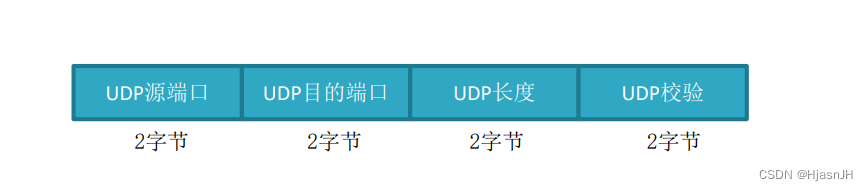
struct udphdr {
unsigned short source;
unsigned short dest;
unsigned short len;
unsigned short check;
};剩下的就是整个UDP包
struct udppkt {
struct ethhdr eh;
struct iphdr ip;
struct udphdr udp;
unsigned char body[0];
};其中用到了柔性数组,body[0],这是在工程中如果作为结构体通信的常用技术手段,为啥这里不用指针,因为指针与指向的地址的内存不连续。这里应该很好理解。
然后,我们来看怎么通过netmap实现对数据包的解析。
主程序实现
int main()
{
struct ethhdr* eh;
struct pollfd pfd = { 0 };
struct nm_pkthdr h;
unsigned char* stream = NULL;
struct nm_desc* nmr = nm_open("netmap:eth0", NULL, 0, NULL);
if (nmr == NULL) {
printf("Error openn");
return -1;
}
pfd.fd = nmr->fd;
pfd.events = POLLIN;
while (1) {
int ret = poll(&pfd, 1, -1);
if (ret < 0) continue;
if (pfd.revents & POLLIN) {
stream = nm_nextpkt(nmr, &h);
eh = (struct ethhdr*)stream;
if (ntohs(eh->h_proto) == PROTO_IP) {
struct udppkt* udp = (struct udppkt*)stream;
if (udp->ip.protocol == PROTO_UDP) {
struct in_addr addr;
addr.s_addr = udp->ip.saddr;
int udp_length = ntohs(udp->udp.len);
printf("%s:%d:length:%d, ip_len:%d --> ", inet_ntoa(addr), udp->udp.source,
udp_length, ntohs(udp->ip.tot_len));
printf("udp --> ");
for (int i = 0; i < udp_length - 8; i++)
{
printf("%c", udp->body[i]);
}
printf("n");
}
}
}
}
}从程序看上,首先,通过nm_open("netmap:eth0", NULL, 0, NULL)获取nm_desc的对象
然后poll等待对应的fd上有数据,stream = nm_nextpkt(nmr, &h);
nm_nextpkt,可见,netmap应该是为我们的UDP数据获取了一块类似内存池的分配机制,我们只要直接从其中取出数据既可。
eh = (struct ethhdr*)stream;
从取出的stream中获取到以太网头,然后匹配对应的协议,如果是IP协议才处理
struct udppkt* udp = (struct udppkt*)stream;
然后转换为UDP包,然后解析出对应的协议。
测试结果:
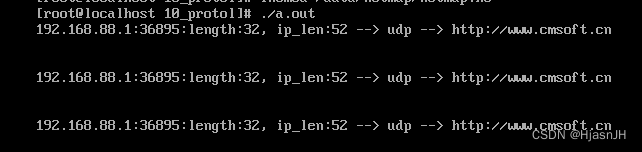
这简单了获取了udp的数据包。并打印出来,其实还是有bug的,没有处理arp和ICMP协议,会导致中间发了一会就收不到。
完整的实现代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/poll.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#define NETMAP_WITH_LIBS
#include <net/netmap_user.h>
#pragma pack(1)
#define ETH_ALEN 6
#define PROTO_IP 0x0800
#define PROTO_ARP 0x0806
#define PROTO_UDP 17
#define PROTO_ICMP 1
#define PROTO_IGMP 2
struct ethhdr {
unsigned char h_dest[ETH_ALEN];
unsigned char h_source[ETH_ALEN];
unsigned short h_proto;
};
struct iphdr {
unsigned char version;
unsigned char tos;
unsigned short tot_len;
unsigned short id;
unsigned short flag_off;
unsigned char ttl;
unsigned char protocol;
unsigned short check;
unsigned int saddr;
unsigned int daddr;
};
struct udphdr {
unsigned short source;
unsigned short dest;
unsigned short len;
unsigned short check;
};
struct udppkt {
struct ethhdr eh;
struct iphdr ip;
struct udphdr udp;
unsigned char body[128];
};
struct arphdr {
unsigned short h_type;
unsigned short h_proto;
unsigned char h_addrlen;
unsigned char protolen;
unsigned short oper;
unsigned char smac[ETH_ALEN];
unsigned int sip;
unsigned char dmac[ETH_ALEN];
unsigned int dip;
};
struct arppkt {
struct ethhdr eh;
struct arphdr arp;
};
struct icmphdr {
unsigned char type;
unsigned char code;
unsigned short check;
unsigned short identifier;
unsigned short seq;
unsigned char data[32];
};
struct icmppkt {
struct ethhdr eh;
struct iphdr ip;
struct icmphdr icmp;
};
void print_mac(unsigned char *mac) {
int i = 0;
for (i = 0;i < ETH_ALEN-1;i ++) {
printf("%02x:", mac[i]);
}
printf("%02x", mac[i]);
}
void print_ip(unsigned char *ip) {
int i = 0;
for (i = 0;i < 3;i ++) {
printf("%d.", ip[i]);
}
printf("%d", ip[i]);
}
void print_arp(struct arppkt *arp) {
print_mac(arp->eh.h_dest);
printf(" ");
print_mac(arp->eh.h_source);
printf(" ");
printf("0x%04x ", ntohs(arp->eh.h_proto));
printf(" ");
}
int str2mac(char *mac, char *str) {
char *p = str;
unsigned char value = 0x0;
int i = 0;
while (p != '�') {
if (*p == ':') {
mac[i++] = value;
value = 0x0;
} else {
unsigned char temp = *p;
if (temp <= '9' && temp >= '0') {
temp -= '0';
} else if (temp <= 'f' && temp >= 'a') {
temp -= 'a';
temp += 10;
} else if (temp <= 'F' && temp >= 'A') {
temp -= 'A';
temp += 10;
} else {
break;
}
value <<= 4;
value |= temp;
}
p ++;
}
mac[i] = value;
return 0;
}
void echo_arp_pkt(struct arppkt *arp, struct arppkt *arp_rt, char *hmac) {
memcpy(arp_rt, arp, sizeof(struct arppkt));
memcpy(arp_rt->eh.h_dest, arp->eh.h_source, ETH_ALEN);
str2mac(arp_rt->eh.h_source, hmac);
arp_rt->eh.h_proto = arp->eh.h_proto;
arp_rt->arp.h_addrlen = 6;
arp_rt->arp.protolen = 4;
arp_rt->arp.oper = htons(2);
str2mac(arp_rt->arp.smac, hmac);
arp_rt->arp.sip = arp->arp.dip;
memcpy(arp_rt->arp.dmac, arp->arp.smac, ETH_ALEN);
arp_rt->arp.dip = arp->arp.sip;
}
void echo_udp_pkt(struct udppkt *udp, struct udppkt *udp_rt) {
memcpy(udp_rt, udp, sizeof(struct udppkt));
memcpy(udp_rt->eh.h_dest, udp->eh.h_source, ETH_ALEN);
memcpy(udp_rt->eh.h_source, udp->eh.h_dest, ETH_ALEN);
udp_rt->ip.saddr = udp->ip.daddr;
udp_rt->ip.daddr = udp->ip.saddr;
udp_rt->udp.source = udp->udp.dest;
udp_rt->udp.dest = udp->udp.source;
}
unsigned short in_cksum(unsigned short *addr, int len)
{
register int nleft = len;
register unsigned short *w = addr;
register int sum = 0;
unsigned short answer = 0;
while (nleft > 1) {
sum += *w++;
nleft -= 2;
}
if (nleft == 1) {
*(u_char *)(&answer) = *(u_char *)w ;
sum += answer;
}
sum = (sum >> 16) + (sum & 0xffff);
sum += (sum >> 16);
answer = ~sum;
return (answer);
}
void echo_icmp_pkt(struct icmppkt *icmp, struct icmppkt *icmp_rt) {
memcpy(icmp_rt, icmp, sizeof(struct icmppkt));
icmp_rt->icmp.type = 0x0; //
icmp_rt->icmp.code = 0x0; //
icmp_rt->icmp.check = 0x0;
icmp_rt->ip.saddr = icmp->ip.daddr;
icmp_rt->ip.daddr = icmp->ip.saddr;
memcpy(icmp_rt->eh.h_dest, icmp->eh.h_source, ETH_ALEN);
memcpy(icmp_rt->eh.h_source, icmp->eh.h_dest, ETH_ALEN);
icmp_rt->icmp.check = in_cksum((unsigned short*)&icmp_rt->icmp, sizeof(struct icmphdr));
}
int main() {
struct ethhdr *eh;
struct pollfd pfd = {0};
struct nm_pkthdr h;
unsigned char *stream = NULL;
struct nm_desc *nmr = nm_open("netmap:eth0", NULL, 0, NULL);
if (nmr == NULL) {
printf("Error openn");
return -1;
}
pfd.fd = nmr->fd;
pfd.events = POLLIN;
while (1) {
int ret = poll(&pfd, 1, -1);
if (ret < 0) continue;
if (pfd.revents & POLLIN) {
stream = nm_nextpkt(nmr, &h);
eh = (struct ethhdr*)stream;
if (ntohs(eh->h_proto) == PROTO_IP) {
struct udppkt *udp = (struct udppkt*)stream;
if (udp->ip.protocol == PROTO_UDP) {
struct in_addr addr;
addr.s_addr = udp->ip.saddr;
int udp_length = ntohs(udp->udp.len);
printf("%s:%d:length:%d, ip_len:%d --> ", inet_ntoa(addr), udp->udp.source,
udp_length, ntohs(udp->ip.tot_len));
udp->body[udp_length-8] = '�';
printf("udp --> %sn", udp->body);
#if 1
struct udppkt udp_rt;
echo_udp_pkt(udp, &udp_rt);
nm_inject(nmr, &udp_rt, sizeof(struct udppkt));
#endif
#if 0
} else if (udp->ip.protocol == PROTO_ICMP) {
struct icmppkt *icmp = (struct icmppkt*)stream;
printf("icmp ---------- --> %d, %xn", icmp->icmp.type, icmp->icmp.check);
if (icmp->icmp.type == 0x08) {
struct icmppkt icmp_rt = {0};
echo_icmp_pkt(icmp, &icmp_rt);
//printf("icmp check %xn", icmp_rt.icmp.check);
nm_inject(nmr, &icmp_rt, sizeof(struct icmppkt));
}
#endif
} else if (udp->ip.protocol == PROTO_IGMP) {
} else {
printf("other ip packet");
}
#if 0
} else if (ntohs(eh->h_proto) == PROTO_ARP) {
struct arppkt *arp = (struct arppkt *)stream;
struct arppkt arp_rt;
if (arp->arp.dip == inet_addr("192.168.2.217")) {
echo_arp_pkt(arp, &arp_rt, "00:50:56:33:1c:ca");
nm_inject(nmr, &arp_rt, sizeof(struct arppkt));
}
#endif
}
}
}
}
最后
以上就是自信仙人掌最近收集整理的关于用户态协议栈-基于netmap的UDP实现UD什么时网络协议栈?netmap的代码实现完整的实现代码的全部内容,更多相关用户态协议栈-基于netmap内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复