文章目录
- 什么是AVOption
- Non-constant option和named constant option
- AVOption的作用
什么是AVOption
AVOption是一个通用的结构体,可用来在任意结构(“对象”)上声明配置选项。其具体定义如下:
// 配置选项结构体
typedef struct AVOption {
const char *name; // 配置选项名
const char *help; // 简短的配置选项说明
int offset; // 1. 如果配置选项是context结构体成员, offset为该成员在context结构体中的偏移值;2. 如果配置选项类型是AV_OPT_TYPE_CONST,offset为0
enum AVOptionType type; // 配置选项类型
union {
int64_t i64;
double dbl;
const char *str;
/* TODO those are unused now */
AVRational q;
} default_val; // 配置选项值,支持多种数据类型
double min; // 配置选项的最小值
double max; // 配置选项的最大值
int flags; // 标志位用来标记配置选型的使用属性
const char *unit; // 配置选项所属的逻辑单元,Non-constant option和named constant option共享相同的unit;该成员可以为NULL
} AVOption;
从AVOption的定义可以看出,一个配置选项除了有name和default_val外,还有其他的属性。
其特点为:
- 支持多种数据类型;整数,浮点数,字符串,分数;
- 支持配置选项值的范围表示;[min, max];
- 支持"对象"成员的可配置;即可将"对象"的成员作为配置选项,通过
offset来记录"对象"成员的偏移;
Non-constant option和named constant option
// 配置选项类型枚举定义
enum AVOptionType{
AV_OPT_TYPE_FLAGS,
AV_OPT_TYPE_INT,
AV_OPT_TYPE_INT64,
AV_OPT_TYPE_DOUBLE,
AV_OPT_TYPE_FLOAT,
AV_OPT_TYPE_STRING,
AV_OPT_TYPE_RATIONAL,
AV_OPT_TYPE_BINARY, ///< offset must point to a pointer immediately followed by an int for the length
AV_OPT_TYPE_DICT,
AV_OPT_TYPE_UINT64,
AV_OPT_TYPE_CONST,
AV_OPT_TYPE_IMAGE_SIZE, ///< offset must point to two consecutive integers
AV_OPT_TYPE_PIXEL_FMT,
AV_OPT_TYPE_SAMPLE_FMT,
AV_OPT_TYPE_VIDEO_RATE, ///< offset must point to AVRational
AV_OPT_TYPE_DURATION,
AV_OPT_TYPE_COLOR,
AV_OPT_TYPE_CHANNEL_LAYOUT,
AV_OPT_TYPE_BOOL,
};
named constant option: 表示AVOptionType为AV_OPT_TYPE_CONST的配置选项;
Non-constant option: 表示AVOptionType不为AV_OPT_TYPE_CONST的其他配置选项;
AVOption的作用
前面介绍AVOption的特点时提到支持"对象"成员的可配置,但并没有详细说明,到底是怎样配置的;下面通过具体的例子来讲解。要讲清楚这个特点,还需要引入另外两个结构体AVClass和AVIOContext,本节中仅对这两个结构体中涉及配置选项的成员进行介绍,其他成员将会忽略。
AVOption、AVClass、AV*Context三种结构体之间的关系
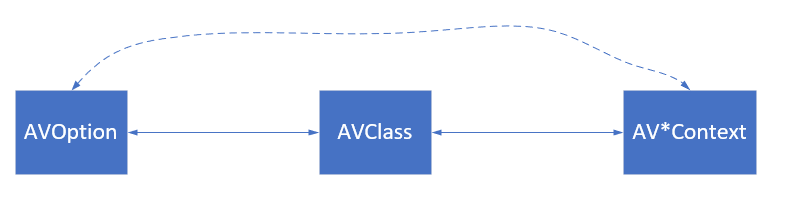
AVClass相当于一个中间媒介,将AVOption和AV*Context联系起来。
typedef struct AVClass {
const char* class_name;
const char* (*item_name)(void* ctx);
const struct AVOption *option; // option指针
int version;
int log_level_offset_offset;
int parent_log_context_offset;
void* (*child_next)(void *obj, void *prev);
const struct AVClass* (*child_class_next)(const struct AVClass *prev);
AVClassCategory category;
AVClassCategory (*get_category)(void* ctx);
int (*query_ranges)(struct AVOptionRanges **, void *obj, const char *key, int flags);
}
typedef struct AVFormatContext {
/**
* A class for logging and @ref avoptions. Set by avformat_alloc_context().
* Exports (de)muxer private options if they exist.
*/
const AVClass *av_class;
...
/**
* Maximum size of the data read from input for determining
* the input container format.
* Demuxing only, set by the caller before avformat_open_input().
*/
int64_t probesize;
...
/**
* avio flags, used to force AVIO_FLAG_DIRECT.
* - encoding: unused
* - decoding: Set by user
*/
int avio_flags;
} AVFormatContext;
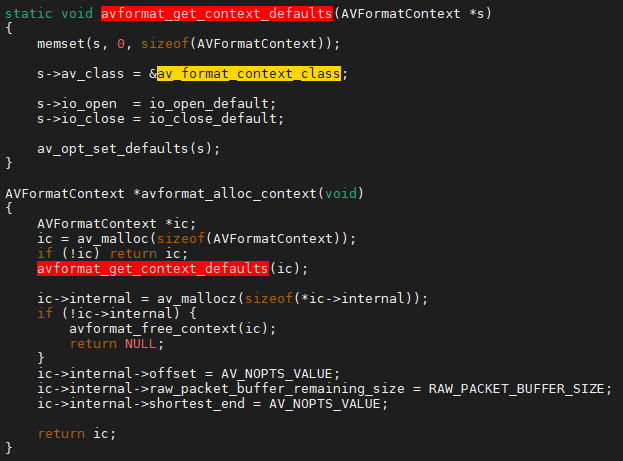
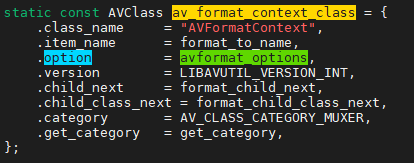
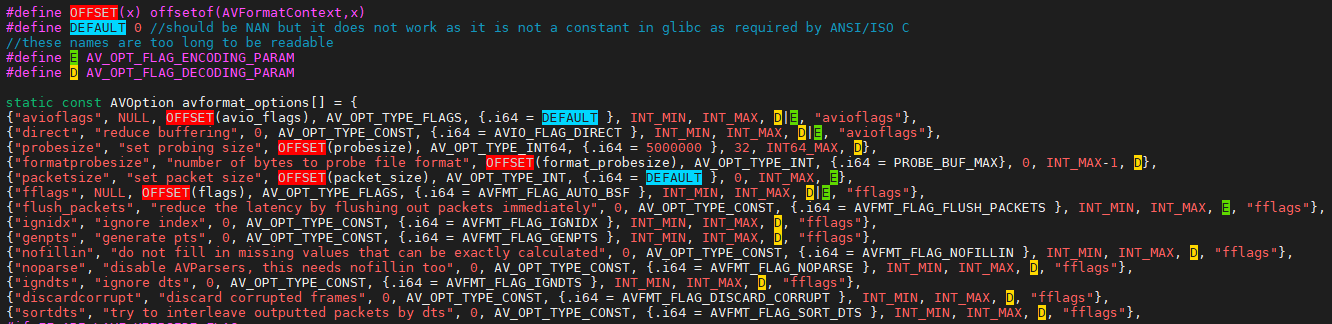
从上图的代码可以看出,AVFormatContext结构体通过av_class成员指针指向av_format_context_class,而av_format_context_class的option成员指针指向avformat_options二维数组,如此,便通过AVClass将AVOption和AV*Context联系起来了。
前文提到的"对象",可以看做是AVFormatContext结构体;AVFormatContext中有一个成员int avio_flags,从目前所掌握的信息可知,AVFormatContext对象的成员avio_flags是可配置的(但具体怎么实现还看不出来,请继续往后看);avioflags配置选项的默认值是DEFALUT(0)。
接下来,再以av_opt_set_default2()函数为例,介绍一下,遍历avformat_options数组以及每个配置项的值的具体设置过程。
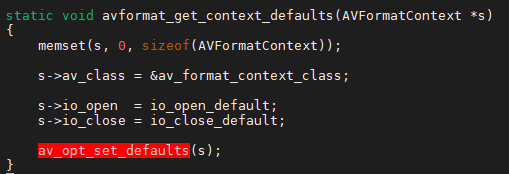
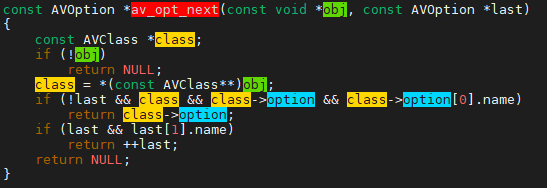
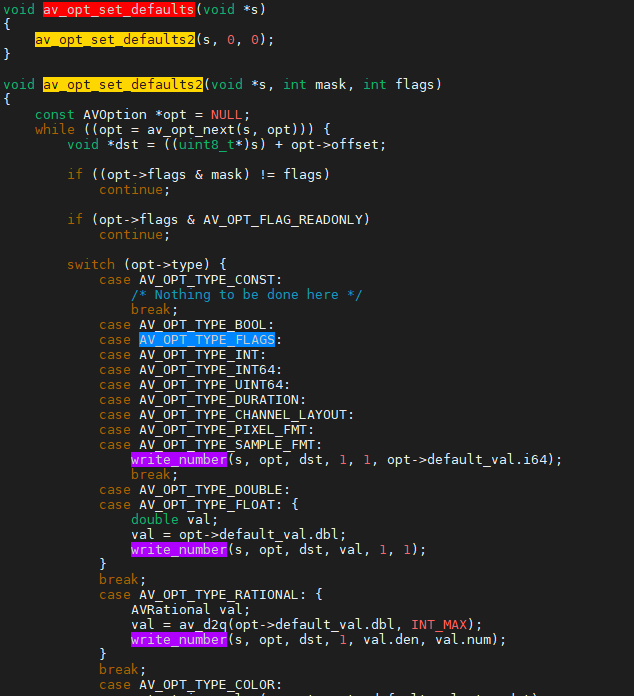
av_opt_next遍历指定"对象"的av_class->option指针,每个opt指向指定"对象"的配置选项,void *dst = ((uint8_t*)s) + opt->offset;获取指定"对象"的配置选项所在的地址,如,dst为AVFormatContext对象的成员avio_flags的地址;然后,执行write_number(s, opt, dst, 1, 1, opt->default_val.i64);将配置选项的值写到AVFormatContext对象的成员avio_flags中。
综上所述,配置选项的值可写入到"对象"中,换句话说就是**"对象"成员可配置**。
最后
以上就是眯眯眼小白菜最近收集整理的关于ffmpeg-AVOption详解什么是AVOptionAVOption的作用的全部内容,更多相关ffmpeg-AVOption详解什么是AVOptionAVOption内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复