%**************************************************************************
% DIGITAL COMMUNICATION SYSTEM
% BPSK MODEL
%**************************************************************************
%IMORTANT VARIABLES USED
%t - Modeled system time
%fm - Main frequency of message signal
%harm - Frequency components of the message signal
%amp - Amplitude of the corresonding harmonic frequency component
%sampling_rate - System sampling rate . Default rate is 20 samples per cycle of maximum freqency component
%range - Range of the time sampling is done . Default range is 2 cycles of minimum frequncy component
%msg - Message signal to be trasnmitted
%minamp - Minimum amplitude that can be used in this model
%n_sample - Number of samples per cycle of the message signal
%fs - Sampling frequency for sampling the message signal
%msamp - Sampled version of the message signale with sampling frequency fs
%no_of_levels - Number of quantization levels
%quantile - Quantile interval
%code - Representation levels
%mq - Quantization output of sampled message signal
%mq1 - Sampled version of quantized sample message signal
%bits - Binary sequence of sampled quantized signal (output of ADC)
%fc - Carrier signal frequency
%nsamp - System Samples per cycle of carrier signal
%ncyc - Number of cycles of carrier signal for one bit interval
%tb - Bit interval
%t_tran - Total transmission time , in order to find diffrence between already existing time variable 't' see Note-1
%mod_sig - BPSK modulated carrier signal
%tran_sig - Siganl after transmission through AWGN channel , so that Awg noise is added with the original transmitted signal
%f_freq - Frequency range used for visualising FFT of the signal
%f_tran - Noise added transmitted signal representation in frequency domain
%f_rece - Received signal after removing noise ,in frequency domain
%dec_data - Binaray data extracted from BPSK modulated carrier signal
%mq_rece - Decoded sampled quantized message signal data calculated from extracted binary sequence
%f_out - Reconstruted signal in frequency domain after filtering
%out - Reconstruted signal from the received signal ,in time domain i.e, output of the receiver
%gain - gain of the amplifier expressed in ratio not in db
%
%ABBREVATIONS
%ADC - Analog to Digital Convertor
% Converts analog signal to digital signal
%AWGN - Anti-White Gaussian Noise
% A channel model with zero mean noise , commonly used channel model .
%DAC - Digital to Analog Convertor
% Converts digital signal to analog signal
%Rx - Receiver
%Tx - Transmitter
%*****************************-TRANSMITTER-********************************
clear all;
clc;
%MESSAGE SIGNAL PARAMETERS
fm=1e3; %Main frequency of message signal
harm=[ 1 0.5 2 1 ]; %Frequency components of the message signal
%In this model the message signal is represented by fourier sine series
amp=[ 1 2 3 1 ]; %Amplitude of the corresonding harmonic frequency component
sampling_rate=1/(20*max(fm*harm)); %System sampling rate . Default rate is 20 samples per cycle of maximum freqency component
range=2/min(fm*harm); %Range of the time sampling is done . Default range is 2 cycles of minimum frequncy component
t=0:sampling_rate:range; %System timing
%MESSAGE SIGNAL
msg=zeros(size(t));
for k=1:length(harm)
msg=msg+amp(k)*sin(2*pi*harm(k)*fm*t);
end
minamp=min(msg); %Minimum amplitude that can be used in this model . Normally ,it need to be kept as a global constant
%But for flexibility of program it is made here as variable depending on message signal value
%SAMPLING
n_sample=5;
fs=n_sample*max(harm*fm); %Sampling ferqency .
msamp=zeros(size(msg));
msamp(1:1/(fs*sampling_rate):length(t))=msg(1:1/(sampling_rate*fs):length(t)); %Sampled output signal
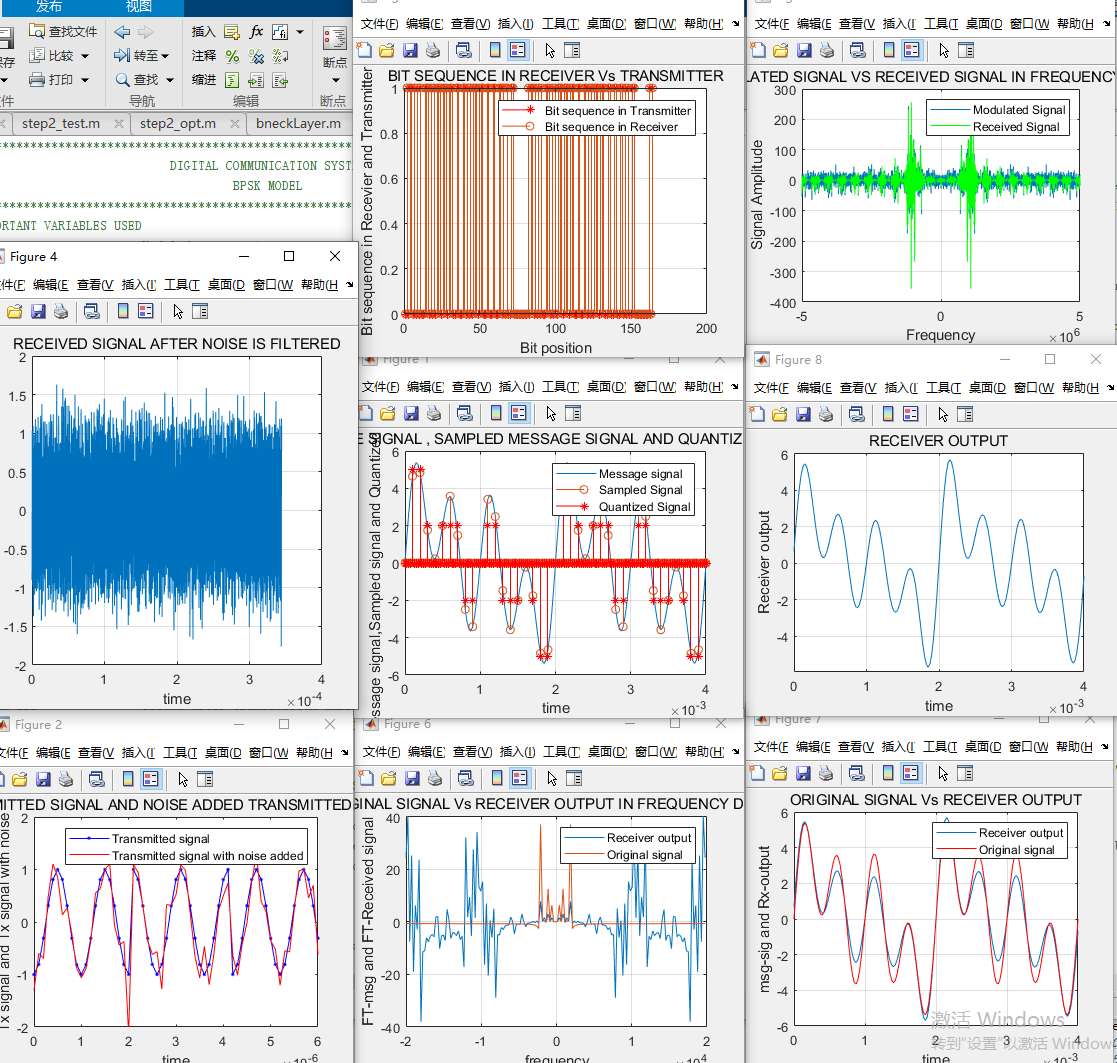
figure(1);plot(t,msg); grid on
hold on
stem(t,msamp);
xlabel('time');ylabel('Message signal,Sampled signal and Quantized signal');
title('MESSAGE SIGNAL , SAMPLED MESSAGE SIGNAL AND QUANTIZED SIGNAL');
legend('Message signal','Sampled Signal','Quantized Signal');
%QUANTIZATION
no_of_levels=4; %Number of quantization levels
quantile=(max(msamp)-min(msamp))/(no_of_levels); %Quantile interval
code=min(msamp):quantile:max(msamp); %Representation levels
mq=zeros(size(msamp));
for k=1:length(code)
values=(( msamp>(code(k)-quantile/2) & msamp<(code(k)+quantile/2)));
mq(values)=round(code(k)); %Quantization output of sampled message signal
end
clear values;
stem(t,mq,'r*');grid on
legend('Message signal','Sampled Signal','Quantized Signal');
%ENCODING
if min(mq)>=0
minamp=0;
end
mq1=mq-round(minamp); %Shifting negative values to postive side for conversion to binary and sampling
%quantized message signal
bits=de2bi(mq1(1:1/(fs*sampling_rate):length(mq)),4,'left-msb')';
bits=bits(:)'; %ADC - Generating binary sequence of sampled quantized signal
figure(5);stem(bits,'*r');hold on;
legend('Bit sequence in Transmitter','Bit sequence in Receiver');
%PASS BAND MODULATION (BPSK)
fc=1e6; %Carrier signal frequency
nsamp=10; %System Samples per cycle of carrier signal
ncyc=2; %Number of cycles of carrier signal for one bit interval
tb=0:1/(nsamp*fc):ncyc/fc; %Bit interval
t_tran=0:1/(nsamp*fc):(ncyc*length(bits))/fc+(length(bits)-1)/(nsamp*fc); %Total transmission time
mod_sig=zeros(size(t_tran));
l=1;
for k=1:length(tb):length(mod_sig)
if(bits(l)==1)
mod_sig(k:k+length(tb)-1)=cos(2*pi*fc*tb); %Phase Modulation of carrier for repesenting binary symbol one
else
mod_sig(k:k+length(tb)-1)=-cos(2*pi*fc*tb); %Phase Modulation of carrier for repesenting binary symbol zero
end
l=l+1;
end
%**********************AWGN-CHANNEL****************************************
tran_sig=awgn(mod_sig,10); %Transmisson of modulated carrier signal through AWGN channel
figure(2);plot(t_tran,mod_sig,'.-b',t_tran,tran_sig,'r');
axis([0 3*ncyc/fc -2 2]);
xlabel('time');ylabel('Tx signal and Tx signal with noise');
title('TRANSMITTED SIGNAL AND NOISE ADDED TRANSMITTED SIGNAL');
legend('Transmitted signal','Transmitted signal with noise added');
%*************************RECEIVER*****************************************
%Filter
f_freq=-(nsamp*fc)/2:(nsamp*fc)/length(t_tran):(nsamp*fc)/2-(nsamp*fc)/length(t_tran); %Frequency range used for
%visualising FFT of the signal
f_tran=fft(tran_sig); %FFT of f
figure(3);plot(f_freq,fftshift(f_tran),f_freq,fftshift(fft(mod_sig)),'g');grid on;
xlabel('Frequency');ylabel('Signal Amplitude');
legend('Modulated Signal','Received Signal');
title('MODULATED SIGNAL VS RECEIVED SIGNAL IN FREQUENCY DOMAIN');
f_rece=zeros(size(f_tran));
fir=(f_freq < -3*fc | f_freq>3*fc);
f_rece(fir)=f_tran(fir); %Filtering noisy signal in
f_rece(~fir)=0.5*f_tran(~fir); %frequnecy domain to remove noise
t_rece=ifft(f_rece); %Noise removed signal
figure(4);plot(t_tran,t_rece);grid on;
xlabel('time');ylabel('Received Signal');
title('RECEIVED SIGNAL AFTER NOISE IS FILTERED');
delete f_freq f_tran f_rece;
clear f_freq f_tran f_rece;
%Demodulation
dec_data=zeros(size(bits));
l=1;
for k=1:length(tb):length(t_tran) %Extracting binary data from carrier using correlation method
a=corrcoef(cos(2*pi*fc*tb),t_rece(k:k+length(tb)-1));
b=mean(real(a(:)));
if b>0.5
dec_data(l)=1;
else
dec_data(l)=0;
end
l=l+1;
end
figure(5);stem(dec_data);grid on;
xlabel('Bit position');ylabel('Bit sequence in Recevier and Transmitter');
title('BIT SEQUENCE IN RECEIVER Vs TRANSMITTER');
legend('Bit sequence in Transmitter','Bit sequence in Receiver');
%DECODING
dec_data=reshape(dec_data,4,length(bits)/4)';
mq_rece=zeros(size(mq));
mq_rece(1:1/(fs*sampling_rate):length(mq))=bi2de(dec_data,'left-msb')'+min(mq); %DAC - Extracting sampled quantized data from decoded binary sequence
%SIGNAL RECONSTRUCTION
f_freq=-1/(2*sampling_rate):1/(sampling_rate*length(t)):1/(2*sampling_rate)-1/(sampling_rate*length(t));
f_rece=fft(mq_rece); %FFT of received extracted sampled quantized signal
f_out=zeros(size(f_rece));
figure(6);plot(f_freq,fftshift(f_rece),f_freq,fftshift((fft(msg))));grid on;
xlabel('frequency');ylabel('FT-msg and FT-Received signal');
title('ORIGINAL SIGNAL Vs RECEIVER OUTPUT IN FREQUENCY DOMAIN');
legend('Receiver output','Original signal');
f_out((f_freq < -17000 | f_freq > 17000))=f_rece((f_freq < -17000 | f_freq > 17000)); %Filtering in frequency domain for reconstruction of signal from sampled
%quantized data
out=ifft(f_out); %Reconstructed output signal
figure(7);plot(t,4*out,t,msg,'r');grid on;
xlabel('time');ylabel('msg-sig and Rx-output');
title('ORIGINAL SIGNAL Vs RECEIVER OUTPUT');
legend('Receiver output','Original signal');
gain=4; %Gain of amplifier (simple ratio not in db)
out=out*gain; %Output after amplification
figure(8);plot(t,out);grid on;
xlabel('time');ylabel('Receiver output');
title('RECEIVER OUTPUT');
%clear all;
clc;
%NOTE
% 1)The progrma contains two time variables t and t_tran
% i)The first time variable(t) represents the continuous
% real time of the modeled system as the system is modeled
% using the deveice (i.e., laptop or computer) which cannot
% process data at infinite resolution
% ii)The second time varible(t_tran) reprsents the total time
% interval needed for the carrier signal to carry all the
% binary data
% 2)The frequency specification mention in this model is not exact
% as the fourier trasformed signals are not shifted to center.
% So , the filtered used in this model seem like highpass
% filter , but as the frequency domain converted signal is not
% centered at the origin ,therefore the filters are lowpass
% filters .
% 3)Filter in this model is done by removing directly the
% unwanted frequency component in frequency domain , which helps
% in understanding the concept of filtreing even though it is
% not practical
最后
以上就是苗条咖啡最近收集整理的关于BPSK调制解调基础程序的全部内容,更多相关BPSK调制解调基础程序内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复