0、说明
GPIO完成对CPU支持GPIO的访问,如拉高,拉低等。本文分析linux下gpio子系统。
1、环境
1.1 硬件环境
- Xilinx ZYNQ开发板
1.2 软件环境
- VM ubuntu 18.04
- windows 10
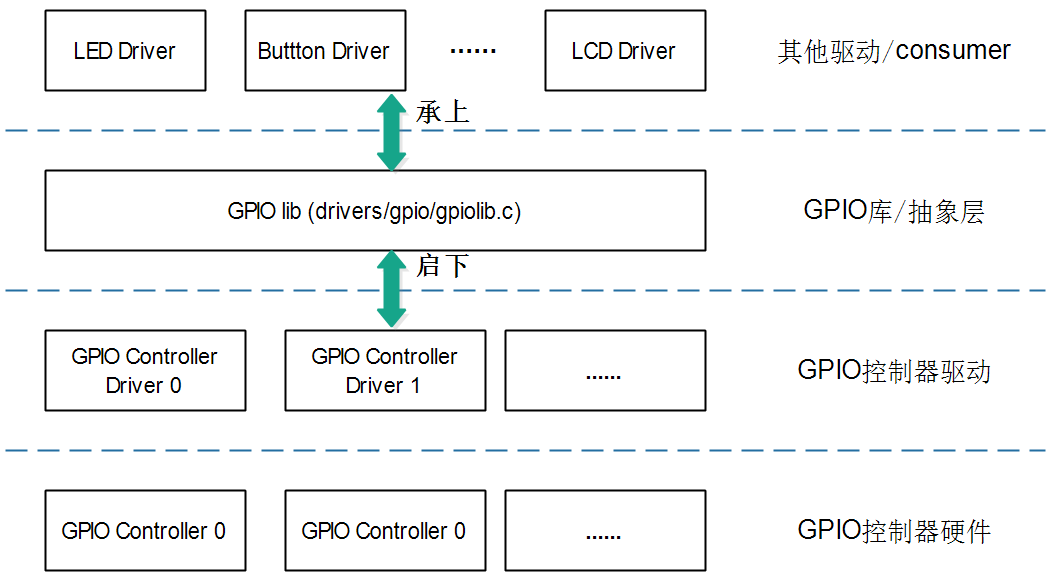
2、GPIO子系统数据结构
2.1 代码路径
drivers/gpio/gpiolib.c
drivers/gpio/gpio-zynq.c2.2 关键结构体
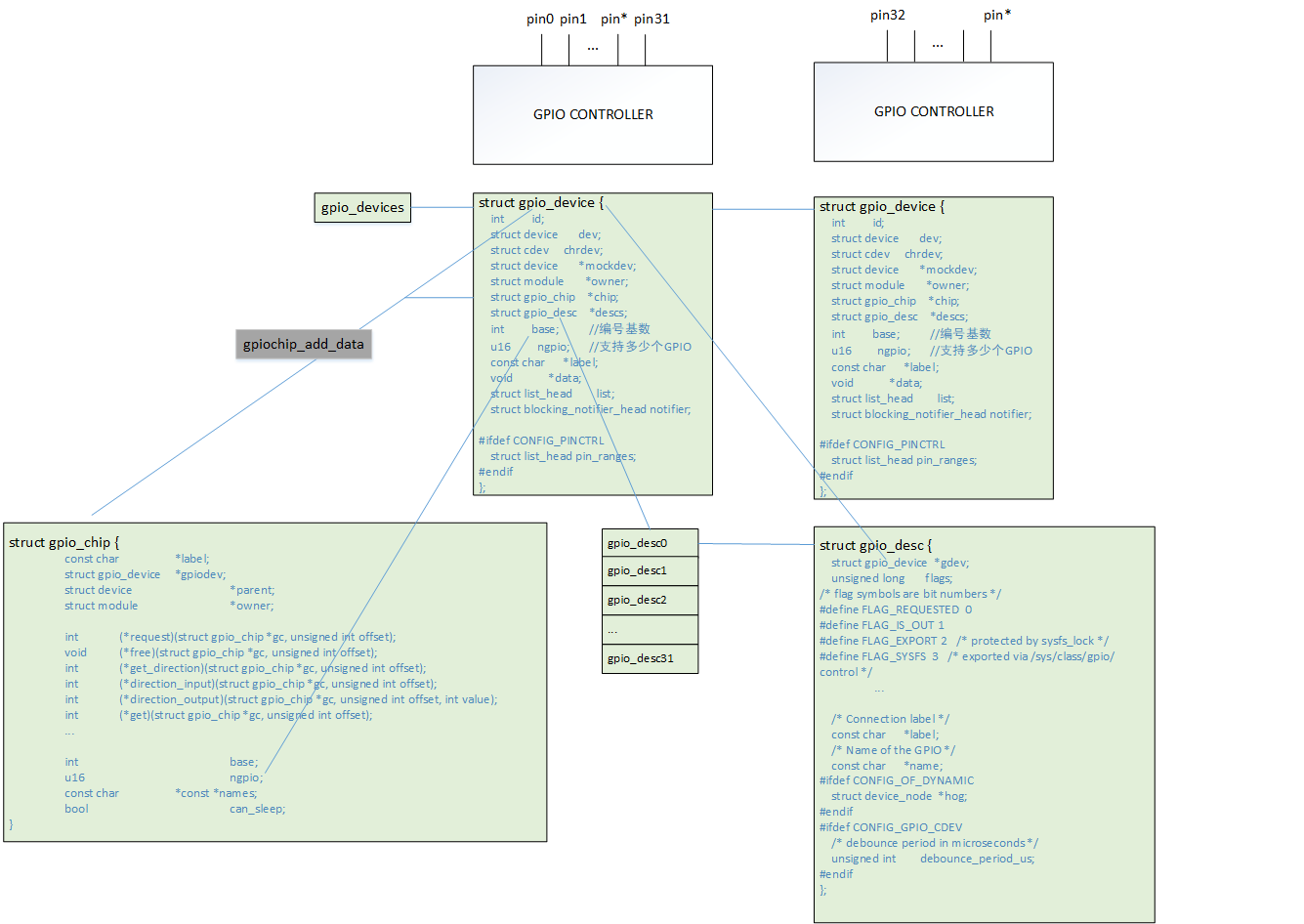
gpio_device
一个GPIO控制器对应一个gpio_device。
struct gpio_device {
int id;
struct device dev;
struct cdev chrdev;
struct device *mockdev;
struct module *owner;
struct gpio_chip *chip;
struct gpio_desc *descs; //数组,支持的所有gpio描述信息
int base; //编号基数
u16 ngpio; //支持多少个GPIO
const char *label;
void *data;
struct list_head list;
struct blocking_notifier_head notifier;
#ifdef CONFIG_PINCTRL
/*
* If CONFIG_PINCTRL is enabled, then gpio controllers can optionally
* describe the actual pin range which they serve in an SoC. This
* information would be used by pinctrl subsystem to configure
* corresponding pins for gpio usage.
*/
struct list_head pin_ranges;
#endif
};gpio_desc
一个gpio对应一个gpio_desc,在使用gpiod_get时返回该GPIO对应的gpio_desc,gpio_desc中存有gpio_device信息,可以找到所属控制器。
struct gpio_desc {
struct gpio_device *gdev;
unsigned long flags;
/* flag symbols are bit numbers */
#define FLAG_REQUESTED 0
#define FLAG_IS_OUT 1
#define FLAG_EXPORT 2 /* protected by sysfs_lock */
#define FLAG_SYSFS 3 /* exported via /sys/class/gpio/control */
#define FLAG_ACTIVE_LOW 6 /* value has active low */
#define FLAG_OPEN_DRAIN 7 /* Gpio is open drain type */
#define FLAG_OPEN_SOURCE 8 /* Gpio is open source type */
#define FLAG_USED_AS_IRQ 9 /* GPIO is connected to an IRQ */
#define FLAG_IRQ_IS_ENABLED 10 /* GPIO is connected to an enabled IRQ */
#define FLAG_IS_HOGGED 11 /* GPIO is hogged */
#define FLAG_TRANSITORY 12 /* GPIO may lose value in sleep or reset */
#define FLAG_PULL_UP 13 /* GPIO has pull up enabled */
#define FLAG_PULL_DOWN 14 /* GPIO has pull down enabled */
#define FLAG_BIAS_DISABLE 15 /* GPIO has pull disabled */
#define FLAG_EDGE_RISING 16 /* GPIO CDEV detects rising edge events */
#define FLAG_EDGE_FALLING 17 /* GPIO CDEV detects falling edge events */
/* Connection label */
const char *label;
/* Name of the GPIO */
const char *name;
#ifdef CONFIG_OF_DYNAMIC
struct device_node *hog;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_GPIO_CDEV
/* debounce period in microseconds */
unsigned int debounce_period_us;
#endif
}; gpio_chip
GPIO控制器驱动中创建gpio_chip,通过gpiochip_add_data向系统注册gpio_device来描述一个GPIO控制器。
struct gpio_chip {
const char *label;
struct gpio_device *gpiodev;
struct device *parent;
struct module *owner;
int (*request)(struct gpio_chip *gc,
unsigned int offset);
void (*free)(struct gpio_chip *gc,
unsigned int offset);
int (*get_direction)(struct gpio_chip *gc,
unsigned int offset);
int (*direction_input)(struct gpio_chip *gc,
unsigned int offset);
int (*direction_output)(struct gpio_chip *gc,
unsigned int offset, int value);
int (*get)(struct gpio_chip *gc,
unsigned int offset);
int (*get_multiple)(struct gpio_chip *gc,
unsigned long *mask,
unsigned long *bits);
void (*set)(struct gpio_chip *gc,
unsigned int offset, int value);
void (*set_multiple)(struct gpio_chip *gc,
unsigned long *mask,
unsigned long *bits);
int (*set_config)(struct gpio_chip *gc,
unsigned int offset,
unsigned long config);
int (*to_irq)(struct gpio_chip *gc,
unsigned int offset);
void (*dbg_show)(struct seq_file *s,
struct gpio_chip *gc);
int (*init_valid_mask)(struct gpio_chip *gc,
unsigned long *valid_mask,
unsigned int ngpios);
int (*add_pin_ranges)(struct gpio_chip *gc);
int base;
u16 ngpio;
const char *const *names;
bool can_sleep;
#if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_GPIO_GENERIC)
unsigned long (*read_reg)(void __iomem *reg);
void (*write_reg)(void __iomem *reg, unsigned long data);
bool be_bits;
void __iomem *reg_dat;
void __iomem *reg_set;
void __iomem *reg_clr;
void __iomem *reg_dir_out;
void __iomem *reg_dir_in;
bool bgpio_dir_unreadable;
int bgpio_bits;
spinlock_t bgpio_lock;
unsigned long bgpio_data;
unsigned long bgpio_dir;
#endif /* CONFIG_GPIO_GENERIC */
#ifdef CONFIG_GPIOLIB_IRQCHIP
/*
* With CONFIG_GPIOLIB_IRQCHIP we get an irqchip inside the gpiolib
* to handle IRQs for most practical cases.
*/
/**
* @irq:
*
* Integrates interrupt chip functionality with the GPIO chip. Can be
* used to handle IRQs for most practical cases.
*/
struct gpio_irq_chip irq;
#endif /* CONFIG_GPIOLIB_IRQCHIP */
/**
* @valid_mask:
*
* If not %NULL holds bitmask of GPIOs which are valid to be used
* from the chip.
*/
unsigned long *valid_mask;
#if defined(CONFIG_OF_GPIO)
/*
* If CONFIG_OF is enabled, then all GPIO controllers described in the
* device tree automatically may have an OF translation
*/
/**
* @of_node:
*
* Pointer to a device tree node representing this GPIO controller.
*/
struct device_node *of_node;
/**
* @of_gpio_n_cells:
*
* Number of cells used to form the GPIO specifier.
*/
unsigned int of_gpio_n_cells;
/**
* @of_xlate:
*
* Callback to translate a device tree GPIO specifier into a chip-
* relative GPIO number and flags.
*/
int (*of_xlate)(struct gpio_chip *gc,
const struct of_phandle_args *gpiospec, u32 *flags);
#endif /* CONFIG_OF_GPIO */
};of_phandle_args
2.3 关键API
gpiod_get
led_gpio = gpiod_get(&pdev->dev, "led", 0);
struct gpio_desc *__must_check gpiod_get(struct device *dev, const char *con_id, enum gpiod_flags flags)
gpiod_get_index(dev, "led", 0, 0);
desc = of_find_gpio(dev, "led", 0, &lookupflags);
of_get_named_gpiod_flags(dev->of_node, led-gpios, 0, &of_flags);
of_parse_phandle_with_args_map(np, led-gpios, "gpio", 0, &gpiospec);
__of_parse_phandle_with_args(np, led-gpios, gpio-cells, -1, 0, out_args);
chip = of_find_gpiochip_by_xlate(&gpiospec);
desc = of_xlate_and_get_gpiod_flags(chip, &gpiospec, flags);gpio_request
gpiod_set_value
gpiod_set_value(led_gpio_desc, 0);
gpiod_set_value(struct gpio_desc *desc, int value)
gpiod_set_value_nocheck(desc, value);
if (test_bit(FLAG_ACTIVE_LOW, &desc->flags))
value = !value;
gpiod_set_raw_value_commit(desc, value);
gc = desc->gdev->chip;3、GPIO子系统
3.1 设备树中的描述
gpio0: gpio@e000a000 {
compatible = "xlnx,zynq-gpio-1.0";
#gpio-cells = <2>;
clocks = <&clkc 42>;
gpio-controller;
interrupt-controller;
#interrupt-cells = <2>;
interrupt-parent = <&intc>;
interrupts = <0 20 4>;
reg = <0xe000a000 0x1000>;
};3.2 GPIO控制器驱动
3.2.1 GPIO控制器驱动主要任务
如下分析,gpio控制器驱动中主要完成:
- 匹配设备树与驱动中的私有数据
- 获取设备树中的io资源与中断资源
- 初始化配置gpio_chip中的函数
- 设置gpio_chip中的irq资源
- gpiochip_add_data完成gpio注册到内核中
/**
* zynq_gpio_probe - Initialization method for a zynq_gpio device
* @pdev: platform device instance
*
* This function allocates memory resources for the gpio device and registers
* all the banks of the device. It will also set up interrupts for the gpio
* pins.
* Note: Interrupts are disabled for all the banks during initialization.
*
* Return: 0 on success, negative error otherwise.
*/
static int zynq_gpio_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
int ret, bank_num;
struct zynq_gpio *gpio;
struct gpio_chip *chip;
struct gpio_irq_chip *girq;
const struct of_device_id *match;
//分配zynq_gpio,同时分配了gpio_chip
gpio = devm_kzalloc(&pdev->dev, sizeof(*gpio), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!gpio)
return -ENOMEM;
//通过设备树中的配置匹配zynq_gpio_of_match并获取对应的私有数据
match = of_match_node(zynq_gpio_of_match, pdev->dev.of_node);
if (!match) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "of_match_node() failedn");
return -EINVAL;
}
gpio->p_data = match->data;
platform_set_drvdata(pdev, gpio);
//从设备树获取IORESOURCE_MEM资源,即reg属性中的GPIO寄存器基址
gpio->base_addr = devm_platform_ioremap_resource(pdev, 0);
if (IS_ERR(gpio->base_addr))
return PTR_ERR(gpio->base_addr);
//从设备树获取GPIO IRQ资源,记录硬件中断号
gpio->irq = platform_get_irq(pdev, 0);
if (gpio->irq < 0)
return gpio->irq;
//设置gpio_chip的操作函数等,在get/set/request等时调用到chip中函数
/* configure the gpio chip */
chip = &gpio->chip;
chip->label = gpio->p_data->label; //label = "zynq_gpio"
chip->owner = THIS_MODULE;
chip->parent = &pdev->dev;
chip->get = zynq_gpio_get_value;
chip->set = zynq_gpio_set_value;
chip->request = zynq_gpio_request;
chip->free = zynq_gpio_free;
chip->direction_input = zynq_gpio_dir_in;
chip->direction_output = zynq_gpio_dir_out;
chip->get_direction = zynq_gpio_get_direction;
//设置gpio_chip的编号基址
chip->base = of_alias_get_id(pdev->dev.of_node, "gpio");
//支持的个数 118个
chip->ngpio = gpio->p_data->ngpio;
/* Retrieve GPIO clock */
gpio->clk = devm_clk_get(&pdev->dev, NULL);
if (IS_ERR(gpio->clk))
return dev_err_probe(&pdev->dev, PTR_ERR(gpio->clk), "input clock not found.n");
ret = clk_prepare_enable(gpio->clk);
if (ret) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "Unable to enable clock.n");
return ret;
}
spin_lock_init(&gpio->dirlock);
pm_runtime_set_active(&pdev->dev);
pm_runtime_enable(&pdev->dev);
ret = pm_runtime_resume_and_get(&pdev->dev);
if (ret < 0)
goto err_pm_dis;
/* disable interrupts for all banks */
for (bank_num = 0; bank_num < gpio->p_data->max_bank; bank_num++) {
writel_relaxed(ZYNQ_GPIO_IXR_DISABLE_ALL, gpio->base_addr +
ZYNQ_GPIO_INTDIS_OFFSET(bank_num));
if (gpio->p_data->quirks & GPIO_QUIRK_VERSAL)
bank_num = bank_num + VERSAL_UNUSED_BANKS;
}
//设置中断资源,在中断子系统中,需要gpio子系统提供中断handle函数
/* Set up the GPIO irqchip */
girq = &chip->irq;
girq->chip = &zynq_gpio_edge_irqchip; //提供irq_chip相关中断预处理函数
girq->parent_handler = zynq_gpio_irqhandler;//父级handle
girq->num_parents = 1;
girq->parents = devm_kcalloc(&pdev->dev, 1,
sizeof(*girq->parents),
GFP_KERNEL);
if (!girq->parents) {
ret = -ENOMEM;
goto err_pm_put;
}
girq->parents[0] = gpio->irq;
girq->default_type = IRQ_TYPE_NONE;
girq->handler = handle_level_irq;
//注册gpio_chip,将在core层产生gpio_device
ret = gpiochip_add_data(chip, gpio);
if (ret) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "Failed to add gpio chipn");
goto err_pm_put;
}
irq_set_status_flags(gpio->irq, IRQ_DISABLE_UNLAZY);
device_init_wakeup(&pdev->dev, 1);
pm_runtime_put(&pdev->dev);
return 0;
err_pm_put:
pm_runtime_put(&pdev->dev);
err_pm_dis:
pm_runtime_disable(&pdev->dev);
clk_disable_unprepare(gpio->clk);
return ret;
}3.2.2 gpiochip_add_data函数分析
总结
结构体关系
一个GPIO控制器,对应一个gpio_chip结构体在驱动中实现其内部函数的配置,最终通过gpiochip_add_data注册进内核,内核同时生成gpio_device结构体。所有gpio_device被放置在gpio_devices全局链表中。
最后
以上就是结实水池最近收集整理的关于linux GPIO子系统0、说明1、环境2、GPIO子系统数据结构3、GPIO子系统总结的全部内容,更多相关linux内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复