JavaSE_day03【流程控制语句】
- 今日内容
- 学习目标
- 第三章 流程控制
- 3.1 顺序结构
- 3.2 输入语句
- 语法案例演示1:
- 语法案例演示2:next()与nextLine()
- 3.3 分支结构:if语句第一种格式
- 语法案例演示1:
- 语法案例演示2
- 3.4 分支结构:if语句第二种格式
- 语法案例演示1:
- 语法案例演示2:if语句和三元运算符的互换
- 练习:求出最大值
- 3.5 分支结构:if语句第三种格式
- 语法案例演示1:
- 语法案例演示2:
- 3.6 分支结构:if..else嵌套
- 语法案例演示1:
- 语法案例演示2:
- 3.7 分支结构:switch选择结构
- 语法案例演示1:
- 语法案例演示2:case的穿透性
- 常见错误实现1:
- 常见错误实现2:
- 3.8 循环结构:while循环
- 需求:打印10次的HelloWorld
- 语法演示案例1:求1加到100的和
- 3.9 循环结构:do...while循环
- 语法演示案例2:输入密码和确认密码,比较是否一致
- 练习:猜数
- 3.10 循环语句:for循环
- 语法演示案例3:求出1-100之间偶数和
- 3.11 循环语句的区别
- 3.12 控制语句
- 3.12.1 break
- 语法案例演示1:判断某个数是否是素数
- 语法案例演示2:统计正数、负数个数
- 语法案例演示3:break同时存在switch和循环中
- 3.12.2 continue
- 练习:打印1-100之间的整数,跳过7的倍数和7结尾的数
- 3.13 嵌套循环
- 语法案例演示1:打印5行5列矩形
- 语法案例演示2:打印5行直角三角形
- 练习1:
- 练习2:
今日内容
- if else判断语句
- switch选择语句
- for循环语句
- while循环语句
- do…while循环语句
- break
- continue
学习目标
-
掌握键盘输入各种数据类型的值
-
理解if语句的格式和执行流程
-
理解if…else语句的格式和执行流程
-
理解if…else if语句的格式和执行流程
-
理解switch选择语句的格式和执行流程
-
掌握switch选择语句接收的数据类型
-
理解case的穿透性
-
掌握break在switch中的使用
-
掌握default在switch中的使用
-
理解while语句的格式和执行流程
-
了解do…while语句的格式和执行流程
-
理解for语句的格式和执行流程
-
了解跳出语句break,continue的意义
-
理解死循环的执行流程
-
理解循环嵌套的执行流程
第三章 流程控制
不论哪一种编程语言,都会提供两种基本的流程控制结构:分支结构和循环结构。其中分支结构用于实现根据条件来选择性地执行某段代码,循环结构则用于实现根据循环条件重复执行某段代码。
3.1 顺序结构
任何编程语言中最常见的程序结构就是顺序结构。顺序结构就是程序从上到下逐行地执行,中间没有任何判断和跳转。如果main方法的多行代码之间没有任何流程控制,则程序总是从上向下依次执行,排在前面的代码先执行,排在后面的代码后执行。
public static void main(String[] args){
//顺序执行,根据编写的顺序,从上到下运行
System.out.println(1);
System.out.println(2);
System.out.println(3);
}
3.2 输入语句
键盘输入代码的三个步骤:
1、准备Scanner类型的变量
2、提示输入xx
3、接收输入内容
示例代码:
//1、准备Scanner类型的变量
//Scanner是一个引用数据类型,它的全名称是java.util.Scanner
//input就是一个引用数据类型的变量了,赋给它的值是一个对象
java.util.Scanner input = new java.util.Scanner(System.in);//System.in默认代表键盘输入
//2、提示输入xx
System.out.print("请输入一个整数:");
//3、接收输入内容
int num = input.nextInt();
//列出各种数据类型的输入
int num = input.nextInt();
long bigNum = input.nextLong();
double d = input.nextDouble();
boolean b = input.nextBoolean();
String s = input.next();
char c = input.next().charAt(0);//先按照字符串接收,然后再取字符串的第一个字符(下标为0)
语法案例演示1:
从键盘输入个人信息
class Day03_Test02_Input{
public static void main(String[] args){
//这里变量取什么名,下面就用什么.
//例如:这里取名input,下面就用input.
java.util.Scanner input = new java.util.Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入姓名:");
String name = input.next();
System.out.print("请输入年龄:");
int age = input.nextInt();
System.out.print("请输入性别:");
//input.next()得到字符串,不管你输入几个字符,
//.charAt(0):从字符串中取出一个字符,(0)表示取第一个字符,(1)表示取第二个字符
//charAt(index):也是一个方法,从第二个单词开始首字母大写,所以A是大写
char gender = input.next().charAt(0);
System.out.print("请输入体重:");
double weight = input.nextDouble();
System.out.print("请输入是否已婚(true/false):");
boolean isMarry = input.nextBoolean();
System.out.println("姓名:" + name);
System.out.println("年龄:" + age);
System.out.println("性别:" + gender);
System.out.println("体重:" + weight);
System.out.println("婚否:" + (isMarry?"是":"否"));
}
}
语法案例演示2:next()与nextLine()
/*
next()方法:
遇到空格等空白符,就认为输入结束
nextLine()方法:
遇到回车换行,就认为输入结束
如果你在键盘输入过程中,遇到java.util.InputMismatchException,
说明你输入的数据类型与接收数据的变量的类型不匹配
*/
class Day03_Test04_Input2{
public static void main(String[] args){
java.util.Scanner input = new java.util.Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入姓名:");
//String name = input.next();//张 三 只能接收张,后面的空格和三无法接收,被下面的输入接收
String name = input.nextLine();
System.out.println("name = " + name);
System.out.print("请输入年龄:");
int age = input.nextInt(); //23回车换行 这里只接收23,回车换行被下面的输入接收
input.nextLine();//读取23后面的回车换行,但是这个不需要接收,只有下面一个输入是nextLine()情况下才需要这样,如果下面的输入是next()或者是nextInt(),nextDouble()等就不需要这么干
System.out.println("age = " + age);
System.out.print("请输入电话号码:");
String tel = input.nextLine();
System.out.println("tel = " + tel);
}
}
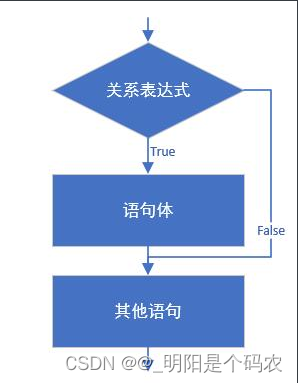
3.3 分支结构:if语句第一种格式
- if语句第一种格式: if
if(条件表达式){
语句体;
}
-
执行流程
-
首先判断条件表达式看其结果是true还是false
-
如果是true就执行语句体
-
如果是false就不执行语句体
-
语法案例演示1:
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.println("开始");
// 定义两个变量
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
//变量使用if判断
if (a == b){
System.out.println("a等于b");
}
int c = 10;
if(a == c){
System.out.println("a等于c");
}
System.out.println("结束");
}
语法案例演示2
案例:从键盘输入年份,请输出该年的2月份的总天数。闰年2月份29天,平年28天。
闰年:
(1)能被4整除,不能被100整除
(2)能被400整除
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
java.util.Scanner input = new java.util.Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入年份:");
int year = input.nextInt();
int days = 28;
if(year%4==0 && year%100!=0 || year%400==0){
days++;
}
System.out.println(year + "年的2月份共" + days + "天");
input.close();
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
java.util.Scanner input = new java.util.Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入年份:");
int year = input.nextInt();
int days = 28;
if(year%4==0 && year%100!=0 || year%400==0)
days++;//当语句块只有一句时,可以省略{},但是建议还是保留比较靠谱
System.out.println(year + "年的2月份共" + days + "天");
input.close();
}
}
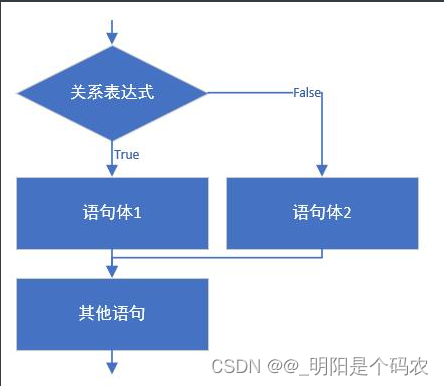
3.4 分支结构:if语句第二种格式
- if语句第二种格式: if…else
if(关系表达式) {
语句体1;
}else {
语句体2;
}
-
执行流程
-
首先判断关系表达式看其结果是true还是false
-
如果是true就执行语句体1
-
如果是false就执行语句体2
-
语法案例演示1:
public static void main(String[] args){
// 判断给定的数据是奇数还是偶数
// 定义变量
int a = 1;
if(a % 2 == 0) {
System.out.println("a是偶数");
} else{
System.out.println("a是奇数");
}
System.out.println("结束");
}
语法案例演示2:if语句和三元运算符的互换
在某些简单的应用中,if语句是可以和三元运算符互换使用的。
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
//定义变量,保存a和b的较大值
int max;
if(a > b) {
max = a;
} else {
max = b;
}
//可以上述功能改写为三元运算符形式
max = a > b ? a : b;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
//定义变量,保存a和b的较大值
int max;
if(a > b)
max = a;//当语句块只有一个语句时,可以省略{},但是不建议省略{}
else
max = b;
}
练习:求出最大值
从键盘输入三个数,求出最大值,用单分支if和双分支if…else来计算
class Day03_Test08_MaxValueExer{
public static void main(String[] args){
java.util.Scanner input = new java.util.Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入第1个整数:");
int a = input.nextInt();
System.out.print("请输入第2个整数:");
int b = input.nextInt();
System.out.print("请输入第3个整数:");
int c = input.nextInt();
/*
int max;//存储三个数中的最大值
if(a > b){
max = a;
}else{
max = b;
}
if(c > max){
max = c;
}
*/
int max = a>b ? a : b;
max = max>c ? max : c;
System.out.println(a+","+b+","+c+"中最大的是:"+ max);
}
}
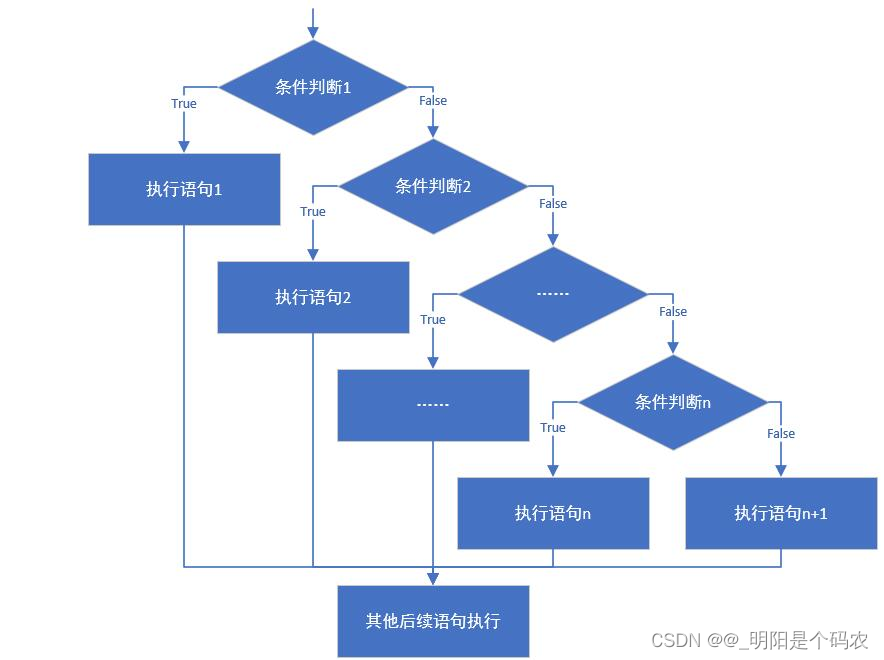
3.5 分支结构:if语句第三种格式
- if语句第三种格式: if…else if …else
if (判断条件1) {
执行语句1;
} else if (判断条件2) {
执行语句2;
}
...
}else if (判断条件n) {
执行语句n;
} else {
执行语句n+1;
}
-
执行流程
-
首先判断关系表达式1看其结果是true还是false
-
如果是true就执行语句体1,然后结束当前多分支
-
如果是false就继续判断关系表达式2看其结果是true还是false
-
如果是true就执行语句体2,然后结束当前多分支
-
如果是false就继续判断关系表达式…看其结果是true还是false
-
…
-
如果没有任何关系表达式为true,就执行语句体n+1,然后结束当前多分支。
-
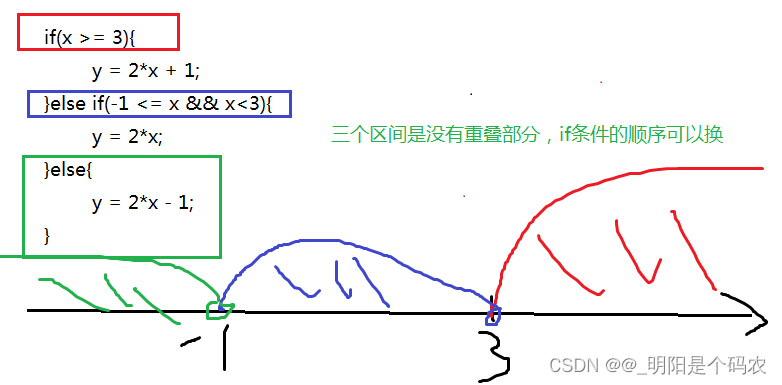
语法案例演示1:
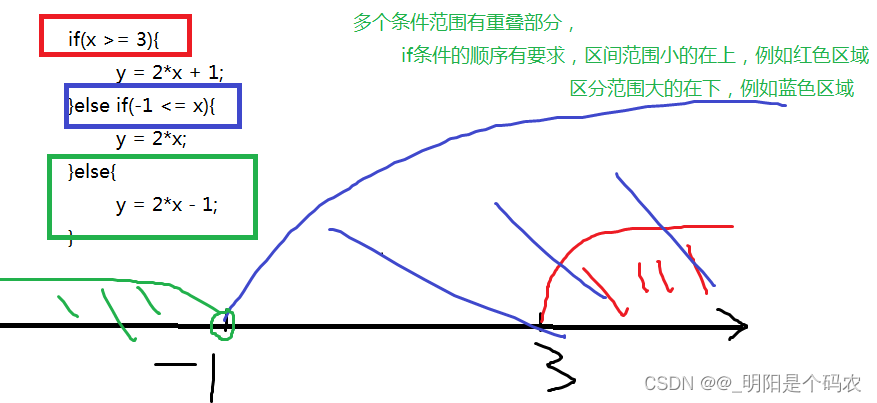
计算如下函数:x和y的关系满足如下:
(1)x>=3; y = 2x + 1;
(2)-1<=x<3; y = 2x;
(3)x<-1; y = 2x – 1;
从键盘输入x的值,计算出y的值并输出。
public static void main(String[] args) {
java.util.Scanner input = new java.util.Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入x的值:");
int x = input.nextInt();
int y;
if (x>= 3) {
y = 2 * x + 1;
} else if (x >= -1 && x < 3) {
y = 2 * x;
} else {
y = 2 * x - 1;
}
System.out.println("y的值是:"+y);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
java.util.Scanner input = new java.util.Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入x的值:");
int x = input.nextInt();
int y;
if (x>= 3) {
y = 2 * x + 1;
} else if (x >= -1) {
y = 2 * x;
} else {
y = 2 * x - 1;
}
System.out.println("y的值是:"+y);
}
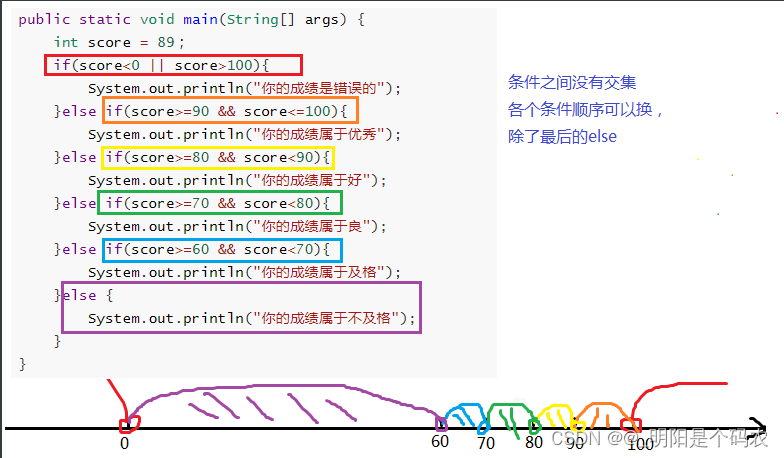
语法案例演示2:
- 通过指定考试成绩,判断学生等级
- 90-100 优秀
- 80-89 好
- 70-79 良
- 60-69 及格
- 60以下 不及格
public static void main(String[] args) {
int score = 89;
if(score<0 || score>100){
System.out.println("你的成绩是错误的");
}else if(score>=90 && score<=100){
System.out.println("你的成绩属于优秀");
}else if(score>=80 && score<90){
System.out.println("你的成绩属于好");
}else if(score>=70 && score<80){
System.out.println("你的成绩属于良");
}else if(score>=60 && score<70){
System.out.println("你的成绩属于及格");
}else {
System.out.println("你的成绩属于不及格");
}
}
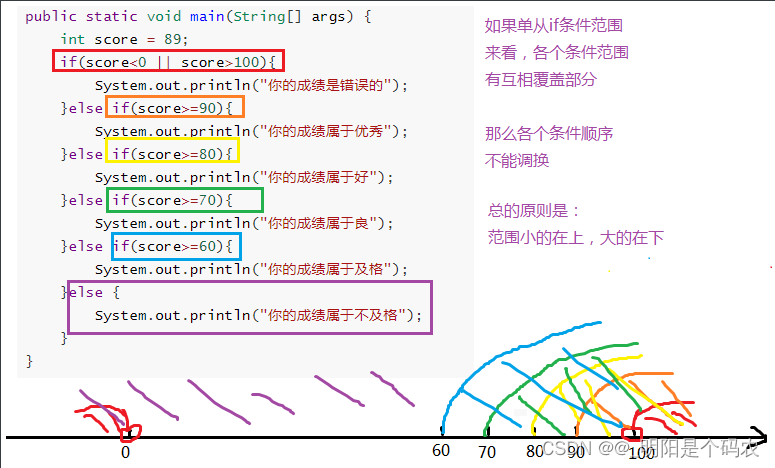
public static void main(String[] args) {
int score = 89;
if(score<0 || score>100){
System.out.println("你的成绩是错误的");
}else if(score>=90){
System.out.println("你的成绩属于优秀");
}else if(score>=80){
System.out.println("你的成绩属于好");
}else if(score>=70){
System.out.println("你的成绩属于良");
}else if(score>=60){
System.out.println("你的成绩属于及格");
}else {
System.out.println("你的成绩属于不及格");
}
}
3.6 分支结构:if…else嵌套
在if的语句块中,或者是在else语句块中,
又包含了另外一个条件判断(可以是单分支、双分支、多分支)
执行的特点:
(1)如果是嵌套在if语句块中的
只有当外部的if条件满足,才会去判断内部的条件
(2)如果是嵌套在else语句块中的
只有当外部的if条件不满足,进入else后,才会去判断内部的条件
语法案例演示1:
public static void main(String[] args) {
int score = 89;
if(score<0 || score>100){
System.out.println("你的成绩是错误的");
}else{
if(score>=90){
System.out.println("你的成绩属于优秀");
}else if(score>=80){
System.out.println("你的成绩属于好");
}else if(score>=70){
System.out.println("你的成绩属于良");
}else if(score>=60){
System.out.println("你的成绩属于及格");
}else {
System.out.println("你的成绩属于不及格");
}
}
}
//省略{}的情况,else中嵌套了一个完整的多分支结构,也算是一个语句,称为复合语句,所以也可以省略{}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int score = 89;
if(score<0 || score>100)
System.out.println("你的成绩是错误的");
else
if(score>=90){
System.out.println("你的成绩属于优秀");
}else if(score>=80){
System.out.println("你的成绩属于好");
}else if(score>=70){
System.out.println("你的成绩属于良");
}else if(score>=60){
System.out.println("你的成绩属于及格");
}else {
System.out.println("你的成绩属于不及格");
}
}
语法案例演示2:
从键盘输入一个年份,和月份,输出该年份该月的总天数
要求:年份为正数,月份1-12
public static void main(String[] args){
//从键盘输入一个年份,和月份
java.util.Scanner input = new java.util.Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("年份:");
int year = input.nextInt();
System.out.print("月份:");
int month = input.nextInt();
if(year>0){
if(month>=1 && month<=12){
//合法的情况
int days;
if(month==2){
if(year%4==0 && year%100!=0 || year%400==0){
days = 29;
}else{
days = 28;
}
}else if(month==4 || month==6 || month==9 || month==11){
days = 30;
}else{
days = 31;
}
System.out.println(year+"年" + month + "月有" + days +"天");
}else{
System.out.println("月份输入不合法");
}
}else{
System.out.println("年份输入不合法");
}
}
3.7 分支结构:switch选择结构
语法格式:
switch(表达式){
case 常量值1:
语句块1;
【break;】
case 常量值2:
语句块2;
【break;】
。。。
【default:
语句块n+1;
【break;】
】
}
执行过程:
(1)入口
①当switch(表达式)的值与case后面的某个常量值匹配,就从这个case进入;
②当switch(表达式)的值与case后面的所有常量值都不匹配,寻找default分支进入;不管default在哪里
(2)一旦从“入口”进入switch,就会顺序往下执行,直到遇到“出口”,即可能发生贯穿
(3)出口
①自然出口:遇到了switch的结束}
②中断出口:遇到了break等
注意:
(1)switch(表达式)的值的类型,只能是:4种基本数据类型(byte,short,int,char),两种引用数据类型(JDK1.5之后枚举、JDK1.7之后String)
(2)case后面必须是常量值,而且不能重复
语法案例演示1:
public class SwitchDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//定义指定的星期
int weekday = 5;
//switch语句实现选择
switch(weekday) {
case 1:
System.out.println("星期一");
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("星期二");
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("星期三");
break;
case 4:
System.out.println("星期四");
break;
case 5:
System.out.println("星期五");
break;
case 6:
System.out.println("星期六");
break;
case 7:
System.out.println("星期日");
break;
default:
System.out.println("你的数字有误");
break;
}
}
}
语法案例演示2:case的穿透性
在switch语句中,如果case的后面不写break,将出现穿透现象,也就是一旦匹配成功,不会在判断下一个case的值,直接向后运行,直到遇到break或者整个switch语句结束,switch语句执行终止。
练习:根据指定的月份输出对应季节(if语句)
/*
* 需求:定义一个月份,输出该月份对应的季节。
* 一年有四季
* 3,4,5 春季
* 6,7,8 夏季
* 9,10,11 秋季
* 12,1,2 冬季
*
* 分析:
* A:指定一个月份
* B:判断该月份是几月,根据月份输出对应的季节
* if
* switch
*/
public class SwitchTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//指定一个月份
int month = 5;
/*
if (month == 1) {
System.out.println("冬季");
} else if (month == 2) {
System.out.println("冬季");
} else if (month == 3) {
System.out.println("春季");
} else if (month == 4) {
System.out.println("春季");
} else if (month == 5) {
System.out.println("春季");
} else if (month == 6) {
System.out.println("夏季");
} else if (month == 7) {
System.out.println("夏季");
} else if (month == 8) {
System.out.println("夏季");
} else if (month == 9) {
System.out.println("秋季");
} else if (month == 10) {
System.out.println("秋季");
} else if (month == 11) {
System.out.println("秋季");
} else if (mouth == 12) {
System.out.println("冬季");
} else {
System.out.println("你输入的月份有误");
}
*/
// 改进版
if ((month == 1) || (month == 2) || (month == 12)) {
System.out.println("冬季");
} else if ((month == 3) || (month == 4) || (month == 5)) {
System.out.println("春季");
} else if ((month == 6) || (month == 7) || (month == 8)) {
System.out.println("夏季");
} else if ((month == 9) || (month == 10) || (month == 11)) {
System.out.println("秋季");
} else {
System.out.println("你输入的月份有误");
}
}
}
练习:根据指定的月份输出对应季节(switch语句)
/*
* 需求:指定一个月份,输出该月份对应的季节。
* 一年有四季
* 3,4,5 春季
* 6,7,8 夏季
* 9,10,11 秋季
* 12,1,2 冬季
*
* 分析:
* A:指定一个月份
* B:判断该月份是几月,根据月份输出对应的季节
* if
* switch
*/
public class SwitchTest02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//指定一个月份
int month = 5;
/*
switch(month) {
case 1:
System.out.println("冬季");
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("冬季");
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("春季");
break;
case 4:
System.out.println("春季");
break;
case 5:
System.out.println("春季");
break;
case 6:
System.out.println("夏季");
break;
case 7:
System.out.println("夏季");
break;
case 8:
System.out.println("夏季");
break;
case 9:
System.out.println("秋季");
break;
case 10:
System.out.println("秋季");
break;
case 11:
System.out.println("秋季");
break;
case 12:
System.out.println("冬季");
break;
default:
System.out.println("你输入的月份有误");
break;
}
*/
// 改进版
switch(month) {
case 1:
case 2:
case 12:
System.out.println("冬季");
break;
case 3:
case 4:
case 5:
System.out.println("春季");
break;
case 6:
case 7:
case 8:
System.out.println("夏季");
break;
case 9:
case 10:
case 11:
System.out.println("秋季");
break;
default:
System.out.println("你输入的月份有误");
break;
}
}
}
常见错误实现1:
switch(month){
case 3|4|5://3|4|5 用了位运算符,11 | 100 | 101结果是 111是7
System.out.println("春季");
break;
case 6|7|8://6|7|8用了位运算符,110 | 111 | 1000结果是1111是15
System.out.println("夏季");
break;
case 9|10|11://9|10|11用了位运算符,1001 | 1010 | 1011结果是1011是11
System.out.println("秋季");
break;
case 12|1|2://12|1|2 用了位运算符,1100 | 1 | 10 结果是1111,是15
System.out.println("冬季");
break;
default:
System.out.println("输入有误");
}
常见错误实现2:
//编译不通过
switch(month){
case 3,4,5:
System.out.println("春季");
break;
case 6,7,8:
System.out.println("夏季");
break;
case 9,10,11:
System.out.println("秋季");
break;
case 12,1,2:
System.out.println("冬季");
break;
default:
System.out.println("输入有误");
}
Switch 表达式也是作为预览语言功能的第一个语言改动被引入Java12 中,开始支持如下写法:
switch(month) {
case 3,4,5 -> System.out.println("春季");
case 6,7,8 -> System.out.println("夏季");
case 9,10,11 -> System.out.println("秋季");
case 12,1,2 -> System.out.println("冬季");
default->System.out.println("月份输入有误!");
};
3.8 循环结构:while循环
需求:打印10次的HelloWorld
public class ForDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//控制台输出10次HelloWorld,不使用循环
System.out.println("HelloWorld");
System.out.println("HelloWorld");
System.out.println("HelloWorld");
System.out.println("HelloWorld");
System.out.println("HelloWorld");
System.out.println("HelloWorld");
System.out.println("HelloWorld");
System.out.println("HelloWorld");
System.out.println("HelloWorld");
System.out.println("HelloWorld");
System.out.println("-------------------------");
//用循环改进,循环10次
//定义变量从10开始,循环条件为<=10
int i = 1;
while(i <= 10){
System.out.println("HelloWorld");
i++;
}
}
}
1、while循环语句标准格式:
while (循环条件语句①) {
循环体语句②;
}
while(true){
循环体语句;//如果此时循环体中没有跳出循环的语句,也是死循环
}
注意:
while(循环条件)中循环条件必须是boolean类型
执行流程:
- 第一步:执行循环条件语句①,看循环条件语句的值是true,还是false;
- 如果是true,执行第二步;
- 如果是false,循环语句中止,循环不再执行。
- 第二步:执行循环体语句②;
- 第三步:循环体语句执行完后,重新从第一步开始再执行一遍
2、while循环语句扩展格式:
初始化语句①;
while (循环条件语句②) {
循环体语句③;
迭代语句④;
}
执行流程:
- 第一步:执行初始化语句①,完成循环变量的初始化;
- 第二步:执行循环条件语句②,看循环条件语句的值是true,还是false;
- 如果是true,执行第三步;
- 如果是false,循环语句中止,循环不再执行。
- 第三步:执行循环体语句③
- 第四步:执行迭代语句④,针对循环变量重新赋值
- 第五步:根据循环变量的新值,重新从第二步开始再执行一遍
语法演示案例1:求1加到100的和
int sum = 0;
int i = 1;
while(i<=100){
sum = sum + i;
i++;
}
System.out.println(sum);
3.9 循环结构:do…while循环
1、do…while循环语句标准格式:
do {
循环体语句①;
} while (循环条件语句②);
注意:
(1)while(循环条件)中循环条件必须是boolean类型
(2)do{}while();最后有一个分号
(3)do…while结构的循环体语句是至少会执行一次,这个和for和while是不一样的
执行流程:
- 第一步:执行循环体语句①;
- 第二步:执行循环条件语句②,看循环条件语句的值是true,还是false;
- 如果是true,执行第三步;
- 如果是false,循环语句终止,循环不再执行。
- 第三步:循环条件语句执行完后,重新从第一步开始再执行一遍
2、do…while循环语句扩展格式:
初始化语句①
do {
循环体语句②;
迭代语句③;
} while (循环条件语句④);
执行流程:
- 第一步:执行初始化语句①,完成循环变量的初始化;
- 第二步:执行循环体语句②;
- 第三步:执行迭代语句③,针对循环变量重新赋值;
- 第四步:执行循环条件语句④,看循环条件语句的值是true,还是false;
- 如果是true,根据循环变量的新值,重新从第二步开始再执行一遍;
- 如果是false,循环语句中止,循环不再执行。
语法演示案例2:输入密码和确认密码,比较是否一致
/*
输入密码和确认密码,如果两次密码一致则显示注册成功,两次密码不一致则提示重新输入
*/
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
String pwdOne = "";
String pwdTwo = "";
do{
System.out.println("请输入密码");
pwdOne = input.next();
System.out.println("请输入确认密码");
pwdTwo = input.next();
if(!pwdOne.equals(pwdTwo)){
System.out.println("两次密码不一致,请重新输入");
}
}while(!pwdOne.equals(pwdTwo));
System.out.println("注册成功");
练习:猜数
随机生成一个100以内的数,猜数字游戏
从键盘输入数,如果大了提示,大了,如果小了,提示小了,如果对了,就不再猜了,并统计一共猜了多少次
提示:随机数 Math.random()
double num = Math.random();// [0,1)的小数
public static void main(String[] args){
//随机生成一个100以内的整数
/*
Math.random() ==> [0,1)的小数
Math.random()* 100 ==> [0,100)的小数
(int)(Math.random()* 100) ==> [0,100)的整数
*/
int num = (int)(Math.random()* 100);
//System.out.println(num);
//声明一个变量,用来存储猜的次数
int count = 0;
java.util.Scanner input = new java.util.Scanner(System.in);
int guess;//提升作用域
do{
System.out.print("请输入100以内的整数:");
guess = input.nextInt();
//输入一次,就表示猜了一次
count++;
if(guess > num){
System.out.println("大了");
}else if(guess < num){
System.out.println("小了");
}
}while(num != guess);
System.out.println("一共猜了:" + count+"次");
}
3.10 循环语句:for循环
循环语句可以在满足循环条件的情况下,反复执行某一段代码,这段被重复执行的代码被称为循环体语句,当反复执行这个循环体时,需要通过修改循环变量使得循环判断条件为false,从而结束循环,否则循环将一直执行下去,形成死循环。
1、for循环语句格式:
for(初始化语句①; 循环条件语句②; 迭代语句④){
循环体语句③
}
for(;;){
循环体语句块;//如果循环体中没有跳出循环体的语句,那么就是死循环
}
注意:
(1)for(;;)中的两个;是不能多也不能少
(2)循环条件必须是boolean类型
(3)如果循环条件语句②省略的话,就默认为循环条件成立
执行流程:
- 第一步:执行初始化语句①,完成循环变量的初始化;
- 第二步:执行循环条件语句②,看循环条件语句的值是true,还是false;
- 如果是true,执行第三步;
- 如果是false,循环语句中止,循环不再执行。
- 第三步:执行循环体语句③
- 第四步:执行迭代语句④,针对循环变量重新赋值
- 第五步:根据循环变量的新值,重新从第二步开始再执行一遍
语法演示案例3:求出1-100之间偶数和
/*
* 练习:求出1-100之间偶数和
*
* 分析:
* 1.定义求和变量,初始化值是0
* 2.获取1-100之间的数据,用for循环实现
* 3.把获取到的数据进行判断,看是否是偶数
* 如果是,就累加
* 4.输出求和结果
*/
public class ForTest03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//定义求和变量,初始化值是0
int sum = 0;
//获取1-100之间的数据,用for循环实现
for(int x=1; x<=100; x++) {
//把获取到的数据进行判断,看是否是偶数
if(x % 2 == 0) {
sum += x;
}
}
//输出求和结果
System.out.println("sum:"+sum);
}
}
3.11 循环语句的区别
-
从循环次数角度分析
- do…while循环至少执行一次循环体语句
- for和while循环先循环条件语句是否成立,然后决定是否执行循环体,至少执行零次循环体语句
-
从循环变量的生命周期角度分析
- for循环的循环变量在for()中声明的,在循环语句结束后,不可以被访问;
- while和do…while循环的循环变量因为在外面声明的,所以while和do…while结束后可以被继续使用的;
-
如何选择
- 遍历有明显的循环次数(范围)的需求,选择for循环
- 遍历没有明显的循环次数(范围)的需求,循环while循环
- 如果循环体语句块至少执行一次,可以考虑使用do…while循环
- 本质上:三种循环之间是可以互相转换的,都能实现循环的功能
-
三种循环结构都具有四要素:
- (1)循环变量的初始化表达式
- (2)循环条件
- (3)循环变量的修改的迭代表达式
- (4)循环体语句块
3.12 控制语句
3.12.1 break
- 使用场景:终止switch或者当前循环
-
在选择结构switch语句中
-
在循环语句中
-
离开使用场景的存在是没有意义的
-
语法案例演示1:判断某个数是否是素数
案例:从键盘输入一个大于1的自然数,判断它是否是素数
提示:素数是指大于1的自然数中,除了1和它本身以外不能再有其他因数的自然数,即某个素数n,在[2,n-1]范围内没有其他自然数可以把n整除
class Test07BreakExer1{
public static void main(String[] args){
java.util.Scanner input = new java.util.Scanner(System.in);
int num;
while(true){
//true是常量,常量是编译期间就可以确定的值
System.out.print("请输入一个大于1的自然数:");
num = input.nextInt();
if(num>1){
break;
}
}
System.out.println("num = " + num);
boolean flag = true;//假设num是素数
//判断它是否是素数
for(int i=2; i<num; i++){
if(num % i ==0){//num被某个i整除了,num就不是素数
System.out.println(num + "不是素数");
flag = false;
break;//找到其中一个可以把num整除的数,就可以结束了,因为num已经可以判定不是素数了
}
}
//只有把[2,num-1]之间的所有数都检查过了,才能下定结论,num是素数
if(flag){
System.out.println(num + "是素数");
}
}
}
class Test07BreakExer1_2{
public static void main(String[] args){
java.util.Scanner input = new java.util.Scanner(System.in);
int num;
while(true){
//true是常量,常量是编译期间就可以确定的值
System.out.print("请输入一个大于1的自然数:");
num = input.nextInt();
if(num>1){
break;
}
}
System.out.println("num = " + num);
boolean flag = true;//假设num是素数
//判断它是否是素数
//在[2, num的平方根]之间如果都没有一个自然数可以把num整除,那么num就是素数
/*
不是素数
9的平方根是3,除1和它本身外的因数:3
16的平方根是4,除1和它本身外的因数:2,4,8
25的平方根是5,除1和它本身外的因数:5
是素数
7的平方根是2.64,除1和它本身外的只需要判断2,如果2不是,那么就不是
无须判断,3,4,5,6
*/
for(int i=2; i<=Math.sqrt(num); i++){
if(num % i ==0){
System.out.println(num + "不是素数");
flag = false;
break;
}
}
System.out.println(num + (flag?"是":"不是") + "素数");
}
}
语法案例演示2:统计正数、负数个数
案例:从键盘输入不断输入整数,输入0表示结束,统计一共有几个正数、负数。
public static void main(String[] args) {
java.util.Scanner input = new java.util.Scanner(System.in);
int positive = 0;
int negative = 0;
while(true){
System.out.print("请输入整数(0)结束:");
int num = input.nextInt();
if(num==0){
break;
}else if(num>0){
positive++;
}else{
negative++;
}
}
System.out.println("正数:" + positive + ",负数:" + negative);
}
语法案例演示3:break同时存在switch和循环中
===ATM=
1、存款
2、取款
3、显示余额
4、退出
请选择:
public static void main(String[] args){
java.util.Scanner input = new java.util.Scanner(System.in);
//声明一个变量表示余额
double balance = 0.0;
boolean flag = true;
while(flag){
System.out.println("=========ATM=======");
System.out.println("t1、存款");
System.out.println("t2、取款");
System.out.println("t3、显示余额");
System.out.println("t4、退出");
System.out.print("请选择:");
int select = input.nextInt();
switch(select){
case 1:
System.out.print("存款的金额:");
double money = input.nextDouble();
balance += money;
break;
case 2:
System.out.print("取款的金额:");
money = input.nextDouble();
balance -= money;
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("现在的余额:" + balance);
break;
case 4:
flag = false;
break;//只能结束switch
}
}
}
3.12.2 continue
- 使用场景:结束本次循环,继续下一次的循环
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
//需求:不打印3的倍数
if(i % 3 == 0){
continue;
}
System.out.println(i);
}
}
练习:打印1-100之间的整数,跳过7的倍数和7结尾的数
public static void main(String[] args){
//打印1-100之间的整数,跳过7的倍数和7结尾的数
for(int i=1; i<=100; i++){
if(i%7==0 || i%10==7){
continue;
//break;
}
System.out.println(i);
}
}
3.13 嵌套循环
- 所谓嵌套循环,是指一个循环的循环体是另一个循环。比如for循环里面还有一个for循环,就是嵌套循环。总共的循环次数=外循环次数*内循环次数。当然可以是三种循环任意互相嵌套。
- 嵌套循环格式:
for(初始化语句①; 循环条件语句②; 迭代语句⑦) {
for(初始化语句③; 循环条件语句④; 迭代语句⑥) {
循环体语句⑤;
}
}
语法案例演示1:打印5行5列矩形
public static void main(String[] args){
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-I9vx59DT-1674876904557)(C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/新建文件夹/img/1561789094346.png)]
语法案例演示2:打印5行直角三角形
*
**
***
****
*****
public static void main(String[] args){
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= i; j++) {
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
练习1:
/*
1
12
123
1234
12345
*/
public static void main(String[] args){
//外循环控制行数
for(int i=1; i<=5; i++){
//内循环控制每一行打印的数字
/*
当i=1,外循环第1次,第1行,j=1
当i=2,外循环第2次,第2行,j=1,2
当i=3,外循环第3次,第3行,j=1,2,3
当i=4,外循环第4次,第4行,j=1,2,3,4
当i=5,外循环第5次,第5行,j=1,2,3,4,5
j=1,j<=i
*/
for(int j=1; j<=i; j++){
System.out.print(j);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
练习2:
/*
1
22
333
4444
55555
*/
public static void main(String[] args){
for(int i=1; i<=5; i++){
//内循环控制每一行打印的数字
/*
当i=1,外循环第1次,第1行,1, 1个i,j=1
当i=2,外循环第2次,第2行,22 2个i,j=1,2
当i=3,外循环第3次,第3行,333 3个i,j=1,2,3
当i=4,外循环第4次,第4行,4444 4个i,j=1,2,3,4
当i=5,外循环第5次,第5行,55555 5个i,j=1,2,3,4,5
说明,打印的是i的值,打印几个i
j=1,j<=i
*/
for(int j=1; j<=i; j++){
System.out.print(i);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
最后
以上就是娇气金针菇最近收集整理的关于JavaSE_day03 流程控制- if else判断语句- switch选择语句- for循环语句- while循环语句- do...while循环语句- break - continue第三章 流程控制的全部内容,更多相关JavaSE_day03内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复