在使用Simulink时,经常看到Continuous和Discrete States这两个术语,对于其理解,查阅到官网的一个问答(What are continuous and discrete states in Simulink?),记录下来
1. 原文回答
In my own words, a crude word to use in place of “state” is “memory”. A state adds memory to a system in such as way that the output at a given time depends not only on its current input, but also on its previous inputs. There is also a more formal explanation about states here:
Discrete states can be thought purely as internal memory - for example a Unit Delay block has one discrete state, and it’s output is computed based on two methods: Outputs and Update, which may be written as follows (u=input, x=state, y=output):
Outputs()
y = x;
Update()
x = u;
Here, the Simulink Engine never reads the discrete states, it only manages the memory allocation/de-allocation for the states. The delay is caused due to the fact that Update() runs after Output(), which means that the current “u” is only read into “y” at the next time-step when Output() runs again.
With continuous states however, Simulink asks the block to provide a derivative (dx/dt) of the state in the Derivatives() method and uses its ODE solver to compute the integral of dx/dt to obtain ‘x’. This ‘x’ can then be accessed in the Outputs() function. For example, to implement an Integrator block, we might write:
Outputs()
y = x;
Derivatives()
x_dot = u;
Here, the Simulink Engine reads x_dot and computes x for use in Outputs.
In both cases, at t=0, the value of ‘x’ is whatever what provided as the Initial Condition by the block.
2. 官方文档
个人认为上述的解释也不完全正确和全面,特查阅文档,官方的帮助文档对这个基础概念做了详细的解释。
2.1 连续状态
连续状态定义为具有所有时刻的值变量(意思是理论上任意时刻t对应的值都应该知道)。
举个例子:模拟速度计上显示的汽车速度,其指针位置随着轮胎的旋转而连续变化。
具有连续状态和初始值(Initial Condition)模块参数(block parameter)的模块有:
- Integrator
- State-Space
- Transfer Fcn
通常而言,除非是特别简单的模型,不存在对于常微分方程的状态进行积分的解析方法,一般都需要用数值方法。
应用数值方法求解意味着也是用离散的方法以有限的精度进行逼近,不是理论上的连续。
2.2 离散状态
离散状态定义为仅在特定时间上的值变量(一般跟采样时间相关)。它是连续状态的一种逼近,状态以周期性或非周期性时间间隔更新。
举个例子:显示在数字速度计上的汽车速度,它每秒更新一次,而不是连续更新。
具有离散状态的模块:
- Discrete-Time Integrator
- Discrete State-Space
- Discrete Transfer Fcn
- Delay
计算模块的离散状态需要知道它在前一个时间步的值以及该模块的当前输入值。Simulink 提供两种类型的离散求解器:
- 固定步长离散求解器——为模型的所有离散状态确定可命中所有采样时间的固定步长,而不管在采样时间命中点上状态是否实际更改了值。
- 可变步长离散求解器——更改步长以确保采样时间命中点仅在状态值更改时发生
3. 积分器举例
3.1 Integrator
Simulink将Integrator看作是具有一个状态的动态系统,模块的动态由以下方程描述:
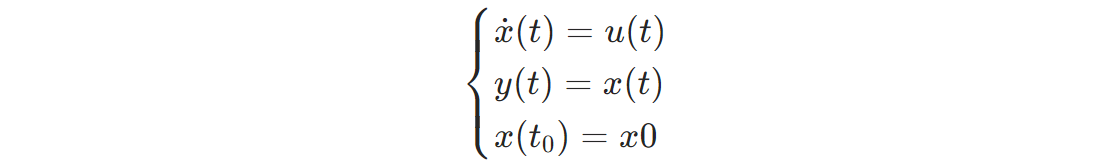
虽然这些方程定义了连续时间下的准确关系,但 Simulink 使用数值逼近方法以有限精度来进行计算。Simulink 可以使用若干不同的数值积分方法来计算模块的输出,每种方法都在特定的应用中各具优势。
Solve窗口菜单可以设置积分器求解方法。
所选求解器会使用当前输入值和前一个时间步的状态值计算 Integrator 模块在当前时间步的输出。为支持此计算模型,Integrator 模块会保存在当前时间步的输出,以供求解器计算其在下一个时间步的输出。该模块还为求解器提供了初始条件,用于计算该模块在仿真开始时的初始状态。初始条件的默认值为 0。
3.2 Discrete-Time Integrator
可以用Discrete-Time Integrator模块替代Integrator模块来创建离散模型。
对于第一个时间步,模块状态为 n = 0,具有初始输出 y(0) = IC 或初始状态 x(0) = IC,具体取决于 Initial condition setting 参数值。
对于仿真时间为 t(n) 的给定步长 n > 0,Simulink® 将更新输出 y(n),如下所示:
- Forward Euler 方法:y(n) = y(n-1) + K*[t(n) - t(n-1)]*u(n-1)
- Backward Euler 方法:y(n) = y(n-1) + K*[t(n) - t(n-1)]*u(n)
- Trapezoidal 方法:y(n) = y(n-1) + K*[t(n)-t(n-1)]*[u(n)+u(n-1)]/2
Simulink 根据模块的采样时间(可以是显式或触发的采样时间)自动选择这些输出方程的状态空间实现。当使用显式采样时间时,对于所有 n > 0 的步长,t(n)-t(n-1) 将减小到采样时间 T。
最后
以上就是完美毛巾最近收集整理的关于【Simulink】什么是连续状态和离散状态?1. 原文回答2. 官方文档3. 积分器举例的全部内容,更多相关【Simulink】什么是连续状态和离散状态?1.内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复