前言
上一篇博客用纯C++程序写完了LQR仿真过程,效果还行,然后这一篇博客用来把这个程序部署到实验平台的ROS系统上进行仿真及实验验证。
建议简单看一下上一篇的一个程序思路:Visual studio C++:LQR轨迹跟踪仿真
思路
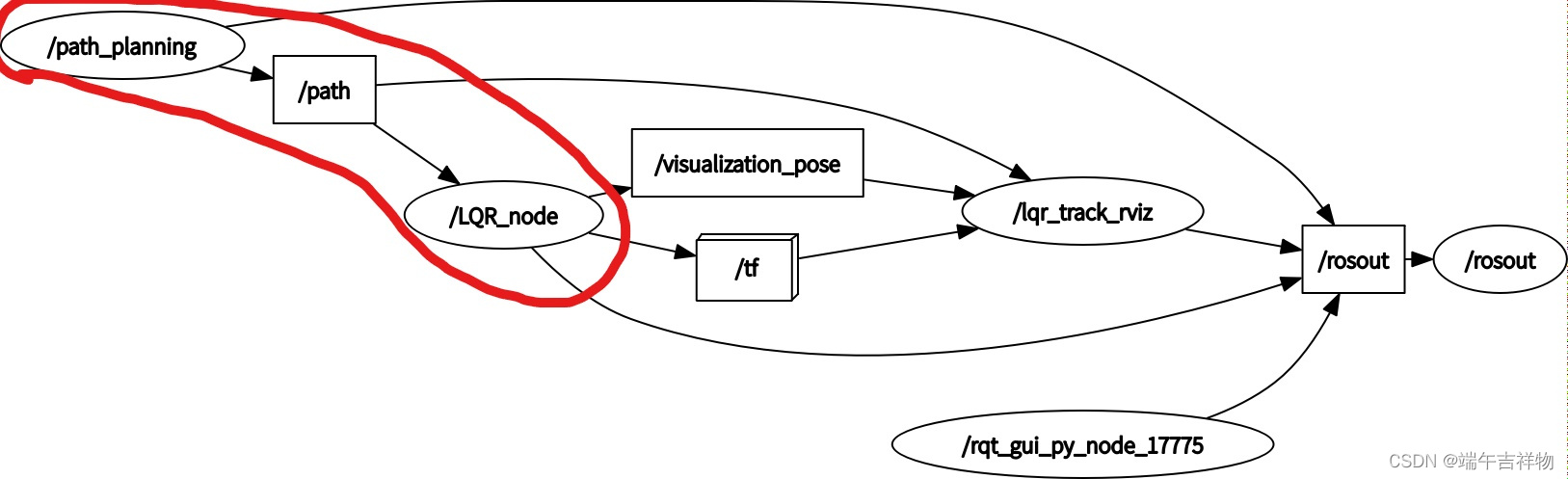
其实思路非常简单,就是path_planning向LQR_node发送目标点就可以了,主要看红圈里面的就行,其他的都是可视化要用的。
path_planning生成路径通过话题/path传给LQR_node中,LQR_node进行跟踪。
代码部署
一、自定义库函数(LQR、tool、trajectory)
基于上一篇博客,已经写了自定义的相关库函数,有LQR、tool、trajectory、matplot,但是在ROS里面可以不用matplot,可以在rviz里面看,所以丢弃。
1.Tool优化
为了让路径生成过程更加条理清晰,对库函数进行了一些优化,Tool里面路径点参数只设置x、y、yaw,而曲率K选择在控制器里面针对获取的路径去算。添加了一个计算曲率K的函数。
Tool.h
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <math.h>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
#define pi acos(-1)
//定义路径点
typedef struct waypoint {
int ID;
double x, y, yaw;//x,y
}waypoint;
//定义小车状态
typedef struct vehicleState {
double x, y, yaw, v, kesi;//x,y,yaw,前轮偏角kesi
}vehicleState;
//定义控制量
typedef struct U {
double v;
double kesi;//速度v,前轮偏角kesi
}U;
double cal_K(vector<waypoint> waypoints, int index);//计算曲率K
Tool.cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<LQR_track/Tool.h>
double cal_K(vector<waypoint> waypoints, int index){
double res;
//差分法求一阶导和二阶导
double dx, dy, ddx, ddy;
if (index == 0) {
dx = waypoints[1].x - waypoints[0].x;
dy = waypoints[1].y - waypoints[0].y;
ddx = waypoints[2].x + waypoints[0].x - 2 * waypoints[1].x;
ddy = waypoints[2].y + waypoints[0].y - 2 * waypoints[1].y;
}
else if (index == (waypoints.size() - 1)) {
dx = waypoints[index].x - waypoints[index - 1].x;
dy = waypoints[index].y - waypoints[index - 1].y;
ddx = waypoints[index].x + waypoints[index - 2].x - 2 * waypoints[index].x;
ddy = waypoints[index].y + waypoints[index - 2].y - 2 * waypoints[index].y;
}
else {
dx = waypoints[index + 1].x - waypoints[index].x;
dy = waypoints[index + 1].y - waypoints[index].y;
ddx = waypoints[index + 1].x + waypoints[index - 1].x - 2 * waypoints[index].x;
ddy = waypoints[index + 1].y + waypoints[index - 1].y - 2 * waypoints[index].y;
}
//res.yaw = atan2(dy, dx);//yaw
//计算曲率:设曲线r(t) =(x(t),y(t)),则曲率k=(x'y" - x"y')/((x')^2 + (y')^2)^(3/2).
res = (ddy * dx - ddx * dy) / (sqrt(pow((pow(dx, 2) + pow(dy, 2)), 3)));
return res;
}
2.trajectory优化
设置了可以从launch文件导入的参数接口,用于设计轨迹起始点,长度限制等信息,添加了用户自定义轨迹custom_path,按照trajectory.h里面的备注慢慢操作就好了。
trajectory.h
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include "LQR_track/Tool.h"
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class trajectory {
private:
vector<waypoint> waypoints;
double x_start,y_start,limit_x,limit_y;
string trajectory_type;
public:
trajectory(double initial_x_,double initial_y_,string type_,double limit_x_,double limit_y_):
x_start(initial_x_),y_start(initial_y_),trajectory_type(type_),limit_x(limit_x_),limit_y(limit_y_){};
//set reference trajectory
void refer_path();
vector<waypoint> get_path();
//If you need to add a custom path:1.please add the function; 2.Overwrite trajectory.cpp synchronously
//void custom_path();
void line();
void wave1();
void wave2();
};trajectory.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include "LQR_track/trajectory.h"
#include <math.h>
using namespace std;
double dt = 0.01;//轨迹计算频率
void trajectory::line(){
waypoint PP;
for (int i = 0; i < limit_x/dt; i++)
{
PP.ID = i;
PP.x = x_start + dt * i;//x:10米
PP.y = y_start ;//y
waypoints.push_back(PP);
}
}
void trajectory::wave1(){
waypoint PP;
for (int i = 0; i < limit_x/dt; i++)
{
PP.ID = i;
PP.x = x_start + dt * i;//x
PP.y = y_start + 1.0 * sin(dt*i / 1.5) + 0.5 * cos(dt*i / 1.0);//y
waypoints.push_back(PP);
}
}
void trajectory::wave2(){
waypoint PP;
for (int i = 0; i < limit_x/dt; i++)
{
PP.ID = i;
PP.x = x_start + dt * i;//x
PP.y = y_start - 0.2 * sin(dt*i / 0.4);//y
waypoints.push_back(PP);
}
}
//write the path you design
/*void trajectory::custom_path(){
waypoint PP;
for (int i = 0; i < limit_x/dt; i++)
{
PP.ID = i;
PP.x = ...;//x
PP.y = ...;//y
waypoints.push_back(PP);
}
}*/
void trajectory::refer_path() {
if(trajectory_type == "wave1")wave1();
else if(trajectory_type == "line")line();
else if(trajectory_type == "wave2")wave2();
//else if(trajectory_type == "custom_path")custom_path();//set the index
//计算切线方向并储存
for (int j=0;j<waypoints.size();j++){
double dx, dy, yaw;
if (j == 0) {
dx = waypoints[1].x - waypoints[0].x;
dy = waypoints[1].y - waypoints[0].y;
}
else if (j == (waypoints.size() - 1)) {
dx = waypoints[j].x - waypoints[j - 1].x;
dy = waypoints[j].y - waypoints[j - 1].y;
}
else {
dx = waypoints[j + 1].x - waypoints[j].x;
dy = waypoints[j + 1].y - waypoints[j].y;
}
yaw = atan2(dy, dx);//yaw
waypoints[j].yaw = yaw;
}
}
vector<waypoint> trajectory::get_path() {
return waypoints;
}
3.LQR优化
这个好像没做优化,跟原来的一样吧,还是附上代码:
LQR.h
#include <iostream>
#include <Eigen/Dense>
#include "LQR_track/Tool.h"
using namespace std;
typedef Eigen::Matrix<double, 3, 3> Matrix3x3;
typedef Eigen::Matrix<double, 3, 1> Matrix3x1;
typedef Eigen::Matrix<double, 2, 1> Matrix2x1;
typedef Eigen::Matrix<double, 2, 2> Matrix2x2;
typedef Eigen::Matrix<double, 3, 2> Matrix3x2;
typedef Eigen::Matrix<double, 2, 3> Matrix2x3;
//状态方程变量: X = [x_e y_e yaw_e]^T
//状态方程控制输入: U = [v_e kesi_e]^T
class LQR
{
private:
Matrix3x3 A_d;
Matrix3x2 B_d;
Matrix3x3 Q;
Matrix2x2 R;
Matrix3x1 X_e;
Matrix2x1 U_e;
double L;//车辆轴距
double T;//采样间隔
double x_car, y_car, yaw_car, x_d, y_d, yaw_d;//车辆位姿和目标点位姿
double v_d, kesi_d;//期望速度和前轮偏角
double Q3[3];//Q权重,三项
double R2[2];//R权重,两项
int temp = 0;
public:
void initial(double L_, double T_, vehicleState car, waypoint waypoint, U U_r, double* Q_, double* R_);//初始化
void param_struct();//构造状态方程参数
Matrix2x3 cal_Riccati();//黎卡提方程求解
U cal_vel();//LQR控制器计算速度
void test();
};
LQR.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "LQR_track/LQR.h"
using namespace std;
void LQR::initial(double L_, double T_, vehicleState car, waypoint waypoint, U U_r, double *Q_, double *R_) {
L = L_;
T = T_;
x_car = car.x; y_car = car.y; yaw_car = car.yaw;
x_d = waypoint.x; y_d = waypoint.y; yaw_d = waypoint.yaw;
v_d = U_r.v;kesi_d = U_r.kesi;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
Q3[i] = Q_[i];
}
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++) {
R2[j] = R_[j];
}
}
void LQR::param_struct() {
Q << Q3[0], 0.0, 0.0,
0.0, Q3[1], 0.0,
0.0, 0.0, Q3[2];
//cout << "Q矩阵为:n" << Q << endl;
R << R2[0], 0.0,
0.0, R2[1];
//cout << "R矩阵为:n" << R << endl;
A_d << 1.0, 0.0, -v_d * T * sin(yaw_d),
0.0, 1.0, v_d* T* cos(yaw_d),
0.0, 0.0, 1.0;
//cout << "A_d矩阵为:n" << A_d << endl;
B_d << T * cos(yaw_d), 0.0,
T* sin(yaw_d), 0.0,
T* tan(kesi_d), v_d* T / (L * cos(kesi_d) * cos(kesi_d));
//cout << "B_d矩阵为:n" << B_d << endl;
X_e << x_car - x_d, y_car - y_d, yaw_car - yaw_d;
//cout << "X_e矩阵为:n" << X_e << endl;
}
Matrix2x3 LQR::cal_Riccati() {
int N = 150;//迭代终止次数
double err = 100;//误差值
double err_tolerance = 0.01;//误差收敛阈值
Matrix3x3 Qf = Q;
Matrix3x3 P = Qf;//迭代初始值
//cout << "P初始矩阵为n" << P << endl;
Matrix3x3 Pn;//计算的最新P矩阵
for (int iter_num = 0; iter_num < N; iter_num++) {
Pn = Q + A_d.transpose() * P * A_d - A_d.transpose() * P * B_d * (R + B_d.transpose() * P * B_d).inverse() * B_d.transpose() * P * A_d;//迭代公式
//cout << "收敛误差为" << (Pn - P).array().abs().maxCoeff() << endl;
//err = (Pn - P).array().abs().maxCoeff();//
err = (Pn - P).lpNorm<Eigen::Infinity>();
if(err < err_tolerance)//
{
P = Pn;
//cout << "迭代次数" << iter_num << endl;
break;
}
P = Pn;
}
//cout << "P矩阵为n" << P << endl;
//P = Q;
Matrix2x3 K = -(R + B_d.transpose() * P * B_d).inverse() * B_d.transpose() * P * A_d;//反馈率K
return K;
}
U LQR::cal_vel() {
U output;
param_struct();
Matrix2x3 K = cal_Riccati();
Matrix2x1 U = K * X_e;
//cout << "反馈增益K为:n" << K << endl;
//cout << "控制输入U为:n" << U << endl;
output.v = U[0] + v_d;
output.kesi = U[1] + kesi_d;
return output;
}
void LQR::test() //控制器效果测试
{
/*param_struct();
while (temp < 1000) {
Matrix2x3 K = cal_Riccati();
Matrix2x1 U = K * X_e;
//cout <<"state variable is:n" <<X_e << endl;
//cout <<"control input is:n"<< U << endl;
Matrix3x1 X_e_ = A_d * X_e + B_d * U;
X_e = X_e_;
temp++;
}*/
Matrix3x3 C,D,F;
C << 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0;
F << 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 4.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 7.0;
D = (C - F);
double BBBB = D.lpNorm<Eigen::Infinity>();
cout << BBBB << endl;
}4.ROS中自定义库的编译生成
可以参考一下这一篇:5.ROS学习之自定义头文件和源文件的调用,如果不想看的话可以就按照我这个过程就好了。
首先参考之前的博客:ROS C++调用osqp-eigen库的具体操作步骤,完成:添加ROS自带的Eigen模块。
然后在Build下面写上如下代码:
注意!!!!:头文件和源文件的绝对路径一定要写成自己的!!
###########
## Build ##
###########
include_directories(
include
${catkin_INCLUDE_DIRS}
${Eigen_INCLUDE_DIRS}
)
####以下绝对路径一定要写成自己的!!!
add_library(LQR_LIBRARIES
/home/dlrobot/dlrobot_robot/src/617_robot/lqr_track/include/LQR_track/Tool.h
/home/dlrobot/dlrobot_robot/src/617_robot/lqr_track/include/LQR_track/trajectory.h
/home/dlrobot/dlrobot_robot/src/617_robot/lqr_track/include/LQR_track/LQR.h
/home/dlrobot/dlrobot_robot/src/617_robot/lqr_track/src/Tool.cpp
/home/dlrobot/dlrobot_robot/src/617_robot/lqr_track/src/trajectory.cpp
/home/dlrobot/dlrobot_robot/src/617_robot/lqr_track/src/LQR.cpp
)
target_link_libraries(LQR_LIBRARIES ${catkin_LIBRARIES})这样就好了。编译一下可以生成lqr_track功能包的名为LQR_LIBRARIES自定义库。
二、调用库函数完成轨迹生成工作(path_planning.cpp)
基于ROS的发布者机制去写一个路径发布程序,路径数据类型为nav_msgs::Path。直接调用trajectory就可以实现路径的获取,然后转换一下数据类型(从vector<waypoint>转换为nav_msgs::Path)就可以发布出去啦。
同时从launch文件传入参数流程是:launch→path_planning→trajectory.h
path_planning.cpp
#include <ros/ros.h>
#include <nav_msgs/Path.h>
#include <geometry_msgs/PoseStamped.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include "LQR_track/trajectory.h"
#include "ros/init.h"
#include "ros/node_handle.h"
#include "ros/publisher.h"
#include "ros/rate.h"
#include "ros/time.h"
#include <math.h>
#include <tf/tf.h>
double x_start,y_start,limit_x,limit_y;
string trajectory_type;
nav_msgs::Path produce_path(){
trajectory* trajec = new trajectory(x_start,y_start,trajectory_type,limit_x,limit_y);//实例化trajectory类;
vector<waypoint> waypoint_vec;//定义vector类用于接收由trajec生成的路径,得到若干组[ID,x,y]
nav_msgs::Path waypoints;//定义nav_msgs::Path类用于构造ROS的Path消息
//获取路径
trajec->refer_path();
waypoint_vec = trajec->get_path();
//构造适用于ROS的Path消息
waypoints.header.stamp = ros::Time::now();
waypoints.header.frame_id = "map";
for(int i =0;i<waypoint_vec.size();i++){
geometry_msgs::PoseStamped this_pose;
this_pose.header.seq = i;
//ROS_INFO("path_id is %d", this_pose.header.seq);
this_pose.header.frame_id = "map";
this_pose.pose.position.x = waypoint_vec[i].x;
this_pose.pose.position.y = waypoint_vec[i].y;
this_pose.pose.position.z = 0;
geometry_msgs::Quaternion goal_quat = tf::createQuaternionMsgFromYaw(waypoint_vec[i].yaw);
//ROS_INFO("the yaw is %f",waypoint_vec[i].yaw);
this_pose.pose.orientation.x = goal_quat.x;
this_pose.pose.orientation.y = goal_quat.y;
this_pose.pose.orientation.z = goal_quat.z;
this_pose.pose.orientation.w = goal_quat.w;
waypoints.poses.push_back(this_pose);
}
return waypoints;//返回适用于ROS的Path消息
}
int main(int argc,char **argv){
ros::init(argc, argv, "path_produce");
ros::NodeHandle n;
ros::NodeHandle n_prv("~");
n_prv.param<double>("x_start",x_start,0.0);
n_prv.param<double>("y_start",y_start,0.0);
n_prv.param<string>("trajectory_type",trajectory_type,"line");
n_prv.param<double>("limit_x",limit_x,10);
n_prv.param<double>("limit_y",limit_y,0.0);
ros::Publisher path_pub = n.advertise<nav_msgs::Path>("path",10);
ros::Rate loop_rate(1);
while(ros::ok()){
nav_msgs::Path path = produce_path();
ROS_INFO("the trajectory size is: %ld",path.poses.size());
path_pub.publish(path);
loop_rate.sleep();
}
}三、调用库函数完成LQR控制器的轨迹跟踪工作
1.仿真程序(LQR_node.cpp)
这个文件中定义了两个类,一个是对订阅到的路径进行处理的类(Class Path),一个是负责轨迹跟踪的类(Class LQR_node),其跟踪功能的实现步骤如下:
跟踪功能实现步骤:
1.获取路径点,在while(ros::ok())函数下面ros::spinOnce()阶段订阅回调函数addpointcallback时完成
2.搜索路径点
3.获取路径点信息,构造期望控制量
4.先进行一次减速判断,确定纵向期望速度v_r,和机器人当前动作:tracking或reached the goal
5.构造权重矩阵,从launch文件的参数Q_set,R_set导入
6.使用LQR控制器,计算速度和前轮转角,其中有限幅过程
7.发布话题,其中有角速度的计算8.用运动学模型计算小车下一时刻位姿
8.判断是否需要关闭控制器,如果到达终点就关闭
9.loop_rate.sleep(),结束一次循环,准备开始下一次个跟踪工作
直接放代码了:
LQR_node.cpp:
#include <ros/ros.h>
#include <iostream>
#include "LQR_track/LQR.h"
#include <vector>
#include "ros/node_handle.h"
#include "ros/publisher.h"
#include "tf/LinearMath/Quaternion.h"
#include "tf/transform_broadcaster.h"
#include "visualization_msgs/Marker.h"
#include <nav_msgs/Path.h>
#include <geometry_msgs/Twist.h>
#include <geometry_msgs/Pose2D.h>
#include <tf/tf.h>
#include <tf/transform_broadcaster.h>
using namespace std;
double freq,L,V_DESIRED;//采样频率,车辆轴距,期望速度
double v_max;//最大速度
bool limit_v_and_kesi;//是否限幅(对于阿卡曼转向车辆需要限幅,全向车倒还好)
double initial_x,initial_y,initial_yaw,initial_v,initial_kesi;//初始化车辆位姿,速度和前轮转角
std::vector<double> Q_set;
std::vector<double> R_set;
double slow_LEVE1_DISTANCE,slow_LEVE2_DISTANCE,slow_LEVE1_V,slow_LEVE2_V,goal_tolerance_DISTANCE;//定义二级减速距离和速度
#define pi acos(-1)
#define T 1/freq //采样时间
vehicleState update_state(U control, vehicleState car) {
car.v = control.v;
car.kesi = control.kesi;
car.x += car.v * cos(car.yaw) * T;
car.y += car.v * sin(car.yaw) * T;
car.yaw += car.v / L * tan(car.kesi) * T;
return car;
}
class Path {
private:
vector<waypoint> path;
public:
//添加新的路径点
void Add_new_point(waypoint& p)
{
path.push_back(p);
}
void Add_new_point(vector<waypoint>& p)
{
path = p;
}
//路径点个数
unsigned int Size()
{
return path.size();
}
//获取路径点
waypoint Get_waypoint(int index)
{
waypoint p;
p.ID = path[index].ID;
p.x = path[index].x;
p.y = path[index].y;
p.yaw = path[index].yaw;
return p;
}
vector<waypoint> Get_waypoints(){
return path;
}
// 搜索路径点, 将小车到起始点的距离与小车到每一个点的距离对比,找出最近的目标点索引值
int Find_target_index(vehicleState state)
{
double min = abs(sqrt(pow(state.x - path[0].x, 2) + pow(state.y - path[0].y, 2)));
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < path.size(); i++)
{
double d = abs(sqrt(pow(state.x - path[i].x, 2) + pow(state.y - path[i].y, 2)));
if (d < min)
{
min = d;
index = i;
}
}
//索引到终点前,当(机器人与下一个目标点的距离Lf)小于(当前目标点到下一个目标点距离L)时,索引下一个目标点
if ((index + 1) < path.size())
{
double current_x = path[index].x; double current_y = path[index].y;
double next_x = path[index + 1].x; double next_y = path[index + 1].y;
double L_ = abs(sqrt(pow(next_x - current_x, 2) + pow(next_y - current_y, 2)));
double L_1 = abs(sqrt(pow(state.x - next_x, 2) + pow(state.y - next_y, 2)));
//ROS_INFO("L is %f,Lf is %f",L,Lf);
if (L_1 < L_)
{
index += 1;
}
}
return index;
}
};
class LQR_node {
private:
//car
vehicleState car;//小车状态
U control;//小车控制量[v,kesi]
double Q[3];
double R[2];
int lastIndex;//最后一个点索引值
waypoint lastPoint;//最后一个点信息
string action;//小车目前动作:跟踪或跟踪完成(tracking or reach goal!)
//ROS
ros::Subscriber path_sub;//订阅路径,消息类型为nav_msgs::Path
ros::Publisher vel_pub;//发布速度信息,消息类型为geometry_msgs::Twist
ros::Publisher actual_state_pub;//发布小车实际位姿,消息类型为geometry_msgs::Pose2D
ros::Publisher visual_state_pub;//向rviz发布小车虚拟轨迹,消息类型为visualization_msgs::Marker
geometry_msgs::Point visual_state_pose;
visualization_msgs::Marker visual_state_trajectory;
geometry_msgs::Pose2D actual_pose;
geometry_msgs::Twist vel_msg;
int temp;//计数,达到终点时,用于判断控制器是否需要关闭
public:
LQR* controller;
Path* path;
LQR_node(ros::NodeHandle& nh)//初始化中添加轨迹、小车初始位姿
{
controller = new LQR();
path = new Path();
//ROS:
path_sub = nh.subscribe("path",10,&LQR_node::addpointcallback,this);
vel_pub = nh.advertise<geometry_msgs::Twist>("cmd_vel",10);
visual_state_pub = nh.advertise<visualization_msgs::Marker>("visualization_pose",10);
actual_state_pub = nh.advertise<geometry_msgs::Pose2D>("LQR_pose",10);
//robot state initialize:
car.x = initial_x;car.y = initial_y;car.yaw = initial_yaw;car.v = initial_v;car.kesi = initial_kesi;
action = "the car is tracking!!";
}
~LQR_node() {
delete(controller);
delete(path);
}
void addpointcallback(const nav_msgs::Path::ConstPtr& msg){
vector<waypoint> waypoints;
for(int i=0;i<msg->poses.size();i++){
waypoint waypoint;
//ROS_INFO("THE PATH[%d]'s ID is %d",i,msg->poses[i].header.seq);
waypoint.ID = msg->poses[i].header.seq;
waypoint.x = msg->poses[i].pose.position.x;
waypoint.y = msg->poses[i].pose.position.y;
//获取角度
double roll,pitch,yaw;
tf::Quaternion quat;
tf::quaternionMsgToTF(msg->poses[i].pose.orientation, quat);
tf::Matrix3x3(quat).getRPY(roll, pitch, yaw);
waypoint.yaw = yaw;
waypoints.push_back(waypoint);
}
path->Add_new_point(waypoints);//路径点vector数组传到path类中
lastIndex = path->Size() - 1;
lastPoint = path->Get_waypoint(lastIndex);
}
double slow_judge(double distance) {
if (distance>=slow_LEVE2_DISTANCE&&distance <= slow_LEVE1_DISTANCE) {
return slow_LEVE1_V;
}
else if (distance>=goal_tolerance_DISTANCE&&distance < slow_LEVE2_DISTANCE) {
return slow_LEVE2_V;
}
else if (distance < goal_tolerance_DISTANCE) {
action = "the car has reached the goal!";
return 0.0;
}
else
{
return V_DESIRED;
}
}
//控制器流程
void LQR_track() {
U U_r;
waypoint Point;
double K;
//ROS_INFO("path size is: %d",path->Size());
if(path->Size()!=0){
//搜索路径点
int target_index = path->Find_target_index(car);
//ROS_INFO("target index is : %d", target_index);
//获取路径点信息,构造期望控制量
Point = path->Get_waypoint(target_index);//获取x,y
//ROS_INFO("waypoint information is x:%f,y:%f,yaw:%f", Point.x, Point.y, Point.yaw);
K = cal_K(path->Get_waypoints(),target_index);//计算曲率
//减速判断
double kesi = atan2(L * K, 1);
double v_distance = abs(sqrt(pow(car.x - lastPoint.x, 2) + pow(car.y - lastPoint.y, 2)));
//ROS_INFO("the distance is %fn", v_distance);
U_r.v = slow_judge(v_distance);U_r.kesi = kesi;
ROS_INFO("%s",action.c_str());//机器人动作
//ROS_INFO("the desired v is: %f,the desired kesi is: %f", U_r.v,U_r.kesi);
//权重矩阵
for(int q =0;q<Q_set.size();q++)Q[q] = Q_set[q];
for(int r =0;r<R_set.size();r++)R[r] = R_set[r];
if(Q[0]>=R[0]||Q[1]>=R[1])
ROS_WARN("Q >= R, the calculation result may be abnormal,please set R < Q ");
//使用LQR控制器,
controller->initial(L, T, car, Point, U_r, Q, R);//初始化控制器
control = controller->cal_vel();//计算输入[v, kesi]
if(U_r.v==0)control.v = 0;//判断,期望速度为0,则机器人停下
if(limit_v_and_kesi)control = v_and_kesi_limit(control);//速度和前轮转角限幅
ROS_INFO("the speed is: %f,the kesi is: %f", control.v, control.kesi);
//ROS_INFO("the car position is x: %f, y: %f", car.x, car.y);
//话题发布
PUB();
//小车位姿状态更新
car = update_state(control, car);
//控制器关闭判断
shutdown_controller();
ROS_INFO("--------------------------------------");
}
}
//控制启停函数
void node_control() {
ros::Rate loop_rate(freq);
Marker_set();//设置Marker属性
//设置tf坐标转换
tf::TransformBroadcaster br;
tf::Transform transform;
tf::Quaternion q;
while (ros::ok()) {
transform.setOrigin(tf::Vector3(car.x, car.y, 0));
q.setRPY(0, 0, car.yaw);
transform.setRotation(q);
br.sendTransform(tf::StampedTransform(transform, ros::Time::now(), "map", "car"));
ros::spinOnce();
LQR_track();
loop_rate.sleep();
}
}
void PUB(){
visual_state_pose.x = car.x; visual_state_pose.y = car.y;
actual_pose.x = car.x; actual_pose.y = car.y; actual_pose.theta = car.yaw;
vel_msg.linear.x = control.v; vel_msg.angular.z = control.v*tan(control.kesi)/L;//横摆角速度为w = v*tan(kesi)/L
visual_state_trajectory.points.push_back(visual_state_pose);//visualization_msgs::Marker为一个容器,所以现需要向里面push_back结构体,再发布
visual_state_pub.publish(visual_state_trajectory);//发布虚拟轨迹
vel_pub.publish(vel_msg);//发布速度
actual_state_pub.publish(actual_pose);//发布位姿
}
void shutdown_controller(){
if(action == "the car has reached the goal!"){
temp+=1;
if(temp ==50){
ROS_WARN("shutdown the LQR controller!");
temp = 0;
ros::shutdown();
}
}
}
void Marker_set(){
//设置消息类型参数
visual_state_trajectory.header.frame_id = "map";
visual_state_trajectory.header.stamp = ros::Time::now();
visual_state_trajectory.action = visualization_msgs::Marker::ADD;
visual_state_trajectory.ns = "LQR";
//设置点的属性
visual_state_trajectory.id = 0;
visual_state_trajectory.type = visualization_msgs::Marker::POINTS;
visual_state_trajectory.scale.x = 0.02;
visual_state_trajectory.scale.y = 0.02;
visual_state_trajectory.color.r = 1.0;
visual_state_trajectory.color.a = 1.0;
}
U v_and_kesi_limit(U control_value){
if(control_value.v>=v_max)//速度限幅
{
control_value.v = v_max;
ROS_WARN("The calculated value may be inaccurate ");
}
else if(control_value.v<=-v_max){
control_value.v = -v_max;
ROS_WARN("The calculated value may be inaccurate ");
}
if(control_value.kesi>=pi/2)//前轮转角限幅
{
control_value.kesi = pi/2;
ROS_WARN("The calculated value may be inaccurate ");
}
else if(control_value.kesi<=-pi/2){
control_value.kesi = -pi/2;
ROS_WARN("The calculated value may be inaccurate ");
}
return control_value;
}
};
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
ros::init(argc, argv, "LQR_node");
ros::NodeHandle n;
ros::NodeHandle n_prv("~");
n_prv.param<double>("freq",freq,20);
n_prv.param<double>("L",L,0.2);
n_prv.param<double>("V_DESIRED",V_DESIRED,0.5);
n_prv.param<double>("v_max",v_max,1.0);
n_prv.param<double>("initial_x",initial_x,0.0);
n_prv.param<double>("initial_y",initial_y,2.0);
n_prv.param<double>("initial_yaw",initial_yaw,0.0);
n_prv.param<double>("initial_v",initial_v,0.0);
n_prv.param<double>("initial_kesi",initial_kesi,0.1);
n_prv.param<double>("slow_LEVE1_DISTANCE",slow_LEVE1_DISTANCE,5.0);
n_prv.param<double>("slow_LEVE2_DISTANCE",slow_LEVE2_DISTANCE,2.0);
n_prv.param<double>("goal_tolerance_DISTANCE",goal_tolerance_DISTANCE,0.1);
n_prv.param<double>("slow_LEVE1_V",slow_LEVE1_V,0.35);
n_prv.param<double>("slow_LEVE2_V",slow_LEVE2_V,0.15);
n_prv.param<bool>("limit_v_and_kesi",limit_v_and_kesi,false);
n_prv.param("Q_set",Q_set,Q_set);
n_prv.param("R_set",R_set,R_set);
LQR_node* node = new LQR_node(n);
node->node_control();
return (0);
}
2.实验程序(LQR_node_world.cpp)
这个实验程序跟仿真程序很类似,只不过不再用运动学模型计算小车位姿,而是采样得到小车位姿,所以增加了一个订阅接口(odom_sub)
跟踪功能实现步骤:
1.获取小车当前位姿和路径点,在while(ros::ok())函数下面ros::spinOnce()阶段订阅回调函数odomcallback和addpointcallback时完成
2.搜索路径点
3.获取路径点信息,构造期望控制量
4.先进行一次减速判断,确定纵向期望速度v_r,和机器人当前动作:tracking或reached the goal
5.构造权重矩阵,从launch文件的参数Q=[],R=[]导入
6.使用LQR控制器,计算速度和前轮转角,其中有限幅过程
7.发布话题,其中有角速度的计算
8.判断是否需要关闭控制器,如果到达终点就关闭
9.loop_rate.sleep(),结束一次循环,准备开始下一次跟踪工作
然后也去除了程序中发布map到小车的tf,定位之后rviz里面会有tf的,所以这里不再需要。
LQR_node_world.cpp
#include <ros/ros.h>
#include <iostream>
#include "LQR_track/LQR.h"
#include <vector>
#include "ros/node_handle.h"
#include "ros/publisher.h"
#include "tf/LinearMath/Quaternion.h"
#include "tf/transform_broadcaster.h"
#include "visualization_msgs/Marker.h"
#include <nav_msgs/Path.h>
#include <geometry_msgs/Twist.h>
#include <geometry_msgs/Pose2D.h>
#include <nav_msgs/Odometry.h>
#include <tf/tf.h>
#include <tf/transform_broadcaster.h>
using namespace std;
double freq,L,V_DESIRED;//采样频率,车辆轴距,期望速度
double v_max;//最大速度
bool limit_v_and_kesi;//是否限幅(对于阿卡曼转向车辆需要限幅,全向车随意)
std::vector<double> Q_set;//Q矩阵
std::vector<double> R_set;//R矩阵
double slow_LEVE1_DISTANCE,slow_LEVE2_DISTANCE,slow_LEVE1_V,slow_LEVE2_V,goal_tolerance_DISTANCE;//定义二级减速距离和速度
#define pi acos(-1)
#define T 1/freq //采样时间
class Path {
private:
vector<waypoint> path;
public:
//添加新的路径点
void Add_new_point(waypoint& p)
{
path.push_back(p);
}
void Add_new_point(vector<waypoint>& p)
{
path = p;
}
//路径点个数
unsigned int Size()
{
return path.size();
}
//获取路径点
waypoint Get_waypoint(int index)
{
waypoint p;
p.ID = path[index].ID;
p.x = path[index].x;
p.y = path[index].y;
p.yaw = path[index].yaw;
return p;
}
vector<waypoint> Get_waypoints(){
return path;
}
// 搜索路径点, 将小车到起始点的距离与小车到每一个点的距离对比,找出最近的目标点索引值
int Find_target_index(vehicleState state)
{
double min = abs(sqrt(pow(state.x - path[0].x, 2) + pow(state.y - path[0].y, 2)));
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < path.size(); i++)
{
double d = abs(sqrt(pow(state.x - path[i].x, 2) + pow(state.y - path[i].y, 2)));
if (d < min)
{
min = d;
index = i;
}
}
//索引到终点前,当(机器人与下一个目标点的距离L_1)小于(当前目标点到下一个目标点距离L_)时,索引下一个目标点
if ((index + 1) < path.size())
{
double current_x = path[index].x; double current_y = path[index].y;
double next_x = path[index + 1].x; double next_y = path[index + 1].y;
double L_ = abs(sqrt(pow(next_x - current_x, 2) + pow(next_y - current_y, 2)));
double L_1 = abs(sqrt(pow(state.x - next_x, 2) + pow(state.y - next_y, 2)));
//ROS_INFO("L is %f,Lf is %f",L,Lf);
if (L_1 < L_)
{
index += 1;
}
}
return index;
}
};
class LQR_node {
private:
//car
vehicleState car;//小车状态
U control;//小车控制量[v,kesi]
double Q[3];
double R[2];
int lastIndex;//最后一个点索引值
waypoint lastPoint;//最后一个点信息
string action;//小车目前动作:跟踪或跟踪完成(tracking or reach goal!)
//ROS
ros::Subscriber path_sub;//订阅路径,消息类型为nav_msgs::Path
ros::Subscriber odom_sub;//订阅小车当前位姿信息,消息类型为nav_msgs::Odometry
ros::Publisher vel_pub;//发布速度信息,消息类型为geometry_msgs::Twist
ros::Publisher actual_state_pub;//发布小车实际位姿,消息类型为geometry_msgs::Pose2D
ros::Publisher visual_state_pub;//向rviz发布小车虚拟轨迹,消息类型为visualization_msgs::Marker
geometry_msgs::Point visual_state_pose;
visualization_msgs::Marker visual_state_trajectory;
geometry_msgs::Pose2D actual_pose;
geometry_msgs::Twist vel_msg;
geometry_msgs::Pose2D pose2d_robot;
int temp;//计数,达到终点时,用于判断控制器是否需要关闭
public:
LQR* controller;
Path* path;
LQR_node(ros::NodeHandle& nh)//初始化中添加轨迹、小车初始位姿
{
controller = new LQR();
path = new Path();
//ROS:
path_sub = nh.subscribe("path",10,&LQR_node::addpointcallback,this);
vel_pub = nh.advertise<geometry_msgs::Twist>("cmd_vel",10);
visual_state_pub = nh.advertise<visualization_msgs::Marker>("visualization_pose",10);
actual_state_pub = nh.advertise<geometry_msgs::Pose2D>("LQR_pose",10);
odom_sub = nh.subscribe<nav_msgs::Odometry>("odom_tf", 1, &LQR_node::odomcallback, this);
//robot state initialize:
//car.x = car.y = car.yaw = car.v = car.kesi = 0;
action = "the car is tracking!!";
}
~LQR_node() {
delete(controller);
delete(path);
}
void odomcallback(const nav_msgs::Odometry::ConstPtr& odom_value)
{
pose2d_robot.x = odom_value->pose.pose.position.x;
pose2d_robot.y = odom_value->pose.pose.position.y;
pose2d_robot.theta = tf::getYaw(odom_value->pose.pose.orientation);
car.x = pose2d_robot.x;
car.y = pose2d_robot.y;
car.yaw = pose2d_robot.theta;
}
void addpointcallback(const nav_msgs::Path::ConstPtr& msg){
vector<waypoint> waypoints;
for(int i=0;i<msg->poses.size();i++){
waypoint waypoint;
//ROS_INFO("THE PATH[%d]'s ID is %d",i,msg->poses[i].header.seq);
waypoint.ID = msg->poses[i].header.seq;
waypoint.x = msg->poses[i].pose.position.x;
waypoint.y = msg->poses[i].pose.position.y;
//获取角度
double roll,pitch,yaw;
tf::Quaternion quat;
tf::quaternionMsgToTF(msg->poses[i].pose.orientation, quat);
tf::Matrix3x3(quat).getRPY(roll, pitch, yaw);
waypoint.yaw = yaw;
waypoints.push_back(waypoint);
}
path->Add_new_point(waypoints);//路径点vector数组传到path类中
lastIndex = path->Size() - 1;
lastPoint = path->Get_waypoint(lastIndex);
}
double slow_judge(double distance) {
if (distance>=slow_LEVE2_DISTANCE&&distance <= slow_LEVE1_DISTANCE) {
return slow_LEVE1_V;
}
else if (distance>=goal_tolerance_DISTANCE&&distance < slow_LEVE2_DISTANCE) {
return slow_LEVE2_V;
}
else if (distance < goal_tolerance_DISTANCE) {
action = "the car has reached the goal!";
return 0.0;
}
else
{
return V_DESIRED;
}
}
//控制器流程
/*步骤:
1.获取小车当前位姿和路径点,在while(ros::ok())函数下面ros::spinOnce()阶段订阅回调函数odomcallback和addpointcallback时完成
2.搜索路径点
3.获取路径点信息,构造期望控制量
4.先进行一次减速判断,确定纵向期望速度v_r,和机器人当前动作:tracking或reached the goal
5.构造权重矩阵,从launch文件的参数Q=[],R=[]导入
6.使用LQR控制器,计算速度和前轮转角,其中有限幅过程
7.发布话题,其中有角速度的计算
8.判断是否需要关闭控制器,如果到达终点就关闭
9.loop_rate.sleep(),结束一次循环,准备开始下一次。
*/
void LQR_track() {
U U_r;
waypoint Point;
double K;
//ROS_INFO("path size is: %d",path->Size());
if(path->Size()!=0){
//搜索路径点
int target_index = path->Find_target_index(car);
//ROS_INFO("target index is : %d", target_index);
//获取路径点信息,构造期望控制量
Point = path->Get_waypoint(target_index);//获取x,y
//ROS_INFO("waypoint information is x:%f,y:%f,yaw:%f", Point.x, Point.y, Point.yaw);
K = cal_K(path->Get_waypoints(),target_index);//计算曲率
//减速判断
double kesi = atan2(L * K, 1);
double v_distance = abs(sqrt(pow(car.x - lastPoint.x, 2) + pow(car.y - lastPoint.y, 2)));
//ROS_INFO("the distance is %fn", v_distance);
U_r.v = slow_judge(v_distance);U_r.kesi = kesi;
ROS_INFO("%s",action.c_str());//机器人动作
//ROS_INFO("the desired v is: %f,the desired kesi is: %f", U_r.v,U_r.kesi);
//权重矩阵
for(int q =0;q<Q_set.size();q++)Q[q] = Q_set[q];
for(int r =0;r<R_set.size();r++)R[r] = R_set[r];
if(Q[0]>=R[0]||Q[1]>=R[1])
ROS_WARN("Q >= R, the calculation result may be abnormal,please set R < Q ");
//使用LQR控制器,
controller->initial(L, T, car, Point, U_r, Q, R);//初始化控制器
control = controller->cal_vel();//计算输入[v, kesi]
if(U_r.v==0)control.v = 0;//判断,期望速度为0,则机器人停下
if(limit_v_and_kesi)control = v_and_kesi_limit(control);//速度和前轮转角限幅
ROS_INFO("the speed is: %f,the kesi is: %f", control.v, control.kesi);
//ROS_INFO("the car position is x: %f, y: %f", car.x, car.y);
//话题发布
PUB();
//控制器关闭判断
shutdown_controller();
ROS_INFO("--------------------------------------");
}
}
//控制启停函数
void node_control() {
ros::Rate loop_rate(freq);
Marker_set();//设置Marker属性
while (ros::ok()) {
ros::spinOnce();
LQR_track();
loop_rate.sleep();
}
}
void PUB(){
visual_state_pose.x = car.x; visual_state_pose.y = car.y;
actual_pose.x = car.x; actual_pose.y = car.y; actual_pose.theta = car.yaw;
vel_msg.linear.x = control.v; vel_msg.angular.z = control.v*tan(control.kesi)/L;//横摆角速度为w = v*tan(kesi)/L
visual_state_trajectory.points.push_back(visual_state_pose);//visualization_msgs::Marker为一个容器,所以现需要向里面push_back结构体,再发布
visual_state_pub.publish(visual_state_trajectory);//发布虚拟轨迹
vel_pub.publish(vel_msg);//发布速度
actual_state_pub.publish(actual_pose);//发布位姿
}
void shutdown_controller(){
if(action == "the car has reached the goal!"){
temp+=1;
if(temp ==50){
ROS_WARN("shutdown the LQR controller!");
temp = 0;
ros::shutdown();
}
}
}
void Marker_set(){
//设置消息类型参数
visual_state_trajectory.header.frame_id = "map";
visual_state_trajectory.header.stamp = ros::Time::now();
visual_state_trajectory.action = visualization_msgs::Marker::ADD;
visual_state_trajectory.ns = "LQR";
//设置点的属性
visual_state_trajectory.id = 0;
visual_state_trajectory.type = visualization_msgs::Marker::POINTS;
visual_state_trajectory.scale.x = 0.02;
visual_state_trajectory.scale.y = 0.02;
visual_state_trajectory.color.r = 1.0;
visual_state_trajectory.color.a = 1.0;
}
U v_and_kesi_limit(U control_value){
if(control_value.v>=v_max)//速度限幅
{
control_value.v = v_max;
ROS_WARN("The calculated value may be inaccurate ");
}
else if(control_value.v<=-v_max){
control_value.v = -v_max;
ROS_WARN("The calculated value may be inaccurate ");
}
if(control_value.kesi>=pi/2)//前轮转角限幅
{
control_value.kesi = pi/2;
ROS_WARN("The calculated value may be inaccurate ");
}
else if(control_value.kesi<=-pi/2){
control_value.kesi = -pi/2;
ROS_WARN("The calculated value may be inaccurate ");
}
return control_value;
}
};
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
ros::init(argc, argv, "LQR_node");
ros::NodeHandle n;
ros::NodeHandle n_prv("~");
n_prv.param<double>("freq",freq,20);
n_prv.param<double>("L",L,0.2);
n_prv.param<double>("V_DESIRED",V_DESIRED,0.5);
n_prv.param<double>("v_max",v_max,1.0);
n_prv.param<double>("slow_LEVE1_DISTANCE",slow_LEVE1_DISTANCE,5.0);
n_prv.param<double>("slow_LEVE2_DISTANCE",slow_LEVE2_DISTANCE,2.0);
n_prv.param<double>("goal_tolerance_DISTANCE",goal_tolerance_DISTANCE,0.1);
n_prv.param<double>("slow_LEVE1_V",slow_LEVE1_V,0.35);
n_prv.param<double>("slow_LEVE2_V",slow_LEVE2_V,0.15);
n_prv.param<bool>("limit_v_and_kesi",limit_v_and_kesi,false);
n_prv.param("Q_set",Q_set,Q_set);
n_prv.param("R_set",R_set,R_set);
LQR_node* node = new LQR_node(n);
node->node_control();
return (0);
}
3.实验中小车的位姿获取(odom_listen_from_tf.cpp)
可能每个人的实验平台上定位话题都不一致,我这里干脆写一个位姿获取程序吧,就是监听map到base_link或者base_footprint的坐标转换关系输出就好了,输出话题为odom_tf,消息类型为nav_msgs::Odometry,这个话题就是LQR_node_world.cpp中订阅得那个小车位姿。
odom_listen_from_tf.cpp
#include <ros/ros.h>
#include <tf2/LinearMath/Vector3.h>
#include <tf2/LinearMath/Quaternion.h>
#include <tf2/LinearMath/Matrix3x3.h>
#include <tf2_ros/transform_listener.h>
#include <geometry_msgs/TransformStamped.h>
#include <nav_msgs/Odometry.h>
std::string base_frame;
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
ros::init(argc, argv, "odom_listener");
ros::NodeHandle n;
ros::NodeHandle nh("~");
tf2_ros::Buffer tfBuffer;
tf2_ros::TransformListener odomListener(tfBuffer);
nh.param<std::string>("base_frame", base_frame, "base_link");
ros::Publisher odom_pub = n.advertise<nav_msgs::Odometry>("odom_tf",10);
ros::Rate r(20);
while(ros::ok()){
geometry_msgs::TransformStamped transform;
try{
transform = tfBuffer.lookupTransform("map", base_frame, ros::Time(0));
}
catch (tf2::TransformException &ex){
ROS_ERROR("%s", ex.what());
ros::Duration(1.0).sleep();
continue;
}
tf2::Vector3 translation;
translation.setValue(transform.transform.translation.x,
transform.transform.translation.y,
transform.transform.translation.z);
tf2::Quaternion rotation;
rotation.setValue(transform.transform.rotation.x,
transform.transform.rotation.y,
transform.transform.rotation.z,
transform.transform.rotation.w);
tf2::Matrix3x3 m(rotation);
double roll, pitch, yaw;
m.getRPY(roll, pitch, yaw);
/*ROS_INFO("n=== Got Transform ===n"
" Translationn"
" x : %fn y : %fn z : %fn"
" Quaternionn"
" x : %fn y : %fn z : %fn w : %fn"
" RPYn"
" R : %fn P : %fn Y : %f",
translation.x(), translation.y(), translation.z(),
rotation.x(), rotation.y(), rotation.z(), rotation.w(),
roll, pitch, yaw);*/
nav_msgs::Odometry odom;
odom.header.stamp = ros::Time::now();
odom.header.frame_id = "odom";
odom.pose.pose.position.x = translation.x();
odom.pose.pose.position.y = translation.y();
odom.pose.pose.position.z = translation.z();
odom.pose.pose.orientation.x = rotation.x();
odom.pose.pose.orientation.y = rotation.y();
odom.pose.pose.orientation.z = rotation.z();
odom.pose.pose.orientation.w = rotation.w();
odom.child_frame_id = base_frame;
odom.twist.twist.linear.x = 0;
odom.twist.twist.linear.y = 0;
odom.twist.twist.linear.z = 0;
odom_pub.publish(odom);
ros::spinOnce();
r.sleep();
}
return 0;
}
四、编译全部的文件
别忘了在target_link_libraries里面加上之前生成的库名字LQR_LIBRARIES:
###########
## Build ##
###########
include_directories(
include
${catkin_INCLUDE_DIRS}
${Eigen_INCLUDE_DIRS}
)
add_library(LQR_LIBRARIES
/home/dlrobot/dlrobot_robot/src/617_robot/lqr_track/include/LQR_track/Tool.h
/home/dlrobot/dlrobot_robot/src/617_robot/lqr_track/include/LQR_track/trajectory.h
/home/dlrobot/dlrobot_robot/src/617_robot/lqr_track/include/LQR_track/LQR.h
/home/dlrobot/dlrobot_robot/src/617_robot/lqr_track/src/Tool.cpp
/home/dlrobot/dlrobot_robot/src/617_robot/lqr_track/src/trajectory.cpp
/home/dlrobot/dlrobot_robot/src/617_robot/lqr_track/src/LQR.cpp
)
target_link_libraries(LQR_LIBRARIES ${catkin_LIBRARIES})
link_directories(
${catkin_LIB_DIRS}
${Eigen_LIB_DIRS}
)
add_executable(LQR_node src/LQR_node.cpp)
add_dependencies(LQR_node ${${PROJECT_NAME}_EXPORTED_TARGETS} ${catkin_EXPORTED_TARGETS})
target_link_libraries(LQR_node ${catkin_LIBRARIES} LQR_LIBRARIES)
add_executable(path_planning src/path_planning.cpp)
add_dependencies(path_planning ${${PROJECT_NAME}_EXPORTED_TARGETS} ${catkin_EXPORTED_TARGETS})
target_link_libraries(path_planning ${catkin_LIBRARIES} LQR_LIBRARIES)
add_executable(lqr_odom_listen src/odom_listen_from_tf.cpp)
add_dependencies(lqr_odom_listen ${${PROJECT_NAME}_EXPORTED_TARGETS} ${catkin_EXPORTED_TARGETS})
target_link_libraries(lqr_odom_listen ${catkin_LIBRARIES} LQR_LIBRARIES)
add_executable(LQR_node_world src/LQR_node_world.cpp)
add_dependencies(LQR_node_world ${${PROJECT_NAME}_EXPORTED_TARGETS} ${catkin_EXPORTED_TARGETS})
target_link_libraries(LQR_node_world ${catkin_LIBRARIES} LQR_LIBRARIES)五、配置rviz文件
rviz中需要显示tf坐标变换、marker(用于显示小车实际轨迹)、path(用于显示参考路径)、map(用于显示地图,仿真中不需要)。
在最后的完整程序链接中,launch文件已经包含了rviz的启动,可以开启launch去看一下rviz中配置了啥。
六、配置launch文件
打开底盘雷达功能和定位功能可以不从该功能包launch文件中启动,但必须从功能包中开启的有三个:
path_planning.launch
trajectory_type参数是根据trajectory.cpp里面写的三种轨迹名字决定的,默认写了三种分别是line、wave1、wave2。
<launch>
<node pkg="lqr_track" type="path_planning" name="path_planning" output="screen">
<param name="x_start" value="0.0"/>
<param name="y_start" value="-0.25"/>
<param name="trajectory_type" value="line"/><!--choose the trajectory type default:line,wave1,wave2-->
<!--If you need to add a custom path, please see trajectory.h-->
<param name="limit_x" value="4.0"/>
<param name="limit_y" value="0.0"/>
</node>
<!--rviz-->
<!--node name="path_rviz" pkg="rviz" type="rviz" required="true"
args="-d $(find lqr_track)/rviz/path_show.rviz">
</node-->
</launch>
LQR_track.launch
里面有车辆信息、初始化位姿、控制器参数配置,注释也写了相关的解释或者注意事项
<launch>
<node pkg="lqr_track" type="LQR_node" name="LQR_node" output="screen">
<!--Basic vehicle information--><!--kesi is the Vehicle front wheel deflection angle-->
<param name="L" value="0.2"/><!--Vehicle wheelbase-->
<param name="V_DESIRED" value="0.5"/>
<param name="v_max" value="1.0"/>
<!--car initial state-->
<param name="initial_x" value="-0.127"/>
<param name="initial_y" value="-0.1474"/>
<param name="initial_yaw" value="0.0138"/>
<param name="initial_kesi" value="0.0"/>
<!--controller information-->
<param name="freq" value="20"/><!--control freq-->
<param name="slow_LEVE1_DISTANCE" value="4.0"/><!--First stage deceleration distance-->
<param name="slow_LEVE2_DISTANCE" value="1.0"/><!--Secondary deceleration distance-->
<param name="goal_tolerance_DISTANCE" value="0.1"/><!--Tracking stop distance-->
<param name="slow_LEVE1_V" value="0.5"/>
<param name="slow_LEVE2_V" value="0.15"/>
<param name="limit_v_and_kesi" value="true"/><!--If it is an akaman steering car, it must be limited. If it is an omni-directional car, it is optional-->
<rosparam param="Q_set">[1.0,1.0,1.0]</rosparam><!--State weight matrix Q = diag{Q1,Q2,Q3},please set Q<R-->
<rosparam param="R_set">[5.0,5.0]</rosparam><!--Control input weight matrix R = diag{R1,R2},please set Q<R-->
</node>
<!--rviz-->
<node name="lqr_track_rviz" pkg="rviz" type="rviz" required="true" args="-d $(find lqr_track)/rviz/track.rviz"/>
</launch>
LQR_track_world.launch
在这个launch里面,为了方便采用通用接口获取小车位姿信息,写了一个lqr_odom_listen节点监听map->base_link(或base_footprint)的坐标转换,至于是base_link还是base_footprint需要自己去看一下小车模型,并在launch中修改一下。
<launch>
<node pkg="lqr_track" type="LQR_node_world" name="LQR_node_world" output="screen">
<!--Basic vehicle information--><!--kesi is the Vehicle front wheel deflection angle-->
<param name="L" value="0.24"/><!--Vehicle wheelbase-->
<param name="V_DESIRED" value="0.5"/>
<param name="v_max" value="1.0"/>
<!--controller information-->
<param name="freq" value="20"/><!--control freq-->
<param name="slow_LEVE1_DISTANCE" value="4.0"/><!--First stage deceleration distance-->
<param name="slow_LEVE2_DISTANCE" value="1.0"/><!--Secondary deceleration distance-->
<param name="goal_tolerance_DISTANCE" value="0.2"/><!--Tracking stop distance-->
<param name="slow_LEVE1_V" value="0.5"/>
<param name="slow_LEVE2_V" value="0.15"/>
<param name="limit_v_and_kesi" value="true"/><!--If it is an akaman steering car, it must be limited. If it is an omni-directional car, it is optional-->
<rosparam param="Q_set">[1.0,1.0,1.0]</rosparam><!--State weight matrix Q = diag{Q1,Q2,Q3},please set Q<R-->
<rosparam param="R_set">[4.0,4.0]</rosparam><!--Control input weight matrix R = diag{R1,R2},please set Q<R-->
</node>
<node pkg="lqr_track" type="lqr_odom_listen" name="lqr_odom_listen" output="screen">
<parma name="base_frame" value="base_link"/> <!--这个地方需要根据自己小车的底盘坐标系名称进行修改-->
</node>
</launch>
仿真结果
本项目一共进行了三次仿真:
一、直线仿真 trajectory_type = line
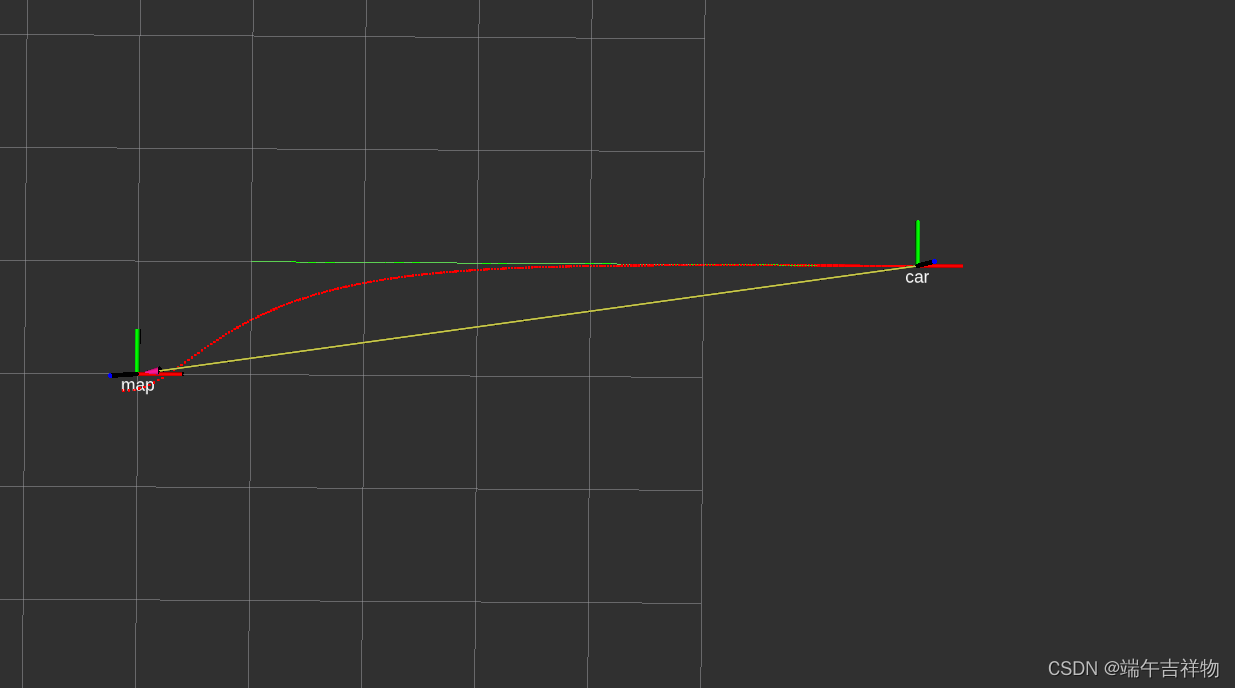
LQR_line_simulation
二、波浪线1仿真 trajectory_type = wave1
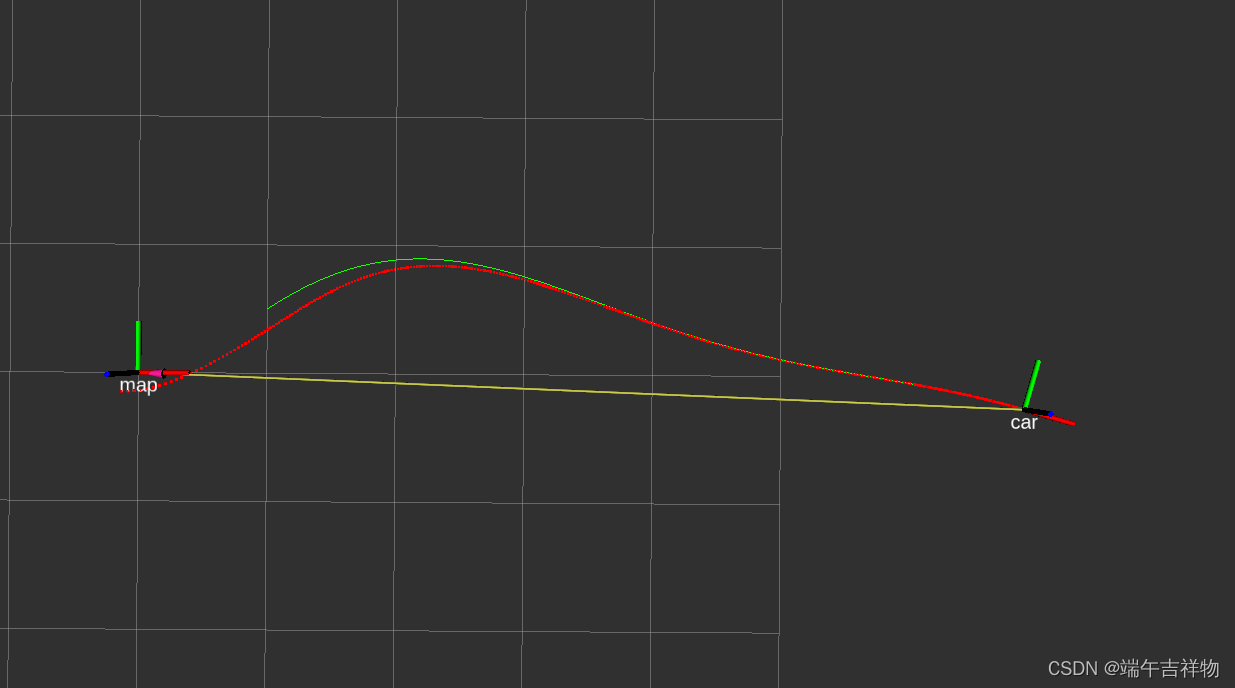
LQR_wave1_simulation
三、波浪线2仿真 trajectory_type = wave2
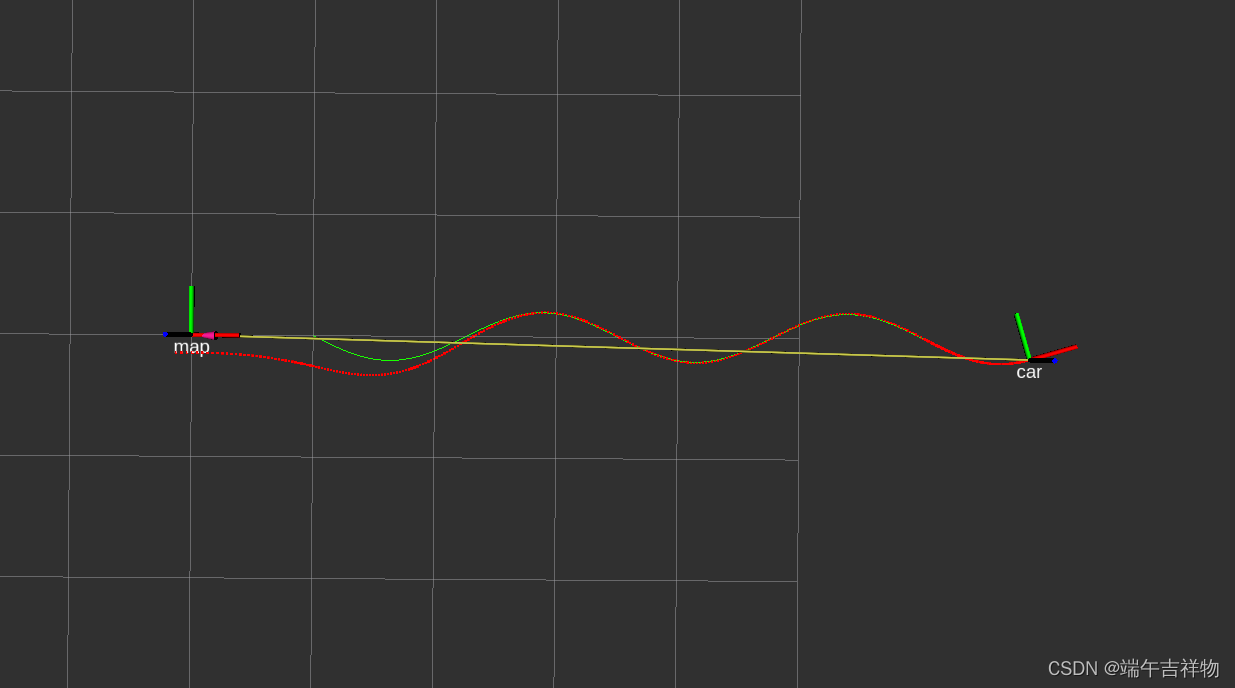
LQR_wave2_simulation
实验结果
实验流程:
1.打开机器人底盘、雷达,保证能接收到雷达数据
可以配置功能包中的launch/turn_on_base_and_ladiar.launch文件来同时启动地盘雷达2.开启机器人定位功能,保证有map到base_link(或base_footprint)的tf转换,
如果有cartographer的话,可以运行如下命令:roslaunch lqr_track carto_robot_localization.launch3.进行机器人定位工作,并前往路径起始点附近,别放在超过路径起始点一米以外,跟踪效果会变差,与控制器参数有关,如Q、P矩阵选取
4.roslaunch lqr_track LQR_track_world.launch
5.roslaunch lqr_track path_planning.launch

其中绿色为期望轨迹,红色为跟踪过程的实际轨迹,跟踪误差可能与车辆参数(如:前后轴距)或控制器参数有关。
具体实验情况如下:
line_track_experiment
完整程序
完整程序请见:Bitbucket
git clone到工作空间下,按照功能包中的README.md操作就好了
最后
以上就是害怕大船最近收集整理的关于LQR轨迹跟踪——基于ROS系统和全向车实验平台前言思路代码部署仿真结果实验结果完整程序的全部内容,更多相关LQR轨迹跟踪——基于ROS系统和全向车实验平台前言思路代码部署仿真结果实验结果完整程序内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复