文章目录
- 3.1音频数据流发送流程
- 3.2 发送中的编码、RTP打包
- 3.3 AudioSendStream类关系
- 3.4`webrtc::AudioSendStream` 创建和初始化
- 3.5 创建 `CreateChannels`
- 3.6 设置transport
- 3.7 音频数据包发送处理
- 3.7.1 音频数据采集
- 3.7.2 编码并添加到pacer队列
- 3.7.3 pacedSender发送RTP包
- 3.7.4 通过socket接口发送数据包
- 3.8 音频数据包的接收处理
- 3.8.1 从网络接收音频 RTP 包
- 3.8.2 音频 RTP 包异步插入 NetEQ
- 3.8.3 获取NetEQ音频包并解码播放
一个完整的音频发送涉及到音频采集、音频增强、混音、音频格式(采样率、声道数)以及编解码和RTP封包以及网络发送环节,在这一过程中WebRTC为了结构上清晰且解耦,对每一层进行了抽象,由于采集端数据是源源不断的,因而数据采集有一个单独的线程实现。
3.1音频数据流发送流程
音频发送流程涉及到的模块如下图所示
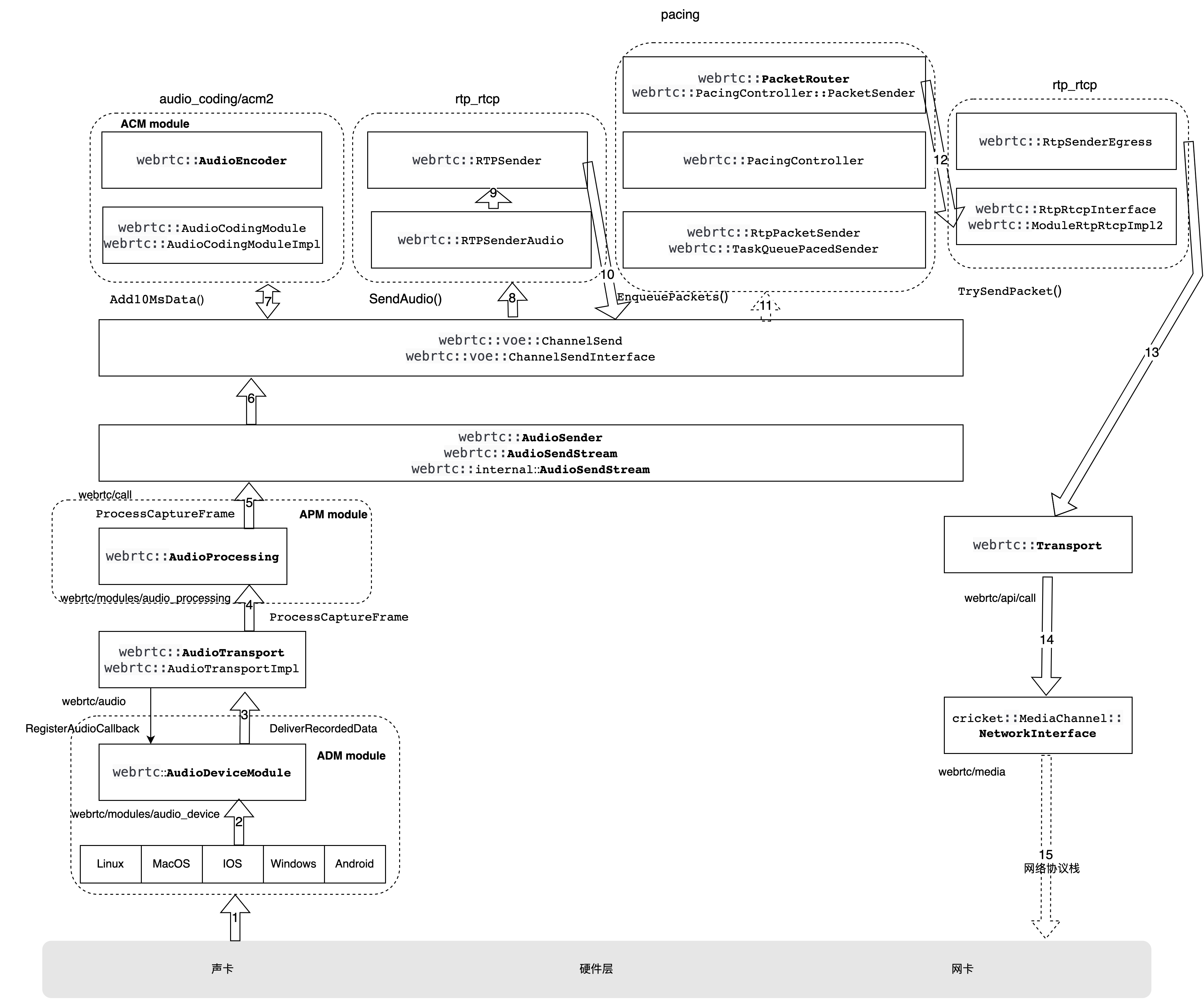
图3-1 WebRTC 音频发送数据流
3.2 发送中的编码、RTP打包
webrtc::AudioTransport 更像是个双向桥梁,既支持发送又支持接收,在发送之后还衔接了一个或多个数据流发送模块webrtc::AudioSendStream,其连接了数据采集和发送两端,但是发送端在发送之前还需要对数据降噪、去回声以及编解码和RTP打包,数据的降噪增强就是APM模块实现的,具体APM各个算法处理的细节可见《实时语音处理实践指南》,此小节看 webrtc::AudioSender/webrtc::AudioSendStream 中音频数据编码、RTP 包打包及发送控制的设计和实现。webrtc::AudioSender/webrtc::AudioSendStream 的实现位于 webrtc/audio/audio_send_stream.h / webrtc/audio/audio_send_stream.cc,相关的类层次结构如下图:
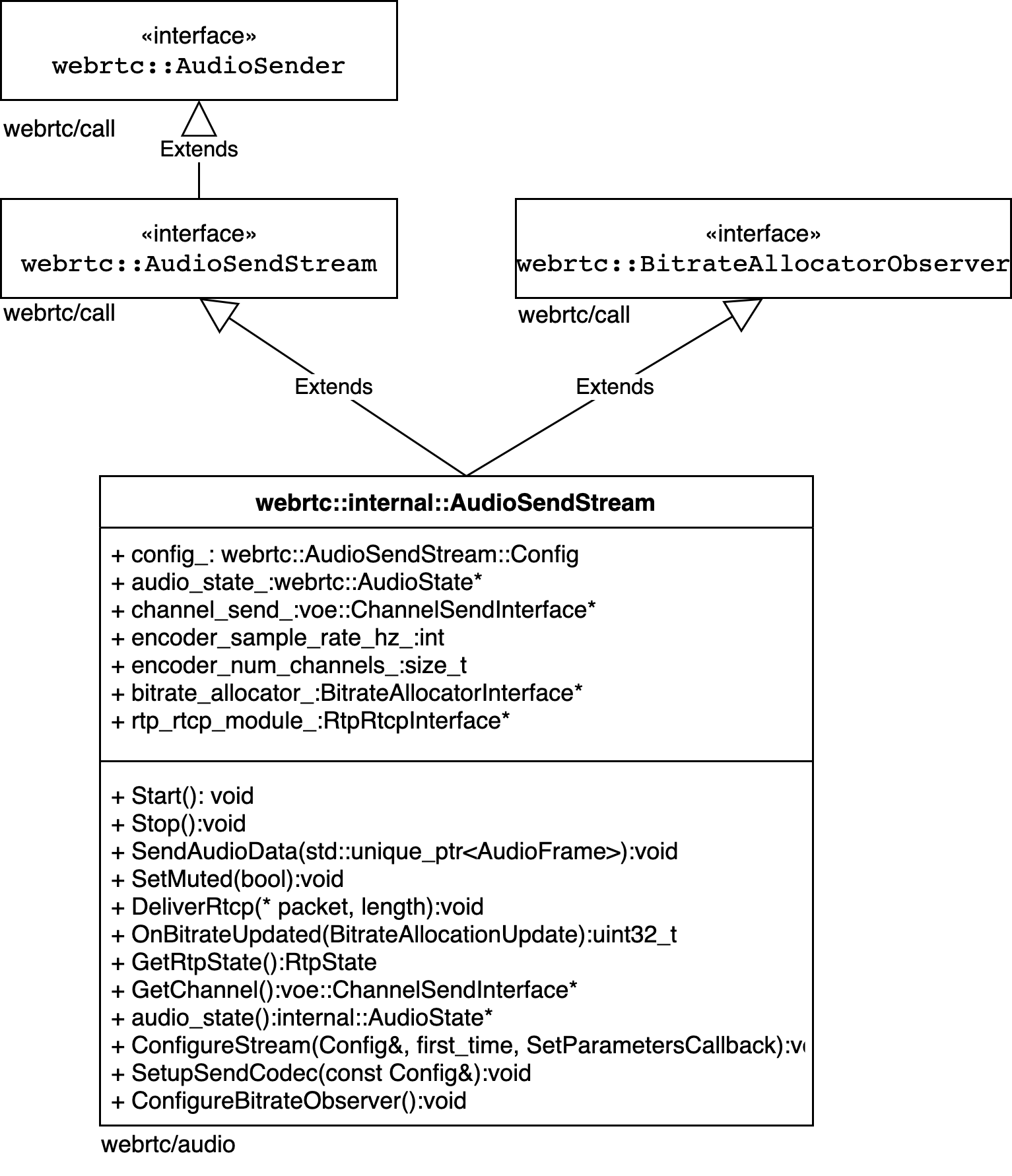
图3-2 SendSteam UML关系图
在交互式实时通信场景中,实时通信音频数据的编码发送不同于直播场景 RTMP 之类的推流方案不同,实时通信的实时性优先,而直播场景的可靠性优先,因而实时通信场景上层一般采用UDP/RTP协议,而直播推流场景采用RTMP/TCP协议,实时通信的实时性优先,并不意味着质量要求不高,基于UDP传输的丢包、抖动乱序都会带来通信质量的下降,因而在接收端WebRTC采用了NetEQ技术,而在发送端则需要根据探测到的网络条件、接收端发回来的 RTCP 包来动态调整控制编码码率。
webrtc::AudioSendStream则是实现发送流式音频的接口类,该类主要功能是已经罗列在UML图中的方法中了,主要有以下几点:
- 使用
bool SetupSendCodec(const Config& new_config)设置编码器类型,以及配置编码器编码目标比特率; - 设置SendStream的最大、最小以及默认优先比特率,及动态更新的分配码率。
webrtc::AudioSendStream的生命周期控制,由图中start()和stop()方法实现;- 对ADM模块采集数据做音量控制、降噪、编码;
- 接收和处理回传的RTCP包,调节编码比特率;
发送流程中的编码、rtp封包、pacing都是在webrtc::AudioSendStream 中实现的,数据流程由图中带编号的数字所示,ADM采集到的PCM数据通过webrtc::AudioTransport经过APM处理后传递给webrtc::AudioSendStream,webrtc::AudioSendStream内部先调用ACM模块编码,然后将编码后的比特流用rtp_rtcp模块打包接口打包成RTP打包,然后使用pacing模块做平滑和优先级发送控制,最后通过rtp_rtcp模块发送接口调 webrtc::Transport 将包交给网络传输层。
3.3 AudioSendStream类关系
webrtc::AudioSendStream 是一个接口类,在其派生类图X.2中webrtc:internal::AudioSendStream实现了音频数据处理流式结构, 音频数据流式处理结构定义搭建过程如下。 webrtc::AudioSendStream 和 webrtc::AudioTransport的关系如下UML所示,
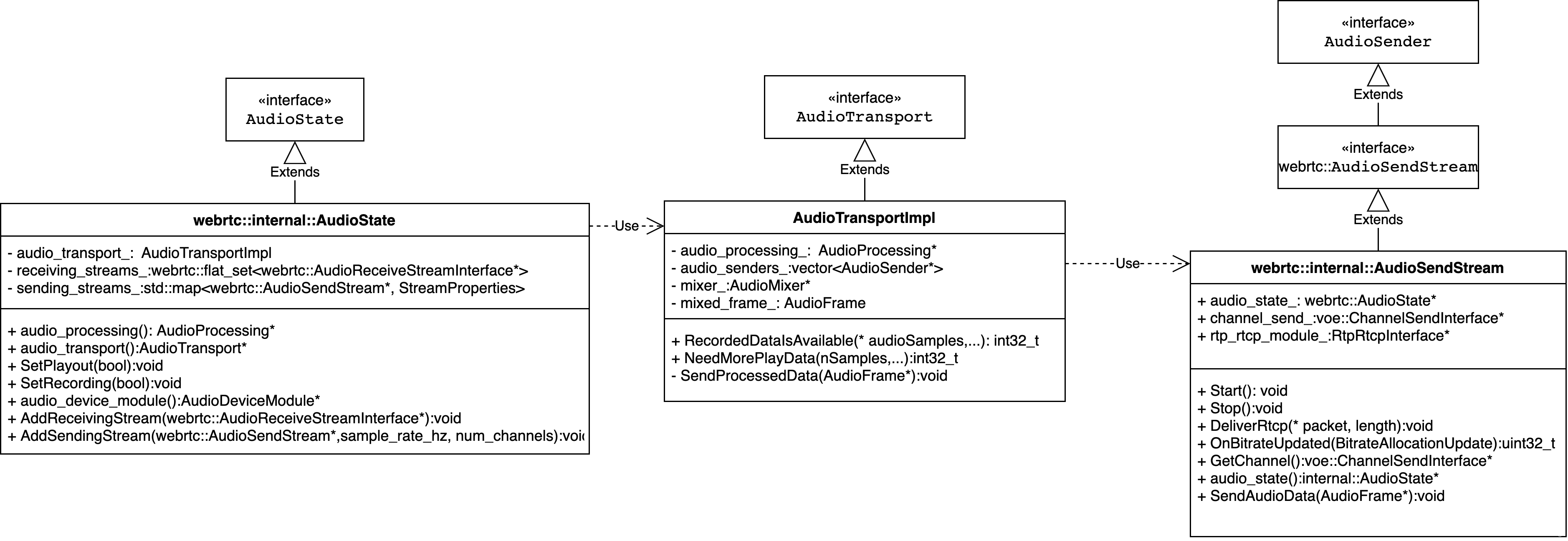
图3-3 AudioSendSteam UML图
该3-3图中AudioTransportImpl的audio_senders_的类型是vector类型的AduioSender,这也印证了前文说的一个AudioTransport可以对应多个AudioSendStream。 webrtc::AudioTransport采集到数据以后会调用RecordedDataIsAvailable方法,这个方法的实现如下:
// Not used in Chromium. Process captured audio and distribute to all sending
// streams, and try to do this at the lowest possible sample rate.
int32_t AudioTransportImpl::RecordedDataIsAvailable(
const void* audio_data,
const size_t number_of_frames,
const size_t bytes_per_sample,
const size_t number_of_channels,
const uint32_t sample_rate,
const uint32_t audio_delay_milliseconds,
const int32_t /*clock_drift*/,
const uint32_t /*volume*/,
const bool key_pressed,
uint32_t& /*new_mic_volume*/,
const int64_t
estimated_capture_time_ns) { // NOLINT: to avoid changing APIs
RTC_DCHECK(audio_data);
RTC_DCHECK_GE(number_of_channels, 1);
RTC_DCHECK_LE(number_of_channels, 2);
RTC_DCHECK_EQ(2 * number_of_channels, bytes_per_sample);
RTC_DCHECK_GE(sample_rate, AudioProcessing::NativeRate::kSampleRate8kHz);
// 100 = 1 second / data duration (10 ms).
RTC_DCHECK_EQ(number_of_frames * 100, sample_rate);
RTC_DCHECK_LE(bytes_per_sample * number_of_frames * number_of_channels,
AudioFrame::kMaxDataSizeBytes);
int send_sample_rate_hz = 0;
size_t send_num_channels = 0;
bool swap_stereo_channels = false;
{
MutexLock lock(&capture_lock_);
send_sample_rate_hz = send_sample_rate_hz_;
send_num_channels = send_num_channels_;
swap_stereo_channels = swap_stereo_channels_;
}
std::unique_ptr<AudioFrame> audio_frame(new AudioFrame());
InitializeCaptureFrame(sample_rate, send_sample_rate_hz, number_of_channels,
send_num_channels, audio_frame.get());
voe::RemixAndResample(static_cast<const int16_t*>(audio_data),
number_of_frames, number_of_channels, sample_rate,
&capture_resampler_, audio_frame.get());
ProcessCaptureFrame(audio_delay_milliseconds, key_pressed,
swap_stereo_channels, audio_processing_,
audio_frame.get());
audio_frame->set_absolute_capture_timestamp_ms(estimated_capture_time_ns /
1000000);
RTC_DCHECK_GT(audio_frame->samples_per_channel_, 0);
if (async_audio_processing_)
async_audio_processing_->Process(std::move(audio_frame));
else
SendProcessedData(std::move(audio_frame));
return 0;
}
RecordedDataIsAvailable()方法会挨个调用audio_senders_向量中的每个 webrtc::internal::AudioSendStream 的SendAudioData()方法,SendAudioData()的作用是调用合适的编码器对数据进行编码和发送编码后的比特流数据,这意味着可以把录制的一份数据使用不同的编码器编码以及使用不同发送控制策略进行发送,如视频会议中使用UDP协议传输RTP协议的包,也可以是直播推流中的TCP协议传输RTMP协议的包,图3-3中显示了这两个类的关系和这两个核心API,这里有个问题,就是audio_senders_是何时被设置进webrtc::AudioTransport的,这是在 webrtc::AudioSendStream 的生命周期函数 Start() 被调用时执行,这个添加的过程大体如下:
//webrtc/audio/audio_transport_impl.cc
#0 webrtc::AudioTransportImpl::UpdateAudioSenders(std::vector<webrtc::AudioSender*, std::allocator<webrtc::AudioSender*> >, int, unsigned long) ()
//webrtc/audio/audio_state.cc
#1 webrtc::internal::AudioState::UpdateAudioTransportWithSendingStreams() ()
//webrtc/audio/audio_state.cc
#2 webrtc::internal::AudioState::AddSendingStream(webrtc::AudioSendStream*, int, unsigned long) ()
webrtc/audio/audio_send_stream.cc:
#3 webrtc::internal::AudioSendStream::Start() ()
webrtc::AudioSendStream 将其自身加进 webrtc::AudioState,webrtc::AudioState 把新加的 webrtc::AudioSendStream 和之前已经添加的 webrtc::AudioSendStream 通过UpdateAudioSenders 添加到webrtc::AudioTransport里。如果新添加的 webrtc::AudioSendStream 是第一个 webrtc::AudioSendStream,则webrtc::AudioState 还将初始化设备并启动录音。
3.4webrtc::AudioSendStream 创建和初始化
webrtc::AudioSendStream 内部数据处理组件见图X.1所示,通过代码可知,创建 webrtc::AudioSendStream 对象,最终会调用 webrtc::voe::(anonymous namespace)::ChannelSend 对象创建一些关键对象/模块,并建立部分各个对象/模块之间的联系,调用过程如下图所示:

图3-4 webrtc::AudioSendStream 初始化函数调用栈
在WebRTC中,音频起始于VoiceEngine,而VoiceEngine中WebRTCVoiceMediaChannel是非常重要的对象,其调用 webrtc::Call 创建创建新的AudioSendStream对象,创建时传递的参数config_是 webrtc::AudioSendStream::Config 类型,包含与编解码、比特率、RTP、加密以及 webrtc::Transport 等配置。
webrtc::voe::(anonymous namespace)::ChannelSend 对象的构造函数创建了大多数和发送有关对象/模块,其构造函数如下:
Clock* clock,
TaskQueueFactory* task_queue_factory,
Transport* rtp_transport,
RtcpRttStats* rtcp_rtt_stats,
RtcEventLog* rtc_event_log,
FrameEncryptorInterface* frame_encryptor,
const webrtc::CryptoOptions& crypto_options,
bool extmap_allow_mixed,
int rtcp_report_interval_ms,
uint32_t ssrc,
rtc::scoped_refptr<FrameTransformerInterface> frame_transformer,
TransportFeedbackObserver* feedback_observer,
const FieldTrialsView& field_trials)
: ssrc_(ssrc),
event_log_(rtc_event_log),
_timeStamp(0), // This is just an offset, RTP module will add it's own
// random offset
input_mute_(false),
previous_frame_muted_(false),
_includeAudioLevelIndication(false),
rtcp_observer_(new VoERtcpObserver(this)),
feedback_observer_(feedback_observer),
//创建一个 `RtpPacketSenderProxy` 对象
rtp_packet_pacer_proxy_(new RtpPacketSenderProxy()),
retransmission_rate_limiter_(
new RateLimiter(clock, kMaxRetransmissionWindowMs)),
frame_encryptor_(frame_encryptor),
crypto_options_(crypto_options),
fixing_timestamp_stall_(
field_trials.IsDisabled("WebRTC-Audio-FixTimestampStall")),
encoder_queue_(task_queue_factory->CreateTaskQueue(
"AudioEncoder",
TaskQueueFactory::Priority::NORMAL)) {
//创建一个 webrtc::AudioCodingModule 对象
audio_coding_.reset(AudioCodingModule::Create(AudioCodingModule::Config()));
RtpRtcpInterface::Configuration configuration;
configuration.bandwidth_callback = rtcp_observer_.get();
configuration.transport_feedback_callback = feedback_observer_;
configuration.clock = (clock ? clock : Clock::GetRealTimeClock());
configuration.audio = true;
configuration.outgoing_transport = rtp_transport;
configuration.paced_sender = rtp_packet_pacer_proxy_.get();
configuration.event_log = event_log_;
configuration.rtt_stats = rtcp_rtt_stats;
configuration.retransmission_rate_limiter =
retransmission_rate_limiter_.get();
configuration.extmap_allow_mixed = extmap_allow_mixed;
configuration.rtcp_report_interval_ms = rtcp_report_interval_ms;
configuration.rtcp_packet_type_counter_observer = this;
configuration.local_media_ssrc = ssrc;
//建了一个 webrtc::ModuleRtpRtcpImpl2 对象
rtp_rtcp_ = ModuleRtpRtcpImpl2::Create(configuration);
rtp_rtcp_->SetSendingMediaStatus(false);
//创建 `webrtc::RTPSenderAudio` 对象
rtp_sender_audio_ = std::make_unique<RTPSenderAudio>(configuration.clock,
rtp_rtcp_->RtpSender());
// Ensure that RTCP is enabled by default for the created channel.
rtp_rtcp_->SetRTCPStatus(RtcpMode::kCompound);
int error = audio_coding_->RegisterTransportCallback(this);
RTC_DCHECK_EQ(0, error);
if (frame_transformer)
InitFrameTransformerDelegate(std::move(frame_transformer));
}
webrtc::voe::(anonymous namespace)::ChannelSend 对象的构造函数的主要完成的事项如下:
- 创建
RtpPacketSenderProxy对象;其方法EnqueuePackets是将RTP包添加到pacing队列,然后根据目标发送比特率以及发送调度优先级发送RTP包 - 创建
webrtc::AudioCodingModule对象,对应图X.1中标号为 7的进AudioCodingModule方向的连接; - 创建
webrtc::ModuleRtpRtcpImpl2对象,其Create方法configuration参数的outgoing_transport配置项指向了传入的webrtc::Transport,对应图X.1中标号为13的连接,configuration参数的paced_sender指向了前面创建的RtpPacketSenderProxy对象,对应图X.1中标号为10的连接 - 创建
webrtc::RTPSenderAudio对象,通过rtp_sender_audio_config的rtp_sender传入了从webrtc::ModuleRtpRtcpImpl2对象获得的webrtc::RTPSender对象,对应图X.1中标号为8和9的连接; - 把
this作为webrtc::AudioPacketizationCallback注册给了webrtc::AudioCodingModule对象,对应图X.1中标号为7 进ChannelSendInterface方向连接。
在这个阶段acm2和rtp_rtcp已经接入 webrtc::voe::(anonymous namespace)::ChannelSend 的模块,而pacing模块的接入在 ChannelSend 的 RegisterSenderCongestionControlObjects() 函数中实现,其调用栈如图X.4所示。ChannelSend 对象的RegisterSenderCongestionControlObjects() 函数的实现如下:
//webrtc/audio/channel_send.cc
706 void ChannelSend::RegisterSenderCongestionControlObjects(
707 RtpTransportControllerSendInterface* transport,
708 RtcpBandwidthObserver* bandwidth_observer) {
709 RTC_DCHECK_RUN_ON(&worker_thread_checker_);
710 RtpPacketSender* rtp_packet_pacer = transport->packet_sender();
711 PacketRouter* packet_router = transport->packet_router();
713 RTC_DCHECK(rtp_packet_pacer);
714 RTC_DCHECK(packet_router);
715 RTC_DCHECK(!packet_router_);
716 rtcp_observer_->SetBandwidthObserver(bandwidth_observer);
717 rtp_packet_pacer_proxy_->SetPacketPacer(rtp_packet_pacer);
718 rtp_rtcp_->SetStorePacketsStatus(true, 600);
719 packet_router_ = packet_router;
720}
ChannelSend::RegisterSenderCongestionControlObjects的710和711行提取 webrtc::RtpTransportControllerSendInterface 对象中的 webrtc::RtpPacketSender 实例和 webrtc::PacketRouter实例,webrtc::RtpPacketSender 实例设置给前面创建的 RtpPacketSenderProxy 对象,这样就建立起了前面的图中标号为11实际连接,11从这时起将不再是虚线,获得的 webrtc::PacketRouter 保存起来备用。
接下来看一下图3-1中ACM module(acm2)模块是如何将编码器接口层和具体编码器关联起来的,音频编码器在 webrtc::AudioSendStream 的配置接口 Reconfigure() 调用时创建,并将编码器注册进 webrtc::AudioCodingModule。这一过程如下:
//third_party/webrtc/audio/audio_send_stream.cc
void AudioSendStream::ConfigureStream(
const webrtc::AudioSendStream::Config& new_config,
bool first_time,
SetParametersCallback callback) {
if (!ReconfigureSendCodec(new_config)) {
RTC_LOG(LS_ERROR) << "Failed to set up send codec state.";
webrtc::InvokeSetParametersCallback(
callback, webrtc::RTCError(webrtc::RTCErrorType::INTERNAL_ERROR,
"Failed to set up send codec state."));
}
}

图3-5 编码器初始化过程
webrtc::AudioSendStream 中调用MakeAudioEncoder创建音频编码器,除了具体的编码器( 如OPUS,AAC ,G7XX)等,还有舒适噪音编码器以及冗余帧 RED 编码器。至此acm2框中编码器的通用接口类和具体的编码器实现连接上了,至于启用哪个编码则取决于SDP协商的结果。
// Apply current codec settings to a single voe::Channel used for sending.
bool AudioSendStream::SetupSendCodec(const Config& new_config) {
RTC_DCHECK(new_config.send_codec_spec);
const auto& spec = *new_config.send_codec_spec;
RTC_DCHECK(new_config.encoder_factory);
//创建特定类型的(由payload_type指定,如113是opus 单声道音频编码器)具体音频编码器
std::unique_ptr<AudioEncoder> encoder =
new_config.encoder_factory->MakeAudioEncoder(
spec.payload_type, spec.format, new_config.codec_pair_id);
if (!encoder) {
RTC_DLOG(LS_ERROR) << "Unable to create encoder for "
<< rtc::ToString(spec.format);
return false;
}
// If a bitrate has been specified for the codec, use it over the
// codec's default.
if (spec.target_bitrate_bps) {
encoder->OnReceivedTargetAudioBitrate(*spec.target_bitrate_bps);
}
// Enable ANA if configured (currently only used by Opus).
if (new_config.audio_network_adaptor_config) {
if (encoder->EnableAudioNetworkAdaptor(
*new_config.audio_network_adaptor_config, event_log_)) {
RTC_LOG(LS_INFO) << "Audio network adaptor enabled on SSRC "
<< new_config.rtp.ssrc;
} else {
RTC_LOG(LS_INFO) << "Failed to enable Audio network adaptor on SSRC "
<< new_config.rtp.ssrc;
}
}
// Wrap the encoder in an AudioEncoderCNG, if VAD is enabled.
if (spec.cng_payload_type) {
AudioEncoderCngConfig cng_config;
cng_config.num_channels = encoder->NumChannels();
cng_config.payload_type = *spec.cng_payload_type;
cng_config.speech_encoder = std::move(encoder);
cng_config.vad_mode = Vad::kVadNormal;
encoder = CreateComfortNoiseEncoder(std::move(cng_config));
RegisterCngPayloadType(*spec.cng_payload_type,
new_config.send_codec_spec->format.clockrate_hz);
}
// Wrap the encoder in a RED encoder, if RED is enabled.
if (spec.red_payload_type) {
AudioEncoderCopyRed::Config red_config;
red_config.payload_type = *spec.red_payload_type;
red_config.speech_encoder = std::move(encoder);
encoder = std::make_unique<AudioEncoderCopyRed>(std::move(red_config),
field_trials_);
}
// Set currently known overhead (used in ANA, opus only).
// If overhead changes later, it will be updated in UpdateOverheadForEncoder.
{
MutexLock lock(&overhead_per_packet_lock_);
size_t overhead = GetPerPacketOverheadBytes();
if (overhead > 0) {
encoder->OnReceivedOverhead(overhead);
}
}
StoreEncoderProperties(encoder->SampleRateHz(), encoder->NumChannels());
channel_send_->SetEncoder(new_config.send_codec_spec->payload_type,
std::move(encoder));
return true;
}
webrtc::PacketRouter 和 webrtc::ModuleRtpRtcpImpl2 是在 webrtc::AudioSendStream 的生命周期函数 Start() 调用时连接起来的,即webrtc::internal::AudioSendStream::Start()调用webrtc::voe::(anonymous namespace)::ChannelSend::StartSend()实现二者的连接,ChannelSend::StartSend() 函数实现如下:
void ChannelSend::StartSend() {
RTC_DCHECK_RUN_ON(&worker_thread_checker_);
RTC_DCHECK(!sending_);
sending_ = true;
RTC_DCHECK(packet_router_);
packet_router_->AddSendRtpModule(rtp_rtcp_.get(), /*remb_candidate=*/false);
rtp_rtcp_->SetSendingMediaStatus(true);
int ret = rtp_rtcp_->SetSendingStatus(true);
RTC_DCHECK_EQ(0, ret);
// It is now OK to start processing on the encoder task queue.
encoder_queue_.PostTask([this] {
RTC_DCHECK_RUN_ON(&encoder_queue_);
encoder_queue_is_active_ = true;
});
}
至此图3-1中各个模块之间建立的关系分析完毕。
3.5 创建 CreateChannels
依然是基于WebRTC的Native层peerconnection_client例子,音频的发送和接收使用了rtp协议,
webrtc::PeerConnection::Initialize(const webrtc::PeerConnectionInterface::RTCConfiguration&, webrtc::PeerConnectionDependencies)函数会调用InitializeTransportController_n方法,最终调用webrtc::JsepTransportController::JsepTransportController创建JsepTransportController,jesp是JavaScript Session Establishment Protocol的缩写,因为webrtc是基于Web的,而Web用java开发的比较多,所以针对这些通用性的协议需求,WebRTC实现了一套服务于Web的协议和实现,这使得基于Web的开发可以直接调用已经实现好的JS(JavaScript)而使得程序编写简单很多,而这里用是c++实现了JESP功能。有了JsepTransportController之后,回调调用webrtc::JsepTransportCollection::RegisterTransport创建并注册transport。之所以在这层创建创建transport是因为WebRTC支持DTLS(Datagram Transport Layer Security )传输协议,这协议之下还影藏了ICE等协议,接下来就是多媒体数据流使用该transport实现具体发送和接收的细节了。
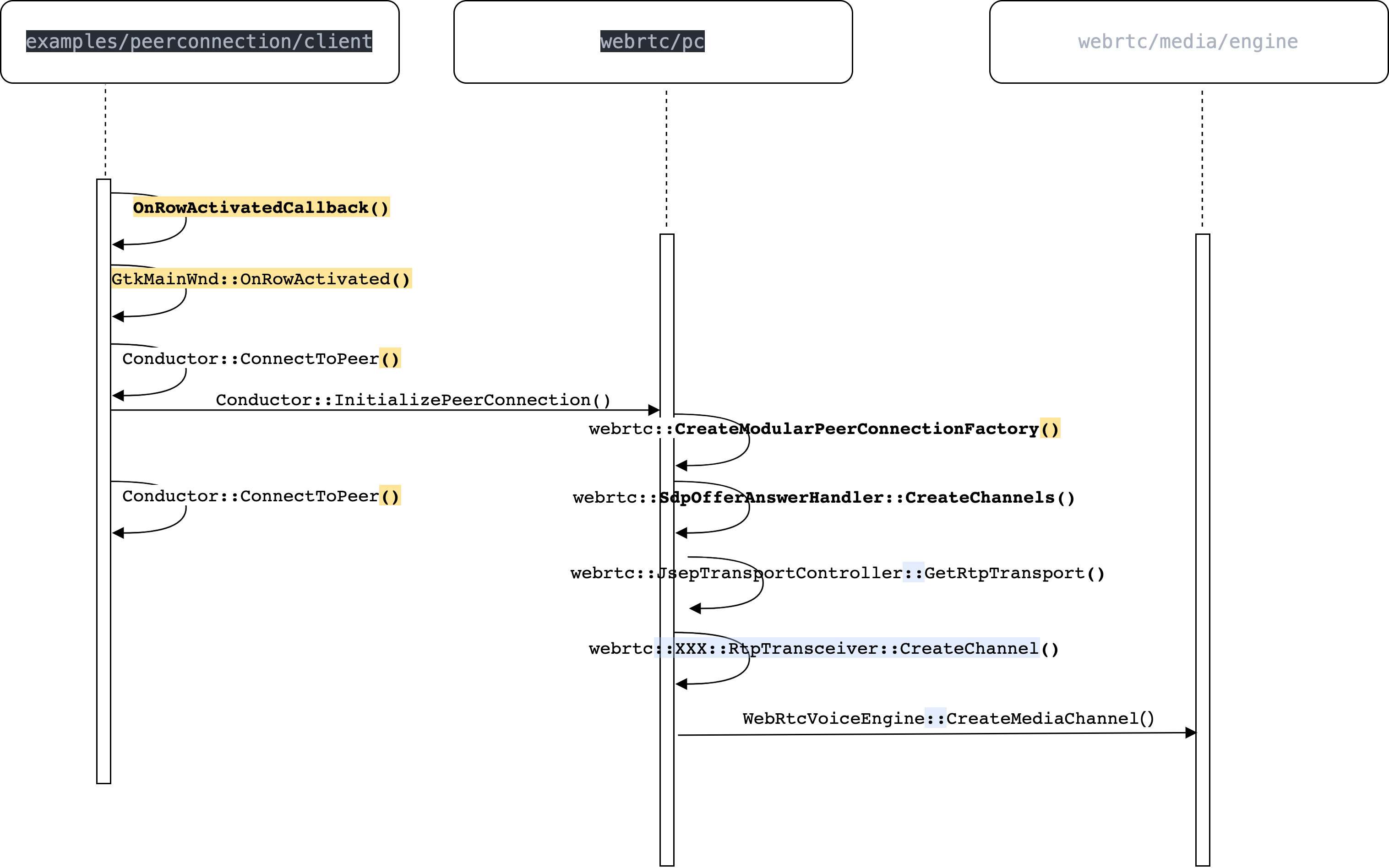
在SDP协商的时候offer端会调用SdpOfferAnswerHandler::ApplyLocalDescription() 而answer端会调用SdpOfferAnswerHandler::ApplyRemoteDescription(),这两个API都会调用SdpOfferAnswerHandler::UpdateTransceiversAndDataChannels()创建音频channel,在 SdpOfferAnswerHandler::CreateChannels() 中根据 mid (media ID)通过 PeerConnection 获得JESP协议创建的 RTP transport。
//webrtc/pc/sdp_offer_answer.cc
//参数desc中包括了媒体的类型,WebRTC目前支持视频、音频以及数据三种类型的Channel创建。
RTCError SdpOfferAnswerHandler::CreateChannels(const SessionDescription& desc) {
TRACE_EVENT0("webrtc", "SdpOfferAnswerHandler::CreateChannels");
// Creating the media channels. Transports should already have been created
// at this point.
RTC_DCHECK_RUN_ON(signaling_thread());
//对于Voice类型的多媒体,其返回值为MEDIA_TYPE_AUDIO
const cricket::ContentInfo* voice = cricket::GetFirstAudioContent(&desc);
if (voice && !voice->rejected &&
//对于还没设置local/remote description的transceiver其channel是还没创建的,因而会执行下面的CreateChannel()方法
!rtp_manager()->GetAudioTransceiver()->internal()->channel()) {
//CreateChannel()最后一个参数std::function<RtpTransportInternal*(absl::string_view)> transport_lookup使用Lambda表达式获取。其return返回的是transport的引用。
auto error =
rtp_manager()->GetAudioTransceiver()->internal()->CreateChannel(
voice->name, pc_->call_ptr(), pc_->configuration()->media_config,
pc_->SrtpRequired(), pc_->GetCryptoOptions(), audio_options(),
video_options(), video_bitrate_allocator_factory_.get(),
[&](absl::string_view mid) {
RTC_DCHECK_RUN_ON(network_thread());
return transport_controller_n()->GetRtpTransport(mid);
});
if (!error.ok()) {
return error;
}
}
//video媒体类型的channel创建
const cricket::ContentInfo* video = cricket::GetFirstVideoContent(&desc);
if (video && !video->rejected &&
!rtp_manager()->GetVideoTransceiver()->internal()->channel()) {
auto error =
rtp_manager()->GetVideoTransceiver()->internal()->CreateChannel(
video->name, pc_->call_ptr(), pc_->configuration()->media_config,
pc_->SrtpRequired(), pc_->GetCryptoOptions(),
audio_options(), video_options(),
video_bitrate_allocator_factory_.get(), [&](absl::string_view mid) {
RTC_DCHECK_RUN_ON(network_thread());
return transport_controller_n()->GetRtpTransport(mid);
});
if (!error.ok()) {
return error;
}
}
//data媒体类型的channel创建
const cricket::ContentInfo* data = cricket::GetFirstDataContent(&desc);
if (data && !data->rejected &&
!data_channel_controller()->data_channel_transport()) {
if (!CreateDataChannel(data->name)) {
return RTCError(RTCErrorType::INTERNAL_ERROR,
"Failed to create data channel.");
}
}
return RTCError::OK();
}
CreateChannel()的最后一个参数使用c++ 11特性的lambda表达式获取,该lambda表达式返回的是transport的引用, JsepTransportController` 根据 mid 通过获取 RTP transport对象,其实现如下:
//webrtc/pc/jsep_transport_controller.cc
RtpTransportInternal* JsepTransportController::GetRtpTransport(
absl::string_view mid) const {
RTC_DCHECK_RUN_ON(network_thread_);
auto jsep_transport = GetJsepTransportForMid(mid);
if (!jsep_transport) {
return nullptr;
}
//根据不同安全传输协议或非加密传输返回对应的transport对象
//const std::unique_ptr<webrtc::RtpTransport> unencrypted_rtp_transport_;
//const std::unique_ptr<webrtc::SrtpTransport> sdes_transport_;
//const std::unique_ptr<webrtc::DtlsSrtpTransport> dtls_srtp_transport_;
return jsep_transport->rtp_transport();
}
RtpTransceiver::CreateChannel()的实现如下,该函数对video和audio都是适用的:
//pc/rtp_transceiver.cc
RTCError RtpTransceiver::CreateChannel(
absl::string_view mid,
Call* call_ptr,
const cricket::MediaConfig& media_config,
bool srtp_required,
CryptoOptions crypto_options,
const cricket::AudioOptions& audio_options,
const cricket::VideoOptions& video_options,
VideoBitrateAllocatorFactory* video_bitrate_allocator_factory,
std::function<RtpTransportInternal*(absl::string_view)> transport_lookup) {
RTC_DCHECK_RUN_ON(thread_);
//判断media_engine_对象是否已经存在
if (!media_engine()) {
// TODO(hta): Must be a better way
return RTCError(RTCErrorType::INTERNAL_ERROR,
"No media engine for mid=" + std::string(mid));
}
std::unique_ptr<cricket::ChannelInterface> new_channel;
//audio channel创建
if (media_type() == cricket::MEDIA_TYPE_AUDIO) {
// TODO(bugs.webrtc.org/11992): CreateVideoChannel internally switches to
// the worker thread. We shouldn't be using the `call_ptr_` hack here but
// simply be on the worker thread and use `call_` (update upstream code).
RTC_DCHECK(call_ptr);
RTC_DCHECK(media_engine());
// TODO(bugs.webrtc.org/11992): Remove this workaround after updates in
// PeerConnection and add the expectation that we're already on the right
// thread.
context()->worker_thread()->BlockingCall([&] {
RTC_DCHECK_RUN_ON(context()->worker_thread());
cricket::VoiceMediaChannel* media_channel =
media_engine()->voice().CreateMediaChannel(
call_ptr, media_config, audio_options, crypto_options);
if (!media_channel) {
return;
}
new_channel = std::make_unique<cricket::VoiceChannel>(
context()->worker_thread(), context()->network_thread(),
context()->signaling_thread(), absl::WrapUnique(media_channel), mid,
srtp_required, crypto_options, context()->ssrc_generator());
});
//video channel创建
} else {
RTC_DCHECK_EQ(cricket::MEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO, media_type());
// TODO(bugs.webrtc.org/11992): CreateVideoChannel internally switches to
// the worker thread. We shouldn't be using the `call_ptr_` hack here but
// simply be on the worker thread and use `call_` (update upstream code).
context()->worker_thread()->BlockingCall([&] {
RTC_DCHECK_RUN_ON(context()->worker_thread());
cricket::VideoMediaChannel* media_channel =
media_engine()->video().CreateMediaChannel(
call_ptr, media_config, video_options, crypto_options,
video_bitrate_allocator_factory);
if (!media_channel) {
return;
}
new_channel = std::make_unique<cricket::VideoChannel>(
context()->worker_thread(), context()->network_thread(),
context()->signaling_thread(), absl::WrapUnique(media_channel), mid,
srtp_required, crypto_options, context()->ssrc_generator());
});
}
if (!new_channel) {
// TODO(hta): Must be a better way
return RTCError(RTCErrorType::INTERNAL_ERROR,
"Failed to create channel for mid=" + std::string(mid));
}
SetChannel(std::move(new_channel), transport_lookup);
return RTCError::OK();
}
3.6 设置transport
在3.1小节创建好audio channel之后,会调用SetChannel函数,该函数完成tranport对象的设置。
//webrtc/pc/rtp_transceiver.cc
void RtpTransceiver::SetChannel(
std::unique_ptr<cricket::ChannelInterface> channel,
std::function<RtpTransportInternal*(const std::string&)> transport_lookup) {
RTC_DCHECK_RUN_ON(thread_);
RTC_DCHECK(channel);
RTC_DCHECK(transport_lookup);
RTC_DCHECK(!channel_);
// Cannot set a channel on a stopped transceiver.
if (stopped_) {
return;
}
RTC_LOG_THREAD_BLOCK_COUNT();
RTC_DCHECK_EQ(media_type(), channel->media_type());
signaling_thread_safety_ = PendingTaskSafetyFlag::Create();
std::unique_ptr<cricket::ChannelInterface> channel_to_delete;
// An alternative to this, could be to require SetChannel to be called
// on the network thread. The channel object operates for the most part
// on the network thread, as part of its initialization being on the network
// thread is required, so setting a channel object as part of the construction
// (without thread hopping) might be the more efficient thing to do than
// how SetChannel works today.
// Similarly, if the channel() accessor is limited to the network thread, that
// helps with keeping the channel implementation requirements being met and
// avoids synchronization for accessing the pointer or network related state.
context()->network_thread()->BlockingCall([&]() {
if (channel_) {
channel_->SetFirstPacketReceivedCallback(nullptr);
channel_->SetRtpTransport(nullptr);
channel_to_delete = std::move(channel_);
}
//保存channel对象
channel_ = std::move(channel);
//设置tranport对象,这是RTP层级的tranport,这些tranport的类型可以是如下几种:
// * An RtpTransport without encryption.
// * An SrtpTransport for SDES.
// * A DtlsSrtpTransport for DTLS-SRTP.
channel_->SetRtpTransport(transport_lookup(channel_->mid()));
//通过lambda表达式设置OnFirstPacketReceived()为第一个数据包接收的回调函数
channel_->SetFirstPacketReceivedCallback(
[thread = thread_, flag = signaling_thread_safety_, this]() mutable {
thread->PostTask(
SafeTask(std::move(flag), [this]() { OnFirstPacketReceived(); }));
});
});
PushNewMediaChannelAndDeleteChannel(nullptr);
RTC_DCHECK_BLOCK_COUNT_NO_MORE_THAN(2);
}
tranport层设置的核心实现如下,
bool BaseChannel::SetRtpTransport(webrtc::RtpTransportInternal* rtp_transport) {
TRACE_EVENT0("webrtc", "BaseChannel::SetRtpTransport");
RTC_DCHECK_RUN_ON(network_thread());
if (rtp_transport == rtp_transport_) {
return true;
}
if (rtp_transport_) {
DisconnectFromRtpTransport_n();
// Clear the cached header extensions on the worker.
worker_thread_->PostTask(SafeTask(alive_, [this] {
RTC_DCHECK_RUN_ON(worker_thread());
rtp_header_extensions_.clear();
}));
}
rtp_transport_ = rtp_transport;
if (rtp_transport_) {
if (!ConnectToRtpTransport_n()) {
return false;
}
RTC_DCHECK(!media_channel_->HasNetworkInterface());
//SetInterface()函数的参数MediaChannelNetworkInterface* iface
media_channel_->SetInterface(this);
media_channel_->OnReadyToSend(rtp_transport_->IsReadyToSend());
UpdateWritableState_n();
// Set the cached socket options.
for (const auto& pair : socket_options_) {
rtp_transport_->SetRtpOption(pair.first, pair.second);
}
if (!rtp_transport_->rtcp_mux_enabled()) {
for (const auto& pair : rtcp_socket_options_) {
rtp_transport_->SetRtcpOption(pair.first, pair.second);
}
}
}
return true;
}
MediaChannel::SetInterface(MediaChannelNetworkInterface* iface)函数的参数是MediaChannel::NetworkInterface的实现,该实现用于MediaChannel收发数据包,
void MediaChannel::SetInterface(MediaChannelNetworkInterface* iface) {
RTC_DCHECK_RUN_ON(network_thread_);
iface ? network_safety_->SetAlive() : network_safety_->SetNotAlive();
network_interface_ = iface;
UpdateDscp();
}
bool MediaChannel::DoSendPacket(rtc::CopyOnWriteBuffer* packet,
bool rtcp,
const rtc::PacketOptions& options) {
RTC_DCHECK_RUN_ON(network_thread_);
if (!network_interface_)
return false;
return (!rtcp) ? network_interface_->SendPacket(packet, options)
: network_interface_->SendRtcp(packet, options);
}
BaseChannel 实现 MediaChannel::NetworkInterface 接口,BaseChannel::SetRtpTransport()将MediaChannel 、BaseChannel 和 RtpTransportInternal 这三个组件连接起来。
3.7 音频数据包发送处理
音频数据包发送分为采集、编码、分包发送、socket发送等过程实现。Linux平台采集过程中涉及的函数及其所属模块调用的关系如下图所示。
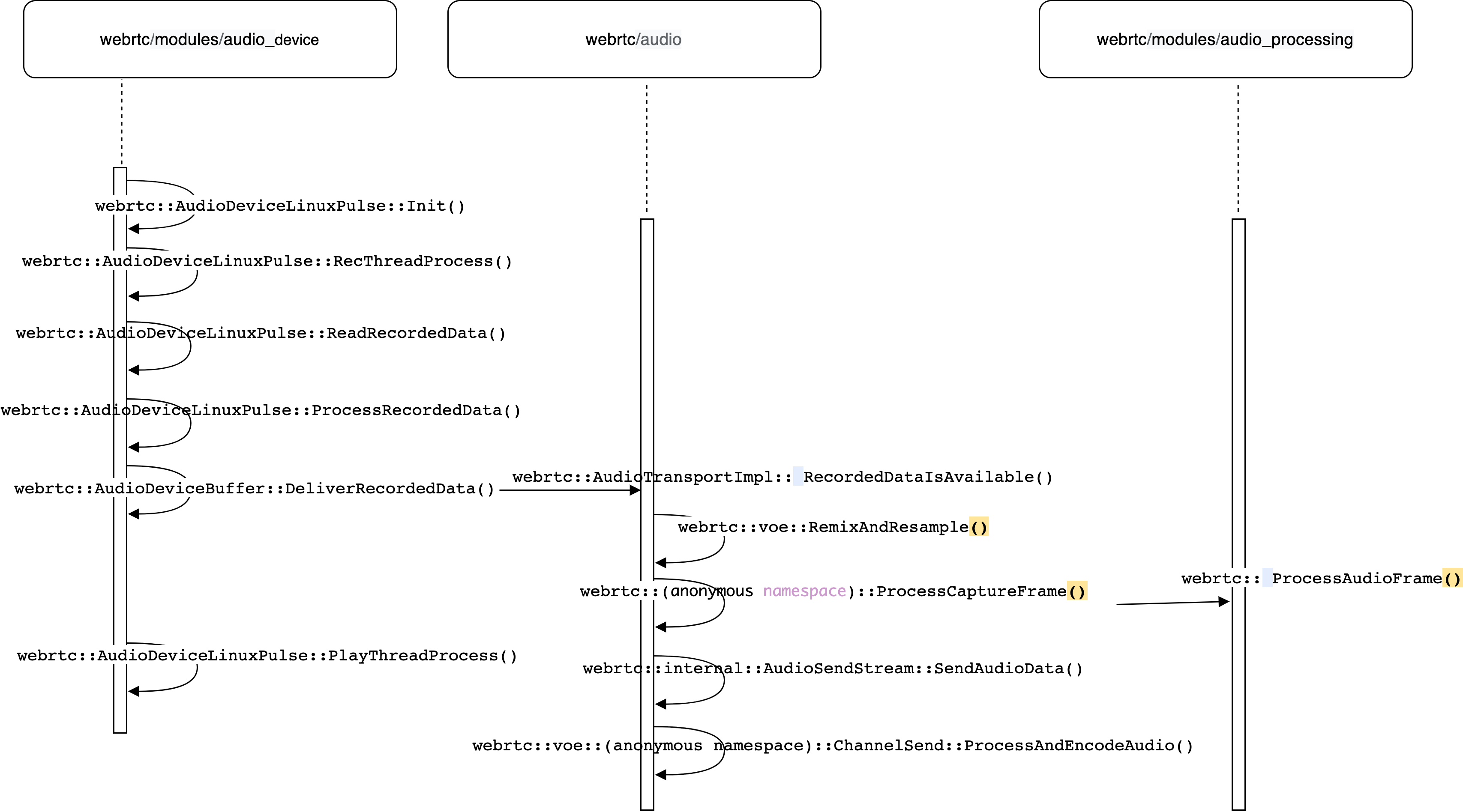
采集模块主要涉及到webrtc/modules/audio_device、webrtc/audio这两个模块,采集是从Linux平台设备初始化开始的。在初始化过程中会创建采集和播放线程,并且调用transport层的回调函数,将其传递到tranport层。
3.7.1 音频数据采集
由于数据是源源不断的产生的,因而通过采集线程间隔10ms取数据并抛给上层,由于不同的系统平台提供的API并不一样,如Android 有AAdudio,Linux听ALSA,mac和windows分别是苹果和微软的API,因而webRTC通过ADM模块进行了接口类封装,这样上层使用同样的API调用device相关的方法,这实现了屏蔽,这里以Linux平台为例,其它平台不再一一赘述。在通过PulsAudio接口时webrtc::AudioDeviceLinuxPulse::Init()会创建采集线程webrtc::AudioDeviceLinuxPulse::RecThreadProcess(),采集线程采集到的数据通过webrtc::AudioDeviceLinuxPulse::ReadRecordedData(void const*, unsigned long)将调用APM处理音频数据webrtc::AudioDeviceLinuxPulse::ProcessRecordedData(signed char*, unsigned int, unsigned int),经过APM处理好的数据通过webrtc::AudioDeviceBuffer::DeliverRecordedData()向transport层送数据,webrtc::AudioTransportImpl::RecordedDataIsAvailable(void const*, unsigned long, unsigned long, unsigned long, unsigned int, unsigned int, int, unsigned int, bool, unsigned int&)会将数据送到channel编码后再发送。
设备初始化和采集线程的创建函数实现如下:
//webrtc/modules/audio_device/linux/audio_device_pulse_linux.cc
AudioDeviceGeneric::InitStatus AudioDeviceLinuxPulse::Init() {
RTC_DCHECK(thread_checker_.IsCurrent());
if (_initialized) {
return InitStatus::OK;
}
// 初始化 PulseAudio
if (InitPulseAudio() < 0) {
RTC_LOG(LS_ERROR) << "failed to initialize PulseAudio";
if (TerminatePulseAudio() < 0) {
RTC_LOG(LS_ERROR) << "failed to terminate PulseAudio";
}
return InitStatus::OTHER_ERROR;
}
// RECORDING
const auto attributes =
rtc::ThreadAttributes().SetPriority(rtc::ThreadPriority::kRealtime);
_ptrThreadRec = rtc::PlatformThread::SpawnJoinable(
//通过c++的lambda表达式启动采集线程
[this] {
while (RecThreadProcess()) {
}
},
"webrtc_audio_module_rec_thread", attributes);
// PLAYOUT
_ptrThreadPlay = rtc::PlatformThread::SpawnJoinable(
//通过c++的lambda表达式启动播放线程
[this] {
while (PlayThreadProcess()) {
}
},
"webrtc_audio_module_play_thread", attributes);
_initialized = true;
return InitStatus::OK;
}
通过lambda表达式启动采集线程之后,采集线程RecThreadProcess()开始工作:
bool AudioDeviceLinuxPulse::RecThreadProcess() {
if (!_timeEventRec.Wait(TimeDelta::Seconds(1))) {
return true;
}
MutexLock lock(&mutex_);
if (quit_) {
return false;
}
if (_startRec) {
RTC_LOG(LS_VERBOSE) << "_startRec true, performing initial actions";
_recDeviceName = NULL;
// Set if not default device
if (_inputDeviceIndex > 0) {
// Get the recording device name
_recDeviceName = new char[kAdmMaxDeviceNameSize];
_deviceIndex = _inputDeviceIndex;
RecordingDevices();
}
PaLock();
RTC_LOG(LS_VERBOSE) << "connecting stream";
// Connect the stream to a source
if (LATE(pa_stream_connect_record)(
_recStream, _recDeviceName, &_recBufferAttr,
(pa_stream_flags_t)_recStreamFlags) != PA_OK) {
RTC_LOG(LS_ERROR) << "failed to connect rec stream, err="
<< LATE(pa_context_errno)(_paContext);
}
RTC_LOG(LS_VERBOSE) << "connected";
// Wait for state change
while (LATE(pa_stream_get_state)(_recStream) != PA_STREAM_READY) {
LATE(pa_threaded_mainloop_wait)(_paMainloop);
}
RTC_LOG(LS_VERBOSE) << "done";
// We can now handle read callbacks
EnableReadCallback();
PaUnLock();
// Clear device name
if (_recDeviceName) {
delete[] _recDeviceName;
_recDeviceName = NULL;
}
_startRec = false;
_recording = true;
_recStartEvent.Set();
return true;
}
if (_recording) {
// Read data and provide it to VoiceEngine
if (ReadRecordedData(_tempSampleData, _tempSampleDataSize) == -1) {
return true;
}
_tempSampleData = NULL;
_tempSampleDataSize = 0;
PaLock();
while (true) {
// Ack the last thing we read
if (LATE(pa_stream_drop)(_recStream) != 0) {
RTC_LOG(LS_WARNING)
<< "failed to drop, err=" << LATE(pa_context_errno)(_paContext);
}
if (LATE(pa_stream_readable_size)(_recStream) <= 0) {
// Then that was all the data
break;
}
// Else more data.
const void* sampleData;
size_t sampleDataSize;
if (LATE(pa_stream_peek)(_recStream, &sampleData, &sampleDataSize) != 0) {
RTC_LOG(LS_ERROR) << "RECORD_ERROR, error = "
<< LATE(pa_context_errno)(_paContext);
break;
}
// Drop lock for sigslot dispatch, which could take a while.
PaUnLock();
// Read data and provide it to VoiceEngine
if (ReadRecordedData(sampleData, sampleDataSize) == -1) {
return true;
}
PaLock();
// Return to top of loop for the ack and the check for more data.
}
EnableReadCallback();
PaUnLock();
} // _recording
采集到的数据通过channel对应的ProcessAndEncodeAudio函数编码后发送出去,函数调用流程如下图:
//audio/audio_transport_impl.cc
webrtc::AudioTransportImpl::SendProcessedData(std::unique_ptr<webrtc::AudioFrame, std::default_delete<webrtc::AudioFrame> >)
//audio/audio_send_stream.cc
ebrtc::internal::AudioSendStream::SendAudioData(std::unique_ptr<webrtc::AudioFrame, std::default_delete<webrtc::AudioFrame> >)
//audio/channel_send.cc
ChannelSend::ProcessAndEncodeAudio(std::unique_ptr<webrtc::AudioFrame, std::default_delete<webrtc::AudioFrame> >)
AudioSendStream::SendAudioData函数的实现如下:
void AudioSendStream::SendAudioData(std::unique_ptr<AudioFrame> audio_frame) {
RTC_CHECK_RUNS_SERIALIZED(&audio_capture_race_checker_);
RTC_DCHECK_GT(audio_frame->sample_rate_hz_, 0);
TRACE_EVENT0("webrtc", "AudioSendStream::SendAudioData");
double duration = static_cast<double>(audio_frame->samples_per_channel_) /
audio_frame->sample_rate_hz_;
{
// Note: SendAudioData() passes the frame further down the pipeline and it
// may eventually get sent. But this method is invoked even if we are not
// connected, as long as we have an AudioSendStream (created as a result of
// an O/A exchange). This means that we are calculating audio levels whether
// or not we are sending samples.
// TODO(https://crbug.com/webrtc/10771): All "media-source" related stats
// should move from send-streams to the local audio sources or tracks; a
// send-stream should not be required to read the microphone audio levels.
MutexLock lock(&audio_level_lock_);
audio_level_.ComputeLevel(*audio_frame, duration);
}
channel_send_->ProcessAndEncodeAudio(std::move(audio_frame));
}
3.7.2 编码并添加到pacer队列
承接3.3.1小节的SendAudioData函数所述的channel_send_->ProcessAndEncodeAudio(std::move(audio_frame));,该函数调用webrtc编码模块提供的方法对数据进行编码并添加到发送的pacer队列中,其涉及的模块和调函数的主要函数如下图所示:

audio模块和rtp模块的衔接传递如下函数,
int32_t ChannelSend::SendRtpAudio(AudioFrameType frameType,
uint8_t payloadType,
uint32_t rtp_timestamp,
rtc::ArrayView<const uint8_t> payload,
int64_t absolute_capture_timestamp_ms) {
if (_includeAudioLevelIndication) {
// Store current audio level in the RTP sender.
// The level will be used in combination with voice-activity state
// (frameType) to add an RTP header extension
rtp_sender_audio_->SetAudioLevel(rms_level_.Average());
}
// E2EE Custom Audio Frame Encryption (This is optional).
// Keep this buffer around for the lifetime of the send call.
rtc::Buffer encrypted_audio_payload;
// We don't invoke encryptor if payload is empty, which means we are to send
// DTMF, or the encoder entered DTX.
// TODO(minyue): see whether DTMF packets should be encrypted or not. In
// current implementation, they are not.
if (!payload.empty()) {
if (frame_encryptor_ != nullptr) {
// TODO(benwright@webrtc.org) - Allocate enough to always encrypt inline.
// Allocate a buffer to hold the maximum possible encrypted payload.
size_t max_ciphertext_size = frame_encryptor_->GetMaxCiphertextByteSize(
cricket::MEDIA_TYPE_AUDIO, payload.size());
encrypted_audio_payload.SetSize(max_ciphertext_size);
// Encrypt the audio payload into the buffer.
size_t bytes_written = 0;
int encrypt_status = frame_encryptor_->Encrypt(
cricket::MEDIA_TYPE_AUDIO, rtp_rtcp_->SSRC(),
/*additional_data=*/nullptr, payload, encrypted_audio_payload,
&bytes_written);
if (encrypt_status != 0) {
RTC_DLOG(LS_ERROR)
<< "Channel::SendData() failed encrypt audio payload: "
<< encrypt_status;
return -1;
}
// Resize the buffer to the exact number of bytes actually used.
encrypted_audio_payload.SetSize(bytes_written);
// Rewrite the payloadData and size to the new encrypted payload.
payload = encrypted_audio_payload;
} else if (crypto_options_.sframe.require_frame_encryption) {
RTC_DLOG(LS_ERROR) << "Channel::SendData() failed sending audio payload: "
"A frame encryptor is required but one is not set.";
return -1;
}
}
// Push data from ACM to RTP/RTCP-module to deliver audio frame for
// packetization.
if (!rtp_rtcp_->OnSendingRtpFrame(rtp_timestamp,
// Leaving the time when this frame was
// received from the capture device as
// undefined for voice for now.
-1, payloadType,
/*force_sender_report=*/false)) {
return -1;
}
// RTCPSender has it's own copy of the timestamp offset, added in
// RTCPSender::BuildSR, hence we must not add the in the offset for the above
// call.
// TODO(nisse): Delete RTCPSender:timestamp_offset_, and see if we can confine
// knowledge of the offset to a single place.
// This call will trigger Transport::SendPacket() from the RTP/RTCP module.
if (!rtp_sender_audio_->SendAudio(
frameType, payloadType, rtp_timestamp + rtp_rtcp_->StartTimestamp(),
payload.data(), payload.size(), absolute_capture_timestamp_ms)) {
RTC_DLOG(LS_ERROR)
<< "ChannelSend::SendData() failed to send data to RTP/RTCP module";
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
添加到pacer队列的核心函数如下:
void PacingController::EnqueuePacket(std::unique_ptr<RtpPacketToSend> packet) {
RTC_DCHECK(pacing_rate_ > DataRate::Zero())
<< "SetPacingRate must be called before InsertPacket.";
RTC_CHECK(packet->packet_type());
prober_.OnIncomingPacket(DataSize::Bytes(packet->payload_size()));
const Timestamp now = CurrentTime();
if (packet_queue_.Empty()) {
// If queue is empty, we need to "fast-forward" the last process time,
// so that we don't use passed time as budget for sending the first new
// packet.
Timestamp target_process_time = now;
Timestamp next_send_time = NextSendTime();
if (next_send_time.IsFinite()) {
// There was already a valid planned send time, such as a keep-alive.
// Use that as last process time only if it's prior to now.
target_process_time = std::min(now, next_send_time);
}
UpdateBudgetWithElapsedTime(UpdateTimeAndGetElapsed(target_process_time));
}
packet_queue_.Push(now, std::move(packet));
seen_first_packet_ = true;
// Queue length has increased, check if we need to change the pacing rate.
MaybeUpdateMediaRateDueToLongQueue(now);
}
核心就是将audio packet放到packet_queue_队列上,通过packer线程发送packet_queue_队列上的数据包。
3.7.3 pacedSender发送RTP包
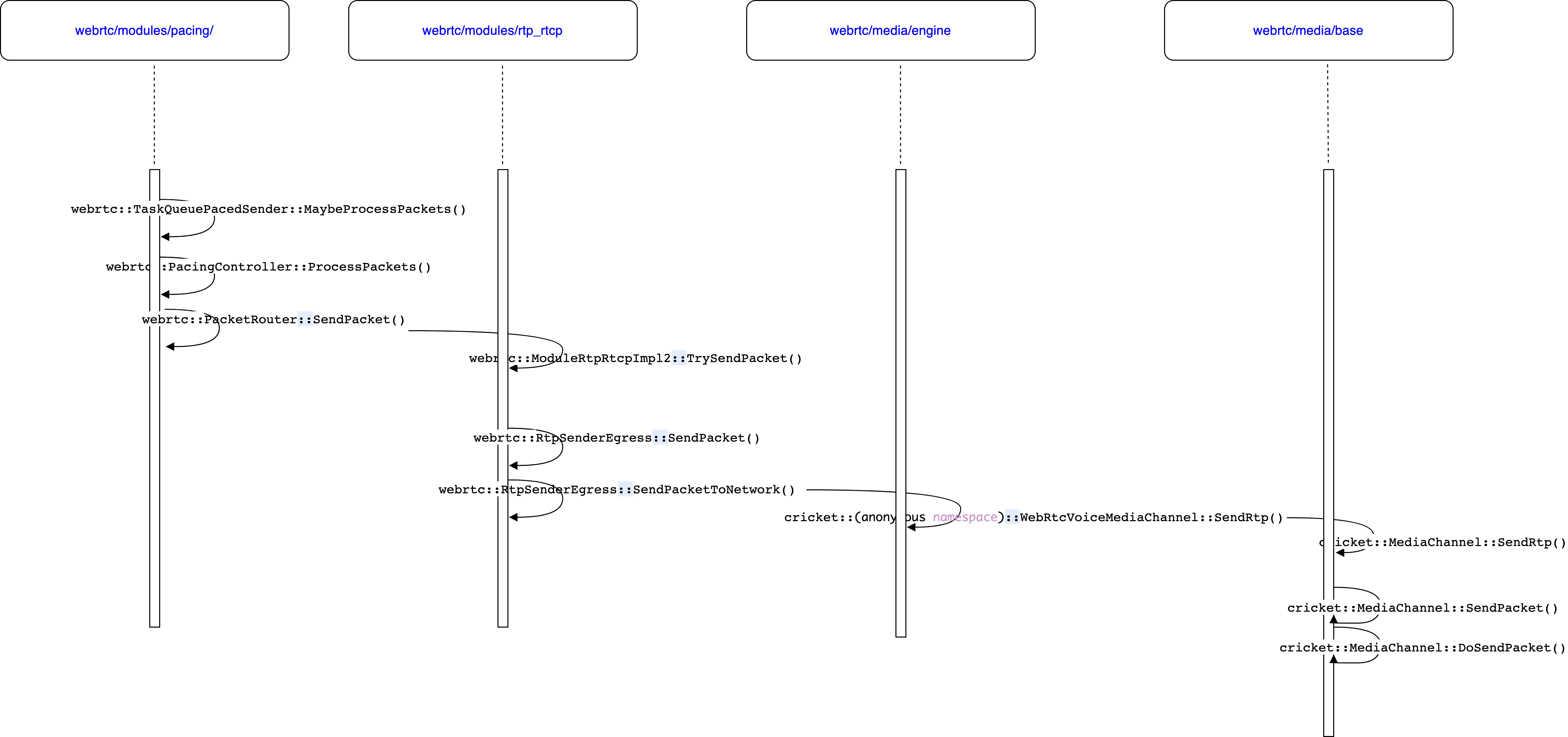
在3.7.2小节将RTP包加到pacer队列之后,会由pacer队列的发送线程发送出去;pacer队列是在Call::CreateAudioReceiveStream创建的时候会调用TaskQueuePacedSender::EnsureStarted()创建发送线程,TaskQueuePacedSender::EnsureStarted()的定义如下,其通过lambda表达式方式启动了该线程。
//webrtc/modules/pacing/task_queue_paced_sender.cc
void TaskQueuePacedSender::EnsureStarted() {
task_queue_.RunOrPost([this]() {
RTC_DCHECK_RUN_ON(&task_queue_);
is_started_ = true;
MaybeProcessPackets(Timestamp::MinusInfinity());
});
}
//webrtc/modules/utility/maybe_worker_thread.cc
void MaybeWorkerThread::RunOrPost(absl::AnyInvocable<void() &&> task) {
if (owned_task_queue_) {
owned_task_queue_->PostTask(std::move(task));
} else {
RTC_DCHECK_RUN_ON(&sequence_checker_);
std::move(task)();
}
}
通过cricket::MediaChannel::DoSendPacket()之后,rtp数据包从media层发送到channel层,通过channel层的socket接口发送出去。
3.7.4 通过socket接口发送数据包
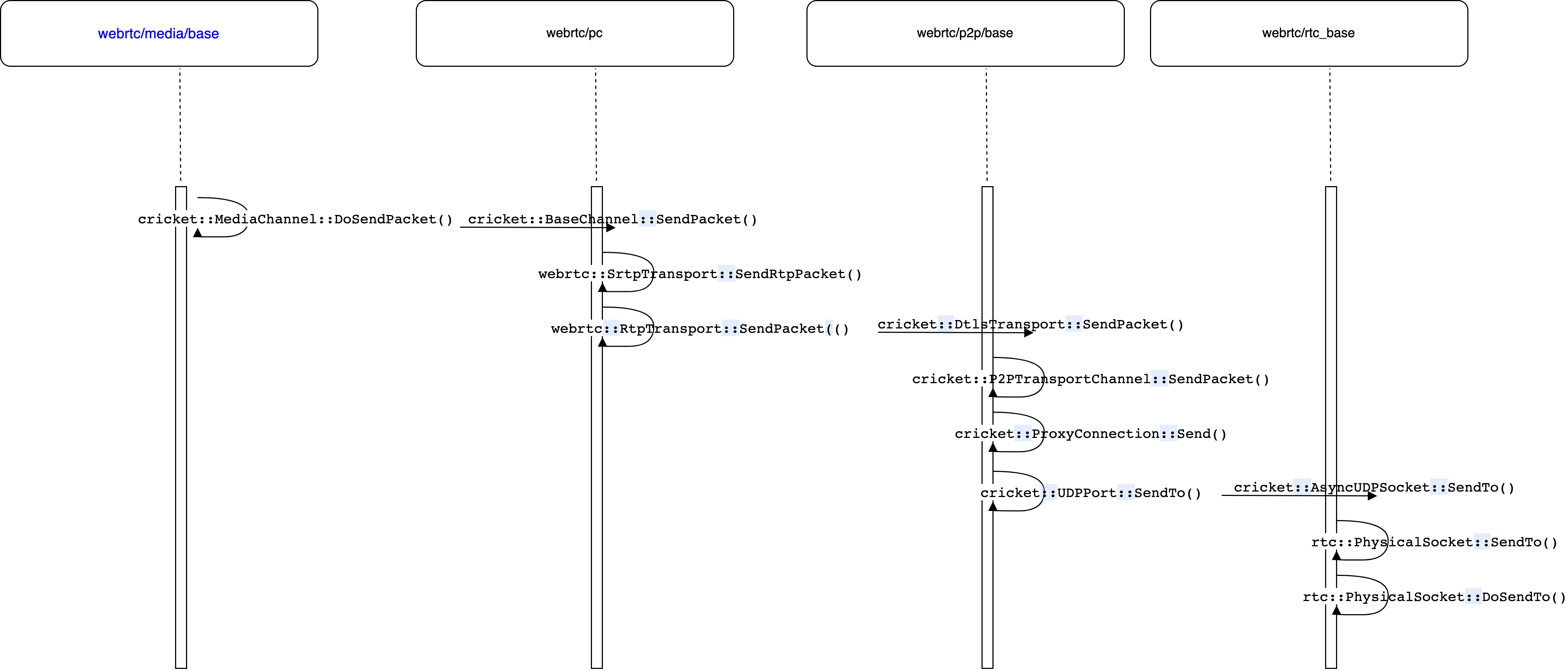
从mediaChannel到socket的调用关系如上图所示。
3.8 音频数据包的接收处理
音频数据包的接收处理分为从网络接收RTP包、将RTP包插入NetEQ模块以及NetEQ解码后播放三个主要模块。
3.8.1 从网络接收音频 RTP 包
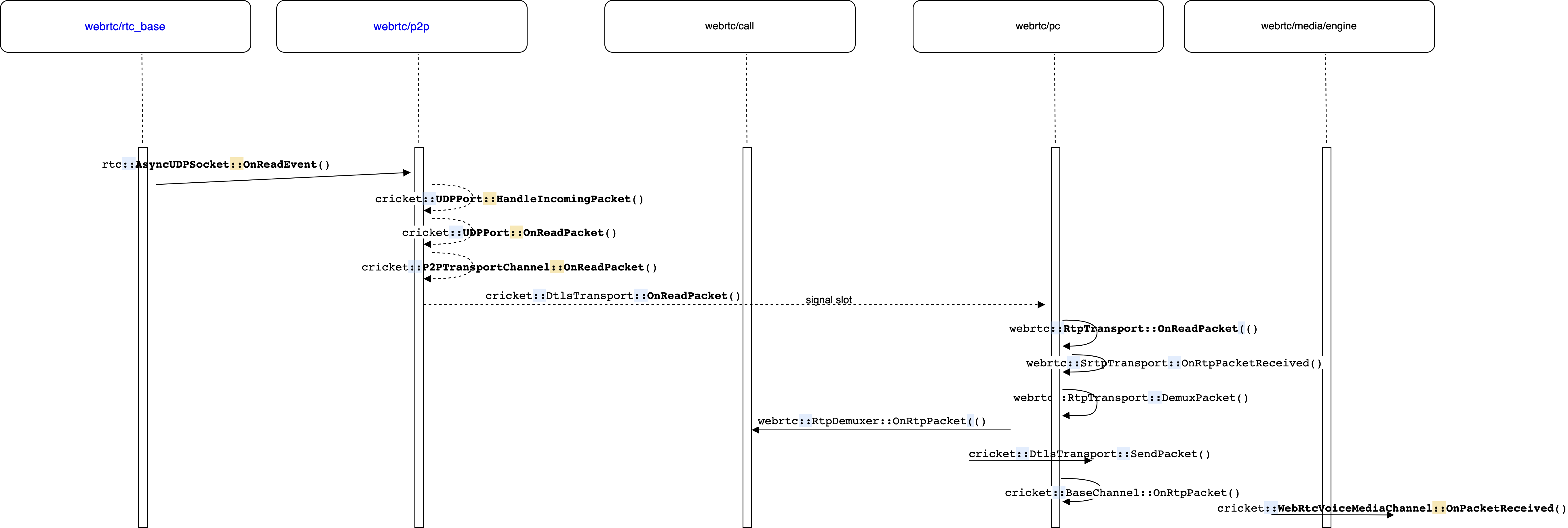
RTP包从cricket::DtlsTransport::OnReadPacket到webrtc::RtpTransport::OnReadPacket则是通过信号异步通知,RtpTransport::OnReadPacket和信号绑定的函数如下:
//third_party/webrtc/pc/rtp_transport.cc
void RtpTransport::SetRtpPacketTransport(
rtc::PacketTransportInternal* new_packet_transport) {
if (new_packet_transport == rtp_packet_transport_) {
return;
}
if (rtp_packet_transport_) {
rtp_packet_transport_->SignalReadyToSend.disconnect(this);
rtp_packet_transport_->SignalReadPacket.disconnect(this);
rtp_packet_transport_->SignalNetworkRouteChanged.disconnect(this);
rtp_packet_transport_->SignalWritableState.disconnect(this);
rtp_packet_transport_->SignalSentPacket.disconnect(this);
// Reset the network route of the old transport.
SignalNetworkRouteChanged(absl::optional<rtc::NetworkRoute>());
}
if (new_packet_transport) {
new_packet_transport->SignalReadyToSend.connect(
this, &RtpTransport::OnReadyToSend);
new_packet_transport->SignalReadPacket.connect(this,
&RtpTransport::OnReadPacket);
new_packet_transport->SignalNetworkRouteChanged.connect(
this, &RtpTransport::OnNetworkRouteChanged);
new_packet_transport->SignalWritableState.connect(
this, &RtpTransport::OnWritableState);
new_packet_transport->SignalSentPacket.connect(this,
&RtpTransport::OnSentPacket);
// Set the network route for the new transport.
SignalNetworkRouteChanged(new_packet_transport->network_route());
}
rtp_packet_transport_ = new_packet_transport;
// Assumes the transport is ready to send if it is writable. If we are wrong,
// ready to send will be updated the next time we try to send.
SetReadyToSend(false,
rtp_packet_transport_ && rtp_packet_transport_->writable());
}
从cricket::UDPPort::HandleIncomingPacket()到cricket::UDPPort::OnReadPacket()以及从cricket::UDPPort::OnReadPacket()到cricket::P2PTransportChannel::OnReadPacket()都是通过signal的方式实现异步及时处理的。最后到了voice engine层,WebRtcVoiceMediaChannel::OnPacketReceived()函数实现如下,该函数通过一个lambda表达式将接收的到rtp包送到了call层,然后通过PostTask方式将这一处理过程放在了新线程执行lamda表达式,lambda表达式中的call_->Receiver()->DeliverRtpPacket()调用非常重要。
void WebRtcVoiceMediaChannel::OnPacketReceived(
const webrtc::RtpPacketReceived& packet) {
RTC_DCHECK_RUN_ON(&network_thread_checker_);
// TODO(bugs.webrtc.org/11993): This code is very similar to what
// WebRtcVideoChannel::OnPacketReceived does. For maintainability and
// consistency it would be good to move the interaction with
// call_->Receiver() to a common implementation and provide a callback on
// the worker thread for the exception case (DELIVERY_UNKNOWN_SSRC) and
// how retry is attempted.
worker_thread_->PostTask(
SafeTask(task_safety_.flag(), [this, packet = packet]() mutable {
RTC_DCHECK_RUN_ON(worker_thread_);
// TODO(bugs.webrtc.org/7135): extensions in `packet` is currently set
// in RtpTransport and does not neccessarily include extensions specific
// to this channel/MID. Also see comment in
// BaseChannel::MaybeUpdateDemuxerAndRtpExtensions_w.
// It would likely be good if extensions where merged per BUNDLE and
// applied directly in RtpTransport::DemuxPacket;
packet.IdentifyExtensions(recv_rtp_extension_map_);
if (!packet.arrival_time().IsFinite()) {
packet.set_arrival_time(webrtc::Timestamp::Micros(rtc::TimeMicros()));
}
call_->Receiver()->DeliverRtpPacket(
webrtc::MediaType::AUDIO, std::move(packet),
absl::bind_front(
&WebRtcVoiceMediaChannel::MaybeCreateDefaultReceiveStream,
this));
}));
}
3.8.2 音频 RTP 包异步插入 NetEQ
在3.8.1小节最后,call_->Receiver()->DeliverRtpPacket是在新线程中调用的,其将RTP数据包传递到了voice engine层,由于网络存在丢包、抖动等非理想因素,因而在满足实时性的要求下还要进行抗丢包和去抖动,NetEQ模块就可以处理一部分抖动和丢包,当然编码器也可能有自己的丢包补偿算法,比如G7XX、Opus编码器,这就可能并不会启动NeteQ的丢包算法,但是抗抖动都依赖于NetEQ处理。将RTP数据包添加到NetEQ buffer的调用流程如下图所示:
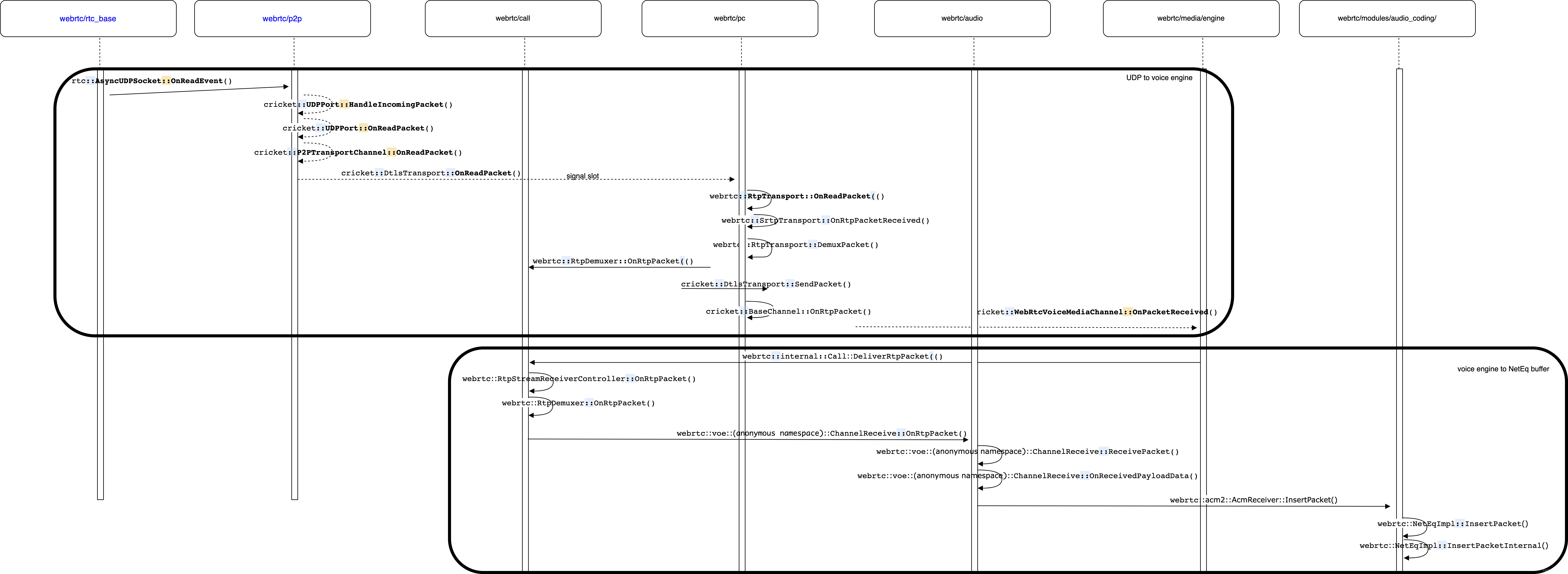
3.8.3 获取NetEQ音频包并解码播放
由于声音是连续的,和音频采集一样,播放也是流式的,在WebRTC中采用10ms播放一次音频数据,因而采用单独的播放线程来播放音频数据,对于Linux平台,音频播放线程的创建在音频设备初始化阶段,对采用PulseAudio框架实现的音频设备管理的初始化如下,在其实现上采用lambda表达式创建采集和播放线程。
AudioDeviceGeneric::InitStatus AudioDeviceLinuxPulse::Init() {
RTC_DCHECK(thread_checker_.IsCurrent());
if (_initialized) {
return InitStatus::OK;
}
// Initialize PulseAudio
if (InitPulseAudio() < 0) {
RTC_LOG(LS_ERROR) << "failed to initialize PulseAudio";
if (TerminatePulseAudio() < 0) {
RTC_LOG(LS_ERROR) << "failed to terminate PulseAudio";
}
return InitStatus::OTHER_ERROR;
}
// RECORDING
const auto attributes =
rtc::ThreadAttributes().SetPriority(rtc::ThreadPriority::kRealtime);
_ptrThreadRec = rtc::PlatformThread::SpawnJoinable(
[this] {
while (RecThreadProcess()) {
}
},
"webrtc_audio_module_rec_thread", attributes);
// PLAYOUT
_ptrThreadPlay = rtc::PlatformThread::SpawnJoinable(
[this] {
while (PlayThreadProcess()) {
}
},
"webrtc_audio_module_play_thread", attributes);
_initialized = true;
return InitStatus::OK;
}

在播放的最后解码部分调用了AudioDecoderOpusImpl::DecodeInternal(),当然也可以调用AudioDecoderG722Impl::DecodeInternal(),至于具体使用哪个编码器,取决于SDP协议协商的结果,关于Opus编码器见音频编码器 opus分析专栏。
最后
以上就是忧郁季节最近收集整理的关于WebRTC音频系统 音频发送和接收的全部内容,更多相关WebRTC音频系统内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复