今天这个是真正的过了信道的信号。
单载波QPSK。QPSK算是通过了。
简直就是个速成班啊……惨…………
关于CMA的介绍,可以参考Matlab的文档。
Reviews:Matlab中关于CMA的介绍
%%
% 单载波QPSK 接收端
% CMA均衡,LMS训练,BER循环计算
% 2017年5月18日10:37:53
clear;
close all;
clc
%%
rand_seed = 0;
rand('seed',rand_seed);
randn('seed',rand_seed);
% Set up parameters and signals.
M = 4; % Alphabet size for modulation
baud_rate = 100; % Baud rate
f_carrier1 = 75; % Carrier frequency
Nsym = 10000; % Number of symbols
msg = randi([0 M-1],Nsym,1); % Random message
hMod = comm.RectangularQAMModulator(M);
modmsg = step(hMod,msg); % Modulate using QAM. % 映射后的基带信号
trainlen = 3000; % Length of training sequence
rolloff = .3; % 滚降因子
span = 20 ; % 截断长度
sps = 10; % Samples per symbol
rrcFilter=rcosdesign(rolloff,span,sps,'sqrt'); %根升余弦滚降滤波器,‘sqrt’均方根升余弦;‘normal’升余弦
fs = baud_rate*sps; % 时间采样率,时间采样间隔为 1/fs 秒
Tsymbol=1/baud_rate;
% 2. 脉冲成型
% txSig = upfirdn(modmsg, rrcFilter, sps); % 发送端的基带复波形信号
rrcLen=length(rrcFilter);
msg_upsample=upsample(modmsg,sps);
msg_pulse_rrc=conv(msg_upsample,rrcFilter);
msg_upsample_len=length(msg_pulse_rrc);
txSig=msg_pulse_rrc(rrcLen/2:msg_upsample_len-rrcLen/2);
t = (0:1/fs:((length(txSig)-1)/fs)).';
T = t(end)+1/fs;
df = 1/T;
freq = -fs/2:df:fs/2-df;
cos1 = cos(2*pi*f_carrier1 * t);
sin1 = sin(2*pi*f_carrier1 * t);
x_upconv = real(txSig).* cos1 + imag(txSig) .* sin1;
%% === 接收端
x_training_wave = x_upconv;
x_training_msg = modmsg;
% x_received = Rx_oscilloscope('osc');
load ./rxdata/oscCAP_7osc.txt;
x_received=oscCAP_7osc;
%%
% 1. 同步
x_resampled = resample(x_received,1,1);
for k = 1 : 5
try
x_sync = sync_two_signals( x_resampled,x_training_wave,k,3);
is_sync = 1;
catch
is_sync = 0;
fprintf('未同步n');
end
if is_sync == 1
fprintf('同步n');
break;
end
end
x_sync = x_sync/max(abs(x_sync));
x_training_wave = x_training_wave/max(abs(x_training_wave));
%%
% close all;
% plot(x_sync(1e3:2000),'r');hold on;
% plot(x_training_wave(1e3:2000),'b');
%%
% 2. 下变频 + 匹配滤波
% x_sync = x_training_wave;
%
t = (0:1/fs:((length(x_sync)-1)/fs)).';
T = t(end)+1/fs;
df = 1/T;
freq = -fs/2:df:fs/2-df;
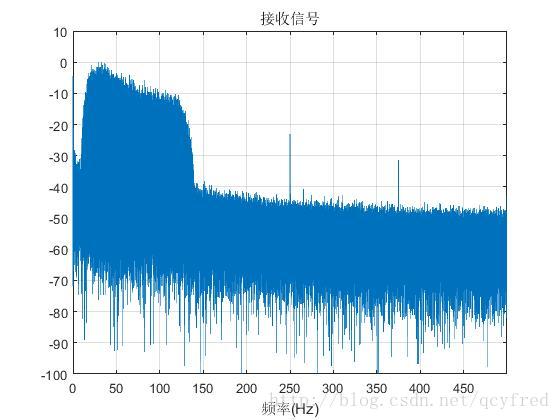
% figure(1);
% plot(freq,20*log10(abs(fftshift(fft(x_sync))/max(abs(fftshift(fft(x_sync)))))));
% ylim([-100,10])
% xlim([0,freq(end)])
% grid on;
% xlabel('频率(Hz)');
% title('接收信号');
cos1 = cos(2*pi*f_carrier1 * t);
sin1 = sin(2*pi*f_carrier1 * t);
xi_dnconv = x_sync .* cos1;
xq_dnconv = x_sync .* sin1;
x_dnconv= xi_dnconv + 1j * xq_dnconv;
dn_offset = 0;
rxMatchFilt=conv(x_dnconv,rrcFilter);
msg_upsample_len=length(rxMatchFilt);
rxFilt=rxMatchFilt(rrcLen/2:msg_upsample_len-rrcLen/2);
rxFilt=downsample(rxFilt,sps,dn_offset);
close all;
scatterplot(rxFilt);
%% CMA(Matlab)
close all;
nWeights = 20;
stepSize = 0.001;
alg = cma(stepSize);
eqCMA = lineareq(nWeights,alg);
eqCMA.SigConst = step(hMod,(0:M-1)')';
eqCMA.leakagefactor = 1;
% eqCMA.ResetBeforeFiltering = 0; % Maintain continuity between iterations.
% eqCMA.Weights = [ones(1,length(eqCMA.Weights)-1) 1];
eqCMA.Weights = [zeros(1,length(eqCMA.Weights)-1),1];
[symbolcma,~] = equalize(eqCMA,rxFilt);
%=========================================================
% CMA引发相位旋转
% The constant modulus algorithm is useful when no training signal is available,
% and works best for constant modulus modulations such as PSK.
% However, if CMA has no additional side information, it can introduce phase ambiguity.
% For example, CMA might find weights that produce a perfect QPSK constellation but
% might introduce a phase rotation of 90, 180, or 270 degrees.
% Alternatively, differential modulation can be used to avoid phase ambiguity.
%=========================================================
rxCma = symbolcma(nWeights:end); %
rxCma = rxCma./mean(abs(rxCma));
scatterplot(rxCma(nWeights+1:end));
%% LMS or RLS
close all;
% rxCma = rxFilt; % 没有CMA
% eq1 = lineareq(40, rls(0.99,0.01));
eq1 = lineareq(6, rls(0.99,0.01)); % Create an equalizer object. % 40 taps,RLS算法,步长0.99,自相关矩阵逆矩阵的初值InvCorrInit
% eq1 = lineareq(10, lms(0.001)); % LMS
eq1.SigConst = step(hMod,(0:M-1)')'; % Set signal constellation. % 标准星座图
[symbolest,~] = equalize(eq1,rxCma,modmsg(1:trainlen)); % Equalize. % 均衡器obj,需要均衡的信号,训练序列
symbolest = symbolest ./ mean(abs(symbolest)) .* mean(abs(eq1.SigConst));
rxFilt_disp = rxFilt ./ mean(abs(rxFilt)) .* mean(abs(eq1.SigConst));
%%
% Plot signals.
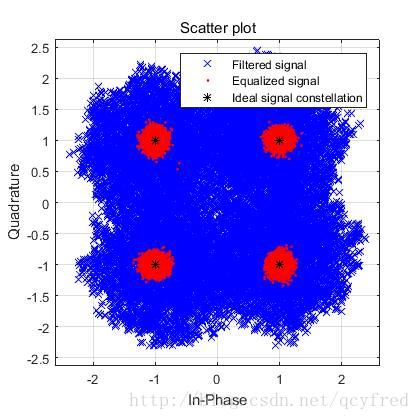
close all;
h = scatterplot(rxFilt_disp(trainlen+1:end),1,trainlen,'bx'); hold on;
scatterplot(symbolest(trainlen+1:end),1,trainlen,'r.',h);
scatterplot(eq1.SigConst,1,0,'k*',h);
legend('Filtered signal','Equalized signal',...
'Ideal signal constellation');
hold off;
%%
% a1 = symbolest(trainlen+1:end);
% a2 = modmsg;
% 之后如何计算BER就不用写了。方法非常magic。
%% 没有相位旋转的时候计算BER
% % Compute error rates with equalization.
% hDemod = comm.RectangularQAMDemodulator(M);
% demodmsg = step(hDemod,symbolest); % Demodulate detected signal from equalizer.
%
% % demodmsg
% % msg
%
% % [hicorrI,lagsiI]=xcorr(demodmsg,msg);
% % [~,offsetindex]=max((hicorrI));
% % figure;plot(lagsiI,abs(hicorrI));
%
% % Create ErrorRate Calculator System object
% serVec = step(comm.ErrorRate,msg(trainlen+1:end),demodmsg(trainlen+1:end));
% srate = serVec(1)
% snum = serVec(2)
% % Convert integers to bits
% hIntToBit = comm.IntegerToBit(log2(M));
% Tx_bit = step(hIntToBit, msg(trainlen+1:end));
% Rx_bit = step(hIntToBit, demodmsg(trainlen+1:end));
% % Calculate BER
% berVec = step(comm.ErrorRate,Rx_bit,Tx_bit);
% brate = berVec(1)
% bnum = berVec(2)100MBuad,QPSK。RRC,alpha = 0.3。

最后
以上就是老实蚂蚁最近收集整理的关于通信系统仿真速成第2天:QPSK调制与解调(实验)的全部内容,更多相关通信系统仿真速成第2天内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复