[Matlab] C_MEX_S学习总结
总流程:
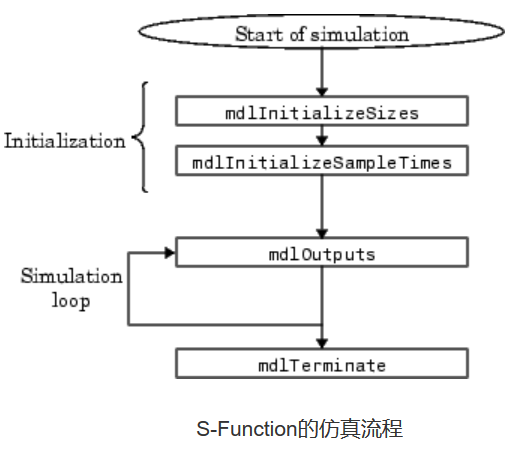 方法开始之前为定义
方法开始之前为定义
#define S_FUNCTION_NAME Fcn //这里把文件名修改为Fcn
#define S_FUNCTION_LEVEL 2
#define INPUT_NUM n //输入端口的数量
#define OUTPUT_NUM n //输出端口的数量
#include "simstruc.h"
#include <math.h>
//定义 变量和函数如:
double Ts;
double para1,para2;
S-Function包含以下几个子方法
1、static void mdlInitializeSizes(SimStruct *S)
说明:初始化模块
(1)设置界面参数的初始化;
ssSetNumSFcnParams(S, n);此函数是从GUI界面读入参数的,其中n表示界面设置的函数个数;
ssSetNumContStates(S,0); 此函数表示读入的参数中连续量的个数;
ssSetNumDiscStates(S, n);此函数表示读入的参数中离散量的个数;一般都是离散量
(2)设置输入的初始化;
ssSetNumInputPorts(S, INPUT_NUM);此函数判断输入接口的个数是否和模块中设置的一样,一般在最前面的申明当中定义输入接口的个数,申明方式为:#define INPUT_NUM 1,其中表示只有一个输入接口。如下
ssSetInputPortWidth(S, 0, 2); 表示输入变量的维度是多少。其中2表示输入的为2维数据,如下图所示,虽然只有一个输入接口,但是却有两个数据,因此,维度设为2.
ssSetInputPortRequiredContiguous(S, 0, true); 设置输入接口的访问方式,true就是临近访问,这样指针的增量后就可以直接访问下个input端口。
(3)设置输出的初始化;
ssSetNumOutputPorts(S, OUTPUT_NUM);此函数判断输出接口的个数是否和模块中设置的一样,一般在最前面的申明当中定义输出接口的个数,申明方式为:#define OUTPUT_NUM 1,其中表示只有一个输出接口。如下
ssSetOutputPortWidth(S, 0, 2); 含义和输入的一样,可以互相参照。
(4)设置采样时间的个数
ssSetNumSampleTimes(S, 1);设置采样时间的个数,一般设置为1,表示只有一个采样时间。
2、static void mdlInitializeSampleTimes(SimStruct *S)
说明:设置采样时间
ssSetSampleTime(S, 0, CONTINUOUS_SAMPLE_TIME);
其中,第二个参数0表示第一个输入端口的采样时间,CONTINUOUS_SAMPLE_TIME表示跟随系统的采样时间。也可以按照需求,设置采样时间。
3、 static void mdlInitializeConditions(SimStruct *S)
说明:初始化工作向量的状态值。
表示对头文件中定义的变量进行初始化处理,
例如:
头文件中定义了变量:A,B,C三个参数,这三个参数为GUI界面所读取而得的参数,后边会用到这些参数,但是需要对这些参数进行初始化,因此,可以在此函数中进行处理,然后将其赋值给一个指针变量,在后面的子方法中应用时,直接调用指针即可。
double *para = ssGetRealDiscStates(S); // 读取GUI中的参数,将这些参数全部赋值给一个指针。
para[0] = A+1; para[1] = B+ 2;para[1] = C+ 3// 对参数进行处理。
4、static void mdlStart(SimStruct *S)
说明:在仿真开始时初始化工作向量及变量的属性。
mxGetPr(ssGetSFcnParam(S,0))表示从GUI界面获取参数变量,0表示第一个参数,1表示第二个变量。获取到的变量参数后,交由mdlInitializeConditions函数来处理。将其变为统一的指针变量。
A = *(mxGetPr(ssGetSFcnParam(S,0)));
B = *(mxGetPr(ssGetSFcnParam(S,1)));
5、static void mdlOutputs(SimStruct *S, int_T tid)
说明:计算模块的输出,此部分主要涉及算法部分,在算法开始时,需要三个函数分别读取GUI的参数、输入端口参数、输出端口的参数。
(1)double *para = ssGetRealDiscStates(S);为读取GUI的参数,并将参数定义为double类型。也可以依据情况定义为real_T(float)类型。
float:占4个字节
double: 占8个字节
const real_T表示恒定不变的float类型。
(2)const double *u = (const double*) ssGetInputPortSignal(S,0);为读取输入端口的数据其中u为指针变量,与输入端口中数据维数有关。
(3)double *y = ssGetOutputPortSignal(S,0); 为输出数据,其中0表示第一个输出端口,y可以为不同维数的输出值。
6、static void mdlUpdate(SimStruct *S, int_T tid)
说明:更新离散状态变量的子方法
一般为:
double *para = ssGetRealDiscStates(S);
para[0] = A ;
para[1] = B;
进行更新第5步骤中改变的参数,并以指针的方式将这些变量存入。
7、static void mdlTerminate(SimStruct *S)
终止程序。
编译程序后,在命令行窗口输入:mex 文件名(Fcn).c,即可生成文件名.mexw64(64位matlab)文件,S-Function模块就可以进行调用了。若是32位matlab则会生成 文件名.mexw32文件。
#define S_FUNCTION_NAME Fcn //这里把文件名Fcn
#define S_FUNCTION_LEVEL 2
#define INPUT_NUM 1
#define OUTPUT_NUM 1
/*
* Need to include simstruc.h for the definition of the SimStruct and
* its associated macro definitions.
*/
#include "simstruc.h"
#include <math.h>
//定义 变量和函数如:
double C;
double A,B;
/*====================*
* S-function methods *
*====================*/
/* Function: mdlInitializeSizes ===============================================
* Abstract:
* The sizes information is used by Simulink to determine the S-function
* block's characteristics (number of inputs, outputs, states, etc.).
*/
static void mdlInitializeSizes(SimStruct *S)
{
//这个函数用来设置输入、输出和参数的
ssSetNumSFcnParams(S, 3); /* 设置参数个数,这里为3 */
if (ssGetNumSFcnParams(S) != ssGetSFcnParamsCount(S)) {
/* Return if number of expected != number of actual parameters */
return;
}
ssSetNumContStates(S,0); //设置连续状态的个数,缺省为0
ssSetNumDiscStates(S, 3); //设置离散状态的个数,缺省为0;
if (!ssSetNumInputPorts(S, INPUT_NUM)) return; //设置输入变量的个数,这里为1
ssSetInputPortWidth(S, 0, 2); //设置输入变量0的维数为2
ssSetInputPortRequiredContiguous(S, 0, true); //设置input0的访问方式,true就是临近访问,这样指针的增量后就可以直接访问下个input端口了
/*
* Set direct feedthrough flag (1=yes, 0=no).
* A port has direct feedthrough if the input is used in either
* the mdlOutputs or mdlGetTimeOfNextVarHit functions.
*/
ssSetInputPortDirectFeedThrough(S, 0, 1); // 设置输入端口的信号是否mdlOutputs函数中使用,这儿设置为true。
if (!ssSetNumOutputPorts(S, OUTPUT_NUM)) return; //设置输出变量的个数,这里输出变量的个数为1
ssSetOutputPortWidth(S, 0, 2);
ssSetNumSampleTimes(S, 1); //设置采样个数,此处为1s。
/* Specify the sim state compliance to be same as a built-in block */
ssSetSimStateCompliance(S, USE_DEFAULT_SIM_STATE);
ssSetOptions(S, 0);
}
/* Function: mdlInitializeSampleTimes =========================================
* Abstract:
* This function is used to specify the sample time(s) for your
* S-function. You must register the same number of sample times as
* specified in ssSetNumSampleTimes.
*/
static void mdlInitializeSampleTimes(SimStruct *S)
{
ssSetSampleTime(S, 0, CONTINUOUS_SAMPLE_TIME);//继承系统采样时间
ssSetOffsetTime(S, 0, 0.0);
}
#define MDL_INITIALIZE_CONDITIONS /* Change to #undef to remove function */
#if defined(MDL_INITIALIZE_CONDITIONS)
/* Function: mdlInitializeConditions ========================================
* Abstract:
* In this function, you should initialize the continuous and discrete
* states for your S-function block. The initial states are placed
* in the state vector, ssGetContStates(S) or ssGetRealDiscStates(S).
* You can also perform any other initialization activities that your
* S-function may require. Note, this routine will be called at the
* start of simulation and if it is present in an enabled subsystem
* configured to reset states, it will be call when the enabled subsystem
* restarts execution to reset the states.
*/
static void mdlInitializeConditions(SimStruct *S)
{
double *para = ssGetRealDiscStates(S);
para[0] = A + 1;
para[1] = B + 2;
para[2] = C;
}
#endif /* MDL_INITIALIZE_CONDITIONS */
#define MDL_START /* Change to #undef to remove function */
#if defined(MDL_START)
/* Function: mdlStart =======================================================
* Abstract:
* This function is called once at start of model execution. If you
* have states that should be initialized once, this is the place
* to do it.
*/
static void mdlStart(SimStruct *S)
{
A = *(mxGetPr(ssGetSFcnParam(S,0)));
B = *(mxGetPr(ssGetSFcnParam(S,1)));
C = *(mxGetPr(ssGetSFcnParam(S,2)));
}
#endif /* MDL_START */
//这里填入相关的运算、算法等
/* Function: mdlOutputs =======================================================
* Abstract:
* In this function, you compute the outputs of your S-function
* block.
*/
static void mdlOutputs(SimStruct *S, int_T tid)
//这里填入相关的运算、算法等
{
double *para = ssGetRealDiscStates(S);
const double *u = (const double*) ssGetInputPortSignal(S,0);
double *y = ssGetOutputPortSignal(S,0);
A = para[0];
B = para[1]
y[0] = A*u[0]+5;
y[1] = B*u[1]+3;
}
#define MDL_UPDATE /* Change to #undef to remove function */
#if defined(MDL_UPDATE)
/* Function: mdlUpdate ======================================================
* Abstract:
* This function is called once for every major integration time step.
* Discrete states are typically updated here, but this function is useful
* for performing any tasks that should only take place once per
* integration step.
*/
static void mdlUpdate(SimStruct *S, int_T tid)
{
double *para = ssGetRealDiscStates(S);
para[0] = A;
para[1] = B;
para[2] = C;
}
#endif /* MDL_UPDATE */
#define MDL_DERIVATIVES /* Change to #undef to remove function */
#if defined(MDL_DERIVATIVES)
/* Function: mdlDerivatives =================================================
* Abstract:
* In this function, you compute the S-function block's derivatives.
* The derivatives are placed in the derivative vector, ssGetdX(S).
*/
static void mdlDerivatives(SimStruct *S)
{
}
#endif /* MDL_DERIVATIVES */
/* Function: mdlTerminate =====================================================
* Abstract:
* In this function, you should perform any actions that are necessary
* at the termination of a simulation. For example, if memory was
* allocated in mdlStart, this is the place to free it.
*/
static void mdlTerminate(SimStruct *S)
{
}
/*=============================*
* Required S-function trailer *
*=============================*/
#ifdef MATLAB_MEX_FILE /* Is this file being compiled as a MEX-file? */
#include "simulink.c" /* MEX-file interface mechanism */
#else
#include "cg_sfun.h" /* Code generation registration function */
#endif
最后
以上就是失眠巨人最近收集整理的关于[Matlab] C_MEX_S学习总结的全部内容,更多相关[Matlab]内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。

![matlab simulink s 函数,[转载]simulink中s函数的总结之一](https://www.shuijiaxian.com/files_image/reation/bcimg13.png)


![[Matlab] C_MEX_S学习总结](https://www.shuijiaxian.com/files_image/reation/bcimg2.png)



发表评论 取消回复