一、随机数与概率的规律
假设我们使用随机数生成器,可以产生1-100范围内随机数。
那么每次产生的随机数,其值可能是1-100范围内任意一个数,每个数的概率均等。
所以可以得出,随机数值V与概率P,有如下规律:
| 数值(V) | 概率(P) |
|---|---|
| 1 <= V <= 100 | 100% |
| V < 1 或 V > 100 | 0% |
| 1 <= V <= 50 | 50% |
| 50 <= V <= 100 | 50% |
| 1 <= V <= 20 | 20% |
| … | … |
二、利用随机数设计一个抽奖程序
假设可以进行无限次抽奖,奖项有一、二、三、四等奖、谢谢参与,如下:
// 奖项
enum Prize
{
First, // 一等奖
Second, // 二等奖
Third, // 三等奖
Fourth, // 四等奖
Thanks // 谢谢参与
};
各奖项抽中的概率为:
| 奖项 | 概率 |
|---|---|
| 一等奖 | 5% |
| 二等奖 | 10% |
| 三等奖 | 20% |
| 四等奖 | 30% |
| 谢谢参与 | 35% |
首先,封装PrizeControl类,实现抽奖逻辑。
PrizeControl.h
#ifndef PRIZECONTROL_H
#define PRIZECONTROL_H
// 奖项
enum Prize
{
First, // 一等奖
Second, // 二等奖
Third, // 三等奖
Fourth, // 四等奖
Thanks // 谢谢参与
};
// 抽奖控制类
class PrizeControl
{
public:
PrizeControl();
// 抽奖,返回抽奖结果
Prize drawLottery();
};
#endif // PRIZECONTROL_H
PrizeControl.cpp
#include "PrizeControl.h"
#include <time.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
PrizeControl::PrizeControl()
{
srand(time(nullptr)); // 设置随机数种子
}
Prize PrizeControl::drawLottery()
{
// 生成一个1 ~ 100范围内的随机数
int value = rand() % 100 + 1; // 1 ~ 100
if (value >= 1 && value <= 5)
{
return First; // 一等奖5%
}
else if (value > 5 && value <= 15)
{
return Second; // 二等奖10%
}
else if (value > 15 && value <= 35)
{
return Third; // 三等奖20%
}
else if (value > 35 && value <= 65)
{
return Fourth; // 四等奖30%
}
else
{
return Thanks; // 谢谢参与35%
}
}
drawLottery()中对生成随机数所在区域进行判断,并返回相应奖项,比较简单,就不多说啦。
然后,在main.cpp中进行测试,如下:
#include <QCoreApplication>
#include <QDebug>
#include "PrizeControl.h"
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QCoreApplication a(argc, argv);
int firstCount = 0; // 一等奖抽中次数
int secondCount = 0; // 二等奖抽中次数
int thirdCount = 0; // 三等奖抽中次数
int fourthCount = 0; // 四等奖抽中次数
int thanksCount = 0; // 谢谢参与抽中次数
PrizeControl prizeControl;
for (int i = 0; i < 2000; i++) // 总共抽奖次数2000
{
Prize prize = prizeControl.drawLottery();
switch (prize)
{
case First:
firstCount++;
break;
case Second:
secondCount++;
break;
case Third:
thirdCount++;
break;
case Fourth:
fourthCount++;
break;
default:
thanksCount++;
break;
}
}
qDebug() << "firstCount:" << firstCount; //100
qDebug() << "secondCount:" << secondCount; //200
qDebug() << "thirdCount:" << thirdCount; //400
qDebug() << "fourthCount:" << fourthCount; //600
qDebug() << "thanksCount:" << thanksCount; //700
return a.exec();
}
运行结果:
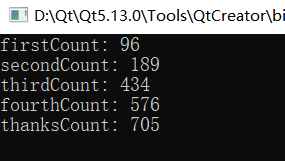
可以看到,共抽奖2000次,各奖项所抽中的比例基本上与原设定值相等。
三、题外话
在开源项目diskspd中,github地址:https://github.com/microsoft/diskspd
在IORequestGenerator.cpp文件中,利用随机数实现IO读写请求比例的控制。
/*****************************************************************************/
// Decide the kind of IO to issue during a mix test
// Future Work: Add more types of distribution in addition to random
__inline static IOOperation DecideIo(Random *pRand, UINT32 ulWriteRatio)
{
return ((pRand->Rand32() % 100 + 1) > ulWriteRatio) ? IOOperation::ReadIO : IOOperation::WriteIO;
}
比如ulWriteRatio=30,则表示生成的IO请求中,IO写占30%,IO读占70%,继而实现了混合读写时,读写IO请求比例的控制。
若对你有帮助,欢迎点赞、收藏、评论,你的支持就是我的最大动力!!!
同时,阿超为大家准备了丰富的学习资料,欢迎关注公众号“超哥学编程”,即可领取。
本文涉及工程代码,公众号回复:54Random,即可下载。

最后
以上就是奋斗香氛最近收集整理的关于利用随机数实现指定概率抽奖一、随机数与概率的规律二、利用随机数设计一个抽奖程序三、题外话的全部内容,更多相关利用随机数实现指定概率抽奖一、随机数与概率内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复