快速全排列的函数 头文件<algorithm>
next_permutation(a,a+n)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
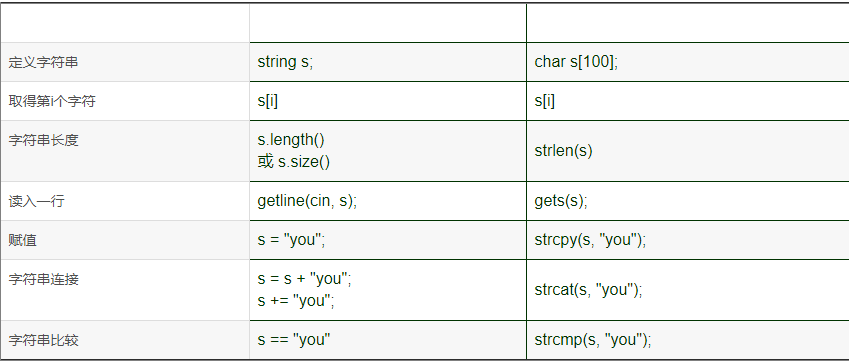
1 - string 与 字符串
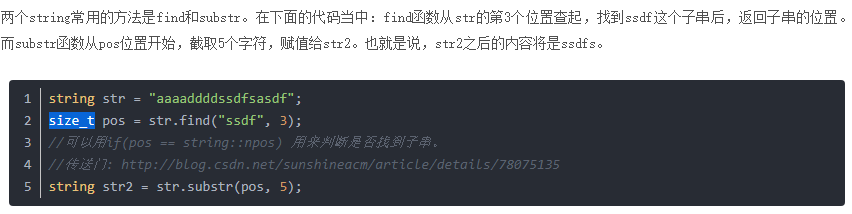
find 搜寻失败会返回 string::npos 的值
string 的 erase() 删除函数
1 b.erase(1,4); //删除从 b[1] 开始 4个元素
一个应用的题目,暑假集训第一周比赛 :17-比赛1 B - 子串计算 string的运用
string类的构造函数:
string(const char *s); //用c字符串s初始化 最好是 string(s,2) 2用来控制string的长度,如果 原字符串没有以�结尾,直接赋值会乱码
string(int n,char c); //用n个字符c初始化
string s2="hello"; //直接初始化
bool empty()const; //当前字符串是否为空 空 返回 1
void resize(int len,char c);//把字符串当前大小置为len,并用字符c填充不足的部分
void swap(string &s2); //交换当前字符串与s2的值
字符串流处理:
通过定义ostringstream和istringstream变量实现,#include <sstream>头文件中
例如:
string input("hello,this is a test");
istringstream is(input);
string s1,s2,s3,s4;
is>>s1>>s2>>s3>>s4;//s1="hello,this",s2="is",s3="a",s4="test"
ostringstream os;
os<<s1<<s2<<s3<<s4;
cout<<os.str();
UVA 1593 Alignment of Code(紫书习题5-1 字符串流)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
2 - stack 容器 (先进后出(FILO)的数据结构) - queue 容器 (先进先出(队列) 的数据结构)
empty() 堆栈为空则返回真 empty() 堆栈为空则返回真
pop() 移除栈顶(最晚入队的)元素 pop() 移除栈顶(最先入队的)元素
push() 在栈顶增加元素 push(x) 将x 接到队列的末端。
size() 返回栈中元素数目 size() 返回栈中元素数目
top() 返回栈顶(最晚入队的)元素 front()访问队首元素,即最早被压入队列的元素
back()访问队尾元素,即最后被压入队列的元素
- priority_queue (优先队列) 默认大的先出队
一个应用的题目:
17-比赛1 D - IPC Trainers (贪心 + 优先队列)
priority_queue<int >q1;priority_queue<pair<int,int> >q2;
priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int> >q3;//定义小的先出队
priority_queue的基本操作均与queue相同
1 //自定义大小顺序 2 class T 3 { 4 public: 5 int x,y,z; 6 T(int a,int b,int c):x(a),y(b),z(c) 7 { 8 } 9 }; 10 bool operator<(const T&t1,const T&t2) 11 { 12 return t1.z<t2.z; 13 } 14 int main(void) 15 { 16 priority_queue<T>q; 17 q.push(T(4,4,3)); 18 q.push(T(2,2,5)); 19 q.push(T(1,5,4)); 20 q.push(T(3,3,6)); 21 while(!q.empty()) 22 { 23 T t=q.top(); 24 q.pop(); 25 cout<<t.x<<" "<<t.y<<" "<<t.z<<endl; 26 } 27 system("Pause"); 28 return 1; 29 }
运行结果是 :
3 3 6
2 2 5
1 5 4
4 4 3
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
先按作者名字从小到大排,再按标题从小到大排序
1 bool operator<(Node a,Node b)
2 {
3 if(a.name==b.name)
4 return a.title<b.title;
5 return a.name<b.name;
6 }
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
3 - map 的定义和使用 (map的key 独一无二,multimap的key 可以重复,所有元素都是pair)
C++中的STL中map用法详解
简单运用
map<key,value> a; → a[key] = value;
clear() 清空;
map.erase(map.begin(),map.end()) 清空元素
例子 :
1 map<int, int> c; 2 c[1] = 10;c[2] = 20;c[3] = 30;c[4] = 40;c[5] = 50; 3 for(auto i : c) 4 { 5 cout<<"["<< i.first <<"] = " << i.second <<" "; 6 }
运行结果为
[1] = 10 [2] = 20 [3] = 30 [4] = 40 [5] = 50
1 map<int, int> c; 2 c[1] = 10;c[4] = 20;c[3] = 30;c[2] = 40;c[5] = 50; 3 for(auto i : c) 4 { 5 cout<<"["<< i.first <<"] = " << i.second <<" "; 6 }
运行结果为
[1] = 10 [2] = 40 [3] = 30 [4] = 20 [5] = 50
key值按照 字典序 默认升序排序
size() map大小
- 迭代器
1 map<int , string> pop;
2
3 map<int, string>::pop iter;
4
5 for(iter =pop.rbegin(); iter != pop.rend(); iter++)
6
7 cout<<iter->first<<" "<<iter->second<<endl;
lower_bound函数用法,这个函数用来返回要查找关键字的下界(是一个迭代器)
upper_bound函数用法,这个函数用来返回要查找关键字的上界(是一个迭代器)
equal_range函数返回一个pair;pair里面第一个变量是Lower_bound返回的迭代器,pair里面第二个迭代器是Upper_bound返回的迭代器,如果这两个迭代器相等的话,则说明 map中不出现这个关键字。
count() 判定关键字是否存在
find() 查找 find会挨个查找map,当到达map.end()时,也就是一个也没找到,返回end
1 map<int, string>::iterator iter;
2
3 iter = pop.find(1);
4
5 if(iter != pop.end())
6
7 cout<<"Find, the value is "<<iter->second<<endl;
erase() 删除
- multimap 键值key与元素value的映照关系是多对多的关系,没有定义[]操作运算
即不能直接用 类似于 t[1] = 2; 的赋值方式
简单运用:
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <algorithm>
3 #include <cstdio>
4 #include <map>
5 using namespace std;
6 int a[20];
7 int n;
8 int main()
9 {
10 multimap<string,int> c;
11 c.insert(pair<string,int>("Allen",18));
12 c.insert(pair<string,int>("Allen",201));
13 c.insert(pair<string,int>("Arim",0));
14 c.insert(pair<string,int>("Arim",9));
15 c.insert(pair<string,int>("Arim",18));
16 c.insert(pair<string,int>("Arim",10));
17 for(auto i:c) //遍历
18 {
19 cout<<i.first<<' '<<i.second<<endl;
20 }
21
22 cout<<"n统计 key 为"Allen"的数目"<<endl;
23 int sum = c.count("Allen");
24 cout<<sum<<endl;
25 multimap<string,int>::iterator iter = c.find("Allen");
26
27 cout<<"n遍历为key为 "Allen" 的 value"<<endl;
28 for(int i = 0 ; i < sum; i++)
29 {
30 cout<<iter->first<<' '<<iter->second<<endl;
31 iter++;
32 }
33 cout<<"n使用 equal_range 遍历为key为 "Allen" 的 value"<<endl;
34 typedef multimap<string,int>::iterator GG;
35 pair<GG,GG> iterpair = c.equal_range("Allen");
36 //pair<multimap<string,int>::iterator,multimap<string,int>::iterator> iterpair = c.equal_range("Allen");
37 for(iter = iterpair.first; iter!=iterpair.second; iter++)
38 {
39 cout<<iter->first<<' '<<iter->second<<endl;
40 }
41
42 cout<<"n删除key为"Allen" 的键值"<<endl;
43 c.erase("Allen");
44 for(auto i:c) //遍历
45 {
46 cout<<i.first<<' '<<i.second<<endl;
47 }
48 }
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
4 - set
https://blog.csdn.net/zxy160/article/details/76461724
set中常用的方法
insert(),在集合中插入元素
erase(),删除集合中的元素
size() ,返回当前set容器中的元素个数
count()–返回某个值元素的个数(根据set的特性,就是判断这个元素在不在,返回0或1)
begin() ,返回set容器的第一个元素的迭代器
end() ,返回set容器的最后一个元素的迭代器
clear() ,删除set容器中的所有的元素
empty() ,判断set容器是否为空(空返回真)
lower_bound()–返回指向大于(或等于)某值的第一个元素的迭代器
upper_bound()–返回大于某个值元素的迭代器
find()会挨个查找set,当到达set.end()时,也就是一个也没找到,返回end
例子 17-比赛1 F - 较小元素
注意事项(若需储存结构体,需重载<运算符)
1 struct node{
2 int i,j;
3 };
4
5 set<node> iset; //直接定义结构体的set是不行的
6
7 //需要重载"<" 运算符
8
9 bool operator<(const node& x,const node& y)
10 {
11 return x.i < y.i; //return x.j < y.j;
12 //根据set的特性 是依据i保存 还是依据 j保存
13 }
===================================================================================================================================
5 - vector
C++ vector 容器浅析 | 菜鸟教程
转载于:https://www.cnblogs.com/darkboy/p/9370285.html
最后
以上就是谦让火最近收集整理的关于STL 入门 (17 暑假集训第一周)17-比赛1 D - IPC Trainers (贪心 + 优先队列)C++中的STL中map用法详解set中常用的方法的全部内容,更多相关STL内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。

![[LeetCode 解题报告]013. Roman to Integer](https://www.shuijiaxian.com/files_image/reation/bcimg1.png)

![[C++ 从入门到放弃-06]C++STL之multimap多重映照容器1. multimap创建、元素插入和元素遍历2. 元素删除3. 元素查找](https://www.shuijiaxian.com/files_image/reation/bcimg3.png)




发表评论 取消回复