二叉树
- 树的知识点
- 1.1名词解释
- 二叉树
- 2.1二叉树的性质
- 2.1.1性质
- 2.1.2存储结构
- 2.2 二叉树遍历
- 2.2.1递归实现三种遍历
- 升级二推一
- 1.先序和中序推后序
- 2.中序和后序推先序
- 2.2.2非递归实现三种遍历
- 二叉树遍历——栈实现
- 层次遍历—— 队列实现
- 小结:
树的知识点
1.1名词解释
1.节点的度: 一个节点含有的子树的个数称为该节点的度;
2.树的度: 一棵树中,最大的节点的度称为树的度;
3.叶节点或终端节点: 度为的节点;
4.非终端节点或分支节点: 度不为零的节点;
5.父亲节点或父节点: 若-一个节点含有子节点,则这个节点称为其子节点的父节点;
6.孩子节点或子节点: 一个节点含有的子树的根节点称为该节点的子节点;
7,兄弟节点: 具有相同父节点的节点互称为兄弟节点;
8.节点的层次: 从根开始定义起,根为第1层,根的子节点为第2层,以此类推;
9.深度: 对于任意节点n,n的深度为从根到n的唯一路径长, 根的深度为0;
10.高度:对于任意节点n,n的高度为从n到- -片树叶的最长路径长,所有树叶的高度为0;
11.堂兄弟节点:父节点在同一层的节点互为堂兄弟;
12.节点的祖先:从根到该节点所经分支上的所有节点;
13.子孙:以某节点为恨的子树中任一节点都称为该节点的子孙q
14. 森林:由m (m>=0)棵互不相交的树的集合称为森林;
15.树中任意节点的子节点之间没有顺序关系,这种树称为无序树,也称为自由树。反之是有序树。
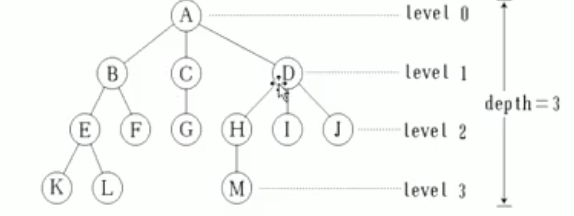
二叉树
2.1二叉树的性质
2.1.1性质
●若二叉树的层次从0开始 则在二 叉树的第i层最多有2i个结点。(i>= 0) [证明用数学归纳法
●高度为k的二叉树最多有2*+1-1个结点。 (k>= -1) [证明用求等比级数前 k项和的公式
●对任何一棵二叉树如果其叶结点个数为n0,度为2的非叶结点个数为n2,则有n0=n2+ 1.
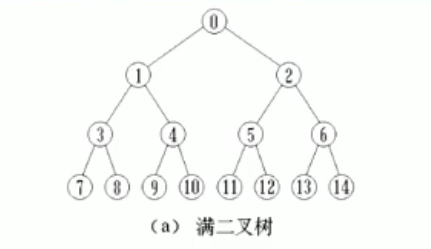
定义:满二叉树(Full Binary Tree):每一 个层的结点数都达到最大值,则这个二叉树就是满二叉树。
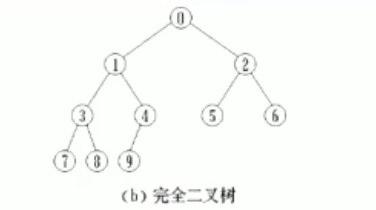
定义:完全二叉树(Complete Binary Tree):若设二 叉树的高度为h,则共有h+1层。除第h层外,其它各层(0 - h- 1)的结点数部达到最大个数,第h层从右向左连续缺若干结点,这就是完全二叉树。
●具有n 个结点的完全二叉树的高度为「log2(n+1)7 -1
证明:设完全二叉树的高度为h,则有2h-1<n≤(2h+1)-1 => 2h<n+1≤2h+1=>取对数h< log2^(n+1)<= h+1
2.1.2存储结构
●数据元素之间的关系有两种不同的表示方法: 顺序映象和非顺序映象,并由此得到两种不同的存储
结构:顺序存储结构和链式存储结构。数据的存储结构是指数据的逻辑结构在计算机中的表示。
1.顺序存储表示:
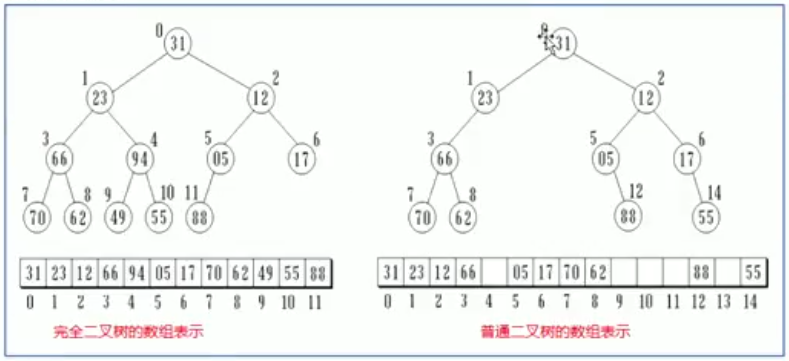
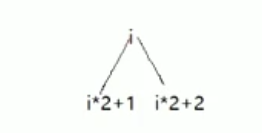
2.链式存储表示
满二叉树与完全二叉树适合用数组进行顺序存储,不浪费空间,如果普通二叉树用数组存储的话太浪费内存,数组有好多空缺,所以使用链式存储形式。
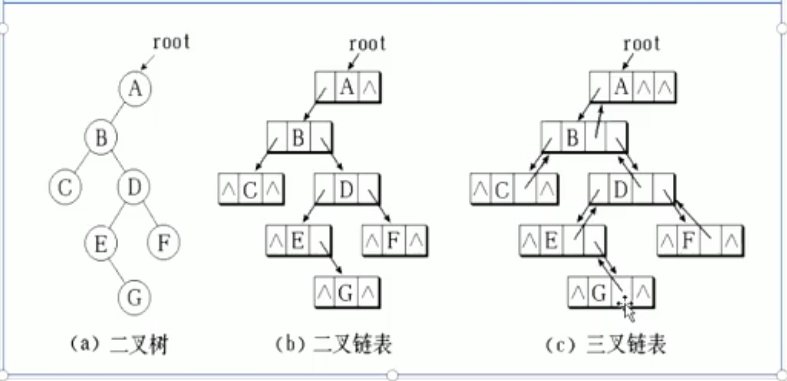
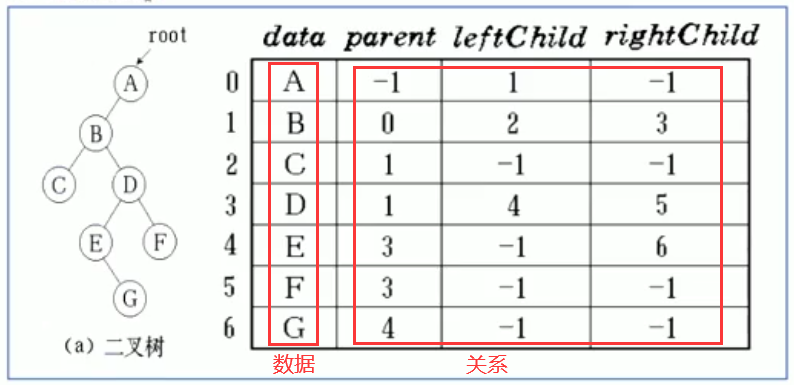
3.二叉链表的静态结构
2.2 二叉树遍历
二叉树遍历(Binary Tree Traversal),所谓树的遍历,就是按某种次序访问树中的结点,要求每个结点访问一次且仅访问一次。
设访问根结点记作V;
遍历根的左子树记作L;
遍历根的右子树记作 R;
则可能的遍历次序有:
| 遍历方法 | 表示 | 镜像 | 表示 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 前序 | VLR | 镜像 | VRL |
| 中序 | LVR | 镜像 | RVL |
| 后序 | LRV | 镜像 | RLV |
做个题:
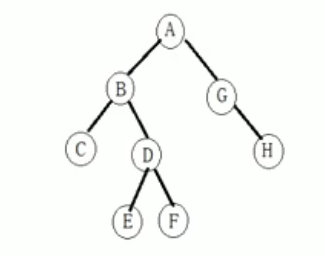
前序遍历:ABCDEFGH
中序遍历:CBEDFAGH
后序遍历:CEFDBHGA
代码讲解:
使用链式存储,递归实现二叉树的遍历
代码头
#include<stack>
#include<queue>
#include<list>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define END '#'
typedef char ElemType;
/*//三叉链表的定义
typedef struct BtNode
{
BtNode* leftchild;
BtNode* parent;
BtNode* rightchild;
ElemType data;
};
*/
//二叉
typedef struct BtNode
{
BtNode* leftchild;
//BtNode* parent;
BtNode* rightchild;
ElemType data;
}BtNode, * BinaryTree;;
//买节点操作
BtNode* Buynode() {
BtNode* s = (BtNode*)malloc(sizeof(BtNode));
if (NULL == s)
exit(1);//弄死它
memset(s, 0, sizeof(BtNode));//s 的值变为 0
return s;
}
定义一个结构体 。
定义一个买节点的函数。
2.2.1递归实现三种遍历
typedef struct BtNode
{
BtNode* leftchild;
BtNode* rightchild;
ElemType data;
}BtNode, * BinaryTree;;
//前序遍历
void PreOrder(BtNode* ptr) {
if (ptr != NULL) {
cout << ptr->data;
PreOrder(ptr->leftchild);
PreOrder(ptr->rightchild);
}
}
//中序遍历
void InOrder(BtNode* ptr) {
if (ptr != NULL) {
InOrder(ptr->leftchild);
cout << ptr->data;
InOrder(ptr->rightchild);
}
}
//后序遍历
void PastOrder(BtNode* ptr) {
if (ptr != NULL) {
PastOrder(ptr->leftchild);
PastOrder(ptr->rightchild);
cout << ptr->data;
}
}
//创建一个二叉树
BtNode* CreateTree() {
ElemType ch;
BtNode* s = NULL;
cin >> ch;
if (ch != END) {
s = Buynode(); //购买一个节点
s->data = ch;
s->leftchild = CreateTree();
s->rightchild = CreateTree();
}
return s;
}
int main() {
//输入 ABC##DE##F##G3H##
BinaryTree root = NULL;
root = CreateTree();
PreOrder(root);
cout <<endl;
InOrder(root);
cout << endl;
PastOrder(root);
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
升级二推一
这基本太简单,一般出题都是二推一,
给出先序和中序推后序
给出中序和后序推先序
但先序和后序无法推中序( 无法确定根节点,并且会出现多种情况)
接下来看代码。
1.先序和中序推后序
//寻找pos 在中序中寻找这个值
int FindPos(const char* is, int n, ElemType val) {
int pos = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (is[i] == val) {
pos = i;//返回它的下标
break;
}
}
return pos;
}
// 先序和中序推后续
BtNode* CreatePI(const char* ps, const char* is, int n) {
BtNode* s = NULL;
if (n > 0) {
s = Buynode();//购买一个节点
s->data = ps[0];
int pos = FindPos(is, n, ps[0]);// 寻找pos
if (pos == -1)exit(1);// 如果没找到 终止程序
s->leftchild = CreatePI(ps + 1, is, pos);// pos 数据变小
s->rightchild = CreatePI(ps + 1+pos, is+1+pos, n-1-pos);//从树根节点后面的数据进行
}
return s;
}
BtNode* CreateBTreePI(const char* ps,const char* is, int n) {
if (ps == NULL || is == NULL || n < 1) {
return NULL;
}
else return CreatePI(ps, is, n);
}
2.中序和后序推先序
//寻找pos 在中序中寻找这个值
int FindPos(const char* is, int n, ElemType val) {
int pos = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (is[i] == val) {
pos = i;//返回它的下标
break;
}
}
return pos;
}
//中序和后序推先序
BtNode* CreateIL(const char* is, const char* ls, int n) {
BtNode* s = NULL;
if (n > 0) {
s = Buynode();
s->data = ls[n - 1];
int pos = FindPos(is, n, ls[n - 1]);
if (pos == -1)exit(1);
s->leftchild = CreateIL( is, ls,pos );
s->rightchild = CreateIL( is+pos+1,ls+pos ,n-pos-1 );
}
return s;
}
//创建二叉树
BtNode* CreateBTreeIL(const char* ls, const char* is, int n) {
if (ls == NULL || is == NULL || n < 1) {
return NULL;
}
else return CreateIL(ls, is, n);
}
实现递归遍历并不能满足我们的需求,再看非递归实现
2.2.2非递归实现三种遍历
二叉树遍历——栈实现
代码:
/*
*
* 使用栈实现
*/
// 先序遍历非递归
void NicePreOrder(BtNode* ptr)
{
if (ptr == NULL) return;
stack<BtNode*> st; // 使用栈
st.push(ptr);
while (!st.empty())
{
ptr = st.top(); st.pop();
cout << ptr->data << " ";
if (ptr->rightchild != NULL)
st.push(ptr->rightchild);
if (ptr->leftchild != NULL)
st.push(ptr->leftchild );
}
cout << endl;
}
// 中序遍历非递归
void NiceInOrder(BtNode* ptr)
{
if (ptr == NULL) return;
stack<BtNode*> st; // 使用栈
while (!st.empty() || ptr !=NULL )
{
while (ptr != NULL)
{
st.push(ptr);// 入栈
ptr = ptr->leftchild;
}
ptr = st.top();//取栈顶指针
st.pop();//出栈
cout << ptr->data << " ";//输出
ptr = ptr->rightchild;
}
cout << endl;
}
// 后序遍历非递归
void NicePastOrder(BtNode* ptr)
{
if (ptr == NULL) return;
stack<BtNode*> st; // 使用栈
BtNode* tag = NULL;
while (!st.empty() || ptr != NULL)
{
while (ptr != NULL)
{
st.push(ptr);// 入栈
ptr = ptr->leftchild;
}
ptr = st.top();//取栈顶指针
st.pop();//出栈
if (ptr->rightchild == NULL || ptr->rightchild == tag)
{
cout << ptr->data << " ";//输出
tag = ptr;//tag 跟着打印出来的数据
ptr = NULL;//注意 一定要为空!!!
}
else
{
st.push(ptr);
ptr = ptr->rightchild;
}
}
cout << endl;
}
层次遍历—— 队列实现
/*
使用层次遍历
队列
*/
void NiceLevelOrder(BtNode* ptr)
{
if (ptr == NULL) return;
queue<BtNode*> st; // 使用队列
st.push(ptr);
while (!st.empty())
{
ptr = st.front(); st.pop();
cout << ptr->data << " ";
if (ptr->leftchild != NULL)
st.push(ptr->leftchild);
if (ptr->rightchild != NULL)
st.push(ptr->rightchild);
}
cout << endl;
}
附完整代码:
递归遍历
#include<stack>
#include<queue>
#include<list>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define END '#'
typedef char ElemType;
#if 1
/*//三叉链表的定义
typedef struct BtNode
{
BtNode* leftchild;
BtNode* parent;
BtNode* rightchild;
ElemType data;
};
*/
//二叉
typedef struct BtNode
{
BtNode* leftchild;
//BtNode* parent;
BtNode* rightchild;
ElemType data;
}BtNode, * BinaryTree;;
BtNode* Buynode() {
BtNode* s = (BtNode*)malloc(sizeof(BtNode));
if (NULL == s)
exit(1);//弄死它
memset(s, 0, sizeof(BtNode));//s 的值变为 0
return s;
}
//前序遍历
void PreOrder(BtNode* ptr) {
if (ptr != NULL) {
cout << ptr->data;
PreOrder(ptr->leftchild);
PreOrder(ptr->rightchild);
}
}
//中序遍历
void InOrder(BtNode* ptr) {
if (ptr != NULL) {
InOrder(ptr->leftchild);
cout << ptr->data;
InOrder(ptr->rightchild);
}
}
//后序遍历
void PastOrder(BtNode* ptr) {
if (ptr != NULL) {
PastOrder(ptr->leftchild);
PastOrder(ptr->rightchild);
cout << ptr->data;
}
}
BtNode* CreateTree() {
ElemType ch;
BtNode* s = NULL;
cin >> ch;
if (ch != END) {
s = Buynode(); //购买一个节点
s->data = ch;
s->leftchild = CreateTree();
s->rightchild = CreateTree();
}
return s;
}
#if 0
int main() {
//输入 ABC##DE##F##G3H##
BinaryTree root = NULL;
root = CreateTree();
PreOrder(root);
cout <<endl;
InOrder(root);
cout << endl;
PastOrder(root);
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
#endif
//寻找pos 在中序中寻找这个值
int FindPos(const char* is, int n, ElemType val) {
int pos = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (is[i] == val) {
pos = i;//返回它的下标
break;
}
}
return pos;
}
// 先序和中序推后续
BtNode* CreatePI(const char* ps, const char* is, int n) {
BtNode* s = NULL;
if (n > 0) {
s = Buynode();//购买一个节点
s->data = ps[0];
int pos = FindPos(is, n, ps[0]);// 寻找pos
if (pos == -1)exit(1);// 如果没找到 终止程序
s->leftchild = CreatePI(ps + 1, is, pos);// pos 数据变小
s->rightchild = CreatePI(ps + 1+pos, is+1+pos, n-1-pos);//从树根节点后面的数据进行
}
return s;
}
//实现不了先序和后序推中序
BtNode* CreatePL(const char* ps, const char* ls, int n) {
BtNode* s = NULL;
if (n > 0) {
s = Buynode();
s->data = ps[0];
int pos = FindPos(ls, n, ps[0]);
if (pos == -1)exit(1);
s->leftchild = CreatePL(ps+1,ls ,pos );
s->rightchild = CreatePL(ps+pos+1 ,ls+pos ,n-pos -1);
}
return s;
}
//中序和后序推先序
BtNode* CreateIL(const char* is, const char* ls, int n) {
BtNode* s = NULL;
if (n > 0) {
s = Buynode();
s->data = ls[n - 1];
int pos = FindPos(is, n, ls[n - 1]);
if (pos == -1)exit(1);
s->leftchild = CreateIL( is, ls,pos );
s->rightchild = CreateIL( is+pos+1,ls+pos ,n-pos-1 );
}
return s;
}
//创建二叉树
BtNode* CreateBTreePI(const char* ps,const char* is, int n) {
if (ps == NULL || is == NULL || n < 1) {
return NULL;
}
else return CreatePI(ps, is, n);
}
BtNode* CreateBTreePL(const char* ps, const char* ls, int n) {
if (ps == NULL ||ls == NULL || n < 1) {
return NULL;
}
else return CreatePL(ps, ls, n);
}
BtNode* CreateBTreeIL(const char* ls, const char* is, int n) {
if (ls == NULL || is == NULL || n < 1) {
return NULL;
}
else return CreateIL(ls, is, n);
}
int main() {
const char ps[] = "ABCDEFGH";
const char is[] = "CBEDFAGH";
const char ls[] = "CEFDBHGA";
int n = strlen(ps);
BinaryTree root = NULL;
//root = CreateBTreePI(ps,is, n);
//root = CreateBTreePL(ps,ls, n);//不能根据先序和后序推中序
//root = CreateBTreeIL(is,ls, n);
PreOrder(root);
cout << endl;
InOrder(root);
cout << endl;
PastOrder(root);
cout << endl;
}
#endif
非递归遍历
#include<stack>
#include<queue>
#include<list>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define END '#'
typedef char ElemType;
typedef struct BtNode
{
BtNode* leftchild;
//BtNode* parent;
BtNode* rightchild;
ElemType data;
}BtNode, * BinaryTree;;
BtNode* Buynode() {
BtNode* s = (BtNode*)malloc(sizeof(BtNode));
if (NULL == s)
exit(1);//弄死它
memset(s, 0, sizeof(BtNode));//s 的值变为 0
return s;
}
//寻找pos 在中序中寻找这个值
int FindPos(const char* is, int n, ElemType val) {
int pos = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (is[i] == val) {
pos = i;//返回它的下标
break;
}
}
return pos;
}
/*
*
* 使用栈实现
*/
// 先序遍历非递归
void NicePreOrder(BtNode* ptr)
{
if (ptr == NULL) return;
stack<BtNode*> st; // 使用栈
st.push(ptr);
while (!st.empty())
{
ptr = st.top(); st.pop();
cout << ptr->data << " ";
if (ptr->rightchild != NULL)
st.push(ptr->rightchild);
if (ptr->leftchild != NULL)
st.push(ptr->leftchild );
}
cout << endl;
}
// 中序遍历非递归
void NiceInOrder(BtNode* ptr)
{
if (ptr == NULL) return;
stack<BtNode*> st; // 使用栈
while (!st.empty() || ptr !=NULL )
{
while (ptr != NULL)
{
st.push(ptr);// 入栈
ptr = ptr->leftchild;
}
ptr = st.top();//取栈顶指针
st.pop();//出栈
cout << ptr->data << " ";//输出
ptr = ptr->rightchild;
}
cout << endl;
}
// 后序遍历非递归
void NicePastOrder(BtNode* ptr)
{
if (ptr == NULL) return;
stack<BtNode*> st; // 使用栈
BtNode* tag = NULL;
while (!st.empty() || ptr != NULL)
{
while (ptr != NULL)
{
st.push(ptr);// 入栈
ptr = ptr->leftchild;
}
ptr = st.top();//取栈顶指针
st.pop();//出栈
if (ptr->rightchild == NULL || ptr->rightchild == tag)
{
cout << ptr->data << " ";//输出
tag = ptr;//tag 跟着打印出来的数据
ptr = NULL;//注意 一定要为空!!!
}
else
{
st.push(ptr);
ptr = ptr->rightchild;
}
}
cout << endl;
}
/*
使用层次遍历
队列
*/
void NiceLevelOrder(BtNode* ptr)
{
if (ptr == NULL) return;
queue<BtNode*> st; // 使用队列
st.push(ptr);
while (!st.empty())
{
ptr = st.front(); st.pop();
cout << ptr->data << " ";
if (ptr->leftchild != NULL)
st.push(ptr->leftchild);
if (ptr->rightchild != NULL)
st.push(ptr->rightchild);
}
cout << endl;
}
//中序和后序推先序
BtNode* CreateIL(const char* is, const char* ls, int n) {
BtNode* s = NULL;
if (n > 0) {
s = Buynode();
s->data = ls[n - 1];
int pos = FindPos(is, n, ls[n - 1]);
if (pos == -1)exit(1);
s->leftchild = CreateIL(is, ls, pos);
s->rightchild = CreateIL(is + pos + 1, ls + pos, n - pos - 1);
}
return s;
}
BtNode* CreateBTreeIL(const char* ls, const char* is, int n) {
if (ls == NULL || is == NULL || n < 1) {
return NULL;
}
else return CreateIL(ls, is, n);
}
int main() {
const char ps[] = "ABCDEFGH";
const char is[] = "CBEDFAGH";
const char ls[] = "CEFDBHGA";
int n = strlen(ps);
BinaryTree root = NULL;
root = CreateBTreeIL(is,ls, n);
NicePreOrder(root);
NiceInOrder(root);
NicePastOrder(root);
NiceLevelOrder(root);// 层次遍历
cout << endl;
}
小结:
1.现阶段二叉树的遍历就要求掌握三种:先序 ,中序,后序
二叉树的遍历还可以进行多样形式的遍历:
-
层次遍历 (上面有提到)
-
s 型层次遍历.
-
反s 型层次遍历。
-
…
2.先序中序推后序,后序中序推前序,得记住前后不能推中。
3.熟悉掌握队列、栈、链表的使用,以及运行过程,解决二叉树不是问题。
最后
以上就是儒雅棒球最近收集整理的关于【算法与数据结构】二叉树 (二叉树遍历、递归与非递归实现先中后序遍历、层次遍历)树的知识点二叉树小结:的全部内容,更多相关【算法与数据结构】二叉树内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复