Leetcode刷题java之21. 合并两个有序链表
解法一:
class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
}
public class Solution_2 {
public void mergeTwoLists(ListNode n1,ListNode n2) {
ListNode newNode = new ListNode(0);
ListNode cur = newNode;
while(n1!=null && n2!=null) {
if(n1.val < n2.val) {
cur.next = n1;
cur = cur.next;
n1 = n1.next;
}else {
cur.next = n2;
cur = cur.next;
n2 = n2.next;
}
}
//任一为空,直接连接另条表
if(n1 == null) {
cur.next = n2;
}else {
cur.next = n1;
}
cur=newNode.next;
System.out.print("l3: ");
while(cur!=null) {
System.out.print(cur.val);
cur=cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[]args) {
//l1初始化
ListNode l1=new ListNode(1);//新建节点
ListNode pre=l1;//创建头指针
pre.next=new ListNode(2);
pre=pre.next;//移动指针
pre.next=new ListNode(5);
pre=pre.next;
//l2初始化
ListNode l2=new ListNode(1);
ListNode pre2=l2;
pre2.next=new ListNode(3);
pre2=pre2.next;
pre2.next=new ListNode(6);
pre2=pre2.next;
Solution_2 s = new Solution_2();
s.mergeTwoLists( l1, l2);
//l1被破坏
System.out.print("l1: ");
pre=l1;
while(pre!=null) {
System.out.print(pre.val);
pre=pre.next;
}
System.out.println();
//l2被破坏
System.out.print("l2: ");
pre2=l2;
while(pre2!=null) {
System.out.print(pre2.val);
pre2=pre2.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
但解法一有明显的不足。在原程序中,l1:1->2->5,l2: 1->3->6。
但在执行完后,l1 l2均被改变。

通过测试程序不难发现,l1 l2已经被破坏。
解法二:新建l3链表,并且使得l1 l2保持原样
/*本程序在不破坏l1 l2的基础上,新建了l3链表
*
* */
//ListNode数据结构定义
class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
}
public class Solution {
public void mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode l3=new ListNode(0);
/*创建l3头节点
* 由于ListNode没有无参的构造函数,所以参数写0
* 返回时从第二个节点返回即可 */
ListNode pre=l3;//创建指针
ListNode pre1=l1;
ListNode pre2=l2;
while(pre1!=null&&pre2!=null) {
if(pre1.val<=pre2.val) {
pre.next=new ListNode(pre1.val);
pre=pre.next;
pre1=pre1.next;
//l3=l3.next;
}
else {
pre.next=new ListNode(pre2.val);
pre=pre.next;
pre2=pre2.next;
}
}
if(pre1==null) {
while(pre2!=null) {
pre.next=new ListNode(pre2.val);
pre=pre.next;
pre2=pre2.next;
//l2=l2.next;
}
}
if(pre2==null) {
while(pre1!=null) {
pre.next=new ListNode(pre1.val);
pre=pre.next;
pre1=pre1.next;
}
}
//对l3输出
pre=l3.next;
while(pre!=null) {
System.out.print(pre.val);
pre=pre.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[]args) {
//l1初始化
ListNode l1=new ListNode(1);//新建节点
ListNode pre=l1;//创建头指针
pre.next=new ListNode(2);
pre=pre.next;//移动指针
pre.next=new ListNode(5);
pre=pre.next;
//l2初始化
ListNode l2=new ListNode(1);
ListNode pre2=l2;
pre2.next=new ListNode(3);
pre2=pre2.next;
pre2.next=new ListNode(6);
pre2=pre2.next;
Solution s = new Solution();
//l1可正常输出
s.mergeTwoLists( l1, l2);
System.out.println();
pre=l1;
while(pre!=null) {
System.out.print(pre.val);
pre=pre.next;
}
System.out.println();
//l2可正常输出
pre2=l2;
while(pre2!=null) {
System.out.print(pre2.val);
pre2=pre2.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
}输出结果如下:
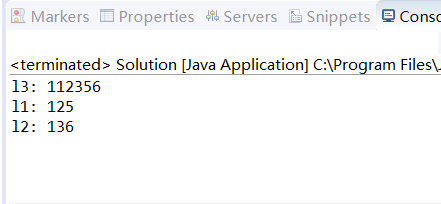
由结果可知,l1 l2并没有被改变。
但缺点多使用了内存空间。
解法三:递归调用
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
if(l1==null)
{
return l2;
}
if(l2==null)
{
return l1;
}
if(l1.val<l2.val)
{
l1.next=mergeTwoLists(l1.next,l2);//递归
return l1;
}else
{
l2.next=mergeTwoLists(l1,l2.next);
return l2;
}
}
}
最后
以上就是还单身蜜蜂最近收集整理的关于数据结构——链表(一)Leetcode刷题java之21. 合并两个有序链表的全部内容,更多相关数据结构——链表(一)Leetcode刷题java之21.内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复