1. 问题描述
复现合并排序问题,用用分治算法来解决这个问题,并分析其时间复杂度。
2. 问题分析
用分治算法来解决这个问题,以下是分治算法的基本思路:
- 把原问题分解成若干个子问题
- 递归求每一个子问题的解
- 合并子问题的解
在合并排序中:
输入: 给定的n 个元素的序列A
输出为:A[0] <= A[1] <= A[2] <=…<= A[n-1]
用分治算法的思路来考虑此问题:
1.我们的目标是把乱序的数组A 变成有序的sorted A,将问题分解,把A 沿中间切分

2.这样问题一分为二,
Problem1 : LA− > SortedLA
Problem2 : RA− > SortedRA
假设合并函数为MergeSort(A),那么
SLA = MergeSort(LA) <= Problem1
RLA = MergeSort(RA) <= Problem2
3.合并子问题
合并(SLA,SRA) = SA, 把两个有序的子序列合并成一个序列。
3. 时间复杂度分析
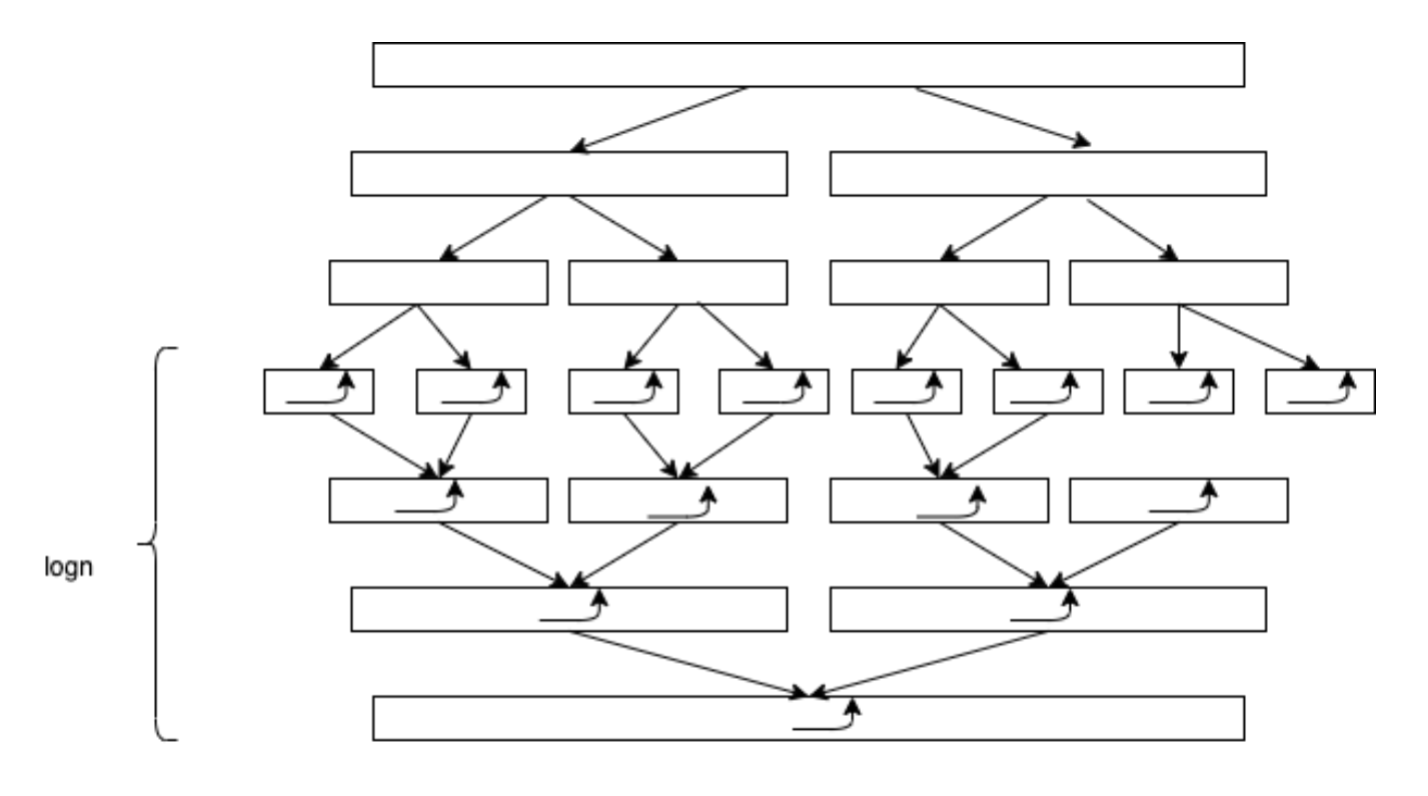
由图表可知合并排序的计算流程,在合并时,每一层的比较次数是n,一共有logn 层,由此可得,该排序的时间复杂度是O(nlogn)。
在做合并的时候将有序的特征进行传递,因此得到了性能的提升。
4. 实验代码
import time
import random
import matplotlib . pyplot as plt import numpy as np
from scipy . optimize import curve_ fit
# 自 定 义 函 数 e 指 数 形 式
def func(x, a, b, c):
return a* np. sqrt( x)*( b* np. square( x) +c)
def random _ list( length ):
randomlist = []
for i in range( length ):
randomlist. append ( i+1)
random . shuffle( randomlist)
return randomlist
# 生 成 随 机 数 组
def random _ int_ list( start , stop , length ):
start , stop = ( int( start), int( stop )) if start <= stop else ( int( stop ), int( start))
length = int( abs( length )) if length else 0
random _ list = []
for i in range( length ): random _ list. append ( random . randint( start , stop ))
random _ list. sort ()
return random _ list
def merge_ sort( A):
if len ( A) <= 1:
return A
else:
mid = len ( A) //2
LA = A[: mid ]
RA = A[ mid :]
SLA = merge_ sort( LA)
SRA = merge_ sort( RA)
SA = merge( SLA , SRA )
return SA
def merge(a, b):
result = []
i=0
j=0
while i< len ( a) and j < len ( b):
if a[ i] < b[ j]:
result. append ( a[ i])
i = i + 1
else:
result. append ( b[ j])
j = j + 1
while i < len ( a):
result. append ( a[ i])
i = i + 1
while j < len ( b):
result. append ( b[ j])
j = j + 1
return result
if __ name __ == "__ main __":
x = [10 ,100 ,1000 ,10000 ,100000]
time_ list = []
for index in range( len ( x)):
average_ time = []
for i in range (100):
# print(’ x:’, x[ index ])
randomlist = random _ list( x[ index ])
# randomlist = random _ int_ list(1 , x[ index ], x[ index ])
total_ time = 0
time_ start= time. time ()
merge_ sort( randomlist)
time_ end = time. time ()
total_ time = time_ end - time_ start
average_ time. append ( total_ time)
# 求 平 均 值
average = np. mean ( average_ time)
time_ list. append ( average)
print( time_ list)
# 用matplotlib 画 图
# plt. figure ()
# plt. plot(x, time_list , marker=’*’, label = " merge sort ")
# plt. show ()
# 定 义x 、 y 散 点 坐 标
x = np. array ( x)
num = time_ list
y = np. array ( num )
# 非 线 性 最 小 二 乘 法 拟 合
popt , pcov = curve_ fit( func , x, y)
# 获 取 popt 里 面 是 拟 合 系 数
print( popt)
a = popt [0]
b = popt [1]
c = popt [2]
yvals = func(x,a,b, c) # 拟 合y 值
print(’ popt:’, popt)
print(’ 系 数a:’, a)
print(’ 系 数b:’, b)
print(’ 系 数 c:’, c)
print(’ 系 数pcov :’, pcov )
print(’ 系 数 yvals:’, yvals)
# 绘图
plot 1 = plt. plot(x, y, ’s’, label=’ original values ’)
plot 2 = plt. plot(x, yvals , ’r’, label=’ polyfit values ’) plt. xlabel(’x ’)
plt. ylabel(’y ’)
plt. legend ( loc =4) # 指 定legend 的 位 置 右 下 角
plt. title(’ curve_fit ’)
plt. show ()
5. 实验结果
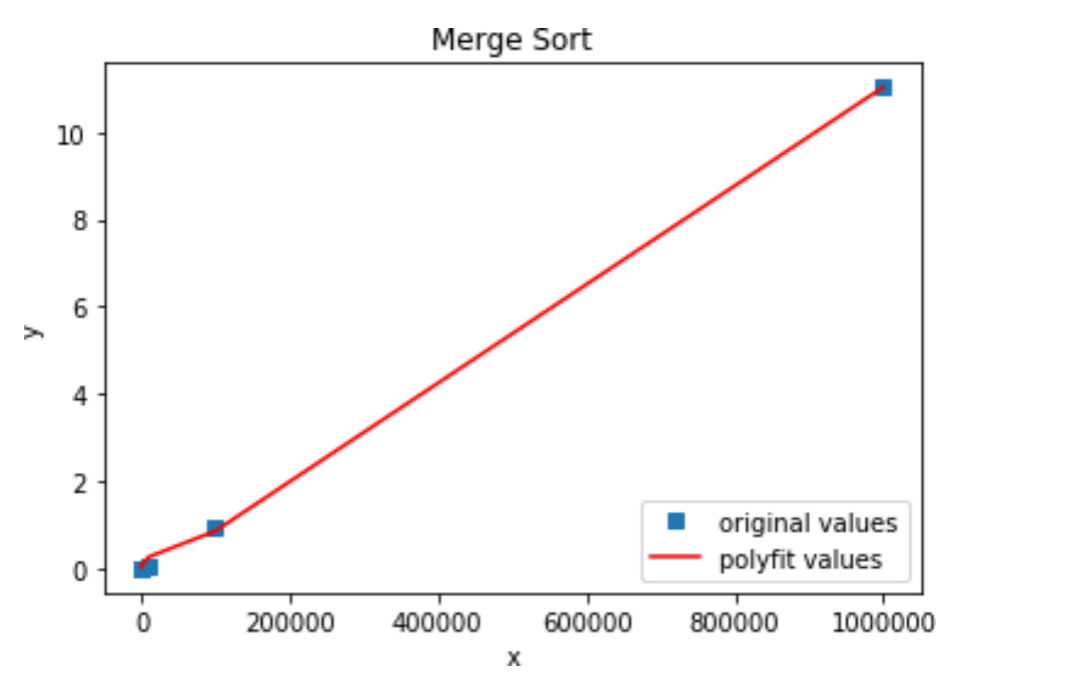
计算不同范围大小下的随机数组进行合并排序所要消耗的时间,在多次实验求平均值,并对图 像进行拟合处理后,得到上述图像。可以看到,合并排序的时间复杂度图像近似于 nlogn,这与我们理论验证的结果相同。
参考与致谢
- 算法分析和设计 http://www.icourse163.org/spoc/learn/ZJUT- 1460190163?tid=1460863458#/learn/content?type=detail&id=1238944804&sm=1
- python 中任意曲线的拟合方法 https://blog.csdn.net/changdejie/article/details/83089933
最后
以上就是高兴泥猴桃最近收集整理的关于【算法】合并排序问题1. 问题描述2. 问题分析3. 时间复杂度分析4. 实验代码5. 实验结果参考与致谢的全部内容,更多相关【算法】合并排序问题1.内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复